Copyright © 2010-2011 Linux Foundation
Permission is granted to copy, distribute and/or modify this document under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 2.0 UK: England & Wales as published by Creative Commons.
Note
Due to production processes, there could be differences between the Yocto Project documentation bundled in the release tarball and The Yocto Project Development Manual on the Yocto Project website. For the latest version of this manual, see the manual on the website.| Revision History | |
|---|---|
| Revision 1.1 | 6 October 2011 |
| The initial document released with the Yocto Project 1.1 Release. | |
Table of Contents
- 1. The Yocto Project Development Manual
- 2. Getting Started with the Yocto Project
- 3. The Yocto Project Open Source Development Environment
- 4. Common Development Models
- A. BSP Development Example
- B. Kernel Modification Example
- B.1. Modifying the Kernel Source Code
- B.1.1. Understanding the Files You Need
- B.1.2. Setting Up the Local Yocto Project Files Git Repository
- B.1.3. Setting Up the poky-extras Git Repository
- B.1.4. Setting Up the Bare Clone and its Copy
- B.1.5. Building and Booting the Default QEMU Kernel Image
- B.1.6. Changing the Source Code and Pushing it to the Bare Clone
- B.1.7. Changing Build Parameters for Your Build
- B.1.8. Building and Booting the Modified QEMU Kernel Image
- B.2. Changing the Kernel Configuration
- B.3. Adding Kernel Recipes
Table of Contents
Welcome to the Yocto Project Development Manual! This manual gives you an idea of how to use the Yocto Project to develop embedded Linux images and user-space applications to run on targeted devices. Reading this manual gives you an overview of image, kernel, and user-space application development using the Yocto Project. Because much of the information in this manual is general, it contains many references to other sources where you can find more detail. For example, detailed information on Git, repositories and open source in general can be found in many places. Another example is how to get set up to use the Yocto Project, which our Yocto Project Quick Start covers.
The Yocto Project Development Manual, however, does provide detailed examples on how to create a Board Support Package (BSP), change the kernel source code, and re-configure the kernel. You can find this information in the appendices of the manual.
The following list describes what you can get from this guide:
Information that lets you get set up to develop using the Yocto Project.
Information to help developers that are new to the open source environment and to the distributed revision control system Git, which the Yocto Project uses.
An understanding of common end-to-end development models.
Development case overviews for both system development and user-space applications.
An overview and understanding of the emulation environment used with the Yocto Project (QEMU).
An understanding of basic kernel architecture and concepts.
Many references to other sources of related information.
This manual will not give you the following:
Step-by-step instructions if those instructions exist in other Yocto Project documentation. For example, The Application Development Toolkit (ADT) User’s Guide contains detailed instruction on how to obtain and configure the Eclipse™ Yocto Plug-in.
Reference material. This type of material resides in an appropriate reference manual. For example, system variables are documented in the Yocto Project Reference Manual.
Detailed public information that is not specific to the Yocto Project. For example, exhaustive information on how to use Git is covered better through the Internet than in this manual.
Because this manual presents overview information for many different topics, you will need to supplement it with other information. The following list presents other sources of information you might find helpful:
The Yocto Project Website: The home page for the Yocto Project provides lots of information on the project as well as links to software and documentation.
The Yocto Project Quick Start: This short document lets you get started with the Yocto Project quickly and start building an image.
The Yocto Project Reference Manual: This manual is a reference guide to the Yocto Project build component known as "Poky." The manual also contains a reference chapter on Board Support Package (BSP) layout.
The Yocto Project Application Development Toolkit (ADT) User's Guide: This guide provides information that lets you get going with the ADT to develop projects using the Yocto Project.
The Yocto Project Board Support Package (BSP) Developer's Guide: This guide defines the structure for BSP components. Having a commonly understood structure encourages standardization.
The Yocto Project Kernel Architecture and Use Manual: This manual describes the architecture of the Yocto Project kernel and provides some work flow examples.
Yocto Eclipse Plug-in: A step-by-step instructional video that demonstrates how an application developer uses Yocto Plug-in features within the Eclipse IDE.
FAQ: A list of commonly asked questions and their answers.
Release Notes: Features, updates and known issues for the current release of the Yocto Project.
Bugzilla: The bug tracking application the Yocto Project uses. If you find problems with the Yocto Project, you should report them using this application.
Yocto Project Mailing Lists: To subscribe to the Yocto Project mailing lists, click on the following URLs and follow the instructions:
http://lists.yoctoproject.org/listinfo/yocto for a Yocto Project Discussions mailing list.
http://lists.yoctoproject.org/listinfo/poky for a Yocto Project Discussions mailing list about the Poky build system.
http://lists.yoctoproject.org/listinfo/yocto-announce for a mailing list to receive offical Yocto Project announcements for developments and as well as Yocto Project milestones.
Internet Relay Chat (IRC): Two IRC channels on freenode are available for Yocto Project and Poky discussions:
#yoctoand#poky.OpenedHand: The company where the Yocto Project build system Poky was first developed. OpenedHand has since been acquired by Intel Corporation.
Intel Corporation: The company who acquired OpenedHand in 2008 and continues development on the Yocto Project.
OpenEmbedded: The upstream, generic, embedded distribution the Yocto Project build system (Poky) derives from and to which it contributes.
BitBake: The tool used to process Yocto Project metadata.
BitBake User Manual: A comprehensive guide to the BitBake tool.
Pimlico: A suite of lightweight Personal Information Management (PIM) applications designed primarily for handheld and mobile devices.
QEMU: An open-source machine emulator and virtualizer.
Table of Contents
This chapter introduces the Yocto Project and gives you an idea of what you need to get started. You can find enough information to set up your development host and build or use images for hardware supported by the Yocto Project by reading The Yocto Project Quick Start.
The remainder of this chapter summarizes what is in the Yocto Project Quick Start and provides some higher-level concepts you might want to consider.
The Yocto Project is an open-source collaboration project focused on embedded Linux development. The project currently provides a build system, which is sometimes referred to as "Poky", and provides various ancillary tools suitable for the embedded developer. The Yocto Project also features the Sato reference User Interface, which is optimized for stylus driven, low-resolution screens.
You can use the Yocto Project, which uses the BitBake build tool, to develop complete Linux images and associated user-space applications for architectures based on ARM, MIPS, PowerPC, x86 and x86-64. While the Yocto Project does not provide a strict testing framework, it does provide or generate for you artifacts that let you perform target-level and emulated testing and debugging. Additionally, if you are an Eclipse™ IDE user, you can install an Eclipse Yocto Plug-in to allow you to develop within that familiar environment.
Here is what you need to get set up to use the Yocto Project:
Host System: You should have a reasonably current Linux-based host system. You will have the best results with a recent release of Fedora, OpenSUSE, or Ubuntu as these releases are frequently tested against the Yocto Project and officially supported. You should also have about 100 gigabytes of free disk space for building images.
Packages: The Yocto Project requires certain packages exist on your development system (e.g. Python 2.6 or 2.7). See "The Packages" section in the Yocto Project Quick start for the exact package requirements and the installation commands to install them for the supported distributions.
Yocto Project Release: You need a release of the Yocto Project. You can get set up with local Yocto Project files one of two ways depending on whether you are going to be contributing back into the Yocto Project source repository or not.
Note
Regardless of the method you use, this manual refers to the resulting hierarchical set of files as "the Yocto Project files" or "the Yocto Project file structure."Tarball Extraction: If you are not going to contribute back into the Yocto Project, you can simply download the Yocto Project release you want from the website’s download page. Once you have the tarball, just extract it into a directory of your choice.
For example, the following command extracts the Yocto Project 1.1 release tarball into the current working directory and sets up the Yocto Project file structure with a top-level directory named
poky-edison-6.0:$ tar xfj poky-edison-6.0.tar.bz2This method does not produce a Git repository. Instead, you simply end up with a local snapshot of the Yocto Project files that are based on the particular release in the tarball.
Git Repository Method: If you are going to be contributing back into the Yocto Project, you should use Git commands to set up a local Git repository of the Yocto Project files. Doing so creates a Git repository with a complete history of changes and allows you to easily submit your changes upstream to the project.
The following transcript shows how to clone the Yocto Project files' Git repository into the current working directory. The command creates the repository in a directory named
poky. For information on the Yocto Project and Git, see the "Git" section.$ git clone git://git.yoctoproject.org/poky Initialized empty Git repository in /home/scottrif/poky/.git/ remote: Counting objects: 116882, done. remote: Compressing objects: 100% (35987/35987), done. remote: Total 116882 (delta 80651), reused 113045 (delta 77578) Receiving objects: 100% (116882/116882), 72.13 MiB | 2.68 MiB/s, done. Resolving deltas: 100% (80651/80651), done.For another example of how to set up your own local Git repositories, see this wiki page, which describes how to create both
pokyandmeta-intelGit repositories.
Linux Yocto Kernel: If you are going to be making modifications to a supported Linux Yocto kernel, you need to establish local copies of the source. This setup involves creating a bare clone of the Linux Yocto kernel and then cloning that repository. You can create the bare clone and the copy of the bare clone anywhere you like. For simplicity, it is recommended that you create these structures outside of the Yocto Project files' Git repository.
As an example, the following transcript shows how to create the bare clone of the
linux-yocto-3.0kernel and then create a copy of that clone.Note
When you have a local Linux Yocto kernel Git repository, you can reference that repository rather than the upstream Git repository as part of theclonecommand. Doing so can speed up the process.In the following example, the bare clone is named
linux-yocto-3.0.git, while the copy is namedlinux-yocto-3.0:$ git clone --bare git://git.yoctoproject.org/linux-yocto-3.0 linux-yocto-3.0.git Initialized empty Git repository in /home/scottrif/linux-yocto-3.0.git/ remote: Counting objects: 2123870, done. remote: Compressing objects: 100% (341338/341338), done. remote: Total 2123870 (delta 1778780), reused 2107534 (delta 1762583) Receiving objects: 100% (2123870/2123870), 445.72 MiB | 2.06 MiB/s, done. Resolving deltas: 100% (1778780/1778780), done.Now create a clone of the bare clone just created:
$ git clone linux-yocto-3.0.git linux-yocto-3.0 Initialized empty Git repository in /home/scottrif/linux-yocto-3.0/.git/ Checking out files: 100% (36898/36898), done.The
poky-extrasGit Repository: Thepoky-extrasGit repository contains metadata needed to build the kernel image. In particular, it contains the kernel.bbappendfiles that you edit to point to your locally modified kernel source files and to build the kernel image. Pointing to these local files is much more efficient than requiring a download of the source files from upstream each time you make changes to the kernel.It is good practice to create this Git repository inside the Yocto Project files Git repository. Following is an example that creates the
poky-extrasGit repository inside the Yocto Project files Git repository, which is namedpokyin this case:$ cd ~/poky $ git clone git://git.yoctoproject.org/poky-extras poky-extras Initialized empty Git repository in /home/scottrif/poky/poky-extras/.git/ remote: Counting objects: 543, done. remote: Compressing objects: 100% (483/483), done. remote: Total 543 (delta 144), reused 307 (delta 39) Receiving objects: 100% (543/543), 520.55 KiB, done. Resolving deltas: 100% (144/144), done.Supported Board Support Packages (BSPs): Similar considerations exist for BSPs. You can get set up for BSP development one of two ways: tarball extraction or with a local Git repository. Regardless of the method you use, the Yocto Project uses the following BSP layer naming scheme:
meta-<BSP_name>where <BSP_name> is the recognized BSP name. Here are some examples:
meta-crownbay meta-emenlow meta-n450Tarball Extraction: You can download any released BSP tarball from the same download site used to get the Yocto Project release. Once you have the tarball, just extract it into a directory of your choice. Again, this method just produces a snapshot of the BSP layer in the form of a hierarchical directory structure.
Git Repository Method: If you are working with a Yocto Project files Git repository, you should also set up a
meta-intelGit repository. Typically, you set up themeta-intelGit repository inside the Yocto Project files Git repository.For example, the following transcript shows the steps to clone the
meta-intelGit repository inside thepokyGit repository.$ cd poky $ git clone git://git.yoctoproject.org/meta-intel.git Initialized empty Git repository in /home/scottrif/poky/meta-intel/.git/ remote: Counting objects: 1325, done. remote: Compressing objects: 100% (1078/1078), done. remote: Total 1325 (delta 546), reused 85 (delta 27) Receiving objects: 100% (1325/1325), 1.56 MiB | 330 KiB/s, done. Resolving deltas: 100% (546/546), done.The same wiki page referenced earlier covers how to set up the
meta-intelGit repository.
