Copyright © 2010-2014 Linux Foundation
Permission is granted to copy, distribute and/or modify this document under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 2.0 UK: England & Wales as published by Creative Commons.
Manual Notes
This version of the Yocto Project Development Manual is for the 1.5.4 release of the Yocto Project. To be sure you have the latest version of the manual for this release, go to the Yocto Project documentation page and select the manual from that site. Manuals from the site are more up-to-date than manuals derived from the Yocto Project released TAR files.
If you located this manual through a web search, the version of the manual might not be the one you want (e.g. the search might have returned a manual much older than the Yocto Project version with which you are working). You can see all Yocto Project major releases by visiting the Releases page. If you need a version of this manual for a different Yocto Project release, visit the Yocto Project documentation page and select the manual set by using the "ACTIVE RELEASES DOCUMENTATION" or "DOCUMENTS ARCHIVE" pull-down menus.
To report any inaccuracies or problems with this manual, send an email to the Yocto Project discussion group at
yocto@yoctoproject.comor log into the freenode#yoctochannel.
| Revision History | |
|---|---|
| Revision 1.1 | 6 October 2011 |
| The initial document released with the Yocto Project 1.1 Release. | |
| Revision 1.2 | April 2012 |
| Released with the Yocto Project 1.2 Release. | |
| Revision 1.3 | October 2012 |
| Released with the Yocto Project 1.3 Release. | |
| Revision 1.4 | April 2013 |
| Released with the Yocto Project 1.4 Release. | |
| Revision 1.5 | October 2013 |
| Released with the Yocto Project 1.5 Release. | |
| Revision 1.5.1 | January 2014 |
| Released with the Yocto Project 1.5.1 Release. | |
| Revision 1.5.2 | May 2014 |
| Released with the Yocto Project 1.5.2 Release. | |
| Revision 1.5.3 | July 2014 |
| Released with the Yocto Project 1.5.3 Release. | |
| Revision 1.5.4 | December 2014 |
| Released with the Yocto Project 1.5.4 Release. | |
Table of Contents
- 1. The Yocto Project Development Manual
- 2. Getting Started with the Yocto Project
- 3. The Yocto Project Open Source Development Environment
- 4. Common Development Models
- 5. Common Tasks
- 5.1. Understanding and Creating Layers
- 5.2. Customizing Images
- 5.3. Writing a Recipe to Add a Package to Your Image
- 5.4. Adding a New Machine
- 5.5. Working With Libraries
- 5.6. Creating Partitioned Images
- 5.7. Configuring the Kernel
- 5.8. Patching the Kernel
- 5.9. Creating Your Own Distribution
- 5.10. Building a Tiny System
- 5.11. Working with Packages
- 5.12. Building Software from an External Source
- 5.13. Selecting an Initialization Manager
- 5.14. Excluding Recipes From the Build
- 5.15. Using an External SCM
- 5.16. Creating a Read-Only Root Filesystem
- 5.17. Performing Automated Runtime Testing
- 5.18. Debugging With the GNU Project Debugger (GDB) Remotely
- 5.19. Examining Builds Using the Toaster API
- 5.20. Profiling with OProfile
- 5.21. Maintaining Open Source License Compliance During Your Product's Lifecycle
Table of Contents
Welcome to the Yocto Project Development Manual! This manual provides information on how to use the Yocto Project to develop embedded Linux images and user-space applications that run on targeted devices. The manual provides an overview of image, kernel, and user-space application development using the Yocto Project. Because much of the information in this manual is general, it contains many references to other sources where you can find more detail. For example, you can find detailed information on Git, repositories, and open source in general in many places on the Internet. Another example specific to the Yocto Project is how to quickly set up your host development system and build an image, which you find in the Yocto Project Quick Start.
The Yocto Project Development Manual does, however, provide guidance and examples on how to change the kernel source code, reconfigure the kernel, and develop an application using the popular Eclipse™ IDE.
Note
By default, using the Yocto Project creates a Poky distribution. However, you can create your own distribution by providing key Metadata. A good example is Angstrom, which has had a distribution based on the Yocto Project since its inception. Other examples include commercial distributions like Wind River Linux, Mentor Embedded Linux, and ENEA Linux. See the "Creating Your Own Distribution" section for more information.The following list describes what you can get from this manual:
Information that lets you get set up to develop using the Yocto Project.
Information to help developers who are new to the open source environment and to the distributed revision control system Git, which the Yocto Project uses.
An understanding of common end-to-end development models and tasks.
Information about common development tasks generally used during image development for embedded devices.
Many references to other sources of related information.
This manual will not give you the following:
Step-by-step instructions when those instructions exist in other Yocto Project documentation: For example, the Yocto Project Application Developer's Guide contains detailed instructions on how to run the ADT Installer, which is used to set up a cross-development environment.
Reference material: This type of material resides in an appropriate reference manual. For example, system variables are documented in the Yocto Project Reference Manual.
Detailed public information that is not specific to the Yocto Project: For example, exhaustive information on how to use Git is covered better through the Internet than in this manual.
Because this manual presents overview information for many different topics, supplemental information is recommended for full comprehension. The following list presents other sources of information you might find helpful:
Yocto Project Website: The home page for the Yocto Project provides lots of information on the project as well as links to software and documentation.
Yocto Project Quick Start: This short document lets you get started with the Yocto Project and quickly begin building an image.
Yocto Project Reference Manual: This manual is a reference guide to the OpenEmbedded build system, which is based on BitBake. The build system is sometimes referred to as "Poky".
Yocto Project Application Developer's Guide: This guide provides information that lets you get going with the Application Development Toolkit (ADT) and stand-alone cross-development toolchains to develop projects using the Yocto Project.
Yocto Project Board Support Package (BSP) Developer's Guide: This guide defines the structure for BSP components. Having a commonly understood structure encourages standardization.
Yocto Project Linux Kernel Development Manual: This manual describes how to work with Linux Yocto kernels as well as provides a bit of conceptual information on the construction of the Yocto Linux kernel tree.
Yocto Project Profiling and Tracing Manual: This manual presents a set of common and generally useful tracing and profiling schemes along with their applications (as appropriate) to each tool.
Eclipse IDE Yocto Plug-in: A step-by-step instructional video that demonstrates how an application developer uses Yocto Plug-in features within the Eclipse IDE.
FAQ: A list of commonly asked questions and their answers.
Release Notes: Features, updates and known issues for the current release of the Yocto Project.
Hob: A graphical user interface for BitBake. Hob's primary goal is to enable a user to perform common tasks more easily.
Build Appliance: A virtual machine that enables you to build and boot a custom embedded Linux image with the Yocto Project using a non-Linux development system. For more information, see the Build Appliance page.
Bugzilla: The bug tracking application the Yocto Project uses. If you find problems with the Yocto Project, you should report them using this application.
Yocto Project Mailing Lists: To subscribe to the Yocto Project mailing lists, click on the following URLs and follow the instructions:
http://lists.yoctoproject.org/listinfo/yocto for a Yocto Project Discussions mailing list.
http://lists.yoctoproject.org/listinfo/poky for a Yocto Project Discussions mailing list about the OpenEmbedded build system (Poky).
http://lists.yoctoproject.org/listinfo/yocto-announce for a mailing list to receive official Yocto Project announcements as well as Yocto Project milestones.
http://lists.yoctoproject.org/listinfo for a listing of all public mailing lists on
lists.yoctoproject.org.
Internet Relay Chat (IRC): Two IRC channels on freenode are available for Yocto Project and Poky discussions:
#yoctoand#poky, respectively.OpenEmbedded: The build system used by the Yocto Project. This project is the upstream, generic, embedded distribution that the Yocto Project derives its build system (Poky) from and to which it contributes.
BitBake: The tool used by the OpenEmbedded build system to process project metadata.
BitBake User Manual: A comprehensive guide to the BitBake tool. If you want information on BitBake, see the user manual included in the
bitbake/doc/manualdirectory of the Source Directory.Quick EMUlator (QEMU): An open-source machine emulator and virtualizer.
Table of Contents
This chapter introduces the Yocto Project and gives you an idea of what you need to get started. You can find enough information to set up your development host and build or use images for hardware supported by the Yocto Project by reading the Yocto Project Quick Start.
The remainder of this chapter summarizes what is in the Yocto Project Quick Start and provides some higher-level concepts you might want to consider.
The Yocto Project is an open-source collaboration project focused on embedded Linux development. The project currently provides a build system that is referred to as the OpenEmbedded build system in the Yocto Project documentation. The Yocto Project provides various ancillary tools for the embedded developer and also features the Sato reference User Interface, which is optimized for stylus driven, low-resolution screens.
You can use the OpenEmbedded build system, which uses BitBake, to develop complete Linux images and associated user-space applications for architectures based on ARM, MIPS, PowerPC, x86 and x86-64.
Note
By default, using the Yocto Project creates a Poky distribution. However, you can create your own distribution by providing key Metadata. See the "Creating Your Own Distribution" section for more information.While the Yocto Project does not provide a strict testing framework, it does provide or generate for you artifacts that let you perform target-level and emulated testing and debugging. Additionally, if you are an Eclipse™ IDE user, you can install an Eclipse Yocto Plug-in to allow you to develop within that familiar environment.
Here is what you need to use the Yocto Project:
Host System: You should have a reasonably current Linux-based host system. You will have the best results with a recent release of Fedora, openSUSE, Debian, Ubuntu, or CentOS as these releases are frequently tested against the Yocto Project and officially supported. For a list of the distributions under validation and their status, see the "Supported Linux Distributions" section in the Yocto Project Reference Manual and the wiki page at Distribution Support.
You should also have about 100 gigabytes of free disk space for building images.
Packages: The OpenEmbedded build system requires that certain packages exist on your development system (e.g. Python 2.6 or 2.7). See "The Packages" section in the Yocto Project Quick Start and the "Required Packages for the Host Development System" section in the Yocto Project Reference Manual for the exact package requirements and the installation commands to install them for the supported distributions.
Yocto Project Release: You need a release of the Yocto Project installed locally on your development system. This local area is referred to as the Source Directory and is created when you use Git to clone a local copy of the upstream
pokyrepository, or when you download an official release of the corresponding tarball.Working from a copy of the upstream repository allows you to contribute back into the Yocto Project or simply work with the latest software on a development branch. Because Git maintains and creates an upstream repository with a complete history of changes and you are working with a local clone of that repository, you have access to all the Yocto Project development branches and tag names used in the upstream repository.
Note
You can view the Yocto Project Source Repositories at http://git.yoctoproject.org/cgit.cgiTarball Extraction: If you are not going to contribute back into the Yocto Project, you can simply go to the Yocto Project Website, select the "Downloads" tab, and choose what you want. Once you have the tarball, just extract it into a directory of your choice.
For example, the following command extracts the Yocto Project 1.5.4 release tarball into the current working directory and sets up the local Source Directory with a top-level folder named
poky-dora-10.0.4:$ tar xfj poky-dora-10.0.4.tar.bz2This method does not produce a local Git repository. Instead, you simply end up with a snapshot of the release.
Git Repository Method: If you are going to be contributing back into the Yocto Project or you simply want to keep up with the latest developments, you should use Git commands to set up a local Git repository of the upstream
pokysource repository. Doing so creates a repository with a complete history of changes and allows you to easily submit your changes upstream to the project. Because you clone the repository, you have access to all the Yocto Project development branches and tag names used in the upstream repository.Note
You can view the Yocto Project Source Repositories at http://git.yoctoproject.org/cgit.cgiThe following transcript shows how to clone the
pokyGit repository into the current working directory. The command creates the local repository in a directory namedpoky. For information on Git used within the Yocto Project, see the "Git" section.$ git clone git://git.yoctoproject.org/poky Cloning into 'poky'... remote: Counting objects: 203728, done. remote: Compressing objects: 100% (52371/52371), done. remote: Total 203728 (delta 147444), reused 202891 (delta 146614) Receiving objects: 100% (203728/203728), 95.54 MiB | 308 KiB/s, done. Resolving deltas: 100% (147444/147444), done.For another example of how to set up your own local Git repositories, see this wiki page, which describes how to create both
pokyandmeta-intelGit repositories.
Yocto Project Kernel: If you are going to be making modifications to a supported Yocto Project kernel, you need to establish local copies of the source. You can find Git repositories of supported Yocto Project kernels organized under "Yocto Linux Kernel" in the Yocto Project Source Repositories at http://git.yoctoproject.org/cgit.cgi.
This setup can involve creating a bare clone of the Yocto Project kernel and then copying that cloned repository. You can create the bare clone and the copy of the bare clone anywhere you like. For simplicity, it is recommended that you create these structures outside of the Source Directory (usually
poky).As an example, the following transcript shows how to create the bare clone of the
linux-yocto-3.10kernel and then create a copy of that clone.Note
When you have a local Yocto Project kernel Git repository, you can reference that repository rather than the upstream Git repository as part of theclonecommand. Doing so can speed up the process.In the following example, the bare clone is named
linux-yocto-3.10.git, while the copy is namedmy-linux-yocto-3.10-work:$ git clone ‐‐bare git://git.yoctoproject.org/linux-yocto-3.10 linux-yocto-3.10.git Cloning into bare repository 'linux-yocto-3.10.git'... remote: Counting objects: 3364487, done. remote: Compressing objects: 100% (507178/507178), done. remote: Total 3364487 (delta 2827715), reused 3364481 (delta 2827709) Receiving objects: 100% (3364487/3364487), 722.95 MiB | 423 KiB/s, done. Resolving deltas: 100% (2827715/2827715), done.Now create a clone of the bare clone just created:
$ git clone linux-yocto-3.10.git my-linux-yocto-3.10-work Cloning into 'my-linux-yocto-3.10-work'... done.The
meta-yocto-kernel-extrasGit Repository: Themeta-yocto-kernel-extrasGit repository contains Metadata needed only if you are modifying and building the kernel image. In particular, it contains the kernel BitBake append (.bbappend) files that you edit to point to your locally modified kernel source files and to build the kernel image. Pointing to these local files is much more efficient than requiring a download of the kernel's source files from upstream each time you make changes to the kernel.You can find the
meta-yocto-kernel-extrasGit Repository in the "Yocto Metadata Layers" area of the Yocto Project Source Repositories at http://git.yoctoproject.org/cgit.cgi. It is good practice to create this Git repository inside the Source Directory.Following is an example that creates the
meta-yocto-kernel-extrasGit repository inside the Source Directory, which is namedpokyin this case:$ cd ~/poky $ git clone git://git.yoctoproject.org/meta-yocto-kernel-extras meta-yocto-kernel-extras Cloning into 'meta-yocto-kernel-extras'... remote: Counting objects: 727, done. remote: Compressing objects: 100% (452/452), done. remote: Total 727 (delta 260), reused 719 (delta 252) Receiving objects: 100% (727/727), 536.36 KiB | 102 KiB/s, done. Resolving deltas: 100% (260/260), done.Supported Board Support Packages (BSPs): The Yocto Project provides a layer called
meta-inteland it is maintained in its own separate Git repository. Themeta-intellayer contains many supported BSP Layers.Similar considerations exist for setting up the
meta-intellayer. You can get set up for BSP development one of two ways: tarball extraction or with a local Git repository. It is a good idea to use the same method that you used to set up the Source Directory. Regardless of the method you use, the Yocto Project uses the following BSP layer naming scheme:meta-<BSP_name>where
<BSP_name>is the recognized BSP name. Here are some examples:meta-crownbay meta-emenlow meta-n450See the "BSP Layers" section in the Yocto Project Board Support Package (BSP) Developer's Guide for more information on BSP Layers.
Tarball Extraction: You can download any released BSP tarball from the same "Downloads" page of the Yocto Project Website to get the Yocto Project release. Once on the "Download" page, look to the right of the page and scroll down to find the BSP tarballs.
Once you have the tarball, just extract it into a directory of your choice. Again, this method just produces a snapshot of the BSP layer in the form of a hierarchical directory structure.
Git Repository Method: If you are working with a local Git repository for your Source Directory, you should also use this method to set up the
meta-intelGit repository. You can locate themeta-intelGit repository in the "Yocto Metadata Layers" area of the Yocto Project Source Repositories at http://git.yoctoproject.org/cgit.cgi.Using Git to create a local clone of the upstream repository can be helpful if you are working with BSPs. Typically, you set up the
meta-intelGit repository inside the Source Directory. For example, the following transcript shows the steps to clonemeta-intel.$ cd ~/poky $ git clone git://git.yoctoproject.org/meta-intel.git Cloning into 'meta-intel'... remote: Counting objects: 7366, done. remote: Compressing objects: 100% (2491/2491), done. remote: Total 7366 (delta 3997), reused 7299 (delta 3930) Receiving objects: 100% (7366/7366), 2.31 MiB | 95 KiB/s, done. Resolving deltas: 100% (3997/3997), done.The same wiki page referenced earlier covers how to set up the
meta-intelGit repository.
Eclipse Yocto Plug-in: If you are developing applications using the Eclipse Integrated Development Environment (IDE), you will need this plug-in. See the "Setting up the Eclipse IDE" section for more information.
The build process creates an entire Linux distribution, including the toolchain, from source. For more information on this topic, see the "Building an Image" section in the Yocto Project Quick Start.
The build process is as follows:
Make sure you have set up the Source Directory described in the previous section.
Initialize the build environment by sourcing a build environment script.
Optionally ensure the
conf/local.confconfiguration file, which is found in the Build Directory, is set up how you want it. This file defines many aspects of the build environment including the target machine architecture through theMACHINEvariable, the development machine's processor use through theBB_NUMBER_THREADSandPARALLEL_MAKEvariables, and a centralized tarball download directory through theDL_DIRvariable.Build the image using the
bitbakecommand. If you want information on BitBake, see the user manual included in thebitbake/doc/manualdirectory of the Source Directory.Run the image either on the actual hardware or using the QEMU emulator.
Another option you have to get started is to use pre-built binaries. The Yocto Project provides many types of binaries with each release. See the "Images" chapter in the Yocto Project Reference Manual for descriptions of the types of binaries that ship with a Yocto Project release.
Using a pre-built binary is ideal for developing software applications to run on your target hardware. To do this, you need to be able to access the appropriate cross-toolchain tarball for the architecture on which you are developing. If you are using an SDK type image, the image ships with the complete toolchain native to the architecture. If you are not using an SDK type image, you need to separately download and install the stand-alone Yocto Project cross-toolchain tarball.
Regardless of the type of image you are using, you need to download the pre-built kernel that you will boot in the QEMU emulator and then download and extract the target root filesystem for your target machine’s architecture. You can get architecture-specific binaries and file systems from machines. You can get installation scripts for stand-alone toolchains from toolchains. Once you have all your files, you set up the environment to emulate the hardware by sourcing an environment setup script. Finally, you start the QEMU emulator. You can find details on all these steps in the "Using Pre-Built Binaries and QEMU" section of the Yocto Project Quick Start.
Using QEMU to emulate your hardware can result in speed issues
depending on the target and host architecture mix.
For example, using the qemux86 image in the emulator
on an Intel-based 32-bit (x86) host machine is fast because the target and
host architectures match.
On the other hand, using the qemuarm image on the same Intel-based
host can be slower.
But, you still achieve faithful emulation of ARM-specific issues.
To speed things up, the QEMU images support using distcc
to call a cross-compiler outside the emulated system.
If you used runqemu to start QEMU, and the
distccd application is present on the host system, any
BitBake cross-compiling toolchain available from the build system is automatically
used from within QEMU simply by calling distcc.
You can accomplish this by defining the cross-compiler variable
(e.g. export CC="distcc").
Alternatively, if you are using a suitable SDK image or the appropriate
stand-alone toolchain is present,
the toolchain is also automatically used.
Note
Several mechanisms exist that let you connect to the system running on the QEMU emulator:QEMU provides a framebuffer interface that makes standard consoles available.
Generally, headless embedded devices have a serial port. If so, you can configure the operating system of the running image to use that port to run a console. The connection uses standard IP networking.
SSH servers exist in some QEMU images. The
core-image-satoQEMU image has a Dropbear secure shell (SSH) server that runs with the root password disabled. Thecore-image-basicandcore-image-lsbQEMU images have OpenSSH instead of Dropbear. Including these SSH servers allow you to use standardsshandscpcommands. Thecore-image-minimalQEMU image, however, contains no SSH server.You can use a provided, user-space NFS server to boot the QEMU session using a local copy of the root filesystem on the host. In order to make this connection, you must extract a root filesystem tarball by using the
runqemu-extract-sdkcommand. After running the command, you must then point therunqemuscript to the extracted directory instead of a root filesystem image file.
Table of Contents
This chapter helps you understand the Yocto Project as an open source development project. In general, working in an open source environment is very different from working in a closed, proprietary environment. Additionally, the Yocto Project uses specific tools and constructs as part of its development environment. This chapter specifically addresses open source philosophy, using the Yocto Project in a team environment, source repositories, Yocto Project terms, licensing, the open source distributed version control system Git, workflows, bug tracking, and how to submit changes.
Open source philosophy is characterized by software development directed by peer production and collaboration through an active community of developers. Contrast this to the more standard centralized development models used by commercial software companies where a finite set of developers produces a product for sale using a defined set of procedures that ultimately result in an end product whose architecture and source material are closed to the public.
Open source projects conceptually have differing concurrent agendas, approaches, and production. These facets of the development process can come from anyone in the public (community) that has a stake in the software project. The open source environment contains new copyright, licensing, domain, and consumer issues that differ from the more traditional development environment. In an open source environment, the end product, source material, and documentation are all available to the public at no cost.
A benchmark example of an open source project is the Linux Kernel, which was initially conceived and created by Finnish computer science student Linus Torvalds in 1991. Conversely, a good example of a non-open source project is the Windows® family of operating systems developed by Microsoft® Corporation.
Wikipedia has a good historical description of the Open Source Philosophy here. You can also find helpful information on how to participate in the Linux Community here.
It might not be immediately clear how you can use the Yocto Project in a team environment, or scale it for a large team of developers. One of the strengths of the Yocto Project is that it is extremely flexible. Thus, you can adapt it to many different use cases and scenarios. However, these characteristics can cause a struggle if you are trying to create a working setup that scales across a large team.
To help with these types of situations, this section presents some of the project's most successful experiences, practices, solutions, and available technologies that work well. Keep in mind, the information here is a starting point. You can build off it and customize it to fit any particular working environment and set of practices.
Systems across a large team should meet the needs of two types of developers: those working on the contents of the operating system image itself and those developing applications. Regardless of the type of developer, their workstations must be both reasonably powerful and run Linux.
For developers who mainly do application level work on top of an existing software stack, here are some practices that work best:
Use a pre-built toolchain that contains the software stack itself. Then, develop the application code on top of the stack. This method works well for small numbers of relatively isolated applications.
When possible, use the Yocto Project plug-in for the Eclipse™ IDE and other pieces of Application Development Technology (ADT). For more information, see the "Application Development Workflow" section as well as the Yocto Project Application Developer's Guide.
Keep your cross-development toolchains updated. You can do this through provisioning either as new toolchain downloads or as updates through a package update mechanism using
opkgto provide updates to an existing toolchain. The exact mechanics of how and when to do this are a question for local policy.Use multiple toolchains installed locally into different locations to allow development across versions.
For core system development, it is often best to have the build system itself available on the developer workstations so developers can run their own builds and directly rebuild the software stack. You should keep the core system unchanged as much as possible and do your work in layers on top of the core system. Doing so gives you a greater level of portability when upgrading to new versions of the core system or Board Support Packages (BSPs). You can share layers amongst the developers of a particular project and contain the policy configuration that defines the project.
Aside from the previous best practices, there exists a number of tips and tricks that can help speed up core development projects:
Use a Shared State Cache (sstate) among groups of developers who are on a fast network. The best way to share sstate is through a Network File System (NFS) share. The first user to build a given component for the first time contributes that object to the sstate, while subsequent builds from other developers then reuse the object rather than rebuild it themselves.
Although it is possible to use other protocols for the sstate such as HTTP and FTP, you should avoid these. Using HTTP limits the sstate to read-only and FTP provides poor performance.
Have autobuilders contribute to the sstate pool similarly to how the developer workstations contribute. For information, see the Autobuilders section.
Build stand-alone tarballs that contain "missing" system requirements if for some reason developer workstations do not meet minimum system requirements such as latest Python versions,
chrpath, or other tools. You can install and relocate the tarball exactly as you would the usual cross-development toolchain so that all developers can meet minimum version requirements on most distributions.Use a small number of shared, high performance systems for testing purposes (e.g. dual six core Xeons with 24GB RAM and plenty of disk space). Developers can use these systems for wider, more extensive testing while they continue to develop locally using their primary development system.
Enable the PR Service when package feeds need to be incremental with continually increasing PR values. Typically, this situation occurs when you use or publish package feeds and use a shared state. You should enable the PR Service for all users who use the shared state pool. For more information on the PR Service, see the "Working With a PR Service".
Keeping your Metadata and any software you are developing under the control of an SCM system that is compatible with the OpenEmbedded build system is advisable. Of the SCMs BitBake supports, the Yocto Project team strongly recommends using Git. Git is a distributed system that is easy to backup, allows you to work remotely, and then connects back to the infrastructure.
Note
For information about BitBake and SCMs, see the BitBake manual located in thebitbake/doc/manual directory of the
Source Directory.
It is relatively easy to set up Git services and create
infrastructure like
http://git.yoctoproject.org,
which is based on server software called
gitolite with cgit
being used to generate the web interface that lets you view the
repositories.
The gitolite software identifies users
using ssh keys and allows branch-based
access controls to repositories that you can control as little
or as much as necessary.
Note
The setup of these services is beyond the scope of this manual. However, sites such as these exist that describe how to perform setup:Git documentation: Describes how to install
gitoliteon the server.The
gitolitemaster index: All topics forgitolite.Interfaces, frontends, and tools: Documentation on how to create interfaces and frontends for Git.
Autobuilders are often the core of a development project. It is here that changes from individual developers are brought together and centrally tested and subsequent decisions about releases can be made. Autobuilders also allow for "continuous integration" style testing of software components and regression identification and tracking.
See "Yocto Project Autobuilder" for more information and links to buildbot. The Yocto Project team has found this implementation works well in this role. A public example of this is the Yocto Project Autobuilders, which we use to test the overall health of the project.
The features of this system are:
Highlights when commits break the build.
Populates an sstate cache from which developers can pull rather than requiring local builds.
Allows commit hook triggers, which trigger builds when commits are made.
Allows triggering of automated image booting and testing under the QuickEMUlator (QEMU).
Supports incremental build testing and from scratch builds.
Shares output that allows developer testing and historical regression investigation.
Creates output that can be used for releases.
Allows scheduling of builds so that resources can be used efficiently.
The Yocto Project itself uses a hierarchical structure and a
pull model.
Scripts exist to create and send pull requests
(i.e. create-pull-request and
send-pull-request).
This model is in line with other open source projects where
maintainers are responsible for specific areas of the project
and a single maintainer handles the final "top-of-tree" merges.
Note
You can also use a more collective push model. Thegitolite software supports both the
push and pull models quite easily.
As with any development environment, it is important to document the policy used as well as any main project guidelines so they are understood by everyone. It is also a good idea to have well structured commit messages, which are usually a part of a project's guidelines. Good commit messages are essential when looking back in time and trying to understand why changes were made.
If you discover that changes are needed to the core layer of the project, it is worth sharing those with the community as soon as possible. Chances are if you have discovered the need for changes, someone else in the community needs them also.
This section summarizes the key recommendations described in the previous sections:
Use Git as the source control system.
Maintain your Metadata in layers that make sense for your situation. See the "Understanding and Creating Layers" section for more information on layers.
Separate the project's Metadata and code by using separate Git repositories. See the "Yocto Project Source Repositories" section for information on these repositories. See the "Getting Set Up" section for information on how to set up various Yocto Project related Git repositories.
Set up the directory for the shared state cache (
SSTATE_DIR) where it makes sense. For example, set up the sstate cache on a system used by developers in the same organization and share the same source directories on their machines.Set up an Autobuilder and have it populate the sstate cache and source directories.
The Yocto Project community encourages you to send patches to the project to fix bugs or add features. If you do submit patches, follow the project commit guidelines for writing good commit messages. See the "How to Submit a Change" section.
Send changes to the core sooner than later as others likely run into the same issues. For some guidance on mailing lists to use, see the list in the "How to Submit a Change" section. For a description of the available mailing lists, see the "Mailing Lists" section in the Yocto Project Reference Manual.
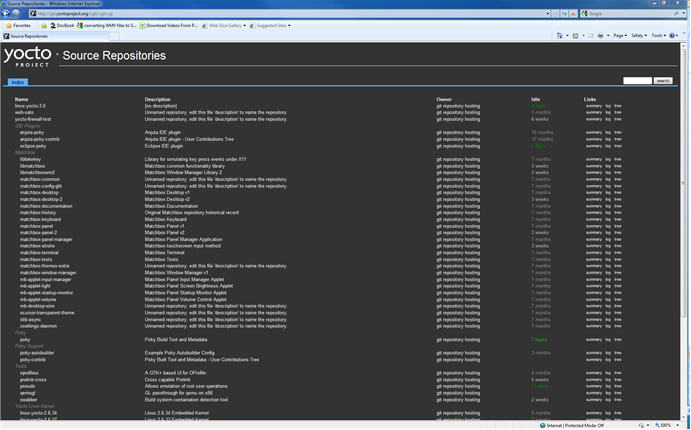
The Yocto Project team maintains complete source repositories for all Yocto Project files at http://git.yoctoproject.org/cgit/cgit.cgi. This web-based source code browser is organized into categories by function such as IDE Plugins, Matchbox, Poky, Yocto Linux Kernel, and so forth. From the interface, you can click on any particular item in the "Name" column and see the URL at the bottom of the page that you need to clone a Git repository for that particular item. Having a local Git repository of the Source Directory (poky) allows you to make changes, contribute to the history, and ultimately enhance the Yocto Project's tools, Board Support Packages, and so forth.