Eclipse Yocto Plug-in: If you are developing applications using the Eclipse Integrated Development Environment (IDE), you will need this plug-in. See the "Setting up the Eclipse IDE" section in the Yocto Application Development Toolkit (ADT) User’s Guide for more information.
The build process creates an entire Linux distribution, including the toolchain, from source. For more information on this topic, see the "Building an Image" section in the Yocto Project Quick Start.
The build process is as follows:
Make sure you have the Yocto Project files as described in the previous section.
Initialize the build environment by sourcing a build environment script.
Optionally ensure the
conf/local.confconfiguration file is set up how you want it. This file defines the target machine architecture and other build options.Build the image using the bitbake command. If you want information on BitBake, see the user manual at http://docs.openembedded.org/bitbake/html.
Run the image either on the actual hardware or using the QEMU emulator.
Another option you have to get started is to use pre-built binaries. This scenario is ideal for developing software applications to run on your target hardware. To do this, you need to install the stand-alone Yocto Project cross-toolchain tarball and then download the pre-built kernel that you will boot in the QEMU emulator. Next, you must download and extract the target root filesystem for your target machine’s architecture. Finally, you set up the environment to emulate the hardware and then start the QEMU emulator.
You can find details on all these steps in the "Using Pre-Built Binaries and QEMU" section of the Yocto Project Quick Start.
Table of Contents
This chapter helps you understand the Yocto Project as an open source development project. In general, working in an open source environment is very different from working in a closed, proprietary environment. Additionally, the Yocto Project uses specific tools and constructs as part of its development environment. The chapter specifically addresses open source philosophy, licensing issues, code repositories, the open source distributed version control system Git, and best practices using the Yocto Project.
Open source philosophy is characterized by software development directed by peer production and collaboration through an active community of developers. Contrast this to the more standard centralized development models used by commercial software companies where a finite set of developers produce a product for sale using a defined set of procedures that ultimately result in an end product whose architecture and source material are closed to the public.
Open source projects conceptually have differing concurrent agendas, approaches, and production. These facets of the development process can come from anyone in the public (community) that has a stake in the software project. The open source environment contains new copyright, licensing, domain, and consumer issues that differ from the more traditional development environment. In an open source environment, the end product, source material, and documentation are all available to the public at no cost.
A benchmark example of an open source project is the Linux Kernel, which was initially conceived and created by Finnish computer science student Linus Torvalds in 1991. Conversely, a good example of a non-open source project is the Windows® family of operating systems developed by Microsoft® Corporation.
Wikipedia has a good historical description of the Open Source Philosophy here. You can also find helpful information on how to participate in the Linux Community here.
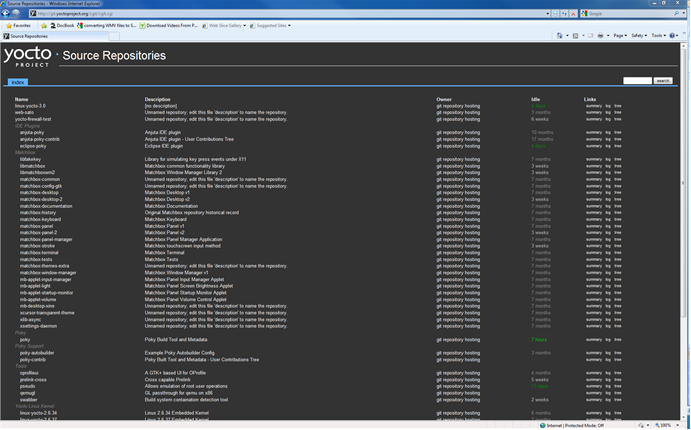
The Yocto Project team maintains complete source repositories for all Yocto Project files here. This web-based source code browser is organized into categories by function such as IDE Plugins, Matchbox, Poky, Yocto Linux Kernel, and so forth. From the interface, you can click on any particular item in the "Name" column and see the URL at the bottom of the page that you need to set up a Git repository for that particular item. Having a local Git repository of the Yocto Project files allows you to make changes, contribute to the history, and ultimately enhance the Yocto Project's tools, Board Support Packages, and so forth.
Conversely, if you are a developer that is not interested in contributing back to the Yocto Project, you have the ability to simply download and extract release tarballs and use them within the Yocto Project environment. All that is required is a particular release of Yocto Project, a kernel, and your application source code.
For any supported release of Yocto Project, you can go to the Yocto Project website’s download page and get a tarball of the release. You can also go to this site to download any supported BSP tarballs. Unpacking the tarball gives you a hierarchical directory structure of Yocto Project files that lets you develop using the Yocto Project.
Once you are set up through either tarball extraction or creation of Git repositories, you are ready to develop.
In summary, here is where you can get the Yocto Project files needed for development:
Source Repositories: This area contains IDE Plugins, Matchbox, Poky, Poky Support, Tools, Yocto Linux Kernel, and Yocto Metadata Layers. You can create Git repositories for each of these areas.
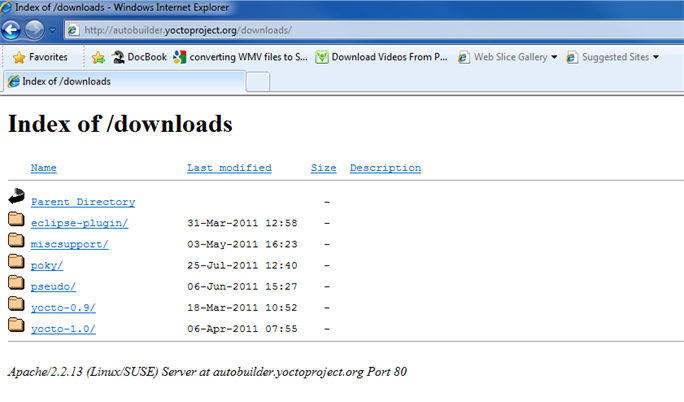
Index of /releases: This area contains an index of downloads such as the Eclipse™ Yocto Plug-in, miscellaneous support, Poky, pseudo, cross-development toolchains, and all released versions of Yocto Project in the form of images or tarballs. Downloading and extracting these files does not produce a Git repository but rather a snapshot of a particular release or image.
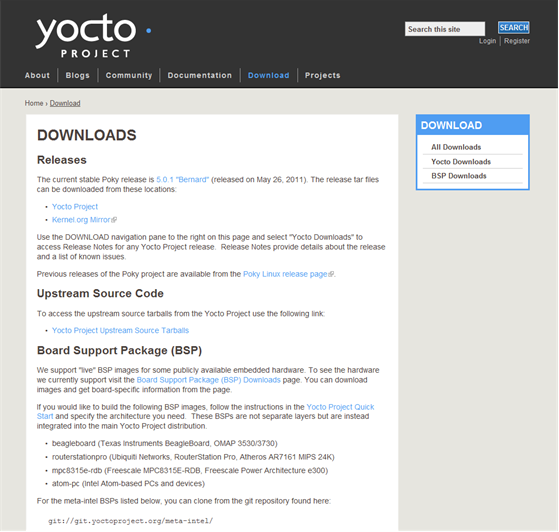
Yocto Project Download Page This page on the Yocto Project website allows you to download any Yocto Project release or Board Support Package (BSP) in tarball form. The tarballs are similar to those found in the Index of /releases: area.
Following is a list of terms and definitions users new to the Yocto Project development environment might find helpful. While some of these terms are universal, the list includes them just in case:
Append Files: Files that append build information to a recipe file. Information in append files overrides the information in the similarly-named recipe file. Append files use the
.bbappendfilename suffix.BitBake: The task executor and scheduler used by the Yocto Project to build images. For more information on BitBake, see the BitBake documentation.
Classes: Files that provide for logic encapsulation and inheritance allowing commonly used patterns to be defined once and easily used in multiple recipes. Class files end with the
.bbclassfilename extension.Configuration File: Configuration information in various
.conffiles provides global definitions of variables. Theconf/local.confconfiguration file in the Yocto Project build directory contains user-defined variables that affect each build. Themeta-yocto/conf/distro/poky.confconfiguration file defines Yocto ‘distro’ configuration variables used only when building with this policy. Machine configuration files, which are located throughout the Yocto Project file structure, define variables for specific hardware and are only used when building for that target (e.g. themachine/beagleboard.confconfiguration file defines variables for the Texas Instruments ARM Cortex-A8 development board). Configuration files end with a.conffilename extension.Cross-Development Toolchain: A collection of software development tools and utilities that allow you to develop software for targeted architectures. This toolchain contains cross-compilers, linkers, and debuggers that are specific to an architecture. You can use the Yocto Project to build cross-development toolchains in tarball form that when unpacked contain the development tools you need to cross-compile and test your software. The Yocto Project ships with images that contain toolchains for supported architectures as well. Sometimes this toolchain is referred to as the meta-toolchain.
Image: An image is the result produced when BitBake processes a given collection of recipes and related metadata. Images are the binary output that runs on specific hardware and for specific use cases. For a list of the supported image types that the Yocto Project provides, see the "Reference: Images" appendix in The Yocto Project Reference Manual.
Layer: A collection of recipes representing the core, a BSP, or an application stack.
Metadata: The files that BitBake parses when building an image. Metadata includes recipes, classes, and configuration files.
OE-Core: A core set of metadata originating with OpenEmbedded (OE) that is shared between OE and the Yocto Project. This metadata is found in the
metadirectory of the Yocto Project files.Package: The packaged output from a baked recipe. A package is generally the compiled binaries produced from the recipe's sources. You ‘bake’ something by running it through BitBake.
Poky: The build tool that the Yocto Project uses to create images.
Recipe: A set of instructions for building packages. A recipe describes where you get source code and which patches to apply. Recipes describe dependencies for libraries or for other recipes, and they also contain configuration and compilation options. Recipes contain the logical unit of execution, the software/images to build, and use the
.bbfile extension.Tasks: Arbitrary groups of software Recipes. You simply use Tasks to hold recipes that, when built, usually accomplish a single task. For example, a task could contain the recipes for a company’s proprietary or value-add software. Or, the task could contain the recipes that enable graphics. A task is really just another recipe. Because task files are recipes, they end with the
.bbfilename extension.Upstream: A reference to source code or repositories that are not local to the development system but located in a master area that is controlled by the maintainer of the source code. For example, in order for a developer to work on a particular piece of code, they need to first get a copy of it from an "upstream" source.
Yocto Project Files: This term refers to the directory structure created as a result of downloading and unpacking a Yocto Project release tarball or setting up a Git repository by cloning
git://git.yoctoproject.org/poky. Sometimes the term "the Yocto Project Files structure" is used as well.The Yocto Project files contain BitBake, Documentation, metadata and other files that all support the development environment. Consequently, you must have the Yocto Project files in place on your development system in order to do any development using the Yocto Project.
The name of the top-level directory of the Yocto Project file structure is derived from the Yocto Project release tarball. For example, downloading and unpacking
poky-edison-6.0.tar.bz2results in a Yocto Project file structure whose Yocto Project source directory is namedpoky-edison-6.0. If you create a Git repository, then you can name the repository anything you like.You can find instruction on how to set up the Yocto Project files on your host development system by reading the "Getting Setup" section.
Yocto Project Build Directory: This term refers to the area used by the Yocto Project for builds. The area is created when you
sourcethe Yocto Project setup environment script that is found in the Yocto Project files area. (e.g.oe-init-build-env). You can create the Yocto Project build directory anywhere you want on your development system. Here is an example that creates the directory inmybuildsand names the Yocto Project build directoryYP-6.0:$ source poky-edison-6.0/oe-init-build-env $HOME/mybuilds/YP-6.0If you don't specifically name the directory, BitBake creates it in the current directory and uses the name
build. Also, if you supply an existing directory, then BitBake uses that directory as the Yocto Project build directory and populates the build hierarchy beneath it.
Because open source projects are open to the public, they have different licensing structures in place. License evolution for both Open Source and Free Software has an interesting history. If you are interested in this history, you can find basic information here:
In general, the Yocto Project is broadly licensed under the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) License. MIT licensing permits the reuse of software within proprietary software as long as the license is distributed with that software. MIT is also compatible with the GNU General Public License (GPL). Patches to the Yocto Project follow the upstream licensing scheme. You can find information on the MIT license at here. You can find information on the GNU GPL here.
When you build an image using Yocto Project, the build process uses a known list of licenses to
ensure compliance.
You can find this list in the Yocto Project files directory at
meta/files/common-licenses.
Once the build completes, the list of all licenses found and used during that build are
kept in the Yocto Project build directory at
tmp/deploy/images/licenses.