Conversely, if you are a developer that is not interested in contributing back to the Yocto Project, you have the ability to simply download and extract release tarballs and use them within the Yocto Project environment. All that is required is a particular release of the Yocto Project and your application source code.
For any supported release of Yocto Project, you can go to the
Yocto Project Website and
select the "Downloads" tab and get a released tarball of the
poky repository or any supported BSP tarballs.
Unpacking these tarballs gives you a snapshot of the released
files.
Note
The recommended method for setting up the Yocto Project Source Directory and the files for supported BSPs (e.g.,meta-intel) is to
use Git to create a local copy of the
upstream repositories.
In summary, here is where you can get the project files needed for development:
Source Repositories: This area contains IDE Plugins, Matchbox, Poky, Poky Support, Tools, Yocto Linux Kernel, and Yocto Metadata Layers. You can create local copies of Git repositories for each of these areas.
Index of /releases: This area contains index releases such as the Eclipse™ Yocto Plug-in, miscellaneous support, poky, pseudo, installers for cross-development toolchains, and all released versions of Yocto Project in the form of images or tarballs. Downloading and extracting these files does not produce a local copy of the Git repository but rather a snapshot of a particular release or image.
"Downloads" page for the Yocto Project Website: Access this page by going to the website and then selecting the "Downloads" tab. This page allows you to download any Yocto Project release or Board Support Package (BSP) in tarball form. The tarballs are similar to those found in the Index of /releases: area.
Following is a list of terms and definitions users new to the Yocto Project development environment might find helpful. While some of these terms are universal, the list includes them just in case:
Append Files: Files that append build information to a recipe file. Append files are known as BitBake append files and
.bbappendfiles. The OpenEmbedded build system expects every append file to have a corresponding recipe (.bb) file. Furthermore, the append file and corresponding recipe file must use the same root filename. The filenames can differ only in the file type suffix used (e.g.formfactor_0.0.bbandformfactor_0.0.bbappend).Information in append files overrides the information in the similarly-named recipe file. For an example of an append file in use, see the "Using .bbappend Files" section.
BitBake: The task executor and scheduler used by the OpenEmbedded build system to build images. For more information on BitBake, see the BitBake documentation in the
bitbake/doc/manualdirectory of the Source Directory.Build Directory: This term refers to the area used by the OpenEmbedded build system for builds. The area is created when you
sourcethe setup environment script that is found in the Source Directory (i.e.oe-init-build-envoroe-init-build-env-memres). TheTOPDIRvariable points to the Build Directory.You have a lot of flexibility when creating the Build Directory. Following are some examples that show how to create the directory. The examples assume your Source Directory is named
poky:Create the Build Directory inside your Source Directory and let the name of the Build Directory default to
build:$ cd $HOME/poky $ source oe-init-build-envCreate the Build Directory inside your home directory and specifically name it
test-builds:$ cd $HOME $ source poky/oe-init-build-env test-buildsProvide a directory path and specifically name the build directory. Any intermediate folders in the pathname must exist. This next example creates a Build Directory named
YP-10.0.4in your home directory within the existing directorymybuilds:$cd $HOME $ source $HOME/poky/oe-init-build-env $HOME/mybuilds/YP-10.0.4
Build System: In the context of the Yocto Project, this term refers to the OpenEmbedded build system used by the project. This build system is based on the project known as "Poky." For some historical information about Poky, see the Poky term.
Classes: Files that provide for logic encapsulation and inheritance so that commonly used patterns can be defined once and then easily used in multiple recipes. Class files end with the
.bbclassfilename extension.Configuration File: Configuration information in various
.conffiles provides global definitions of variables. Theconf/local.confconfiguration file in the Build Directory contains user-defined variables that affect each build. Themeta-yocto/conf/distro/poky.confconfiguration file defines Yocto "distro" configuration variables used only when building with this policy. Machine configuration files, which are located throughout the Source Directory, define variables for specific hardware and are only used when building for that target (e.g. themachine/beagleboard.confconfiguration file defines variables for the Texas Instruments ARM Cortex-A8 development board). Configuration files end with a.conffilename extension.Cross-Development Toolchain: In general, a cross-development toolchain is a collection of software development tools and utilities that run on one architecture and allow you to develop software for a different, or targeted, architecture. These toolchains contain cross-compilers, linkers, and debuggers that are specific to the target architecture.
The Yocto Project supports two different cross-development toolchains:
A toolchain only used by and within BitBake when building an image for a target architecture.
A relocatable toolchain used outside of BitBake by developers when developing applications that will run on a targeted device. Sometimes this relocatable cross-development toolchain is referred to as the meta-toolchain.
Creation of these toolchains is simple and automated. For information on toolchain concepts as they apply to the Yocto Project, see the "Cross-Development Toolchain Generation" section in the Yocto Project Reference Manual. You can also find more information on using the relocatable toolchain in the Yocto Project Application Developer's Guide.
Image: An image is the result produced when BitBake processes a given collection of recipes and related Metadata. Images are the binary output that run on specific hardware or QEMU and for specific use cases. For a list of the supported image types that the Yocto Project provides, see the "Images" chapter in the Yocto Project Reference Manual.
Layer: A collection of recipes representing the core, a BSP, or an application stack. For a discussion on BSP Layers, see the "BSP Layers" section in the Yocto Project Board Support Packages (BSP) Developer's Guide.
Meta-Toolchain: A term sometimes used for Cross-Development Toolchain.
Metadata: The files that BitBake parses when building an image. In general, Metadata includes recipes, classes, and configuration files. In the context of the kernel ("kernel Metadata"), it refers to Metadata in the
metabranches of the kernel source Git repositories.OE-Core: A core set of Metadata originating with OpenEmbedded (OE) that is shared between OE and the Yocto Project. This Metadata is found in the
metadirectory of the Source Directory.Package: In the context of the Yocto Project, this term refers to the packaged output from a baked recipe. A package is generally the compiled binaries produced from the recipe's sources. You "bake" something by running it through BitBake.
It is worth noting that the term "package" can, in general, have subtle meanings. For example, the packages referred to in the "The Packages" section are compiled binaries that when installed add functionality to your Linux distribution.
Another point worth noting is that historically within the Yocto Project, recipes were referred to as packages - thus, the existence of several BitBake variables that are seemingly mis-named, (e.g.
PR,PRINC,PV, andPE).Package Groups: Arbitrary groups of software Recipes. You use package groups to hold recipes that, when built, usually accomplish a single task. For example, a package group could contain the recipes for a company’s proprietary or value-add software. Or, the package group could contain the recipes that enable graphics. A package group is really just another recipe. Because package group files are recipes, they end with the
.bbfilename extension.Poky: The term "poky" can mean several things. In its most general sense, it is an open-source project that was initially developed by OpenedHand. With OpenedHand, poky was developed off of the existing OpenEmbedded build system becoming a build system for embedded images. After Intel Corporation acquired OpenedHand, the project poky became the basis for the Yocto Project's build system. Within the Yocto Project source repositories,
pokyexists as a separate Git repository that can be cloned to yield a local copy on the host system. Thus, "poky" can refer to the local copy of the Source Directory used to develop within the Yocto Project.Recipe: A set of instructions for building packages. A recipe describes where you get source code and which patches to apply. Recipes describe dependencies for libraries or for other recipes, and they also contain configuration and compilation options. Recipes contain the logical unit of execution, the software/images to build, and use the
.bbfile extension.Source Directory: This term refers to the directory structure created as a result of either downloading and unpacking a Yocto Project release tarball or creating a local copy of the
pokyGit repositorygit://git.yoctoproject.org/poky. Sometimes you might hear the term "poky directory" used to refer to this directory structure.Note
The OpenEmbedded build system does not support file or directory names that contain spaces. Be sure that the Source Directory you use does not contain these types of names.The Source Directory contains BitBake, Documentation, Metadata and other files that all support the Yocto Project. Consequently, you must have the Source Directory in place on your development system in order to do any development using the Yocto Project.
For tarball expansion, the name of the top-level directory of the Source Directory is derived from the Yocto Project release tarball. For example, downloading and unpacking
poky-dora-10.0.4.tar.bz2results in a Source Directory whose top-level folder is namedpoky-dora-10.0.4. If you create a local copy of the Git repository, you can name the repository anything you like. Throughout much of the documentation,pokyis used as the name of the top-level folder of the local copy of the poky Git repository. So, for example, cloning thepokyGit repository results in a local Git repository whose top-level folder is also namedpoky.It is important to understand the differences between the Source Directory created by unpacking a released tarball as compared to cloning
git://git.yoctoproject.org/poky. When you unpack a tarball, you have an exact copy of the files based on the time of release - a fixed release point. Any changes you make to your local files in the Source Directory are on top of the release. On the other hand, when you clone thepokyGit repository, you have an active development repository. In this case, any local changes you make to the Source Directory can be later applied to active development branches of the upstreampokyGit repository.Finally, if you want to track a set of local changes while starting from the same point as a release tarball, you can create a local Git branch that reflects the exact copy of the files at the time of their release. You do this by using Git tags that are part of the repository.
For more information on concepts related to Git repositories, branches, and tags, see the "Repositories, Tags, and Branches" section.
Task: A unit of execution for BitBake (e.g.
do_compile,do_fetch,do_patch, and so forth).Upstream: A reference to source code or repositories that are not local to the development system but located in a master area that is controlled by the maintainer of the source code. For example, in order for a developer to work on a particular piece of code, they need to first get a copy of it from an "upstream" source.
Because open source projects are open to the public, they have different licensing structures in place. License evolution for both Open Source and Free Software has an interesting history. If you are interested in this history, you can find basic information here:
In general, the Yocto Project is broadly licensed under the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) License. MIT licensing permits the reuse of software within proprietary software as long as the license is distributed with that software. MIT is also compatible with the GNU General Public License (GPL). Patches to the Yocto Project follow the upstream licensing scheme. You can find information on the MIT license at here. You can find information on the GNU GPL here.
When you build an image using the Yocto Project, the build process uses a
known list of licenses to ensure compliance.
You can find this list in the
Source Directory at
meta/files/common-licenses.
Once the build completes, the list of all licenses found and used during that build are
kept in the
Build Directory at
tmp/deploy/licenses.
If a module requires a license that is not in the base list, the build process generates a warning during the build. These tools make it easier for a developer to be certain of the licenses with which their shipped products must comply. However, even with these tools it is still up to the developer to resolve potential licensing issues.
The base list of licenses used by the build process is a combination of the Software Package Data Exchange (SPDX) list and the Open Source Initiative (OSI) projects. SPDX Group is a working group of the Linux Foundation that maintains a specification for a standard format for communicating the components, licenses, and copyrights associated with a software package. OSI is a corporation dedicated to the Open Source Definition and the effort for reviewing and approving licenses that are OSD-conformant.
You can find a list of the combined SPDX and OSI licenses that the Yocto Project uses here.
For information that can help you to maintain compliance with various open source licensing during the lifecycle of a product created using the Yocto Project, see the "Maintaining Open Source License Compliance During Your Product's Lifecycle" section.
The Yocto Project makes extensive use of Git, which is a free, open source distributed version control system. Git supports distributed development, non-linear development, and can handle large projects. It is best that you have some fundamental understanding of how Git tracks projects and how to work with Git if you are going to use the Yocto Project for development. This section provides a quick overview of how Git works and provides you with a summary of some essential Git commands.
For more information on Git, see http://git-scm.com/documentation. If you need to download Git, go to http://git-scm.com/download.
As mentioned earlier in the section "Yocto Project Source Repositories", the Yocto Project maintains source repositories at http://git.yoctoproject.org/cgit.cgi. If you look at this web-interface of the repositories, each item is a separate Git repository.
Git repositories use branching techniques that track content change (not files) within a project (e.g. a new feature or updated documentation). Creating a tree-like structure based on project divergence allows for excellent historical information over the life of a project. This methodology also allows for an environment from which you can do lots of local experimentation on projects as you develop changes or new features.
A Git repository represents all development efforts for a given project.
For example, the Git repository poky contains all changes
and developments for Poky over the course of its entire life.
That means that all changes that make up all releases are captured.
The repository maintains a complete history of changes.
You can create a local copy of any repository by "cloning" it with the Git
clone command.
When you clone a Git repository, you end up with an identical copy of the
repository on your development system.
Once you have a local copy of a repository, you can take steps to develop locally.
For examples on how to clone Git repositories, see the
"Getting Set Up" section.
It is important to understand that Git tracks content change and not files.
Git uses "branches" to organize different development efforts.
For example, the poky repository has
denzil, danny,
dylan, dora,
and master branches among others.
You can see all the branches by going to
http://git.yoctoproject.org/cgit.cgi/poky/ and
clicking on the
[...]
link beneath the "Branch" heading.
Each of these branches represents a specific area of development.
The master branch represents the current or most recent
development.
All other branches represent off-shoots of the master
branch.
When you create a local copy of a Git repository, the copy has the same set
of branches as the original.
This means you can use Git to create a local working area (also called a branch)
that tracks a specific development branch from the source Git repository.
in other words, you can define your local Git environment to work on any development
branch in the repository.
To help illustrate, here is a set of commands that creates a local copy of the
poky Git repository and then creates and checks out a local
Git branch that tracks the Yocto Project 1.5.4 Release (dora) development:
$ cd ~
$ git clone git://git.yoctoproject.org/poky
$ cd poky
$ git checkout -b dora origin/dora
In this example, the name of the top-level directory of your local
Source Directory
is poky,
and the name of that local working area (local branch) you just
created and checked out is dora.
The files in your local repository now reflect the same files that
are in the dora development
branch of the Yocto Project's poky
upstream repository.
It is important to understand that when you create and checkout a
local working branch based on a branch name,
your local environment matches the "tip" of that development branch
at the time you created your local branch, which could be
different from the files at the time of a similarly named release.
In other words, creating and checking out a local branch based on the
dora branch name is not the same as
cloning and checking out the master branch.
Keep reading to see how you create a local snapshot of a Yocto Project Release.
Git uses "tags" to mark specific changes in a repository.
Typically, a tag is used to mark a special point such as the final change
before a project is released.
You can see the tags used with the poky Git repository
by going to http://git.yoctoproject.org/cgit.cgi/poky/ and
clicking on the
[...]
link beneath the "Tag" heading.
Some key tags are bernard-5.0, denzil-7.0,
and dora-10.0.4.
These tags represent Yocto Project releases.
When you create a local copy of the Git repository, you also have access to all the tags. Similar to branches, you can create and checkout a local working Git branch based on a tag name. When you do this, you get a snapshot of the Git repository that reflects the state of the files when the change was made associated with that tag. The most common use is to checkout a working branch that matches a specific Yocto Project release. Here is an example:
$ cd ~
$ git clone git://git.yoctoproject.org/poky
$ cd poky
$ git checkout -b my-dora-10.0.4 dora-10.0.4
In this example, the name of the top-level directory of your local Yocto Project
Files Git repository is poky.
And, the name of the local branch you have created and checked out is
my-dora-10.0.4.
The files in your repository now exactly match the Yocto Project 1.5.4
Release tag (dora-10.0.4).
It is important to understand that when you create and checkout a local
working branch based on a tag, your environment matches a specific point
in time and not the entire development branch.
Git has an extensive set of commands that lets you manage changes and perform collaboration over the life of a project. Conveniently though, you can manage with a small set of basic operations and workflows once you understand the basic philosophy behind Git. You do not have to be an expert in Git to be functional. A good place to look for instruction on a minimal set of Git commands is here. If you need to download Git, you can do so here.
If you don’t know much about Git, you should educate yourself by visiting the links previously mentioned.
The following list briefly describes some basic Git operations as a way to get started. As with any set of commands, this list (in most cases) simply shows the base command and omits the many arguments they support. See the Git documentation for complete descriptions and strategies on how to use these commands:
git init: Initializes an empty Git repository. You cannot use Git commands unless you have a.gitrepository.git clone: Creates a clone of a repository. During collaboration, this command allows you to create a local repository that is on equal footing with a fellow developer’s repository.git add: Stages updated file contents to the index that Git uses to track changes. You must stage all files that have changed before you can commit them.git commit: Creates a "commit" that documents the changes you made. Commits are used for historical purposes, for determining if a maintainer of a project will allow the change, and for ultimately pushing the change from your local Git repository into the project’s upstream (or master) repository.git status: Reports any modified files that possibly need to be staged and committed.git checkout <branch-name>: Changes your working branch. This command is analogous to "cd".git checkout –b <working-branch>: Creates a working branch on your local machine where you can isolate work. It is a good idea to use local branches when adding specific features or changes. This way if you do not like what you have done you can easily get rid of the work.git branch: Reports existing local branches and tells you the branch in which you are currently working.git branch -D <branch-name>: Deletes an existing local branch. You need to be in a local branch other than the one you are deleting in order to delete<branch-name>.git pull: Retrieves information from an upstream Git repository and places it in your local Git repository. You use this command to make sure you are synchronized with the repository from which you are basing changes (.e.g. the master branch).git push: Sends all your committed local changes to an upstream Git repository (e.g. a contribution repository). The maintainer of the project draws from these repositories when adding changes to the project’s master repository or other development branch.git merge: Combines or adds changes from one local branch of your repository with another branch. When you create a local Git repository, the default branch is named "master". A typical workflow is to create a temporary branch for isolated work, make and commit your changes, switch to your local master branch, merge the changes from the temporary branch into the local master branch, and then delete the temporary branch.git cherry-pick: Choose and apply specific commits from one branch into another branch. There are times when you might not be able to merge all the changes in one branch with another but need to pick out certain ones.gitk: Provides a GUI view of the branches and changes in your local Git repository. This command is a good way to graphically see where things have diverged in your local repository.git log: Reports a history of your changes to the repository.git diff: Displays line-by-line differences between your local working files and the same files in the upstream Git repository that your branch currently tracks.
This section provides some overview on workflows using Git. In particular, the information covers basic practices that describe roles and actions in a collaborative development environment. Again, if you are familiar with this type of development environment, you might want to just skip this section.
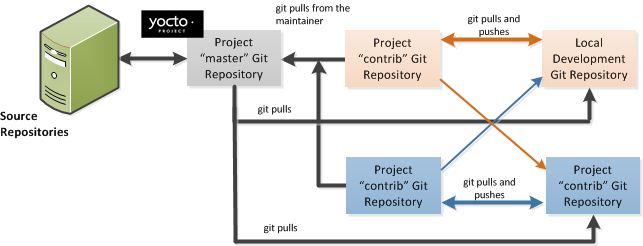
The Yocto Project files are maintained using Git in a "master" branch whose Git history tracks every change and whose structure provides branches for all diverging functionality. Although there is no need to use Git, many open source projects do so. For the Yocto Project, a key individual called the "maintainer" is responsible for the "master" branch of a given Git repository. The "master" branch is the “upstream” repository where the final builds of the project occur. The maintainer is responsible for allowing changes in from other developers and for organizing the underlying branch structure to reflect release strategies and so forth.
Note
For information on finding out who is responsible (maintains) for a particular area of code, see the "How to Submit a Change" section.
The project also has contribution repositories known as "contrib" areas. These areas temporarily hold changes to the project that have been submitted or committed by the Yocto Project development team and by community members that contribute to the project. The maintainer determines if the changes are qualified to be moved from the "contrib" areas into the "master" branch of the Git repository.
Developers (including contributing community members) create and maintain cloned repositories of the upstream "master" branch. These repositories are local to their development platforms and are used to develop changes. When a developer is satisfied with a particular feature or change, they "push" the changes to the appropriate "contrib" repository.
Developers are responsible for keeping their local repository up-to-date with "master". They are also responsible for straightening out any conflicts that might arise within files that are being worked on simultaneously by more than one person. All this work is done locally on the developer’s machines before anything is pushed to a "contrib" area and examined at the maintainer’s level.
A somewhat formal method exists by which developers commit changes and push them into the "contrib" area and subsequently request that the maintainer include them into "master" This process is called “submitting a patch” or "submitting a change." For information on submitting patches and changes, see the "How to Submit a Change" section.
To summarize the environment: we have a single point of entry for changes into the project’s "master" branch of the Git repository, which is controlled by the project’s maintainer. And, we have a set of developers who independently develop, test, and submit changes to "contrib" areas for the maintainer to examine. The maintainer then chooses which changes are going to become a permanent part of the project.
 |
While each development environment is unique, there are some best practices or methods that help development run smoothly. The following list describes some of these practices. For more information about Git workflows, see the workflow topics in the Git Community Book.
Make Small Changes: It is best to keep the changes you commit small as compared to bundling many disparate changes into a single commit. This practice not only keeps things manageable but also allows the maintainer to more easily include or refuse changes.
It is also good practice to leave the repository in a state that allows you to still successfully build your project. In other words, do not commit half of a feature, then add the other half as a separate, later commit. Each commit should take you from one buildable project state to another buildable state.
Use Branches Liberally: It is very easy to create, use, and delete local branches in your working Git repository. You can name these branches anything you like. It is helpful to give them names associated with the particular feature or change on which you are working. Once you are done with a feature or change and have merged it into your local master branch, simply discard the temporary branch.
Merge Changes: The
git mergecommand allows you to take the changes from one branch and fold them into another branch. This process is especially helpful when more than a single developer might be working on different parts of the same feature. Merging changes also automatically identifies any collisions or "conflicts" that might happen as a result of the same lines of code being altered by two different developers.Manage Branches: Because branches are easy to use, you should use a system where branches indicate varying levels of code readiness. For example, you can have a "work" branch to develop in, a "test" branch where the code or change is tested, a "stage" branch where changes are ready to be committed, and so forth. As your project develops, you can merge code across the branches to reflect ever-increasing stable states of the development.
Use Push and Pull: The push-pull workflow is based on the concept of developers "pushing" local commits to a remote repository, which is usually a contribution repository. This workflow is also based on developers "pulling" known states of the project down into their local development repositories. The workflow easily allows you to pull changes submitted by other developers from the upstream repository into your work area ensuring that you have the most recent software on which to develop. The Yocto Project has two scripts named
create-pull-requestandsend-pull-requestthat ship with the release to facilitate this workflow. You can find these scripts in thescriptsfolder of the Source Directory. For information on how to use these scripts, see the "Using Scripts to Push a Change Upstream and Request a Pull" section.Patch Workflow: This workflow allows you to notify the maintainer through an email that you have a change (or patch) you would like considered for the "master" branch of the Git repository. To send this type of change, you format the patch and then send the email using the Git commands
git format-patchandgit send-email. For information on how to use these scripts, see the "How to Submit a Change" section.
The Yocto Project uses its own implementation of Bugzilla to track bugs. Implementations of Bugzilla work well for group development because they track bugs and code changes, can be used to communicate changes and problems with developers, can be used to submit and review patches, and can be used to manage quality assurance. The home page for the Yocto Project implementation of Bugzilla is http://bugzilla.yoctoproject.org.
Sometimes it is helpful to submit, investigate, or track a bug against the Yocto Project itself such as when discovering an issue with some component of the build system that acts contrary to the documentation or your expectations. Following is the general procedure for submitting a new bug using the Yocto Project Bugzilla. You can find more information on defect management, bug tracking, and feature request processes all accomplished through the Yocto Project Bugzilla on the wiki page here.
Always use the Yocto Project implementation of Bugzilla to submit a bug.
When submitting a new bug, be sure to choose the appropriate Classification, Product, and Component for which the issue was found. Defects for the Yocto Project fall into one of six classifications: Yocto Project Components, Infrastructure, Build System & Metadata, Documentation, QA/Testing, and Runtime. Each of these Classifications break down into multiple Products and, in some cases, multiple Components.
Use the bug form to choose the correct Hardware and Architecture for which the bug applies.
Indicate the Yocto Project version you were using when the issue occurred.
Be sure to indicate the Severity of the bug. Severity communicates how the bug impacted your work.
Select the appropriate "Documentation change" item for the bug. Fixing a bug may or may not affect the Yocto Project documentation.
Provide a brief summary of the issue. Try to limit your summary to just a line or two and be sure to capture the essence of the issue.
Provide a detailed description of the issue. You should provide as much detail as you can about the context, behavior, output, and so forth that surrounds the issue. You can even attach supporting files for output from logs by using the "Add an attachment" button.
Be sure to copy the appropriate people in the "CC List" for the bug. See the "How to Submit a Change" section for information about finding out who is responsible for code.
Submit the bug by clicking the "Submit Bug" button.
Contributions to the Yocto Project and OpenEmbedded are very welcome. Because the system is extremely configurable and flexible, we recognize that developers will want to extend, configure or optimize it for their specific uses. You should send patches to the appropriate mailing list so that they can be reviewed and merged by the appropriate maintainer.
Before submitting any change, be sure to find out who you should be notifying. Several methods exist through which you find out who you should be copying or notifying:
Maintenance File: Examine the
maintainers.incfile, which is located in the Source Directory atmeta-yocto/conf/distro/include, to see who is responsible for code.Board Support Package (BSP) README Files: For BSP maintainers of supported BSPs, you can examine individual BSP
READMEfiles. In addition, some layers (such as themeta-intellayer), include aMAINTAINERSfile which contains a list of all supported BSP maintainers for that layer.Search by File: Using Git, you can enter the following command to bring up a short list of all commits against a specific file:
git shortlog -- <filename>Just provide the name of the file for which you are interested. The information returned is not ordered by history but does include a list of all committers grouped by name. From the list, you can see who is responsible for the bulk of the changes against the file.
For a list of the Yocto Project and related mailing lists, see the "Mailing lists" section in the Yocto Project Reference Manual.
Here is some guidance on which mailing list to use for what type of change:
For changes to the core Metadata, send your patch to the openembedded-core mailing list. For example, a change to anything under the
metaorscriptsdirectories should be sent to this mailing list.For changes to BitBake (anything under the
bitbakedirectory), send your patch to the bitbake-devel mailing list.For changes to
meta-yocto, send your patch to the poky mailing list.For changes to other layers hosted on
yoctoproject.org(unless the layer's documentation specifies otherwise), tools, and Yocto Project documentation, use the yocto mailing list.For additional recipes that do not fit into the core Metadata, you should determine which layer the recipe should go into and submit the change in the manner recommended by the documentation (e.g. README) supplied with the layer. If in doubt, please ask on the yocto or openembedded-devel mailing lists.
When you send a patch, be sure to include a "Signed-off-by:" line in the same style as required by the Linux kernel. Adding this line signifies that you, the submitter, have agreed to the Developer's Certificate of Origin 1.1 as follows:
Developer's Certificate of Origin 1.1
By making a contribution to this project, I certify that:
(a) The contribution was created in whole or in part by me and I
have the right to submit it under the open source license
indicated in the file; or
(b) The contribution is based upon previous work that, to the best
of my knowledge, is covered under an appropriate open source
license and I have the right under that license to submit that
work with modifications, whether created in whole or in part
by me, under the same open source license (unless I am
permitted to submit under a different license), as indicated
in the file; or
(c) The contribution was provided directly to me by some other
person who certified (a), (b) or (c) and I have not modified
it.
(d) I understand and agree that this project and the contribution
are public and that a record of the contribution (including all
personal information I submit with it, including my sign-off) is
maintained indefinitely and may be redistributed consistent with
this project or the open source license(s) involved.
In a collaborative environment, it is necessary to have some sort of standard or method through which you submit changes. Otherwise, things could get quite chaotic. One general practice to follow is to make small, controlled changes. Keeping changes small and isolated aids review, makes merging/rebasing easier and keeps the change history clean when anyone needs to refer to it in future.
When you make a commit, you must follow certain standards established by the OpenEmbedded and Yocto Project development teams. For each commit, you must provide a single-line summary of the change and you should almost always provide a more detailed description of what you did (i.e. the body of the commit message). The only exceptions for not providing a detailed description would be if your change is a simple, self-explanatory change that needs no further description beyond the summary. Here are the guidelines for composing a commit message:
Provide a single-line, short summary of the change. This summary is typically viewable in the "shortlist" of changes. Thus, providing something short and descriptive that gives the reader a summary of the change is useful when viewing a list of many commits. This short description should be prefixed by the recipe name (if changing a recipe), or else the short form path to the file being changed.
For the body of the commit message, provide detailed information that describes what you changed, why you made the change, and the approach you used. It may also be helpful if you mention how you tested the change. Provide as much detail as you can in the body of the commit message.
If the change addresses a specific bug or issue that is associated with a bug-tracking ID, include a reference to that ID in your detailed description. For example, the Yocto Project uses a specific convention for bug references - any commit that addresses a specific bug should include the bug ID in the description (typically at the beginning) as follows:
[YOCTO #<bug-id>] <detailed description of change>
You can find more guidance on creating well-formed commit messages at this OpenEmbedded wiki page: http://www.openembedded.org/wiki/Commit_Patch_Message_Guidelines.
The next two sections describe general instructions for both pushing changes upstream and for submitting changes as patches.
The basic flow for pushing a change to an upstream "contrib" Git repository is as follows:
Make your changes in your local Git repository.
Stage your changes by using the
git addcommand on each file you changed.Commit the change by using the
git commitcommand and push it to the "contrib" repository. Be sure to provide a commit message that follows the project’s commit message standards as described earlier.Notify the maintainer that you have pushed a change by making a pull request. The Yocto Project provides two scripts that conveniently let you generate and send pull requests to the Yocto Project. These scripts are
create-pull-requestandsend-pull-request. You can find these scripts in thescriptsdirectory within the Source Directory.Using these scripts correctly formats the requests without introducing any whitespace or HTML formatting. The maintainer that receives your patches needs to be able to save and apply them directly from your emails. Using these scripts is the preferred method for sending patches.
For help on using these scripts, simply provide the
-hargument as follows:$ poky/scripts/create-pull-request -h $ poky/scripts/send-pull-request -h
You can find general Git information on how to push a change upstream in the Git Community Book.