If a module requires a license that is not in the base list, the build process generates a warning during the build. These tools make it easier for a developer to be certain of the licenses with which their shipped products must comply. However, even with these tools it is still up to the developer to resolve potential licensing issues.
The base list of licenses used by the build process is a combination of the Software Package Data Exchange (SPDX) list and the Open Source Initiative (OSI) projects. SPDX Group is a working group of the Linux Foundation that maintains a specification for a standard format for communicating the components, licenses, and copyrights associated with a software package. OSI is a corporation dedicated to the Open Source Definition and the effort for reviewing and approving licenses that are OSD-conformant.
You can find a list of the combined SPDX and OSI licenses that the Yocto Project uses here. This wiki page discusses the license infrastructure used by the Yocto Project.
The Yocto Project uses Git, which is a free, open source distributed version control system. Git supports distributed development, non-linear development, and can handle large projects. It is best that you know how to work with Git if you are going to use Yocto Project for development.
Git has an extensive set of commands that lets you manage changes and perform collaboration over the life of a project. Conveniently though, you can manage with a small set of basic operations and workflows once you understand the basic philosophy behind Git. You do not have to be an expert in Git to be functional. A good place to look for instruction on a minimal set of Git commands is here. If you need to download Git, you can do so here.
Git works by using branching techniques that track content change (not files) within a project (e.g. a new feature or updated documentation). Creating a tree-like structure based on project divergence allows for excellent historical information over the life of a project. This methodology also allows for an environment in which you can do lots of experimentation on your project as you develop changes or new features. For example, you can create a “branch”, experiment with some feature, and then if you like the feature, you incorporate the branch into the tree. If you don’t, you cut the branch off by deleting it.
If you don’t know much about Git, we suggest you educate yourself by visiting the links previously mentioned.
The following list briefly describes some basic Git operations as a way to get started. As with any set of commands, this list (in most cases) simply shows the base command and omits the many arguments they support. See the Git documentation for complete descriptions and strategies on how to use these commands:
git init: Initializes an empty Git repository. You cannot use Git commands unless you have a.gitrepository.git clone: Creates a clone of a repository. During collaboration, this command allows you to create a local repository that is on equal footing with a fellow developer’s repository.git add: Adds updated file contents to the index that Git uses to track changes. You must add all files that have changed before you can commit them.git commit: Creates a “commit” that documents the changes you made. Commits are used for historical purposes, for determining if a maintainer of a project will allow the change, and for ultimately pushing the change from your local Git repository into the project’s upstream (or master) repository.git status: Reports any modified files that possibly need to be added and committed.git checkout <branch-name>: Changes your working branch. This command is analogous to “cd”.git checkout –b <working-branch>: Creates a working branch on your local machine where you can isolate work. It is a good idea to use local branches when adding specific features or changes. This way if you don’t like what you have done you can easily get rid of the work.git branch: Reports existing branches and tells you which branch in which you are currently working.git branch -D <branch-name>: Deletes an existing branch. You need to be in a branch other than the one you are deleting in order to delete <branch-name>.git pull: Retrieves information from an upstream Git repository and places it in your local Git repository. You use this command to make sure you are synchronized with the repository from which you are basing changes (.e.g. the master repository).git push: Sends all your local changes you have committed to an upstream Git repository (e.g. a contribution repository). The maintainer of the project draws from these repositories when adding your changes to the project’s master repository.git merge: Combines or adds changes from one local branch of your repository with another branch. When you create a local Git repository, the default branch is named “master”. A typical workflow is to create a temporary branch for isolated work, make and commit your changes, switch to your local master branch, merge the changes from the temporary branch into the local master branch, and then delete the temporary branch.git cherry-pick: Choose and apply specific commits from one branch into another branch. There are times when you might not be able to merge all the changes in one branch with another but need to pick out certain ones.gitk: Provides a GUI view of the branches and changes in your local Git repository. This command is a good way to graphically see where things have diverged in your local repository.git log: Reports a history of your changes to the repository.git diff: Displays line-by-line differences between your local working files and the same files in the upstream Git repository that your branch currently tracks.
This section provides some overview on workflows using Git. In particular, the information covers basic practices that describe roles and actions in a collaborative development environment. Again, if you are familiar with this type of development environment, you might want to just skip this section.
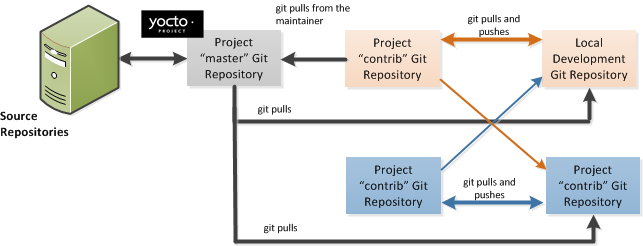
The Yocto Project files are maintained using Git in a "master" branch whose Git history tracks every change and whose structure provides branches for all diverging functionality. Although there is no need to use Git, many open source projects do so. For the Yocto Project, a key individual called the "maintainer" is responsible for the "master" branch of the Git repository. The "master" branch is the “upstream” repository where the final builds of the project occur. The maintainer is responsible for allowing changes in from other developers and for organizing the underlying branch structure to reflect release strategies and so forth.
Note
You can see who is the maintainer for Yocto Project files by examining thedistro_tracking_fields.inc file in the Yocto Project
meta/conf/distro/include directory.
The project also has contribution repositories known as “contrib” areas. These areas temporarily hold changes to the project that have been submitted or committed by the Yocto Project development team and by community members that contribute to the project. The maintainer determines if the changes are qualified to be moved from the "contrib" areas into the "master" branch of the Git repository.
Developers (including contributing community members) create and maintain cloned repositories of the upstream "master" branch. These repositories are local to their development platforms and are used to develop changes. When a developer is satisfied with a particular feature or change, they “push” the changes to the appropriate "contrib" repository.
Developers are responsible for keeping their local repository up-to-date with "master". They are also responsible for straightening out any conflicts that might arise within files that are being worked on simultaneously by more than one person. All this work is done locally on the developer’s machine before anything is pushed to a "contrib" area and examined at the maintainer’s level.
A somewhat formal method exists by which developers commit changes and push them into the "contrib" area and subsequently request that the maintainer include them into "master" This process is called “submitting a patch” or “submitting a change.”
To summarize the environment: we have a single point of entry for changes into the project’s "master" branch of the Git repository, which is controlled by the project’s maintainer. And, we have a set of developers who independently develop, test, and submit changes to "contrib" areas for the maintainer to examine. The maintainer then chooses which changes are going to become a permanent part of the project.
 |
While each development environment is unique, there are some best practices or methods that help development run smoothly. The following list describes some of these practices. For more detailed information about these strategies see Git Workflows.
Make Small Changes: It is best to keep the changes you commit small as compared to bundling many disparate changes into a single commit. This practice not only keeps things manageable but also allows the maintainer to more easily include or refuse changes.
It is also good practice to leave the repository in a state that allows you to still successfully build your project. In other words, do not commit half of a feature, then add the other half in a separate, later commit. Each commit should take you from one buildable project state to another buildable state.
Use Branches Liberally: It is very easy to create, use, and delete local branches in your working Git repository. You can name these branches anything you like. It is helpful to give them names associated with the particular feature or change on which you are working. Once you are done with a feature or change, simply discard the branch.
Merge Changes: The
git mergecommand allows you to take the changes from one branch and fold them into another branch. This process is especially helpful when more than a single developer might be working on different parts of the same feature. Merging changes also automatically identifies any collisions or “conflicts” that might happen as a result of the same lines of code being altered by two different developers.Manage Branches: Because branches are easy to use, you should use a system where branches indicate varying levels of code readiness. For example, you can have a “work” branch to develop in, a “test” branch where the code or change is tested, a “stage” branch where changes are ready to be committed, and so forth. As your project develops, you can merge code across the branches to reflect ever-increasing stable states of the development.
Use Push and Pull: The push-pull workflow is based on the concept of developers “pushing” local commits to a remote repository, which is usually a contribution repository. This workflow is also based on developers “pulling” known states of the project down into their local development repositories. The workflow easily allows you to pull changes submitted by other developers from the upstream repository into your work area ensuring that you have the most recent software on which to develop. The Yocto Project has two scripts named
create-pull-requestandsend-pull-requestthat ship with the release to facilitate this workflow. You can find these scripts in the local Yocto Project files Git repository in thescriptsdirectory.Patch Workflow: This workflow allows you to notify the maintainer through an email that you have a change (or patch) you would like considered for the "master" branch of the Git repository. To send this type of change you format the patch and then send the email using the Git commands
git format-patchandgit send-email. You can find information on how to submit later in this chapter.
The Yocto Project uses Bugzilla to track bugs. This bug-tracking application works well for group development because it tracks bugs and code changes, can be used to communicate changes and problems with developers, can be used to submit and review patches, and can be used to manage quality assurance. You can find a good overview of Bugzilla here.
Sometimes it is helpful to submit, investigate, or track a bug against the Yocto Project itself such as when discovering an issue with some component of the build system that acts contrary to the documentation or your expectations. You can find information for Bugzilla configuration and bug tracking procedures specific to the Yocto Project here.
The Yocto Project uses its own version of the Bugzilla application. You can find the home page here. You need to use this implementation of Bugzilla when logging a defect against anything released by the Yocto Project team.
Here are some things to remember when dealing with bugs against the Yocto Project:
The Yocto Project follows a bug-naming convention:
[YOCTO #<number>], where<number>is the assigned defect ID used in Bugzilla. So, for example, a valid way to refer to a defect when creating a commit comment would be[YOCTO #1011]. This convention becomes important if you are submitting patches against the Yocto Project code itself. See the following section for more information.Defects for Yocto Project fall into one of four classifications: Yocto Projects, Infrastructure, Poky, and Yocto Metadata Layers.
Contributions to the Yocto Project are very welcome. You should send patches to the appropriate Yocto Project mailing list to get them in front of the Yocto Project Maintainer. For a list of the Yocto Project mailing lists, see the "Mailing lists" section in The Yocto Project Reference Manual.
Following is some guidance on which mailing list to use for what type of defect:
For defects against the Yocto Project build system Poky, send your patch to the http://lists.yoctoproject.org/listinfo/poky mailing list. This mailing list corresponds to issues that are not specific to the Yocto Project but are part of the OE-core. For example, a defect against anything in the
metalayer or the BitBake Manual could be sent to this mailing list.For defects against Yocto-specific layers, tools, and Yocto Project documentation use the http://lists.yoctoproject.org/listinfo/yocto mailing list. This mailing list corresponds to Yocto-specific areas such as
meta-yocto,meta-intel,linux-yocto, anddocumentation.
When you send a patch, be sure to include a "Signed-off-by:" line in the same style as required by the Linux kernel. Adding this line signifies the developer has agreed to the Developer's Certificate of Origin 1.1 as follows:
Developer's Certificate of Origin 1.1
By making a contribution to this project, I certify that:
(a) The contribution was created in whole or in part by me and I
have the right to submit it under the open source license
indicated in the file; or
(b) The contribution is based upon previous work that, to the best
of my knowledge, is covered under an appropriate open source
license and I have the right under that license to submit that
work with modifications, whether created in whole or in part
by me, under the same open source license (unless I am
permitted to submit under a different license), as indicated
in the file; or
(c) The contribution was provided directly to me by some other
person who certified (a), (b) or (c) and I have not modified
it.
(d) I understand and agree that this project and the contribution
are public and that a record of the contribution (including all
personal information I submit with it, including my sign-off) is
maintained indefinitely and may be redistributed consistent with
this project or the open source license(s) involved.
A Poky contributions tree (poky-contrib,
git://git.yoctoproject.org/poky-contrib.git)
exists for contributors to stage contributions.
If people desire such access, please ask on the mailing list.
Usually, the Yocto Project team will grant access to anyone with a proven track
record of good patches.
In a collaborative environment, it is necessary to have some sort of standard or method through which you submit changes. Otherwise, things could get quite chaotic.
When you create a commit, you must follow certain standards established by the Yocto Project development team. For each commit, you must provide a single-line summary of the change and you almost always provide a more detailed description of what you did (i.e. the body of the commit). The only exceptions for not providing a detailed description would be if your change is a simple, self-explanatory change that needs no description. Here are the Yocto Project commit message guidelines:
Provide a single-line, short summary of the change. This summary is typically viewable by source control systems. Thus, providing something short and descriptive that gives the reader a summary of the change is useful when viewing a list of many commits.