You can submit patches without using the create-pull-request and
send-pull-request scripts described in the previous section.
However, keep in mind, the preferred method is to use the scripts.
Depending on the components changed, you need to submit the email to a specific mailing list. For some guidance on which mailing list to use, see the list in the "How to Submit a Change" section. For a description of the available mailing lists, see the "Mailing Lists" section in the Yocto Project Reference Manual.
Here is the general procedure on how to submit a patch through email without using the scripts:
Make your changes in your local Git repository.
Stage your changes by using the
git addcommand on each file you changed.Commit the change by using the
git commit --signoffcommand. Using the--signoffoption identifies you as the person making the change and also satisfies the Developer's Certificate of Origin (DCO) shown earlier.When you form a commit, you must follow certain standards established by the Yocto Project development team. See the earlier section "How to Submit a Change" for Yocto Project commit message standards.
Format the commit into an email message. To format commits, use the
git format-patchcommand. When you provide the command, you must include a revision list or a number of patches as part of the command. For example, either of these two commands takes your most recent single commit and formats it as an email message in the current directory:$ git format-patch -1or
$ git format-patch HEAD~After the command is run, the current directory contains a numbered
.patchfile for the commit.If you provide several commits as part of the command, the
git format-patchcommand produces a series of numbered files in the current directory – one for each commit. If you have more than one patch, you should also use the--coveroption with the command, which generates a cover letter as the first "patch" in the series. You can then edit the cover letter to provide a description for the series of patches. For information on thegit format-patchcommand, seeGIT_FORMAT_PATCH(1)displayed using theman git-format-patchcommand.Note
If you are or will be a frequent contributor to the Yocto Project or to OpenEmbedded, you might consider requesting a contrib area and the necessary associated rights.Import the files into your mail client by using the
git send-emailcommand.Note
In order to usegit send-email, you must have the the proper Git packages installed. For Ubuntu, Debian, and Fedora the package isgit-email.The
git send-emailcommand sends email by using a local or remote Mail Transport Agent (MTA) such asmsmtp,sendmail, or through a directsmtpconfiguration in your Gitconfigfile. If you are submitting patches through email only, it is very important that you submit them without any whitespace or HTML formatting that either you or your mailer introduces. The maintainer that receives your patches needs to be able to save and apply them directly from your emails. A good way to verify that what you are sending will be applicable by the maintainer is to do a dry run and send them to yourself and then save and apply them as the maintainer would.The
git send-emailcommand is the preferred method for sending your patches since there is no risk of compromising whitespace in the body of the message, which can occur when you use your own mail client. The command also has several options that let you specify recipients and perform further editing of the email message. For information on how to use thegit send-emailcommand, seeGIT-SEND-EMAIL(1)displayed using theman git-send-emailcommand.
Table of Contents
Many development models exist for which you can use the Yocto Project. This chapter overviews simple methods that use tools provided by the Yocto Project:
System Development: System Development covers Board Support Package (BSP) development and kernel modification or configuration. For an example on how to create a BSP, see the "Creating a New BSP Layer Using the yocto-bsp Script" section in the Yocto Project Board Support Package (BSP) Developer's Guide. For more complete information on how to work with the kernel, see the Yocto Project Linux Kernel Development Manual.
User Application Development: User Application Development covers development of applications that you intend to run on target hardware. For information on how to set up your host development system for user-space application development, see the Yocto Project Application Developer's Guide. For a simple example of user-space application development using the Eclipse™ IDE, see the "Application Development Workflow" section.
Temporary Source Code Modification: Direct modification of temporary source code is a convenient development model to quickly iterate and develop towards a solution. Once you implement the solution, you should of course take steps to get the changes upstream and applied in the affected recipes.
Image Development using Hob: You can use the Hob to build custom operating system images within the build environment. Hob provides an efficient interface to the OpenEmbedded build system.
Using a Development Shell: You can use a
devshellto efficiently debug commands or simply edit packages. Working inside a development shell is a quick way to set up the OpenEmbedded build environment to work on parts of a project.
System development involves modification or creation of an image that you want to run on a specific hardware target. Usually, when you want to create an image that runs on embedded hardware, the image does not require the same number of features that a full-fledged Linux distribution provides. Thus, you can create a much smaller image that is designed to use only the features for your particular hardware.
To help you understand how system development works in the Yocto Project, this section covers two types of image development: BSP creation and kernel modification or configuration.
A BSP is a package of recipes that, when applied during a build, results in an image that you can run on a particular board. Thus, the package when compiled into the new image, supports the operation of the board.
Note
For a brief list of terms used when describing the development process in the Yocto Project, see the "Yocto Project Terms" section.
The remainder of this section presents the basic
steps used to create a BSP using the Yocto Project's
BSP Tools.
Although not required for BSP creation, the
meta-intel repository, which contains
many BSPs supported by the Yocto Project, is part of the example.
For an example that shows how to create a new layer using the tools, see the "Creating a New BSP Layer Using the yocto-bsp Script" section in the Yocto Project Board Support Package (BSP) Developer's Guide.
The following illustration and list summarize the BSP creation general workflow.
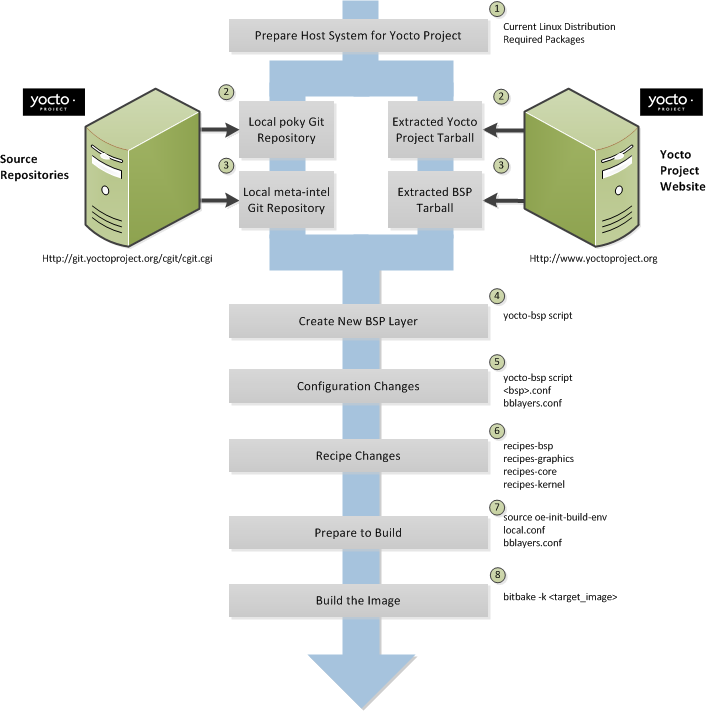 |
Set up your host development system to support development using the Yocto Project: See the "The Linux Distribution" and the "The Packages" sections both in the Yocto Project Quick Start for requirements.
Establish a local copy of the project files on your system: You need this Source Directory available on your host system. Having these files on your system gives you access to the build process and to the tools you need. For information on how to set up the Source Directory, see the "Getting Set Up" section.
Establish the
meta-intelrepository on your system: Having local copies of these supported BSP layers on your system gives you access to layers you might be able to build on or modify to create your BSP. For information on how to get these files, see the "Getting Set Up" section.Create your own BSP layer using the
yocto-bspscript: Layers are ideal for isolating and storing work for a given piece of hardware. A layer is really just a location or area in which you place the recipes and configurations for your BSP. In fact, a BSP is, in itself, a special type of layer. The simplest way to create a new BSP layer that is compliant with the Yocto Project is to use theyocto-bspscript. For information about that script, see the "Creating a New BSP Layer Using the yocto-bsp Script" section in the Yocto Project Board Support (BSP) Developer's Guide.Another example that illustrates a layer is an application. Suppose you are creating an application that has library or other dependencies in order for it to compile and run. The layer, in this case, would be where all the recipes that define those dependencies are kept. The key point for a layer is that it is an isolated area that contains all the relevant information for the project that the OpenEmbedded build system knows about. For more information on layers, see the "Understanding and Creating Layers" section. For more information on BSP layers, see the "BSP Layers" section in the Yocto Project Board Support Package (BSP) Developer's Guide.
Note
Five BSPs exist that are part of the Yocto Project release:genericx86,genericx86-64,beagleboard,mpc8315e, androuterstationpro. The recipes and configurations for these five BSPs are located and dispersed within the Source Directory. On the other hand, BSP layers for Chief River, Crown Bay, Crystal Forest, Emenlow, Fish River Island 2, Jasper Forest, N450, NUC DC3217IYE, Romley, sys940x, Sugar Bay, and tlk exist in their own separate layers within the largermeta-intellayer.When you set up a layer for a new BSP, you should follow a standard layout. This layout is described in the "Example Filesystem Layout" section of the Board Support Package (BSP) Development Guide. In the standard layout, you will notice a suggested structure for recipes and configuration information. You can see the standard layout for a BSP by examining any supported BSP found in the
meta-intellayer inside the Source Directory.Make configuration changes to your new BSP layer: The standard BSP layer structure organizes the files you need to edit in
confand severalrecipes-*directories within the BSP layer. Configuration changes identify where your new layer is on the local system and identify which kernel you are going to use. When you run theyocto-bspscript, you are able to interactively configure many things for the BSP (e.g. keyboard, touchscreen, and so forth).Make recipe changes to your new BSP layer: Recipe changes include altering recipes (
.bbfiles), removing recipes you don't use, and adding new recipes or append files (.bbappend) that you need to support your hardware.Prepare for the build: Once you have made all the changes to your BSP layer, there remains a few things you need to do for the OpenEmbedded build system in order for it to create your image. You need to get the build environment ready by sourcing an environment setup script and you need to be sure two key configuration files are configured appropriately: the
conf/local.confand theconf/bblayers.conffile. You must make the OpenEmbedded build system aware of your new layer. See the "Enabling Your Layer" section for information on how to let the build system know about your new layer.The entire process for building an image is overviewed in the section "Building an Image" section of the Yocto Project Quick Start. You might want to reference this information.
Build the image: The OpenEmbedded build system uses the BitBake tool to build images based on the type of image you want to create. You can find more information about BitBake in the user manual, which is found in the
bitbake/doc/manualdirectory of the Source Directory.The build process supports several types of images to satisfy different needs. See the "Images" chapter in the Yocto Project Reference Manual for information on supported images.
You can view a video presentation on "Building Custom Embedded Images with Yocto" at Free Electrons. You can also find supplemental information in the Yocto Project Board Support Package (BSP) Developer's Guide. Finally, there is a wiki page write up of the example also located here that you might find helpful.
Kernel modification involves changing the Yocto Project kernel, which could involve changing
configuration options as well as adding new kernel recipes.
Configuration changes can be added in the form of configuration fragments, while recipe
modification comes through the kernel's recipes-kernel area
in a kernel layer you create.
The remainder of this section presents a high-level overview of the Yocto Project kernel architecture and the steps to modify the kernel. You can reference the "Patching the Kernel" section for an example that changes the source code of the kernel. For information on how to configure the kernel, see the "Configuring the Kernel" section. For more information on the kernel and on modifying the kernel, see the Yocto Project Linux Kernel Development Manual.
Traditionally, when one thinks of a patched kernel, they think of a base kernel source tree and a fixed structure that contains kernel patches. The Yocto Project, however, employs mechanisms that, in a sense, result in a kernel source generator. By the end of this section, this analogy will become clearer.
You can find a web interface to the Yocto Project kernel source repositories at http://git.yoctoproject.org. If you look at the interface, you will see to the left a grouping of Git repositories titled "Yocto Linux Kernel." Within this group, you will find several kernels supported by the Yocto Project:
linux-yocto-3.4- The stable Yocto Project kernel to use with the Yocto Project Release 1.3. This kernel is based on the Linux 3.4 released kernel.linux-yocto-3.8- The stable Yocto Project kernel to use with the Yocto Project Release 1.4. This kernel is based on the Linux 3.8 released kernel.linux-yocto-3.10- The stable Yocto Project kernel to use with the Yocto Project Release 1.5. This kernel is based on the Linux 3.10 released kernel.linux-yocto-dev- A development kernel based on the latest upstream release candidate available.
The kernels are maintained using the Git revision control system that structures them using the familiar "tree", "branch", and "leaf" scheme. Branches represent diversions from general code to more specific code, while leaves represent the end-points for a complete and unique kernel whose source files, when gathered from the root of the tree to the leaf, accumulate to create the files necessary for a specific piece of hardware and its features. The following figure displays this concept:
 |
Within the figure, the "Kernel.org Branch Point" represents the point in the tree
where a supported base kernel is modified from the Linux kernel.
For example, this could be the branch point for the linux-yocto-3.4
kernel.
Thus, everything further to the right in the structure is based on the
linux-yocto-3.4 kernel.
Branch points to right in the figure represent where the
linux-yocto-3.4 kernel is modified for specific hardware
or types of kernels, such as real-time kernels.
Each leaf thus represents the end-point for a kernel designed to run on a specific
targeted device.
The overall result is a Git-maintained repository from which all the supported kernel types can be derived for all the supported devices. A big advantage to this scheme is the sharing of common features by keeping them in "larger" branches within the tree. This practice eliminates redundant storage of similar features shared among kernels.
Note
Keep in mind the figure does not take into account all the supported Yocto Project kernel types, but rather shows a single generic kernel just for conceptual purposes. Also keep in mind that this structure represents the Yocto Project source repositories that are either pulled from during the build or established on the host development system prior to the build by either cloning a particular kernel's Git repository or by downloading and unpacking a tarball.
Upstream storage of all the available kernel source code is one thing, while representing and using the code on your host development system is another. Conceptually, you can think of the kernel source repositories as all the source files necessary for all the supported kernels. As a developer, you are just interested in the source files for the kernel on which you are working. And, furthermore, you need them available on your host system.
Kernel source code is available on your host system a couple of different ways. If you are working in the kernel all the time, you probably would want to set up your own local Git repository of the kernel tree. If you just need to make some patches to the kernel, you can access temporary kernel source files that were extracted and used during a build. We will just talk about working with the temporary source code. For more information on how to get kernel source code onto your host system, see the "Yocto Project Kernel" bulleted item earlier in the manual.
What happens during the build?
When you build the kernel on your development system, all files needed for the build
are taken from the source repositories pointed to by the
SRC_URI variable
and gathered in a temporary work area
where they are subsequently used to create the unique kernel.
Thus, in a sense, the process constructs a local source tree specific to your
kernel to generate the new kernel image - a source generator if you will.
The following figure shows the temporary file structure created on your host system when the build occurs. This Build Directory contains all the source files used during the build.
 |
Again, for additional information the Yocto Project kernel's architecture and its branching strategy, see the Yocto Project Linux Kernel Development Manual. You can also reference the "Patching the Kernel" section for a detailed example that modifies the kernel.
This illustration and the following list summarizes the kernel modification general workflow.
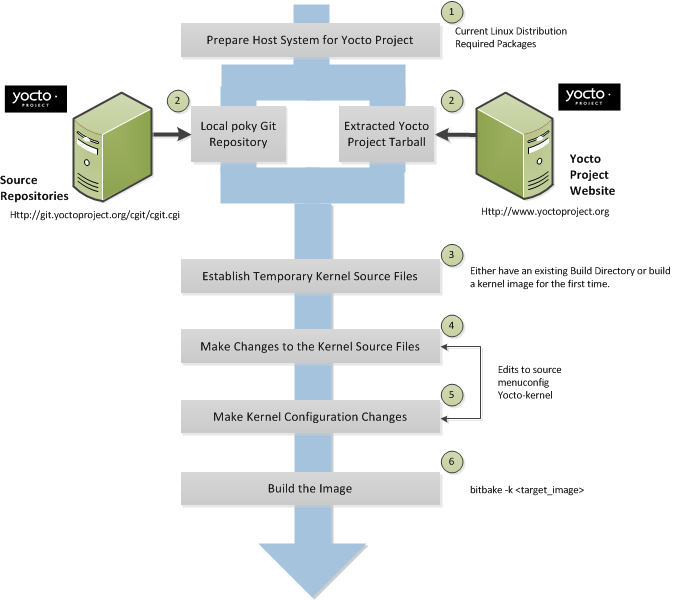 |
Set up your host development system to support development using the Yocto Project: See "The Linux Distribution" and "The Packages" sections both in the Yocto Project Quick Start for requirements.
Establish a local copy of project files on your system: Having the Source Directory on your system gives you access to the build process and tools you need. For information on how to get these files, see the bulleted item "Yocto Project Release" earlier in this manual.
Establish the temporary kernel source files: Temporary kernel source files are kept in the Build Directory created by the OpenEmbedded build system when you run BitBake. If you have never built the kernel you are interested in, you need to run an initial build to establish local kernel source files.
If you are building an image for the first time, you need to get the build environment ready by sourcing the environment setup script. You also need to be sure two key configuration files (
local.confandbblayers.conf) are configured appropriately.The entire process for building an image is overviewed in the "Building an Image" section of the Yocto Project Quick Start. You might want to reference this information. You can find more information on BitBake in the user manual, which is found in the
bitbake/doc/manualdirectory of the Source Directory.The build process supports several types of images to satisfy different needs. See the "Images" chapter in the Yocto Project Reference Manual for information on supported images.
Make changes to the kernel source code if applicable: Modifying the kernel does not always mean directly changing source files. However, if you have to do this, you make the changes to the files in the Build directory.
Make kernel configuration changes if applicable: If your situation calls for changing the kernel's configuration, you can use the
yocto-kernelscript ormenuconfigto enable and disable kernel configurations. Using the script lets you interactively set up kernel configurations. Usingmenuconfigallows you to interactively develop and test the configuration changes you are making to the kernel. When saved, changes usingmenuconfigupdate the kernel's.configfile. Try to resist the temptation of directly editing the.configfile found in the Build Directory attmp/sysroots/<machine-name>/kernel. Doing so, can produce unexpected results when the OpenEmbedded build system regenerates the configuration file.Once you are satisfied with the configuration changes made using
menuconfig, you can directly compare the.configfile against a saved original and gather those changes into a config fragment to be referenced from within the kernel's.bbappendfile.Rebuild the kernel image with your changes: Rebuilding the kernel image applies your changes.
Application development involves creating an application that you want to run on your target hardware, which is running a kernel image created using the OpenEmbedded build system. The Yocto Project provides an Application Development Toolkit (ADT) and stand-alone cross-development toolchains that facilitate quick development and integration of your application into its runtime environment. Using the ADT and toolchains, you can compile and link your application. You can then deploy your application to the actual hardware or to the QEMU emulator for testing. If you are familiar with the popular Eclipse™ IDE, you can use an Eclipse Yocto Plug-in to allow you to develop, deploy, and test your application all from within Eclipse.
While we strongly suggest using the ADT to develop your application, this option might not be best for you. If this is the case, you can still use pieces of the Yocto Project for your development process. However, because the process can vary greatly, this manual does not provide detail on the process.
To help you understand how application development works using the ADT, this section provides an overview of the general development process and a detailed example of the process as it is used from within the Eclipse IDE.
The following illustration and list summarize the application development general workflow.
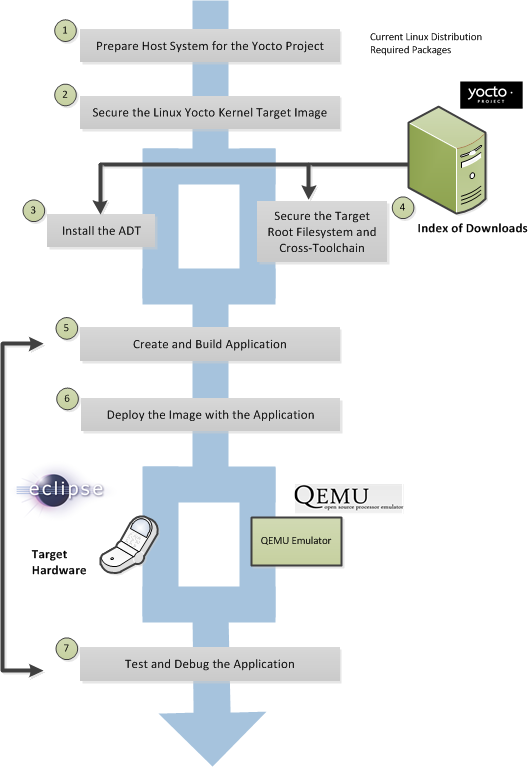 |
Prepare the host system for the Yocto Project: See "The Linux Distribution" and "The Packages" sections both in the Yocto Project Quick Start for requirements.
Secure the Yocto Project kernel target image: You must have a target kernel image that has been built using the OpenEmbedded build system.
Depending on whether the Yocto Project has a pre-built image that matches your target architecture and where you are going to run the image while you develop your application (QEMU or real hardware), the area from which you get the image differs.
Download the image from
machinesif your target architecture is supported and you are going to develop and test your application on actual hardware.Download the image from
machines/qemuif your target architecture is supported and you are going to develop and test your application using the QEMU emulator.Build your image if you cannot find a pre-built image that matches your target architecture. If your target architecture is similar to a supported architecture, you can modify the kernel image before you build it. See the "Patching the Kernel" section for an example.
For information on pre-built kernel image naming schemes for images that can run on the QEMU emulator, see the "Downloading the Pre-Built Linux Kernel" section in the Yocto Project Quick Start.
Install the ADT: The ADT provides a target-specific cross-development toolchain, the root filesystem, the QEMU emulator, and other tools that can help you develop your application. While it is possible to get these pieces separately, the ADT Installer provides an easy, inclusive method. You can get these pieces by running an ADT installer script, which is configurable. For information on how to install the ADT, see the "Using the ADT Installer" section in the Yocto Project Application Developer's Guide.
If applicable, secure the target root filesystem and the Cross-development toolchain: If you choose not to install the ADT using the ADT Installer, you need to find and download the appropriate root filesystem and the cross-development toolchain.
You can find the tarballs for the root filesystem in the same area used for the kernel image. Depending on the type of image you are running, the root filesystem you need differs. For example, if you are developing an application that runs on an image that supports Sato, you need to get a root filesystem that supports Sato.
You can find the cross-development toolchains at
toolchains. Be sure to get the correct toolchain for your development host and your target architecture. See the "Using a Cross-Toolchain Tarball" section in the Yocto Project Application Developer's Guide for information and the "Installing the Toolchain" in the Yocto Project Quick Start for information on finding and installing the correct toolchain based on your host development system and your target architecture.Create and build your application: At this point, you need to have source files for your application. Once you have the files, you can use the Eclipse IDE to import them and build the project. If you are not using Eclipse, you need to use the cross-development tools you have installed to create the image.
Deploy the image with the application: If you are using the Eclipse IDE, you can deploy your image to the hardware or to QEMU through the project's preferences. If you are not using the Eclipse IDE, then you need to deploy the application to the hardware using other methods. Or, if you are using QEMU, you need to use that tool and load your image in for testing.
Test and debug the application: Once your application is deployed, you need to test it. Within the Eclipse IDE, you can use the debugging environment along with the set of user-space tools installed along with the ADT to debug your application. Of course, the same user-space tools are available separately if you choose not to use the Eclipse IDE.
The Eclipse IDE is a popular development environment and it fully supports development using the Yocto Project.
Note
This release of the Yocto Project supports both the Kepler and Juno versions of the Eclipse IDE. Thus, the following information provides setup information for both versions.
When you install and configure the Eclipse Yocto Project Plug-in into the Eclipse IDE, you maximize your Yocto Project experience. Installing and configuring the Plug-in results in an environment that has extensions specifically designed to let you more easily develop software. These extensions allow for cross-compilation, deployment, and execution of your output into a QEMU emulation session as well as actual target hardware. You can also perform cross-debugging and profiling. The environment also supports a suite of tools that allows you to perform remote profiling, tracing, collection of power data, collection of latency data, and collection of performance data.
This section describes how to install and configure the Eclipse IDE Yocto Plug-in and how to use it to develop your application.
To develop within the Eclipse IDE, you need to do the following:
Install the optimal version of the Eclipse IDE.
Configure the Eclipse IDE.
Install the Eclipse Yocto Plug-in.
Configure the Eclipse Yocto Plug-in.
Note
Do not install Eclipse from your distribution's package repository. Be sure to install Eclipse from the official Eclipse download site as directed in the next section.
It is recommended that you have the Kepler 4.3 version of the Eclipse IDE installed on your development system. However, if you currently have the Juno 4.2 version installed and you do not want to upgrade the IDE, you can configure Juno to work with the Yocto Project.
If you do not have the Kepler 4.3 Eclipse IDE installed, you can find the tarball at http://www.eclipse.org/downloads. From that site, choose the Eclipse Standard 4.3 version particular to your development host. This version contains the Eclipse Platform, the Java Development Tools (JDT), and the Plug-in Development Environment.
Once you have downloaded the tarball, extract it into a
clean directory.
For example, the following commands unpack and install the
downloaded Eclipse IDE tarball into a clean directory
using the default name eclipse:
$ cd ~
$ tar -xzvf ~/Downloads/eclipse-standard-kepler-R-linux-gtk-x86_64.tar.gz
This section presents the steps needed to configure the Eclipse IDE.
Before installing and configuring the Eclipse Yocto Plug-in, you need to configure the Eclipse IDE. Follow these general steps:
Start the Eclipse IDE.
Make sure you are in your Workbench and select "Install New Software" from the "Help" pull-down menu.
Select
Kepler - http://download.eclipse.org/releases/keplerfrom the "Work with:" pull-down menu.Note
For Juno, selectJuno - http://download.eclipse.org/releases/junoExpand the box next to "Linux Tools" and select the
LTTng - Linux Tracing Toolkitboxes.Expand the box next to "Mobile and Device Development" and select the following boxes:
C/C++ Remote LaunchRemote System Explorer End-user RuntimeRemote System Explorer User ActionsTarget Management TerminalTCF Remote System Explorer add-inTCF Target Explorer
Expand the box next to "Programming Languages" and select the
Autotools Support for CDTandC/C++ Development Toolsboxes.Complete the installation and restart the Eclipse IDE.
You can install the Eclipse Yocto Plug-in into the Eclipse IDE one of two ways: use the Yocto Project's Eclipse Update site to install the pre-built plug-in or build and install the plug-in from the latest source code.
To install the Eclipse Yocto Plug-in from the update site, follow these steps:
Start up the Eclipse IDE.
In Eclipse, select "Install New Software" from the "Help" menu.
Click "Add..." in the "Work with:" area.
Enter
http://downloads.yoctoproject.org/releases/eclipse-plugin/1.5.4/keplerin the URL field and provide a meaningful name in the "Name" field.Note
If you are using Juno, usehttp://downloads.yoctoproject.org/releases/eclipse-plugin/1.5.4/junoin the URL field.Click "OK" to have the entry added to the "Work with:" drop-down list.
Select the entry for the plug-in from the "Work with:" drop-down list.
Check the boxes next to
Yocto Project ADT Plug-in,Yocto Project Bitbake Commander Plug-in, andYocto Project Documentation plug-in.Complete the remaining software installation steps and then restart the Eclipse IDE to finish the installation of the plug-in.
To install the Eclipse Yocto Plug-in from the latest source code, follow these steps:
Be sure your development system is not using OpenJDK to build the plug-in by doing the following:
Use the Oracle JDK. If you don't have that, go to http://www.oracle.com/technetwork/java/javase/downloads/jdk7-downloads-1880260.html and download the appropriate tarball for your development system and extract it into your home directory.
In the shell you are going to do your work, export the location of the Oracle Java as follows:
export PATH=~/jdk1.7.0_40/bin:$PATH
In the same shell, create a Git repository with:
$ cd ~ $ git clone git://git.yoctoproject.org/eclipse-poky-keplerNote
If you are using Juno, the repository is located atgit://git.yoctoproject.org/eclipse-poky-juno.For this example, the repository is named
~/eclipse-poky-kepler.Change to the directory where you set up the Git repository:
$ cd ~/eclipse-poky-keplerBe sure you are in the right branch for your Git repository. For this release set the branch to
dora:$ git checkout doraChange to the
scriptsdirectory within the Git repository:$ cd scriptsSet up the local build environment by running the setup script:
$ ./setup.shWhen the script finishes execution, it prompts you with instructions on how to run the
build.shscript, which is also in thescriptsof the Git repository created earlier.Run the
build.shscript as directed. Be sure to provide the name of the Git branch along with the Yocto Project release you are using. Here is an example that uses thedorabranch:$ ECLIPSE_HOME=/home/scottrif/eclipse-poky-kepler/scripts/eclipse ./build.sh dora doraAfter running the script, the file
org.yocto.sdk-<release>-<date>-archive.zipis in the current directory.If necessary, start the Eclipse IDE and be sure you are in the Workbench.
Select "Install New Software" from the "Help" pull-down menu.
Click "Add".
Provide anything you want in the "Name" field.
Click "Archive" and browse to the ZIP file you built in step seven. This ZIP file should not be "unzipped", and must be the
*archive.zipfile created by running thebuild.shscript.Click through the "Okay" buttons.
Check the boxes in the installation window and complete the installation.
Restart the Eclipse IDE if necessary.
At this point you should be able to configure the Eclipse Yocto Plug-in as described in the "Configuring the Eclipse Yocto Plug-in" section.
Configuring the Eclipse Yocto Plug-in involves setting the Cross Compiler options and the Target options. The configurations you choose become the default settings for all projects. You do have opportunities to change them later when you configure the project (see the following section).
To start, you need to do the following from within the Eclipse IDE:
Choose "Preferences" from the "Windows" menu to display the Preferences Dialog.
Click "Yocto Project ADT".
To configure the Cross Compiler Options, you must select the type of toolchain, point to the toolchain, specify the sysroot location, and select the target architecture.