For the body of the commit message, provide detailed information that describes what you changed, why you made the change, and the approach you used. Provide as much detail as you can in the body of the commit message.
If the change addresses a specific bug or issue that is associated with a bug-tracking ID, prefix your detailed description with the bug or issue ID. For example, the Yocto Project tracks bugs using a bug-naming convention. Any commits that address a bug must start with the bug ID in the description as follows:
YOCTO #<bug-id>: <Detailed description of commit>
You can find more guidance on creating well-formed commit messages at this OpenEmbedded wiki page: http://www.openembedded.org/wiki/Commit_Patch_Message_Guidelines.
Following are general instructions for both pushing changes upstream and for submitting changes as patches.
The basic flow for pushing a change to an upstream "contrib" Git repository is as follows:
Make your changes in your local Git repository.
Stage your commit (or change) by using the
git addcommand.Commit the change by using the
git commitcommand and push it to the "contrib" repository. Be sure to provide a commit message that follows the project’s commit standards as described earlier.Notify the maintainer that you have pushed a change by making a pull request. The Yocto Project provides two scripts that conveniently let you generate and send pull requests to the Yocto Project. These scripts are
create-pull-requestandsend-pull-request. You can find these scripts in thescriptsdirectory of the Yocto Project file structure.For help on using these scripts, simply provide the
--helpargument as follows:$ ~/poky/scripts/create-pull-request --help $ ~/poky/scripts/send-pull-request --help
You can find general Git information on how to push a change upstream here.
If you have a just a few changes, you can commit them and then submit them as an email to the maintainer. Here is a general procedure:
Make your changes in your local Git repository.
Stage your commit (or change) by using the
git addcommand.Commit the change by using the
git commit --signoffcommand. Using the--signoffoption identifies you as the person making the change and also satisfies the Developer's Certificate of Origin (DCO) shown earlier.When you form a commit you must follow certain standards established by the Yocto Project development team. See the earlier section "How to Submit a Change" for Yocto Project commit message standards.
Format the commit into an email messsage. To format commits, use the
git format-patchcommand. When you provide the command, you must include a revision list or a number of patches as part of the command. For example, these two commands each take the most recent single commit and format it as an email message in the current directory:$ git format-patch -1 $ git format-patch HEAD~After the command is run, the current directory contains a numbered
.patchfile for the commit.If you provide several commits as part of the command, the
git format-patchcommand produces a numbered series of files in the current directory – one for each commit. For information on thegit format-patchcommand, seeGIT_FORMAT_PATCH(1)displayed using theman git-format-patchcommand.Import the files into your mail client by using the
git send-emailcommand.Note
In order to usegit send-email, you must have the the proper Git packages installed. For Ubuntu and Fedora the package isgit-email.The
git send-emailcommand sends email by using a local or remote Mail Transport Agent (MTA) such asmsmtp,sendmail, or through a directsmtpconfiguration in your Gitconfigfile.The
git send-emailcommand is the preferred method for sending your patches since there is no risk of compromising whitespace in the body of the message, which can occur when you use your own mail client. The command also has several options that let you specify recipients and perform further editing of the email message. For information on how to use thegit send-emailcommand, use theman git-send-emailcommand.
Table of Contents
Many development models exist for which you can use the Yocto Project. However, for the purposes of this manual we are going to focus on two common ones: System Development and User Application Development. System Development covers Board Support Package (BSP) development and kernel modification or configuration. User Application Development covers development of applications that you intend to run on some target hardware.
This chapter presents overviews of both system and application models. If you want to examine specific examples of the system development models, see the "BSP Development Example" appendix and the "Kernel Modification Example" appendix. For a user-space application development example that uses the Eclipse™ IDE, see the The Yocto Project Application Development Toolkit (ADT) User's Guide.
System development involves modification or creation of an image that you want to run on a specific hardware target. Usually, when you want to create an image that runs on embedded hardware, the image does not require the same number of features that a full-fledged Linux distribution provides. Thus, you can create a much smaller image that is designed to use only the hardware features for your particular hardware.
To help you understand how system development works in the Yocto Project, this section covers two types of image development: BSP creation and kernel modification or configuration.
A BSP is a package of recipes that, when applied, during a build results in an image you can run on a particular board. Thus, the package, when compiled into the new image, supports the operation of the board.
Note
For a brief list of terms used when describing the development process in the Yocto Project, see the "Yocto Project Terms" section.The remainder of this section presents the basic steps to create a BSP basing it on an existing BSP that ships with the Yocto Project. You can reference the "BSP Development Example" appendix for a detailed example that uses the Crown Bay BSP as a base BSP from which to start.
The following illustration and list summarize the BSP creation general workflow.
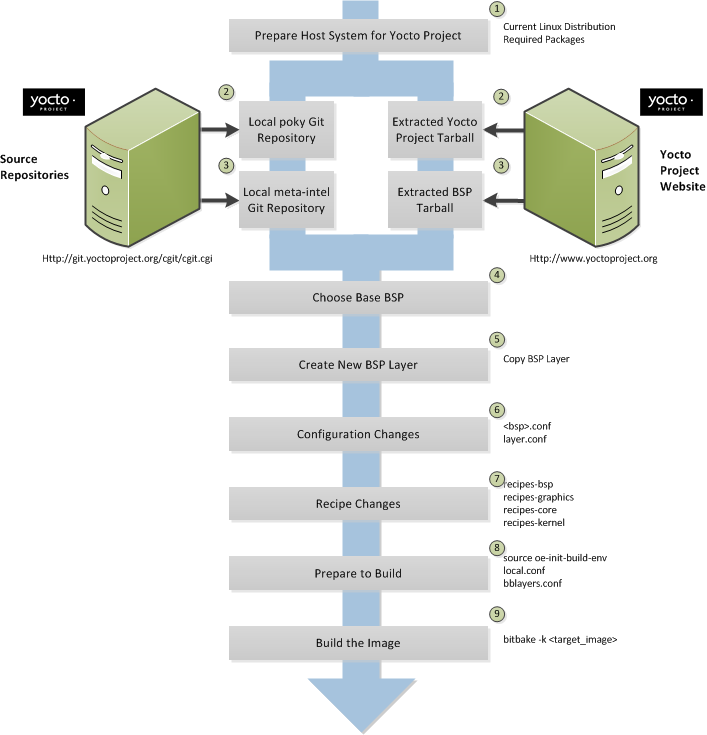 |
Set up your host development system to support development using the Yocto Project: See the "The Linux Distributions" and the "The Packages" sections both in the Yocto Project Quick Start for requirements.
Establish a local copy of the Yocto Project files on your system: You need to have the Yocto Project files available on your host system. Having the Yocto Project files on your system gives you access to the build process and tools you need. For information on how to get these files, see the "Getting Setup" section.
Establish a local copy of the base BSP files: Having the BSP files on your system gives you access to the build process and tools you need for creating a BSP. For information on how to get these files, see the "Getting Setup" section.
Choose a Yocto Project-supported BSP as your base BSP: The Yocto Project ships with several BSPs that support various hardware. It is best to base your new BSP on an existing BSP rather than create all the recipes and configuration files from scratch. While it is possible to create everything from scratch, basing your new BSP on something that is close is much easier. Or, at a minimum, leveraging off an existing BSP gives you some structure with which to start.
At this point you need to understand your target hardware well enough to determine which existing BSP it most closely matches. Things to consider are your hardware’s on-board features, such as CPU type and graphics support. You should look at the README files for supported BSPs to get an idea of which one you could use. A generic Intel® Atom™-based BSP to consider is the Crown Bay that does not support the Intel® Embedded Media Graphics Driver (EMGD). The remainder of this example uses that base BSP.
To see the supported BSPs, go to the Yocto Project download page and click on “BSP Downloads.”
Create your own BSP layer: Layers are ideal for isolating and storing work for a given piece of hardware. A layer is really just a location or area in which you place the recipes for your BSP. In fact, a BSP is, in itself, a special type of layer. Another example that illustrates a layer is an application. Suppose you are creating an application that has library or other dependencies in order for it to compile and run. The layer, in this case, would be where all the recipes that define those dependencies are kept. The key point for a layer is that it is an isolated area that contains all the relevant information for the project that the Yocto Project build system knows about.
Note
The Yocto Project supports four BSPs that are part of the Yocto Project release:atom-pc,beagleboard,mpc8315e, androuterstationpro. The recipes and configurations for these four BSPs are located and dispersed within the local Yocto Project files. Consequently, they are not totally isolated in the spirit of layers unless you think ofmeta-yoctoas a layer itself. On the other hand, BSP layers for Crown Bay, Emenlow, Jasper Forest, N450, and Sugar Bay are isolated.When you set up a layer for a new BSP, you should follow a standard layout. This layout is described in the section "Example Filesystem Layout" section of the Board Support Package (BSP) Development Guide. In the standard layout, you will notice a suggested structure for recipes and configuration information. You can see the standard layout for the Crown Bay BSP in this example by examining the directory structure of the
meta-crownbaylayer inside the local Yocto Project files.Make configuration changes to your new BSP layer: The standard BSP layer structure organizes the files you need to edit in
confand severalrecipes-*directories within the BSP layer. Configuration changes identify where your new layer is on the local system and identify which kernel you are going to use.Make recipe changes to your new BSP layer: Recipe changes include altering recipes (
.bbfiles), removing recipes you don't use, and adding new recipes that you need to support your hardware.Prepare for the build: Once you have made all the changes to your BSP layer, there remains a few things you need to do for the Yocto Project build system in order for it to create your image. You need to get the build environment ready by sourcing an environment setup script and you need to be sure two key configuration files are configured appropriately.
The entire process for building an image is overviewed in the section "Building an Image" section of the Yocto Project Quick Start. You might want to reference this information.
Build the image: The Yocto Project uses the BitBake tool to build images based on the type of image you want to create. You can find more information on BitBake here.
The build process supports several types of images to satisfy different needs. See the "Reference: Images" appendix in the Yocto Project Reference Manualfor information on supported images.
You can view a video presentation on "Building Custom Embedded Images with Yocto" at Free Electrons. You can also find supplemental information in The Board Support Package (BSP) Development Guide. Finally, there is wiki page write up of the example also located here that you might find helpful.
Kernel modification involves changing the Linux Yocto kernel, which could involve changing
configuration options as well as adding new kernel recipes.
Configuration changes can be added in the form of configuration fragments, while recipe
modification comes through the kernel's recipes-kernel area
in a kernel layer you create.
The remainder of this section presents a high-level overview of the Linux Yocto kernel architecture and the steps to modify the Linux Yocto kernel. For a complete discussion of the kernel, see The Yocto Project Kernel Architecture and Use Manual. You can reference the appendix "Kernel Modification Example" for a detailed example that changes the configuration of a kernel.
Traditionally, when one thinks of a patched kernel, they think of a base kernel source tree and a fixed structure that contains kernel patches. The Yocto Project, however, employs mechanisms, that in a sense, result in a kernel source generator. By the end of this section, this analogy will become clearer.
You can find a web interface to the Linux Yocto kernel source repositories at http://git.yoctoproject.org/. If you look at the interface, you will see to the left a grouping of Git repositories titled "Yocto Linux Kernel." Within this group, you will find the four different kernels supported by the Yocto Project:
linux-yocto-2.6.34- The stable Linux Yocto kernel that is based on the Linux 2.6.34 release.linux-yocto-2.6.37- The stable Linux Yocto kernel that is based on the Linux 2.6.37 release.linux-yocto-3.0- The current Linux Yocto kernel that is based on the Linux 3.0 release.linux-yocto-dev- A development kernel based on the latest upstream release candidate available.
The kernels are maintained using the Git revision control system that structures them using the familiar "tree", "branch", and "leaf" scheme. Branches represent diversions from general code to more specific code, while leaves represent the end-points for a complete and unique kernel whose source files when gathered from the root of the tree to the leaf accumulate to create the files necessary for a specific piece of hardware and its features. The following figure displays this concept:
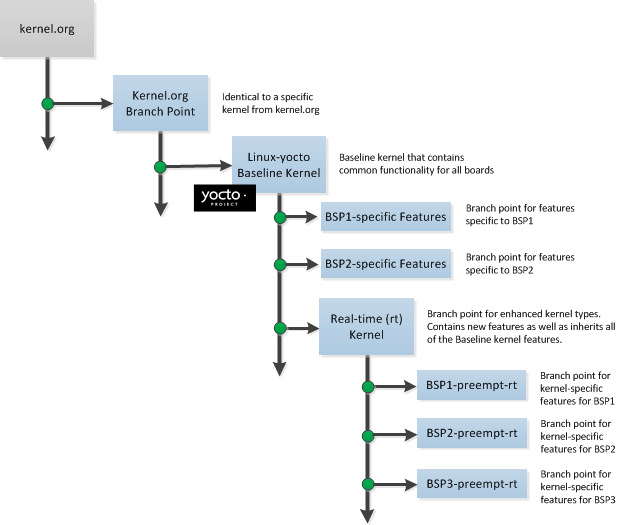 |
Within the figure, the "Kernel.org Branch Point" represents the point in the tree
where a supported base kernel is modified from the Linux kernel.
For example, this could be the branch point for the linux-yocto-3.0
kernel.
Thus, everything further to the right in the structure is based on the
linux-yocto-3.0 kernel.
Branch points to right in the figure represent where the
linux-yocto-3.0 kernel is modified for specific hardware
or types of kernels, such as real-time kernels.
Each leaf thus represents the end-point for a kernel designed to run on a specific
targeted device.
The overall result is a Git-maintained repository from which all the supported Yocto Project kernel types can be derived for all the supported Yocto Project devices. A big advantage to this scheme is the sharing of common features by keeping them in "larger" branches within the tree. This practice eliminates redundant storage of similar features shared among kernels.
Note
Keep in mind the figure does not take into account all four supported Linux Yocto kernel types, but rather shows a single generic kernel just for conceptual purposes. Also keep in mind that this structure represents the Yocto Project source repositories that are either pulled from during the build or established on the host development system prior to the build by either cloning a particular kernel's Git repository or by downloading and unpacking a tarball.
Storage of all the available kernel source code is one thing, while representing the code on your host development system is another. Conceptually, you can think of the Yocto Project kernel source repositories as all the source files necessary for all the supported kernels. As a developer, you are just interested in the source files for the kernel on on which you are working. And, furthermore, you need them available on your host system.
You make kernel source code available on your host development system by using Git to create a bare clone of the Linux Yocto kernel Git repository in which you are interested. Then, you use Git again to clone a copy of that bare clone. This copy represents the directory structure on your host system that is particular to the kernel you want. These are the files you actually modify to change the kernel. See the Linux Yocto Kernel item earlier in this manual for an example of how to set up the kernel source directory structure on your host system.
This next figure illustrates how the kernel source files might be arranged on your host system.
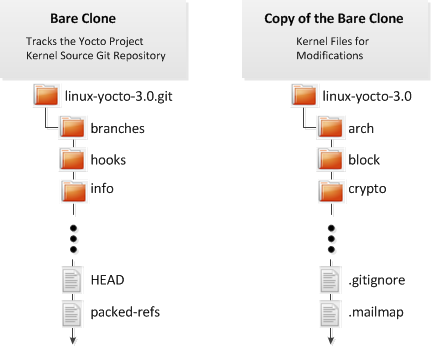 |
In the previous figure, the file structure on the left represents the bare clone set up to track the Yocto Project kernel Git repository. The structure on the right represents the copy of the bare clone. When you make modifcations to the kernel source code, this is the area in which you work. Once you make corrections, you must use Git to push the committed changes to the bare clone. The example in Section B.1, “Modifying the Kernel Source Code” provides a detailed example.
What happens during the build?
When you build the kernel on your development system all files needed for the build
are taken from the Yocto Project source repositories pointed to by the
SRC_URI variable and gathered in a temporary work area
where they are subsequently used to create the unique kernel.
Thus, in a sense, the process constructs a local source tree specific to your
kernel to generate the new kernel image - a source generator if you will.
The following figure shows the temporary file structure created on your host system when the build occurs. This build directory contains all the source files used during the build.
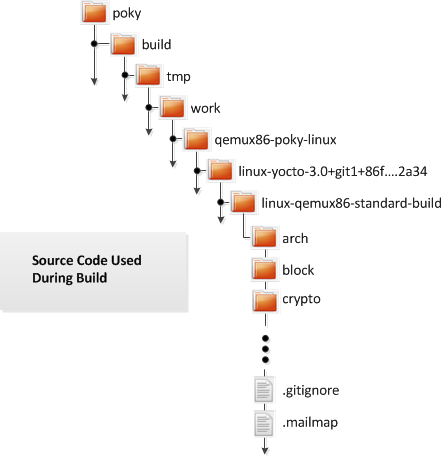 |
Again, for a complete discussion of the Yocto Project kernel's architcture and its branching strategy, see the The Yocto Project Kernel Architecture and Use Manual. Also, you can reference Section B.1, “Modifying the Kernel Source Code” for a detailed example that modifies the kernel.
This illustration and the following list summarizes the kernel modification general workflow.
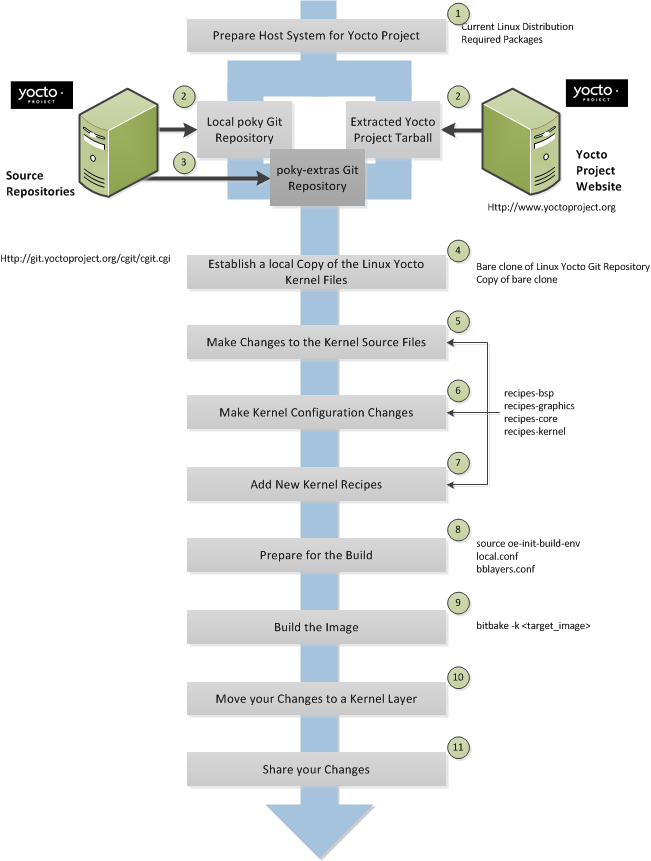 |
Set up your host development system to support development using the Yocto Project: See "The Linux Distributions" and "The Packages" sections both in the Yocto Project Quick Start for requirements.
Establish a local copy of the Yocto Project files on your system: Having the Yocto Project files on your system gives you access to the build process and tools you need. For information on how to get these files, see the bulleted item "Yocto Project Release" earlier in this manual.
Set up the
poky-extrasGit repository: This repository is the area for your configuration fragments, new kernel recipes, and the kernel.bbappendfile used during the build. It is good practice to set this repository up inside the local Yocto Project files Git repository. For information on how to get these files, see the bulleted item "Thepoky-extrasGit Repository" earlier in this manual.Note
While it is certainly possible to modify the kernel without involving a local Git repository, the suggested workflow for kernel modification using the Yocto Project does use a Git repository.Establish a local copy of the Linux Yocto kernel files on your system: In order to make modifications to the kernel you need two things: a bare clone of the Linux Yocto kernel you are modifying and a copy of that bare clone. The bare clone is required by the build process and is the area to which you push your kernel source changes (pulling does not work with bare clones). The copy of the bare clone is a local Git repository that contains all the kernel's source files. You make your changes to the files in this copy of the bare clone. For information on how to set these two items up, see the bulleted item "Linux Yocto Kernel" earlier in this manual.
Make changes to the kernel source code if applicable: Modifying the kernel does not always mean directly changing source files. However, if you have to do this, you make the changes in the local Git repository you set up to hold the source files (i.e. the copy of the bare clone). Once the changes are made, you need to use Git commands to commit the changes and then push them to the bare clone.
Make kernel configuration changes if applicable: If your situation calls for changing the kernel's configuration, you can use
menuconfigto enable and disable kernel configurations. Usingmenuconfigallows you to interactively develop and test the configuration changes you are making to the kernel. When saved, changes usingmenuconfigupdate the kernel's.config. Try to resist the temptation of directly editing the.configfile found in the Yocto Project build directory attmp/sysroots/<machine-name>/kernel. Doing so, can produce unexpected results when the Yocto Project build system regenerates the configuration file.Once you are satisfied with the configuration changes made using
menuconfig, you can directly examine the.configfile against a saved original and gather those changes into a config fragment to be placed inside a.bbappendAdd or extend kernel recipes if applicable: The standard layer structure organizes recipe files inside the
meta-kernel-devlayer that is within thepoky-extrasGit repository. If you need to add new kernel recipes, you add them within this layer. Also within this area, you will find the.bbappendfile that appends information to the kernel's recipe file used during the build.Prepare for the build: Once you have made all the changes to your kernel (configurations, source code changes, recipe additions, or recipe changes), there remains a few things you need to do in order for the Yocto Project build system to create your image. If you have not done so, you need to get the build environment ready by sourcing the environment setup script described earlier. You also need to be sure two key configuration files (
local.confandbblayers.conf) are configured appropriately.The entire process for building an image is overviewed in the "Building an Image" section of the Yocto Project Quick Start. You might want to reference this information. Also, you should look at the detailed examples found in the appendices at at the end of this manual.
Build the image: The Yocto Project build system Poky uses the BitBake tool to build images based on the type of image you want to create. You can find more information on BitBake here.
The build process supports several types of images to satisfy different needs. See the appendix "Reference: Images" in the Yocto Project Reference Manual for information on supported images.
Make your configuration changes available in the kernel layer: Up to this point, all the configuration changes to the kernel have been done and tested iteratively. Once they are tested and ready to go, you can move them into the kernel layer, which allows you to distribute the layer.
If applicable, share your in-tree changes: If the changes you made are suited for all Linux Yocto users, you might want to send them on for inclusion into the Linux Yocto Git repository. If the changes are accepted, the Yocto Project Maintainer pulls them into the master branch of the kernel tree. Doing so makes them available to everyone using the kernel.
Application development involves creation of an application that you want to be able to run on your target hardware, which is running a Linux Yocto image. The Yocto Project provides an Application Development Toolkit (ADT) that facilitates quick development and integration of your application into its run-time environment. Using the ADT you can employ cross-development toolchains designed for your target hardware to compile and link your application. You can then deploy your application to the actual hardware or to the QEMU emulator for testing. If you are familiar with the popular Eclipse IDE, you can use an Eclipse Yocto Plug-in to allow you to develop, deploy, and test your application all from within Eclipse.
While we strongly suggest using the Yocto Project ADT to develop your application, you might not want to. If this is the case, you can still use pieces of the Yocto Project for your development process. However, because the process can vary greatly, this manual does not provide detail on the process.
To help you understand how application development works in the Yocto Project ADT environment, this section provides an overview of the general development process. If you want to see a detailed example of the process as it is used from within the Eclipse IDE, see The Application Development Toolkit (ADT) User's Manual.
This illustration and the following list summarizes the application development general workflow.
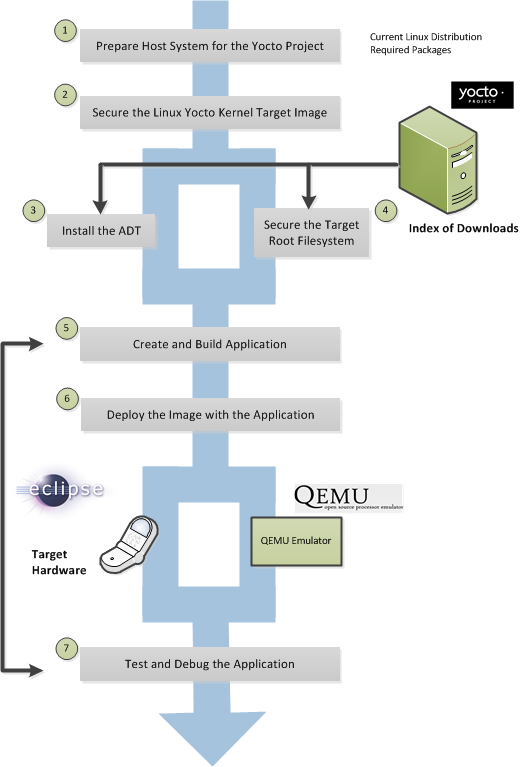 |
Prepare the Host System for the Yocto Project: See "The Linux Distributions" and "The Packages" sections both in the Yocto Project Quick Start for requirements.