Selecting the Toolchain Type: Choose between
Standalone pre-built toolchainandBuild system derived toolchainfor Cross Compiler Options.Standalone Pre-built Toolchain:Select this mode when you are using a stand-alone cross-toolchain. For example, suppose you are an application developer and do not need to build a target image. Instead, you just want to use an architecture-specific toolchain on an existing kernel and target root filesystem.Build System Derived Toolchain:Select this mode if the cross-toolchain has been installed and built as part of the Build Directory. When you selectBuild system derived toolchain, you are using the toolchain bundled inside the Build Directory.
Point to the Toolchain: If you are using a stand-alone pre-built toolchain, you should be pointing to where it is installed. If you used the ADT Installer script and accepted the default installation directory, the toolchain will be installed in the
/opt/poky/1.5.4directory. Sections "Configuring and Running the ADT Installer Script" and "Using a Cross-Toolchain Tarball" in the Yocto Project Application Developer's Guide describe how to install a stand-alone cross-toolchain.If you are using a system-derived toolchain, the path you provide for the
Toolchain Root Locationfield is the Build Directory. See the "Using BitBake and the Build Directory" section in the Yocto Project Application Developer's Guide for information on how to install the toolchain into the Build Directory.Specify the Sysroot Location: This location is where the root filesystem for the target hardware resides. If you used the ADT Installer script and accepted the default installation directory, then the location is
/opt/poky/<release>. Additionally, when you use the ADT Installer script, the same location is used for the QEMU user-space tools and the NFS boot process.If you used either of the other two methods to install the toolchain or did not accept the ADT Installer script's default installation directory, then the location of the sysroot filesystem depends on where you separately extracted and installed the filesystem.
For information on how to install the toolchain and on how to extract and install the sysroot filesystem, see the "Installing the ADT and Toolchains" section.
Select the Target Architecture: The target architecture is the type of hardware you are going to use or emulate. Use the pull-down
Target Architecturemenu to make your selection. The pull-down menu should have the supported architectures. If the architecture you need is not listed in the menu, you will need to build the image. See the "Building an Image" section of the Yocto Project Quick Start for more information.
You can choose to emulate hardware using the QEMU emulator, or you can choose to run your image on actual hardware.
QEMU:Select this option if you will be using the QEMU emulator. If you are using the emulator, you also need to locate the kernel and specify any custom options.If you selected
Build system derived toolchain, the target kernel you built will be located in the Build Directory intmp/deploy/images/<machine>directory. If you selectedStandalone pre-built toolchain, the pre-built image you downloaded is located in the directory you specified when you downloaded the image.Most custom options are for advanced QEMU users to further customize their QEMU instance. These options are specified between paired angled brackets. Some options must be specified outside the brackets. In particular, the options
serial,nographic, andkvmmust all be outside the brackets. Use theman qemucommand to get help on all the options and their use. The following is an example:serial ‘<-m 256 -full-screen>’Regardless of the mode, Sysroot is already defined as part of the Cross-Compiler Options configuration in the
Sysroot Location:field.External HW:Select this option if you will be using actual hardware.
Click the "OK" to save your plug-in configurations.
You can create two types of projects: Autotools-based, or Makefile-based. This section describes how to create Autotools-based projects from within the Eclipse IDE. For information on creating Makefile-based projects in a terminal window, see the section "Using the Command Line" in the Yocto Project Application Developer's Guide.
To create a project based on a Yocto template and then display the source code, follow these steps:
Select "Project" from the "File -> New" menu.
Double click
CC++.Double click
C Projectto create the project.Expand
Yocto Project ADT Project.Select
Hello World ANSI C Autotools Project. This is an Autotools-based project based on a Yocto template.Put a name in the
Project name:field. Do not use hyphens as part of the name.Click "Next".
Add information in the
AuthorandCopyright noticefields.Be sure the
Licensefield is correct.Click "Finish".
If the "open perspective" prompt appears, click "Yes" so that you in the C/C++ perspective.
The left-hand navigation pane shows your project. You can display your source by double clicking the project's source file.
The earlier section, "Configuring the Eclipse Yocto Plug-in", sets up the default project configurations. You can override these settings for a given project by following these steps:
Select "Change Yocto Project Settings" from the "Project" menu. This selection brings up the Yocto Project Settings Dialog and allows you to make changes specific to an individual project.
By default, the Cross Compiler Options and Target Options for a project are inherited from settings you provide using the Preferences Dialog as described earlier in the "Configuring the Eclipse Yocto Plug-in" section. The Yocto Project Settings Dialog allows you to override those default settings for a given project.
Make your configurations for the project and click "OK". If you are running the Juno version of Eclipse, you can skip down to the next section where you build the project. If you are not working with Juno, you need to reconfigure the project as described in the next step.
Select "Reconfigure Project" from the "Project" menu. This selection reconfigures the project by running
autogen.shin the workspace for your project. The script also runslibtoolize,aclocal,autoconf,autoheader,automake --a, and./configure. Click on the "Console" tab beneath your source code to see the results of reconfiguring your project.
To build the project in Juno, right click on the project in the navigator pane and select "Build Project". If you are not running Juno, select "Build Project" from the "Project" menu. The console should update and you can note the cross-compiler you are using.
To start the QEMU emulator from within Eclipse, follow these steps:
Expose and select "External Tools" from the "Run" menu. Your image should appear as a selectable menu item.
Select your image from the menu to launch the emulator in a new window.
If needed, enter your host root password in the shell window at the prompt. This sets up a
Tap 0connection needed for running in user-space NFS mode.Wait for QEMU to launch.
Once QEMU launches, you can begin operating within that environment. For example, you could determine the IP Address for the user-space NFS by using the
ifconfigcommand.
Once the QEMU emulator is running the image, you can deploy your application using the Eclipse IDE and use then use the emulator to perform debugging. Follow these steps to deploy the application.
Select "Debug Configurations..." from the "Run" menu.
In the left area, expand
C/C++Remote Application.Locate your project and select it to bring up a new tabbed view in the Debug Configurations Dialog.
Enter the absolute path into which you want to deploy the application. Use the "Remote Absolute File Path for C/C++Application:" field. For example, enter
/usr/bin/<programname>.Click on the "Debugger" tab to see the cross-tool debugger you are using.
Click on the "Main" tab.
Create a new connection to the QEMU instance by clicking on "new".
Select
TCF, which means Target Communication Framework.Click "Next".
Clear out the "host name" field and enter the IP Address determined earlier.
Click "Finish" to close the New Connections Dialog.
Use the drop-down menu now in the "Connection" field and pick the IP Address you entered.
Click "Run" to bring up a login screen and login.
Accept the debug perspective.
As mentioned earlier in the manual, several tools exist that enhance your development experience. These tools are aids in developing and debugging applications and images. You can run these user-space tools from within the Eclipse IDE through the "YoctoTools" menu.
Once you pick a tool, you need to configure it for the remote target. Every tool needs to have the connection configured. You must select an existing TCF-based RSE connection to the remote target. If one does not exist, click "New" to create one.
Here are some specifics about the remote tools:
OProfile: Selecting this tool causes theoprofile-serveron the remote target to launch on the local host machine. Theoprofile-viewermust be installed on the local host machine and theoprofile-servermust be installed on the remote target, respectively, in order to use. You must compile and install theoprofile-viewerfrom the source code on your local host machine. Furthermore, in order to convert the target's sample format data into a form that the host can use, you must have OProfile version 0.9.4 or greater installed on the host.You can locate both the viewer and server from http://git.yoctoproject.org/cgit/cgit.cgi/oprofileui/. You can also find more information on setting up and using this tool in the "OProfile" section of the Yocto Project Profiling and Tracing Manual.
Note
Theoprofile-serveris installed by default on thecore-image-sato-sdkimage.Lttng2.0 ust trace import: Selecting this tool transfers the remote target'sLttngtracing data back to the local host machine and uses the Lttng Eclipse plug-in to graphically display the output. For information on how to use Lttng to trace an application, see http://lttng.org/documentation and the "LTTng (Linux Trace Toolkit, next generation)" section, which is in the Yocto Project Profiling and Tracing Manual.Note
Do not useLttng-user space (legacy)tool. This tool no longer has any upstream support.Before you use the
Lttng2.0 ust trace importtool, you need to setup the Lttng Eclipse plug-in and create a Tracing project. Do the following:Select "Open Perspective" from the "Window" menu and then select "Tracing".
Click "OK" to change the Eclipse perspective into the Tracing perspective.
Create a new Tracing project by selecting "Project" from the "File -> New" menu.
Choose "Tracing Project" from the "Tracing" menu.
Generate your tracing data on the remote target.
Select "Lttng2.0 ust trace import" from the "Yocto Project Tools" menu to start the data import process.
Specify your remote connection name.
For the Ust directory path, specify the location of your remote tracing data. Make sure the location ends with
ust(e.g./usr/mysession/ust).Click "OK" to complete the import process. The data is now in the local tracing project you created.
Right click on the data and then use the menu to Select "Generic CTF Trace" from the "Trace Type... -> Common Trace Format" menu to map the tracing type.
Right click the mouse and select "Open" to bring up the Eclipse Lttng Trace Viewer so you view the tracing data.
PowerTOP: Selecting this tool runs PowerTOP on the remote target machine and displays the results in a new view called PowerTOP.The "Time to gather data(sec):" field is the time passed in seconds before data is gathered from the remote target for analysis.
The "show pids in wakeups list:" field corresponds to the
-pargument passed toPowerTOP.LatencyTOP and Perf: LatencyTOP identifies system latency, while Perf monitors the system's performance counter registers. Selecting either of these tools causes an RSE terminal view to appear from which you can run the tools. Both tools refresh the entire screen to display results while they run. For more information on setting up and usingperf, see the "perf" section in the Yocto Project Profiling and Tracing Manual.
Within the Eclipse IDE, you can create a Yocto BitBake Commander project, edit the Metadata, and then use Hob to build a customized image all within one IDE.
To create a Yocto BitBake Commander project, follow these steps:
Select "Other" from the "Window -> Open Perspective" menu and then choose "Bitbake Commander".
Click "OK" to change the perspective to Bitbake Commander.
Select "Project" from the "File -> New" menu to create a new Yocto Bitbake Commander project.
Choose "New Yocto Project" from the "Yocto Project Bitbake Commander" menu and click "Next".
Enter the Project Name and choose the Project Location. The Yocto project's Metadata files will be put under the directory
<project_location>/<project_name>. If that directory does not exist, you need to check the "Clone from Yocto Git Repository" box, which would execute agit clonecommand to get the project's Metadata files.Note
Do not specify your BitBake Commander project location as your Eclipse workspace. Doing so causes an error indicating that the current project overlaps the location of another project. This error occurs even if no such project exits.Select
Finishto create the project.
After you create the Yocto Bitbake Commander project, you
can modify the Metadata
files by opening them in the project.
When editing recipe files (.bb files),
you can view BitBake variable values and information by
hovering the mouse pointer over the variable name and
waiting a few seconds.
To edit the Metadata, follow these steps:
Select your Yocto Bitbake Commander project.
Select "BitBake Recipe" from the "File -> New -> Yocto BitBake Commander" menu to open a new recipe wizard.
Point to your source by filling in the "SRC_URL" field. For example, you can add a recipe to your Source Directory by defining "SRC_URL" as follows:
ftp://ftp.gnu.org/gnu/m4/m4-1.4.9.tar.gzClick "Populate" to calculate the archive md5, sha256, license checksum values and to auto-generate the recipe filename.
Fill in the "Description" field.
Be sure values for all required fields exist.
Click "Finish".
To build and customize the image using Hob from within the Eclipse IDE, follow these steps:
Select your Yocto Bitbake Commander project.
Select "Launch Hob" from the "Project" menu.
Enter the Build Directory where you want to put your final images.
Click "OK" to launch Hob.
Use Hob to customize and build your own images. For information on Hob, see the Hob Project Page on the Yocto Project website.
If you want to develop an application without prior installation of the ADT, you still can employ the Cross Development Toolchain, the QEMU emulator, and a number of supported target image files. You just need to follow these general steps:
Install the cross-development toolchain for your target hardware: For information on how to install the toolchain, see the "Using a Cross-Toolchain Tarball" section in the Yocto Project Application Developer's Guide.
Download the Target Image: The Yocto Project supports several target architectures and has many pre-built kernel images and root filesystem images.
If you are going to develop your application on hardware, go to the
machinesdownload area and choose a target machine area from which to download the kernel image and root filesystem. This download area could have several files in it that support development using actual hardware. For example, the area might contain.hddimgfiles that combine the kernel image with the filesystem, boot loaders, and so forth. Be sure to get the files you need for your particular development process.If you are going to develop your application and then run and test it using the QEMU emulator, go to the
machines/qemudownload area. From this area, go down into the directory for your target architecture (e.g.qemux86_64for an Intel®-based 64-bit architecture). Download kernel, root filesystem, and any other files you need for your process.Note
In order to use the root filesystem in QEMU, you need to extract it. See the "Extracting the Root Filesystem" section for information on how to extract the root filesystem.Develop and Test your Application: At this point, you have the tools to develop your application. If you need to separately install and use the QEMU emulator, you can go to QEMU Home Page to download and learn about the emulator.
You might find it helpful during development to modify the temporary source code used by recipes to build packages. For example, suppose you are developing a patch and you need to experiment a bit to figure out your solution. After you have initially built the package, you can iteratively tweak the source code, which is located in the Build Directory, and then you can force a re-compile and quickly test your altered code. Once you settle on a solution, you can then preserve your changes in the form of patches. You can accomplish these steps all within either a Quilt or Git workflow.
During a build, the unpacked temporary source code used by recipes
to build packages is available in the Build Directory as
defined by the
S variable.
Below is the default value for the S variable as defined in the
meta/conf/bitbake.conf configuration file in the
Source Directory:
S = "${WORKDIR}/${BP}"
You should be aware that many recipes override the S variable.
For example, recipes that fetch their source from Git usually set
S to ${WORKDIR}/git.
Note
TheBP
represents the base recipe name, which consists of the name and version:
BP = "${BPN}-${PV}"
The path to the work directory for the recipe
(WORKDIR) depends
on the recipe name and the architecture of the target device.
For example, here is the work directory for recipes and resulting packages that are
not device-dependent:
${TMPDIR}/work/${PACKAGE_ARCH}-poky-${TARGET_OS}/${PN}/${EXTENDPE}${PV}-${PR}
Let's look at an example without variables.
Assuming a top-level Source Directory
named poky
and a default Build Directory of poky/build,
the following is the work directory for the acl recipe that
creates the acl package:
poky/build/tmp/work/i586-poky-linux/acl/2.2.51-r3/
If your resulting package is dependent on the target device, the work directory varies slightly:
${TMPDIR}/work/${MACHINE}-poky-${TARGET_OS}/${PN}/${EXTENDPE}${PV}-${PR}
Again, assuming top-level Source Directory named poky
and a default Build Directory of poky/build, the
following are the work and temporary source directories, respectively,
for the acl package that is being
built for a MIPS-based device:
poky/build/tmp/work/mips-poky-linux/acl/2.2.51-r2
poky/build/tmp/work/mips-poky-linux/acl/2.2.51-r2/acl-2.2.51
Note
To better understand how the OpenEmbedded build system resolves directories during the build process, see the glossary entries for theWORKDIR,
TMPDIR,
TOPDIR,
PACKAGE_ARCH,
MULTIMACH_TARGET_SYS,
TARGET_OS,
PN,
PV,
EXTENDPE,
and
PR
variables in the Yocto Project Reference Manual.