Secure the Linux Yocto Kernel Target Image: You must have a target kernel image that has been built using the Yocto Project.
Depending on whether the Yocto Project has a pre-built image that matches your target architecture and where you are going to run the image while you develop your application (QEMU or real hardware), the area you get the image from differs.
Download the image from
machinesif your target architecture is supported and you are going to develop and test your application on actual hardware.Download the image from the
machines/qemuif your target architecture is supported and you are going to develop and test your application using the QEMU emulator.Build your image if you cannot find a pre-built image that matches your target architecture. If your target architecture is similar to a supported architecture, you can modify the kernel image before you build it. See the "Kernel Modification Workflow" section earlier in this manual for information on how to create a modified Linux Yocto kernel.
For information on pre-built kernel image naming schemes for images that can run on the QEMU emulator, see the "Using Pre-Built Binaries and QEMU" section in The Yocto Project Quick Start.
Install the ADT: The ADT provides a target-specific cross-development toolchain, the root filesystem, the QEMU emulator, and other tools that can help you develop your application. While it is possible to get these pieces separately, the Yocto Project provides an easy method. You can get these pieces by running an ADT installer script, which is configurable. For information on how to install the ADT, see the "Using the ADT Installer" section in The Yocto Project Application Development (ADT) User's Manual.
If Applicable, Secure the Target Root Filesystem: If you choose not to install the ADT using the ADT Installer, you need to find and download the appropriate root filesystems. You can find these tarballs in the same areas used for the kernel images. Depending on the type of image you are running, the root filesystem you need differs. For example, if you are developing an application that runs on an image that supports Sato, you need to get root filesystem that supports Sato.
Create and Build your Application: At this point, you need to have source files for your application. Once you have the files, you can use the Eclipse IDE to import them and build the project. If you are not using Eclipse, you need to use the cross-development tools you have installed to create the image.
Deploy the Image with the Application: If you are using the Eclipse IDE, you can deploy your image to the hardware or to QEMU through the project's preferences. If you are not using the Eclipse IDE, then you need to deploy the application using other methods to the hardware. Or, if you are using QEMU, you need to use that tool and load your image in for testing.
Test and Debug the Application: Once your application is deployed, you need to test it. Within the Eclipse IDE, you can use the debubbing environment along with the set of user-space tools installed along with the ADT to debug your application. Of course, the same user-space tools are available separately to use if you choose not to use the Eclipse IDE.
If you want to develop an application outside of the Yocto Project ADT environment, you can still employ the cross-development toolchain, the QEMU emulator, and a number of supported target image files. You just need to follow these general steps:
Install the cross-development toolchain for your target hardware: For information on how to install the toolchain, see the "Using a Cross-Toolchain Tarball" section in The Yocto Project Application Development (ADT) User's Manual.
Download the Target Image: The Yocto Project supports several target architectures and has many pre-built kernel images and root filesystem images.
If you are going to develop your application on hardware, go to the
machinesdownload area and choose a target machine area from which to download the kernel image and root filesystem. This download area could have several files in it that support development using actual hardware. For example, the area might contain.hddimgfiles that combine the kernel image with the filesystem, boot loaders, etc. Be sure to get the files you need for your particular development process.If you are going to develop your application and then run and test it using the QEMU emulator, go to the
machines/qemudownload area. From this area, go down into the directory for your target architecture (e.g.qemux86_64for an Intel®-based 64-bit architecture). Download kernel, root filesystem, and any other files you need for your process.Note
In order to use the root filesystem in QEMU, you need to extract it. See the "Extracting the Root Filesystem" section for information on how to extract the root filesystem.Develop and Test your Application: At this point, you have the tools to develop your application. If you need to separately install and use the QEMU emulator, you can go to QEMU Home Page to download and learn about the emulator.
Table of Contents
This appendix provides a complete BSP development example. The example assumes the following:
No previous preparation or use of the Yocto Project.
Use of the Crown Bay Board Support Package (BSP) as a "base" BSP from which to work. The example begins with the Crown Bay BSP as the starting point but ends by building a new 'atom-pc' BSP, which was based on the Crown Bay BSP.
Shell commands assume
bashExample was developed on an Intel-based Core i7 platform running Ubuntu 10.04 LTS released in April of 2010.
You need to have the Yocto Project files available on your host system.
You can get files through tarball extraction or by cloning the poky
Git repository.
The following paragraphs describe both methods.
For additional information, see the bulleted item
"Yocto Project Release".
As mentioned, one way to get the Yocto Project files is to use Git to clone the
poky repository:
$ git clone git://git.yoctoproject.org/poky
$ cd poky
Alternatively, you can start with the downloaded Poky "edison" tarball:
$ tar xfj poky-edison-6.0.tar.bz2
$ cd poky
Note
If you're using the tarball method, you can ignore all the following steps that ask you to carry out Git operations. You already have the results of those operations in the form of the edison release tarballs. Consequently, there is nothing left to do other than extract those tarballs into the proper locations.
Once you have the local poky Git repository set up,
you have many development branches from which you can work.
From inside the repository you can see the branch names and the tag names used
in the Git repository using either of the following two commands:
$ git branch -a
$ git tag -l
For this example we are going to use the Yocto Project 1.1 Release, which is code
named "edison".
These commands create a local branch named edison
that tracks the remote branch of the same name.
$ git checkout -b edison origin/edison
Switched to a new branch 'edison'
For this example, the base BSP is the Intel®
Atom™ Processor E660 with Intel Platform
Controller Hub EG20T Development Kit, which is otherwise referred to as "Crown Bay."
The BSP layer is meta-crownbay.
The base BSP is simply the BSP
we will be using as a starting point, so don't worry if you don't actually have Crown Bay
hardware.
The remainder of the example transforms the base BSP into a BSP that should be
able to boot on generic atom-pc (netbook) hardware.
For information on how to choose a base BSP, see "Developing a Board Support Package (BSP)".
You need to have the base BSP layer on your development system. Similar to the local Yocto Project files, you can get the BSP layer in a couple of different ways: download the BSP tarball and extract it, or set up a local Git repository that has the Yocto Project BSP layers. You should use the same method that you used to get the local Yocto Project files earlier. See "Getting Setup" for information on how to get the BSP files.
This example assumes the BSP layer will be located within a directory named
meta-intel contained within the poky
parent directory.
The following steps will automatically create the
meta-intel directory and the contained
meta-crownbay starting point in both the Git and the tarball cases.
If you're using the Git method, you could do the following to create
the starting layout after you have made sure you are in the poky
directory created in the previous steps:
$ git clone git://git.yoctoproject.org/meta-intel.git
$ cd meta-intel
Alternatively, you can start with the downloaded Crown Bay tarball.
You can download the edison version of the BSP tarball from the
Download page of the
Yocto Project website.
Here is the specific link for the tarball needed for this example:
http://downloads.yoctoproject.org/releases/yocto/yocto-1.1/machines/crownbay-noemgd/crownbay-noemgd-edison-6.0.0.tar.bz2.
Again, be sure that you are already in the poky directory
as described previously before installing the tarball:
$ tar xfj crownbay-noemgd-edison-6.0.0.tar.bz2
$ cd meta-intel
The meta-intel directory contains all the metadata
that supports BSP creation.
If you're using the Git method, the following
step will switch to the edison metadata.
If you're using the tarball method, you already have the correct metadata and can
skip to the next step.
Because meta-intel is its own Git repository, you will want
to be sure you are in the appropriate branch for your work.
For this example we are going to use the edison branch.
$ git checkout -b edison origin/edison
Switched to a new branch 'edison'
Now that you have the local Yocto Project files and the base BSP files, you need to create a
new layer for your BSP.
To create your BSP layer, you simply copy the meta-crownbay
layer to a new layer.
For this example, the new layer will be named meta-mymachine.
The name should follow the BSP layer naming convention, which is
meta-<name>.
The following assumes your working directory is meta-intel
inside the local Yocto Project files.
To start your new layer, just copy the new layer alongside the existing
BSP layers in the meta-intel directory:
$ cp -a meta-crownbay/ meta-mymachine
Right now you have two identical BSP layers with different names:
meta-crownbay and meta-mymachine.
You need to change your configurations so that they work for your new BSP and
your particular hardware.
The following sections look at each of these areas of the BSP.
We will look first at the configurations, which are all done in the layer’s
conf directory.
First, since in this example the new BSP will not support EMGD, we will get rid of the
crownbay.conf file and then rename the
crownbay-noemgd.conf file to mymachine.conf.
Much of what we do in the configuration directory is designed to help the Yocto Project
build system work with the new layer and to be able to find and use the right software.
The following two commands result in a single machine configuration file named
mymachine.conf.
$ rm meta-mymachine/conf/machine/crownbay.conf
$ mv meta-mymachine/conf/machine/crownbay-noemgd.conf \
meta-mymachine/conf/machine/mymachine.conf
Next, we need to make changes to the mymachine.conf itself.
The only changes we want to make for this example are to the comment lines.
Changing comments, of course, is never strictly necessary, but it's alway good form to make
them reflect reality as much as possible.
Here, simply substitute the Crown Bay name with an appropriate name for the BSP
(mymachine in this case) and change the description to
something that describes your hardware.
Note that inside the mymachine.conf is the
PREFERRED_PROVIDER_virtual/kernel statement.
This statement identifies the kernel that the BSP is going to use.
In this case, the BSP is using linux-yocto, which is the
current Linux Yocto kernel based on the Linux 3.0 release.
The next configuration file in the new BSP layer we need to edit is
meta-mymachine/conf/layer.conf.
This file identifies build information needed for the new layer.
You can see the
"Layer Configuration File" section in
The Board
Support Packages (BSP) Development Guide
for more information on this configuration file.
Basically, we are changing the existing statements to work with our BSP.
The file contains these statements that reference the Crown Bay BSP:
BBFILE_COLLECTIONS += "crownbay"
BBFILE_PATTERN_crownbay := "^${LAYERDIR}/"
BBFILE_PRIORITY_crownbay = "6"
Simply substitute the machine string name crownbay
with the new machine name mymachine to get the following:
BBFILE_COLLECTIONS += "mymachine"
BBFILE_PATTERN_mymachine := "^${LAYERDIR}/"
BBFILE_PRIORITY_mymachine = "6"
Now we will take a look at the recipes in your new layer.
The standard BSP structure has areas for BSP, graphics, core, and kernel recipes.
When you create a BSP, you use these areas for appropriate recipes and append files.
Recipes take the form of .bb files.
If you want to leverage the existing recipes the Yocto Project build system uses
but change those recipes, you can use .bbappend files.
All new recipes and append files for your layer must go in the layer’s
recipes-bsp, recipes-kernel,
recipes-core, and
recipes-graphics directories.
First, let's look at recipes-bsp.
For this example we are not adding any new BSP recipes.
And, we only need to remove the formfactor we do not want and change the name of
the remaining one that doesn't support EMGD.
These commands take care of the recipes-bsp recipes:
$ rm -rf meta-mymachine/recipes-bsp/formfactor/formfactor/crownbay
$ mv meta-mymachine/recipes-bsp/formfactor/formfactor/crownbay-noemgd/ \
meta-mymachine/recipes-bsp/formfactor/formfactor/mymachine
Now let's look at recipes-graphics.
For this example we want to remove anything that supports EMGD and
be sure to rename remaining directories appropriately.
The following commands clean up the recipes-graphics directory:
$ rm -rf meta-mymachine/recipes-graphics/xorg-xserver/xserver-xf86-config/crownbay
$ mv meta-mymachine/recipes-graphics/xorg-xserver/xserver-xf86-config/crownbay-noemgd \
meta-mymachine/recipes-graphics/xorg-xserver/xserver-xf86-config/mymachine
At this point the recipes-graphics directory just has files that
support Video Electronics Standards Association (VESA) graphics modes and not EMGD.
Now let's look at changes in recipes-core.
The file task-core-tools.bbappend in
recipes-core/tasks appends the similarly named recipe
located in the local Yocto Project files at
meta/recipes-core/tasks.
The "append" file in our layer right now is Crown Bay-specific and supports
EMGD and non-EMGD.
Here are the contents of the file:
RRECOMMENDS_task-core-tools-profile_append_crownbay = " systemtap"
RRECOMMENDS_task-core-tools-profile_append_crownbay-noemgd = " systemtap"
The RRECOMMENDS statements list packages that
extend usability.
The first RRECOMMENDS statement can be removed, while the
second one can be changed to reflect meta-mymachine:
RRECOMMENDS_task-core-tools-profile_append_mymachine = " systemtap"
Finally, let's look at recipes-kernel changes.
Recall that the BSP uses the linux-yocto kernel as determined
earlier in the mymachine.conf.
The recipe for that kernel is not located in the
BSP layer but rather in the local Yocto Project files at
meta/recipes-kernel/linux and is
named linux-yocto_3.0.bb.
The SRCREV_machine and SRCREV_meta
statements point to the exact commits used by the Yocto Project development team
in their source repositories that identify the right kernel for our hardware.
In other words, the SRCREV values are simply Git commit
IDs that identify which commit on each
of the kernel branches (machine and meta) will be checked out and used to build
the kernel.
However, in the meta-mymachine layer in
recipes-kernel/linux resides a .bbappend
file named linux-yocto_3.0.bbappend that
is appended to the recipe of the same name in meta/recipes-kernel/linux.
Thus, the SRCREV statements in the "append" file override
the more general statements found in meta.
The SRCREV statements in the "append" file currently identify
the kernel that supports the Crown Bay BSP with and without EMGD support.
Here are the statements:
SRCREV_machine_pn-linux-yocto_crownbay ?= \
"2247da9131ea7e46ed4766a69bb1353dba22f873"
SRCREV_meta_pn-linux-yocto_crownbay ?= \
"d05450e4aef02c1b7137398ab3a9f8f96da74f52"
SRCREV_machine_pn-linux-yocto_crownbay-noemgd ?= \
"2247da9131ea7e46ed4766a69bb1353dba22f873"
SRCREV_meta_pn-linux-yocto_crownbay-noemgd ?= \
"d05450e4aef02c1b7137398ab3a9f8f96da74f52"
You will notice that there are two pairs of SRCREV statements.
The top pair identifies the kernel that supports
EMGD, which we don’t care about in this example.
The bottom pair identifies the kernel that we will use:
linux-yocto.
At this point though, the unique commit strings all are still associated with
Crown Bay and not meta-mymachine.
To fix this situation in linux-yocto_3.0.bbappend,
we delete the two SRCREV statements that support
EMGD (the top pair).
We also change the remaining pair to specify mymachine
and insert the commit identifiers to identify the kernel in which we
are interested, which will be based on the atom-pc-standard
kernel.
In this case, because we're working with the edison branch of everything, we
need to use the SRCREV values for the atom-pc branch
that are associated with the edison release.
To find those values, we need to find the SRCREV
values that edison uses for the atom-pc branch, which we find in the
poky/meta-yocto/recipes-kernel/linux/linux-yocto_3.0.bbappend
file.
The machine SRCREV we want is in the
SRCREV_machine_atom-pc variable.
The meta SRCREV isn't specified in this file, so it must be
specified in the base kernel recipe in the
poky/meta/recipes-kernel/linux/linux-yocto_3.0.bb
file, in the SRCREV_meta variable found there.
It happens to be the same as the value we already inherited from the
meta-crownbay BSP.
Here are the final SRCREV statements:
SRCREV_machine_pn-linux-yocto_mymachine ?= \
"1e18e44adbe79b846e382370eb29bc4b8cd5a1a0"
SRCREV_meta_pn-linux-yocto_mymachine ?= \
"d05450e4aef02c1b7137398ab3a9f8f96da74f52"
In this example, we're using the SRCREV values we
found already captured in the edison release because we're creating a BSP based on
edison.
If, instead, we had based our BSP on the master branches, we would want to use
the most recent SRCREV values taken directly from the kernel repo.
We will not be doing that for this example.
However, if you do base a future BSP on master and
if you are familiar with Git repositories, you probably won’t have trouble locating the
exact commit strings in the Yocto Project source repositories you need to change
the SRCREV statements.
You can find all the machine and meta
branch points (commits) for the linux-yocto-3.0 kernel at
http://git.yoctoproject.org/cgit/cgit.cgi/linux-yocto-3.0.
If you need a little more assistance after going to the link then do the following:
Expand the list of branches by clicking
[…]Click on the
yocto/standard/common-pc/atom-pcbranchClick on the commit column header to view the top commit
Copy the commit string for use in the
linux-yocto_3.0.bbappendfile
For the SRCREV statement that points to the meta
branch use the same procedure except expand the meta
branch in step 2 above.
Also in the linux-yocto_3.0.bbappend file are
COMPATIBLE_MACHINE, KMACHINE,
and KERNEL_FEATURES statements.
Two sets of these exist: one set supports EMGD and one set does not.
Because we are not interested in supporting EMGD those three can be deleted.
The remaining three must be changed so that mymachine replaces
crownbay-noemgd and crownbay.
Because we are using the atom-pc branch for this new BSP, we can also find
the exact branch we need for the KMACHINE variable in our new BSP from the value
we find in the
poky/meta-yocto/recipes-kernel/linux/linux-yocto_3.0.bbappend
file we looked at in a previous step.
In this case, the value we want is in the KMACHINE_atom-pc variable in that file.
Here is the final linux-yocto_3.0.bbappend file after all
the edits:
FILESEXTRAPATHS_prepend := "${THISDIR}/${PN}:"
COMPATIBLE_MACHINE_mymachine = "mymachine"
KMACHINE_mymachine = "yocto/standard/common-pc/atom-pc"
KERNEL_FEATURES_append_mymachine += " cfg/smp.scc"
SRCREV_machine_pn-linux-yocto_mymachine ?= \
"1e18e44adbe79b846e382370eb29bc4b8cd5a1a0"
SRCREV_meta_pn-linux-yocto_mymachine ?= \
"d05450e4aef02c1b7137398ab3a9f8f96da74f52"
In summary, the edits to the layer’s recipe files result in removal of any files and
statements that do not support your targeted hardware in addition to the inclusion
of any new recipes you might need.
In this example, it was simply a matter of ridding the new layer
meta-mymachine of any code that supported the EMGD features
and making sure we were identifying the kernel that supports our example, which
is the atom-pc-standard kernel.
We did not introduce any new recipes to the layer.
Finally, it is also important to update the layer’s README
file so that the information in it reflects your BSP.
To get ready to build your image that uses the new layer you need to do the following:
Get the environment ready for the build by sourcing the environment script. The environment script is in the top-level of the local Yocto Project files directory structure. The script has the string
init-build-envin the file’s name. For this example, the following command gets the build environment ready:$ source oe-init-build-env yocto-buildWhen you source the script a build directory is created in the current working directory. In our example we were in the
pokydirectory. Thus, entering the previous command created theyocto-builddirectory. If you do not provide a name for the build directory it defaults tobuild. Theyocto-builddirectory contains aconfdirectory that has two configuration files you will need to check:bblayers.confandlocal.conf.Check and edit the resulting
local.conffile. This file minimally identifies the machine for which to build the image by configuring theMACHINEvariable. For this example you must set the variable to mymachine as follows:MACHINE ??= “mymachine”You should also be sure any other variables in which you are interested are set. Some variables to consider are
BB_NUMBER_THREADSandPARALLEL_MAKE, both of which can greatly reduce your build time if you are using a multi-threaded development system (e.g. values of8andj 6, respectively are optimal for a development machine that has four available cores).Update the
bblayers.conffile so that it includes the path to your new BSP layer. In this example you need to include the pathname tometa-mymachine. For this example theBBLAYERSvariable in the file would need to include the following path:$HOME/poky/meta-intel/meta-mymachine
The appendix Reference: Variables Glossary in the Yocto Project Reference Manual has more information on configuration variables.
To build the image for our meta-mymachine BSP enter the following command
from the same shell from which you ran the setup script.
You should run the bitbake command without any intervening shell commands.
For example, moving your working directory around could cause problems.
Here is the command for this example:
$ bitbake -k core-image-sato
This command specifies an image that has Sato support and that can be run from a USB device or from a CD without having to first install anything. The build process takes significant time and includes thousands of tasks, which are reported at the console. If the build results in any type of error you should check for misspellings in the files you changed or problems with your host development environment such as missing packages.
Finally, once you have an image, you can try booting it from a device
(e.g. a USB device).
To prepare a bootable USB device, insert a USB flash drive into your build system and
copy the .hddimg file, located in the
poky/build/tmp/deploy/images
directory after a successful build to the flash drive.
Assuming the USB flash drive takes device /dev/sdf,
use dd to copy the live image to it.
For example:
# dd if=core-image-sato-mymachine-20111101223904.hddimg of=/dev/sdf
# sync
# eject /dev/sdf
You should now have a bootable USB flash device.
Insert the device into a bootable USB socket on the target, and power it on. The system should boot to the Sato graphical desktop. [1]
For reference, the sato image produced by the previous steps for edison should look like the following in terms of size. If your sato image is much different from this, you probably made a mistake in one of the above steps:
358715392 2011-11-01 19:11 core-image-sato-mymachine-20111101223904.hddimg
Note
The previous instructions are also present in the README that was copied from meta-crownbay, which should also be updated to reflect the specifics of your new BSP. That file and theREADME.hardware file in the top-level
poky directory
also provides some suggestions for things to try if booting fails and produces
strange error messages.
[1] Because
this new image is not in any way tailored to the system you're
booting it on, which is assumed to be some sort of atom-pc (netbook) system for this
example, it might not be completely functional though it should at least boot to a text
prompt.
Specifically, it might fail to boot into graphics without some tweaking.
If this ends up being the case, a possible next step would be to replace the
mymachine.conf
contents with the contents of atom-pc.conf and replace
xorg.conf with atom-pc xorg.conf
in meta-yocto and see if it fares any better.
In any case, following the previous steps will give you a buildable image that
will probably boot on most systems.
Getting things working like you want
them to for your hardware will normally require some amount of experimentation with
configuration settings.
Table of Contents
- B.1. Modifying the Kernel Source Code
- B.1.1. Understanding the Files You Need
- B.1.2. Setting Up the Local Yocto Project Files Git Repository
- B.1.3. Setting Up the poky-extras Git Repository
- B.1.4. Setting Up the Bare Clone and its Copy
- B.1.5. Building and Booting the Default QEMU Kernel Image
- B.1.6. Changing the Source Code and Pushing it to the Bare Clone
- B.1.7. Changing Build Parameters for Your Build
- B.1.8. Building and Booting the Modified QEMU Kernel Image
- B.2. Changing the Kernel Configuration
- B.3. Adding Kernel Recipes
Kernel modification involves changing or adding configurations to an existing kernel, changing or adding recipes to the kernel that are needed to support specific hardware features, or even altering the source code itself. This appendix presents simple examples that modify the kernel source code, change the kernel configuration, and add a kernel source recipe.
This example adds some simple QEMU emulator console output at boot time by
adding printk statements to the kernel's
calibrate.c source code file.
Booting the modified image causes the added messages to appear on the emulator's
console.
Before you modify the kernel, you need to know what Git repositories and file structures you need. Briefly, you need the following:
A local Yocto Project files Git repository
The
poky-extrasGit repository placed within the local Yocto Project files Git repositoryA bare clone of the Linux Yocto kernel upstream Git repository to which you want to push your modifications.
A copy of that bare clone in which you make your source modifcations
The following figure summarizes these four areas. Within each rectangular that represents a data structure, a host development directory pathname appears at the lower left-hand corner of the box. These pathnames are the locations used in this example. The figure also provides key statements and commands used during the kernel modification process:
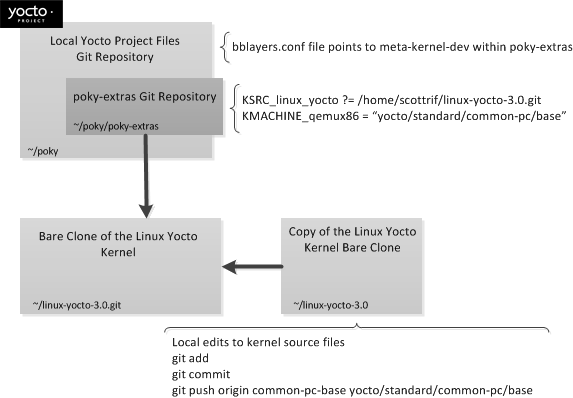 |
Here is a brief description of the four areas:
Local Yocto Project Files Git Repository: This area contains all the metadata that supports building images in the Yocto Project build environment - the local Yocto Project files. The local Yocto Project files Git repository also contains the build directory and a configuration directory that let you control the build. Note also that in this example, the repository also contains the
poky-extrasGit repository.See the bulleted item "Yocto Project Release" for information on how to get these files.
poky-extrasGit Repository: This area contains themeta-kernel-devlayer, which is where you make changes that append the kernel build recipes. You edit.bbappendfiles to locate your local kernel source files and to identify the kernel being built. This Git repository is a gathering place for extensions to the Linux Yocto (or really any) kernel recipes that faciliate the creation and development of kernel features, BSPs or configurations.See the bulleted item "The
poky-extrasGit Repository" for information on how to get these files.Bare Clone of the Linux Yocto kernel: This bare Git repository tracks the upstream Git repository of the Linux Yocto kernel source code you are changing. When you modify the kernel you must work through a bare clone. All source code changes you make to the kernel must be committed and pushed to the bare clone using Git commands. As mentioned, the
.bbappendfile in thepoky-extrasrepository points to the bare clone so that the build process can locate the locally changed source files.See the bulleted item "Linux Yocto Kernel" for information on how to set up the bare clone.
Copy of the Linux Yocto Kernel Bare Clone: This Git repository contains the actual source files that you modify. Any changes you make to files in this location need to ultimately be pushed to the bare clone using the
git pushcommand.See the bulleted item "Linux Yocto Kernel" for information on how to set up the bare clone.
Note
Typically, Git workflows follow a scheme where changes made to a local area are pulled into a Git repository. However, because thegit pullcommand does not work with bare clones, this workflow pushes changes to the repository even though you could use other more complicated methods to get changes into the bare clone.
You can get the local Yocto Project files through tarball extraction or by
cloning the poky Git repository.
This example uses poky as the root directory of the
local Yocto Project files Git repository.
See the bulleted item
"Yocto Project Release"
for information on how to get these files.
Once you have the repository set up, you have many development branches from which you can work. From inside the repository you can see the branch names and the tag names used in the Git repository using either of the following two commands:
$ cd poky
$ git branch -a
$ git tag -l
This example uses the Yocto Project 1.1 Release code named "edison",
which maps to the edison branch in the repository.
The following commands create and checkout the local edison
branch:
$ git checkout -b edison origin/edison
Branch edison set up to track remote branch edison from origin.
Switched to a new branch 'edison'
This example places the poky-extras Git repository inside
of poky.
See the bulleted item
"The
poky-extras Git Repository"
for information on how to get the poky-extras repository.
This example modifies the linux-yocto-3.0 kernel.
Thus, you need to create a bare clone of that kernel and then make a copy of the
bare clone.
See the bulleted item
"Linux Yocto Kernel"
for information on how to do that.
The bare clone exists for the kernel build tools and simply as the receiving end
of git push
commands after you make edits and commits inside the copy of the clone.
The copy (linux-yocto-3.0 in this example) has to have
a local branch created and checked out for your work.
This example uses common-pc-base as the local branch.
The following commands create and checkout the branch:
$ cd ~/linux-yocto-3.0
$ git checkout -b common-pc-base origin/yocto/standard/common-pc/base
Branch common-pc-base set up to track remote branch
yocto/standard/common-pc/base from origin.
Switched to a new branch 'common-pc-base'
Before we make changes to the kernel source files, this example first builds the default image and then boots it inside the QEMU emulator.
Note
Because a full build can take hours, you should check two variables in thebuild directory that is created after you source the
oe-init-build-env script.
You can find these variables
BB_NUMBER_THREADS and PARALLEL_MAKE
in the build/conf directory in the
local.conf configuration file.
By default, these variables are commented out.
If your host development system supports multi-core and multi-thread capabilities,
you can uncomment these statements and set the variables to significantly shorten
the full build time.
As a guideline, set BB_NUMBER_THREADS to twice the number
of cores your machine supports and set PARALLEL_MAKE to one and
a half times the number of cores your machine supports.
The following two commands build the default qemux86 image and
source build environment setup script.
If necessary, the script creates the build directory:
$ cd ~/poky
$ source oe-init-build-env
### Shell environment set up for builds. ###
You can now run 'bitbake <target>'
Common targets are:
core-image-minimal
core-image-sato
meta-toolchain
meta-toolchain-sdk
adt-installer
meta-ide-support
You can also run generated qemu images with a command like 'runqemu qemux86'
The following bitbake command starts the build:
$ bitbake -k core-image-minimal
Note
Be sure to check the settings in thelocal.conf
before starting the build.
After the build completes, you can start the QEMU emulator using the resulting image
qemux86 as follows:
$ runqemu qemux86
As the image boots in the emulator, console message and status output appears
across the terminal window.
Because the output scrolls by quickly, it is difficult to read.
To examine the output, you log into the system using the
login root with no password.
Once you are logged in, issue the following command to scroll through the
console output:
# dmesg | less
Take note of the output as you will want to look for your inserted print command output later in the example.
The file you change in this example is named calibrate.c
and is located in the linux-yocto-3.0 Git repository
(the copy of the bare clone) in init.
This example simply inserts several printk statements
at the beginning of the calibrate_delay function.
Here is the unaltered code at the start of this function:
void __cpuinit calibrate_delay(void)
{
unsigned long lpj;
static bool printed;
if (preset_lpj) {
.
.
.
Here is the altered code showing five new printk statements
just after initializing lps_precision:
void __cpuinit calibrate_delay(void)
{
unsigned long lpj;
static bool printed;
printk("*************************************\n");
printk("* *\n");
printk("* HELLO YOCTO KERNEL *\n");
printk("* *\n");
printk("*************************************\n");
if (preset_lpj) {
.
.
.
After making and saving your changes, you need to stage them for the push. The following Git commands are one method of staging and committing your changes:
$ git add calibrate.c
$ git commit --signoff
Once the source code has been modified, you need to use Git to push the changes to the bare clone. If you do not push the changes, then the Yocto Project build system will not pick up the changed source files.
The following command pushes the changes to the bare clone:
$ git push origin common-pc-base:yocto/standard/common-pc/base
At this point, the source has been changed and pushed. The example now defines some variables used by the Yocto Project build system to locate your kernel source. You essentially need to identify where to find the kernel recipe and the changed source code. You also need to be sure some basic configurations are in place that identify the type of machine you are building and to help speed up the build should your host support multiple-core and thread capabilities.
Do the following to make sure the build parameters are set up for the example.
Once you set up these build parameters, they do not have to change unless you
change the target architecture of the machine you are building or you move
the bare clone, copy of the clone, or the poky-extras repository:
Build for the Correct Target Architecture: The
local.conffile in the build directory defines the build's target architecture. By default,MACHINEis set toqemux86, which specifies a 32-bit Intel® Architecture target machine suitable for the QEMU emulator. In this example,MACHINEis correctly configured.Optimize Build Time: Also in the
local.conffile are two variables that can speed your build time if your host supports multi-core and multi-thread capabilities:BB_NUMBER_THREADSandPARALLEL_MAKE. If the host system has multiple cores then you can optimize build time by settingBB_NUMBER_THREADSto twice the number of cores and settingPARALLEL_MAKEto one and a half times the number of cores.Identify Your
meta-kernel-devLayer: TheBBLAYERSvariable in thebblayers.conffile found in thepoky/build/confdirectory needs to have the path to your localmeta-kernel-devlayer. By default, theBBLAYERSvariable contains paths tometaandmeta-yoctoin thepokyGit repository. Add the path to yourmeta-kernel-devlocation. Be sure to substitute your user information in the statement. Here is an example:BBLAYERS = " \ /home/scottrif/poky/meta \ /home/scottrif/poky/meta-yocto \ /home/scottrif/poky/poky-extras/meta-kernel-dev \ "Identify Your Source Files: In the
linux-yocto_3.0.bbappendfile located in thepoky-extras/meta-kernel-dev/recipes-kernel/linuxdirectory, you need to identify the location of the local source code, which in this example is the bare clone namedlinux-yocto-3.0.git. To do this, set theKSRC_linux_yoctovariable to point to your locallinux-yocto-3.0.gitGit repository by adding the following statement. Be sure to substitute your user information in the statement:KSRC_linux_yocto ?= /home/scottrif/linux-yocto-3.0.gitSpecify the Kernel Machine: Also in the
linux-yocto_3.0.bbappendfile, you need to specify the kernel machine with the following statement:KMACHINE_qemux86 = "yocto/standard/common-pc/base"
Note
Before attempting to build the modified kernel, there is one more set of changes you need to make in themeta-kernel-dev layer.
Because all the kernel .bbappend files are parsed during the
build process regardless of whether you are using them or not, you should either
comment out the COMPATIBLE_MACHINE statements in all
.bbappend files, or you should simply remove all the files
except the one your are using for the build
(i.e. linux-yocto_3.0.bbappend in this example).
Next, you need to build the modified image. Do the following:
Your environment should be set up since you previously sourced the
oe-init-build-envscript. If it isn't, source the script again frompoky.Be sure old images are cleaned out by running the
cleanallBitBake task as follows:$ cd ~/poky $ bitbake -c cleanall linux-yoctoNote
Never remove any files by hand from thetmp/deploydirectory insided the local Yocto Project files build directory. Always use the BitBakecleanalltask to clear out previous builds.Build the kernel image using this command:
$ bitbake -k core-image-minimalFinally, boot the modified image in the QEMU emulator using this command:
$ runqemu qemux86
Log into the machine using root with no password and then
use the following shell command to scroll through the console's boot output.
# dmesg | less
You should see the results of your printk statements
as part of the output.
This example changes the default behavior, which is "off", of the Symmetric
Multi-processing Support (CONFIG_SMP) to "on".
It is a simple example that demonstrates how to reconfigure the kernel.
If you took the time to work through the example that modifies the kernel source code in "Modifying the Kernel Source Code" you should already have the Yocto Project files set up on your host machine.
If you don't have the Yocto Project files established on your system, See "Setting Up the Local Yocto Project Files Git Repository" for information. To reconfigure the kernel, this is the only Git repository you need to have set up.
By default, CONFIG_SMP supports single processor machines.
To see this default setting from within the QEMU emulator, boot your image using
the emulator as follows:
$ runqemu qemux86 qemuparams="-smp 2"
Login to the machine using root with no password.
After logging in, enter the following command to see how many processors are
being supported in the emulator.
The emulator reports support for a single processor:
# cat /proc/cpuinfo | grep processor
processor : 0
#
Logout of the emulator using the exit command and
then close it down.
The menuconfig tool provides an interactive method with which
to set kernel configurations.
You need to run menuconfig inside the Yocto BitBake environment.
Thus, the environment must be set up using the oe-init-build-env
script found in the Yocto Project files Git repository build directory.
If you have not sourced this script do so with the following commands:
$ cd ~/poky
$ source oe-init-build-env
After setting up the environment to run menuconfig, you are ready
to use the tool to interactively change the kernel configuration.
In this example, we are basing our changes on the linux-yocto-3.0
kernel.
The Yocto Project build environment recognizes this kernel as
linux-yocto.
Thus, the following command from the shell in which you previously sourced the
environment initialization script launches menuconfig:
$ bitbake linux-yocto -c menuconfig
Once menuconfig launches, navigate through the user interface
to find the CONFIG_SMP configuration setting.
You can find it at Processor Type and Features.
The configuration selection is
Symmetric Multi-processing Support.
After using the arrow keys to highlight this selection, press "y" to select it.
Then, exit out and save your selections.
Once you save the selection, the .config configuration file
is updated.
This is the file that the build system uses to configure the Linux Yocto kernel
when it is built.
You can find and examine this file in the Yocto Project files Git repository in
the build directory.
This example uses the following.
Note that this example directory is artificially split and many of the characters
in the actually filename are omitted in order to make it more
readable:
~/poky/build/tmp/work/qemux86-poky-linux/linux-yocto-2.6.37+git1+84f...
...r20/linux-qemux86-standard-build
Within the .config file, you can see the following setting:
CONFIG_SMP=y
A good method to isolate changed configurations is to use a combination of the
menuconfig tool and simple shell commands.
Before changing configurations with menuconfig, copy the
existing .config and rename it to something else,
use menuconfig to make
as many changes an you want and save them, then compare the renamed configuration
file against the newly created file.
You can use the resulting differences as your base to create configuration fragments
to permanently save in your kernel layer.
Note
Be sure to make a copy of the.config and don't just
rename it.
The Yocto Project build system needs an existing .config
from which to work.
At this point, you are ready to recompile your kernel image with the new setting in effect using the BitBake commands below:
$ bitbake linux-yocto -c compile -f
$ bitbake linux-yocto
Now run the QEMU emulator:
$ runqemu qemux86 qemuparams="-smp 2"
Login to the machine using root with no password
and test for the number of processors the kernel supports:
# cat /proc/cpuinfo | grep processor
processor : 0
processor : 1
#
From the output, you can see that you have successfully reconfigured the kernel.