Now that you know where to locate the directory that has the temporary source code, you can use a Quilt or Git workflow to make your edits, test the changes, and preserve the changes in the form of patches.
Quilt is a powerful tool that allows you to capture source code changes without having a clean source tree. This section outlines the typical workflow you can use to modify temporary source code, test changes, and then preserve the changes in the form of a patch all using Quilt.
Follow these general steps:
Find the Source Code: The temporary source code used by the OpenEmbedded build system is kept in the Build Directory. See the "Finding the Temporary Source Code" section to learn how to locate the directory that has the temporary source code for a particular package.
Change Your Working Directory: You need to be in the directory that has the temporary source code. That directory is defined by the
Svariable.Create a New Patch: Before modifying source code, you need to create a new patch. To create a new patch file, use
quilt newas below:$ quilt new my_changes.patchNotify Quilt and Add Files: After creating the patch, you need to notify Quilt about the files you plan to edit. You notify Quilt by adding the files to the patch you just created:
$ quilt add file1.c file2.c file3.cEdit the Files: Make your changes in the temporary source code to the files you added to the patch.
Test Your Changes: Once you have modified the source code, the easiest way to test your changes is by calling the
compiletask as shown in the following example:$ bitbake -c compile -f <name_of_package>The
-for--forceoption forces the specified task to execute. If you find problems with your code, you can just keep editing and re-testing iteratively until things work as expected.Note
All the modifications you make to the temporary source code disappear once you-c cleanor-c cleanallwith BitBake for the package. Modifications will also disappear if you use therm_workfeature as described in the "Building an Image" section of the Yocto Project Quick Start.Generate the Patch: Once your changes work as expected, you need to use Quilt to generate the final patch that contains all your modifications.
$ quilt refreshAt this point, the
my_changes.patchfile has all your edits made to thefile1.c,file2.c, andfile3.cfiles.You can find the resulting patch file in the
patches/subdirectory of the source (S) directory.Copy the Patch File: For simplicity, copy the patch file into a directory named
files, which you can create in the same directory that holds the recipe (.bb) file or the append (.bbappend) file. Placing the patch here guarantees that the OpenEmbedded build system will find the patch. Next, add the patch into theSRC_URIof the recipe. Here is an example:SRC_URI += "file://my_changes.patch"Increment the Recipe Revision Number: Finally, don't forget to 'bump' the
PRvalue in the recipe since the resulting packages have changed.
Git is an even more powerful tool that allows you to capture source code changes without having a clean source tree. This section outlines the typical workflow you can use to modify temporary source code, test changes, and then preserve the changes in the form of a patch all using Git. For general information on Git as it is used in the Yocto Project, see the "Git" section.
Note
This workflow uses Git only for its ability to manage local changes to the source code and produce patches independent of any version control system used with the Yocto Project.Follow these general steps:
Find the Source Code: The temporary source code used by the OpenEmbedded build system is kept in the Build Directory. See the "Finding the Temporary Source Code" section to learn how to locate the directory that has the temporary source code for a particular package.
Change Your Working Directory: You need to be in the directory that has the temporary source code. That directory is defined by the
Svariable.If needed, initialize a Git Repository: If the recipe you are working with does not use a Git fetcher, you need to set up a Git repository as follows:
$ git init $ git add * $ git commit -m "initial revision"The above Git commands initialize a Git repository that is based on the files in your current working directory, stage all the files, and commit the files. At this point, your Git repository is aware of all the source code files. Any edits you now make to files can be committed later and will be tracked by Git.
Edit the Files: Make your changes to the temporary source code.
Test Your Changes: Once you have modified the source code, the easiest way to test your changes is by calling the
compiletask as shown in the following example:$ bitbake -c compile -f <name_of_package>The
-for--forceoption forces the specified task to execute. If you find problems with your code, you can just keep editing and re-testing iteratively until things work as expected.Note
All the modifications you make to the temporary source code disappear once you-c clean,-c cleansstate, or-c cleanallwith BitBake for the package. Modifications will also disappear if you use therm_workfeature as described in the "Building an Image" section of the Yocto Project Quick Start.See the List of Files You Changed: Use the
git statuscommand to see what files you have actually edited. The ability to have Git track the files you have changed is an advantage that this workflow has over the Quilt workflow. Here is the Git command to list your changed files:$ git statusStage the Modified Files: Use the
git addcommand to stage the changed files so they can be committed as follows:$ git add file1.c file2.c file3.cCommit the Staged Files and View Your Changes: Use the
git commitcommand to commit the changes to the local repository. Once you have committed the files, you can use thegit logcommand to see your changes:$ git commit -m "<commit-summary-message>" $ git logNote
The name of the patch file created in the next step is based on yourcommit-summary-message.Generate the Patch: Once the changes are committed, use the
git format-patchcommand to generate a patch file:$ git format-patch -1Specifying "-1" causes Git to generate the patch file for the most recent commit.
At this point, the patch file has all your edits made to the
file1.c,file2.c, andfile3.cfiles. You can find the resulting patch file in the current directory and it is named according to thegit commitsummary line. The patch file ends with.patch.Copy the Patch File: For simplicity, copy the patch file into a directory named
files, which you can create in the same directory that holds the recipe (.bb) file or the append (.bbappend) file. Placing the patch here guarantees that the OpenEmbedded build system will find the patch. Next, add the patch into theSRC_URIof the recipe. Here is an example:SRC_URI += "file://0001-<commit-summary-message>.patch"Increment the Recipe Revision Number: Finally, don't forget to 'bump' the
PRvalue in the recipe since the resulting packages have changed.
The Hob is a graphical user interface for the OpenEmbedded build system, which is based on BitBake. You can use the Hob to build custom operating system images within the Yocto Project build environment. Hob simply provides a friendly interface over the build system used during development. In other words, building images with the Hob lets you take care of common build tasks more easily.
For a better understanding of Hob, see the project page at http://www.yoctoproject.org/tools-resources/projects/hob on the Yocto Project website. If you follow the "Documentation" link from the Hob page, you will find a short introductory training video on Hob. The following lists some features of Hob:
You can setup and run Hob using these commands:
$ source oe-init-build-env $ hobYou can set the
MACHINEfor which you are building the image.You can modify various policy settings such as the package format with which to build, the parallelism BitBake uses, whether or not to build an external toolchain, and which host to build against.
You can manage layers.
You can select a base image and then add extra packages for your custom build.
You can launch and monitor the build from within Hob.
When debugging certain commands or even when just editing packages,
devshell can be a useful tool.
When you invoke devshell, source files are
extracted into your working directory and patches are applied.
Then, a new terminal is opened and you are placed in the working directory.
In the new terminal, all the OpenEmbedded build-related environment variables are
still defined so you can use commands such as configure and
make.
The commands execute just as if the OpenEmbedded build system were executing them.
Consequently, working this way can be helpful when debugging a build or preparing
software to be used with the OpenEmbedded build system.
Following is an example that uses devshell on a target named
matchbox-desktop:
$ bitbake matchbox-desktop -c devshell
This command spawns a terminal with a shell prompt within the OpenEmbedded build environment.
The OE_TERMINAL
variable controls what type of shell is opened.
For spawned terminals, the following occurs:
The
PATHvariable includes the cross-toolchain.The
pkgconfigvariables find the correct.pcfiles.The
configurecommand finds the Yocto Project site files as well as any other necessary files.
Within this environment, you can run configure or compile
commands as if they were being run by
the OpenEmbedded build system itself.
As noted earlier, the working directory also automatically changes to the
Source Directory (S).
When you are finished, you just exit the shell or close the terminal window.
Note
It is worth remembering that when using devshell
you need to use the full compiler name such as arm-poky-linux-gnueabi-gcc
instead of just using gcc.
The same applies to other applications such as binutils,
libtool and so forth.
BitBake sets up environment variables such as CC
to assist applications, such as make to find the correct tools.
It is also worth noting that devshell still works over
X11 forwarding and similar situations.
Table of Contents
- 5.1. Understanding and Creating Layers
- 5.2. Customizing Images
- 5.3. Writing a Recipe to Add a Package to Your Image
- 5.4. Adding a New Machine
- 5.5. Working With Libraries
- 5.6. Creating Partitioned Images
- 5.7. Configuring the Kernel
- 5.8. Patching the Kernel
- 5.9. Creating Your Own Distribution
- 5.10. Building a Tiny System
- 5.11. Working with Packages
- 5.12. Building Software from an External Source
- 5.13. Selecting an Initialization Manager
- 5.14. Excluding Recipes From the Build
- 5.15. Using an External SCM
- 5.16. Creating a Read-Only Root Filesystem
- 5.17. Performing Automated Runtime Testing
- 5.18. Debugging With the GNU Project Debugger (GDB) Remotely
- 5.19. Examining Builds Using the Toaster API
- 5.20. Profiling with OProfile
- 5.21. Maintaining Open Source License Compliance During Your Product's Lifecycle
This chapter describes fundamental procedures such as creating layers, adding new software packages, extending or customizing images, porting work to new hardware (adding a new machine), and so forth. You will find that the procedures documented here occur often in the development cycle using the Yocto Project.
The OpenEmbedded build system supports organizing Metadata into multiple layers. Layers allow you to isolate different types of customizations from each other. You might find it tempting to keep everything in one layer when working on a single project. However, the more modular your Metadata, the easier it is to cope with future changes.
To illustrate how layers are used to keep things modular, consider
machine customizations.
These types of customizations typically reside in a special layer,
rather than a general layer, called a Board Support Package (BSP)
Layer.
Furthermore, the machine customizations should be isolated from
recipes and Metadata that support a new GUI environment,
for example.
This situation gives you a couple of layers: one for the machine
configurations, and one for the GUI environment.
It is important to understand, however, that the BSP layer can
still make machine-specific additions to recipes within the GUI
environment layer without polluting the GUI layer itself
with those machine-specific changes.
You can accomplish this through a recipe that is a BitBake append
(.bbappend) file, which is described later
in this section.
The Source Directory
contains both general layers and BSP
layers right out of the box.
You can easily identify layers that ship with a
Yocto Project release in the Source Directory by their
folder names.
Folders that represent layers typically have names that begin with
the string meta-.
Note
It is not a requirement that a layer name begin with the prefixmeta-, but it's a commonly accepted
standard in the Yocto Project community.
For example, when you set up the Source Directory structure,
you will see several layers:
meta, meta-hob,
meta-skeleton,
meta-yocto, and
meta-yocto-bsp.
Each of these folders represents a distinct layer.
As another example, if you set up a local copy of the
meta-intel Git repository
and then explore the folder of that general layer,
you will discover many Intel-specific BSP layers inside.
For more information on BSP layers, see the
"BSP Layers"
section in the Yocto Project Board Support Package (BSP)
Developer's Guide.
It is very easy to create your own layers to use with the OpenEmbedded build system. The Yocto Project ships with scripts that speed up creating general layers and BSP layers. This section describes the steps you perform by hand to create a layer so that you can better understand them. For information about the layer-creation scripts, see the "Creating a New BSP Layer Using the yocto-bsp Script" section in the Yocto Project Board Support Package (BSP) Developer's Guide and the "Creating a General Layer Using the yocto-layer Script" section further down in this manual.
Follow these general steps to create your layer:
Check Existing Layers: Before creating a new layer, you should be sure someone has not already created a layer containing the Metadata you need. You can see the
OpenEmbedded Metadata Indexfor a list of layers from the OpenEmbedded community that can be used in the Yocto Project.Create a Directory: Create the directory for your layer. While not strictly required, prepend the name of the folder with the string
meta-. For example:meta-mylayer meta-GUI_xyz meta-mymachineCreate a Layer Configuration File: Inside your new layer folder, you need to create a
conf/layer.conffile. It is easiest to take an existing layer configuration file and copy that to your layer'sconfdirectory and then modify the file as needed.The
meta-yocto-bsp/conf/layer.conffile demonstrates the required syntax:# We have a conf and classes directory, add to BBPATH BBPATH .= ":${LAYERDIR}" # We have recipes-* directories, add to BBFILES BBFILES += "${LAYERDIR}/recipes-*/*/*.bb \ ${LAYERDIR}/recipes-*/*/*.bbappend" BBFILE_COLLECTIONS += "yoctobsp" BBFILE_PATTERN_yoctobsp = "^${LAYERDIR}/" BBFILE_PRIORITY_yoctobsp = "5" LAYERVERSION_yoctobsp = "2"Here is an explanation of the example:
The configuration and classes directory is appended to
BBPATH.Note
All non-distro layers, which include all BSP layers, are expected to append the layer directory to theBBPATH. On the other hand, distro layers, such asmeta-yocto, can choose to enforce their own precedence overBBPATH. For an example of that syntax, see thelayer.conffile for themeta-yoctolayer.The recipes for the layers are appended to
BBFILES.The
BBFILE_COLLECTIONSvariable is then appended with the layer name.The
BBFILE_PATTERNvariable is set to a regular expression and is used to match files fromBBFILESinto a particular layer. In this case,LAYERDIRis used to makeBBFILE_PATTERNmatch within the layer's path.The
BBFILE_PRIORITYvariable then assigns a priority to the layer. Applying priorities is useful in situations where the same package might appear in multiple layers and allows you to choose what layer should take precedence.The
LAYERVERSIONvariable optionally specifies the version of a layer as a single number.
Note the use of the
LAYERDIRvariable, which expands to the directory of the current layer.Through the use of the
BBPATHvariable, BitBake locates.bbclassfiles, configuration files, and files that are included withincludeandrequirestatements. For these cases, BitBake uses the first file that matches the name found inBBPATH. This is similar to the way thePATHvariable is used for binaries. We recommend, therefore, that you use unique.bbclassand configuration filenames in your custom layer.Add Content: Depending on the type of layer, add the content. If the layer adds support for a machine, add the machine configuration in a
conf/machine/file within the layer. If the layer adds distro policy, add the distro configuration in aconf/distro/file within the layer. If the layer introduces new recipes, put the recipes you need inrecipes-*subdirectories within the layer.Note
In order to be compliant with the Yocto Project, a layer must contain a README file.
To create layers that are easier to maintain and that will not impact builds for other machines, you should consider the information in the following sections.
Avoid "overlaying" entire recipes from other layers in your
configuration.
In other words, do not copy an entire recipe into your
layer and then modify it.
Rather, use .bbappend files to override
only those parts of the original recipe you need to modify.
Avoid duplicating include files.
Use .bbappend files for each recipe
that uses an include file.
Or, if you are introducing a new recipe that requires
the included file, use the path relative to the original
layer directory to refer to the file.
For example, use
require recipes-core/somepackage/somefile.inc
instead of require somefile.inc.
If you're finding you have to overlay the include file,
it could indicate a deficiency in the include file in
the layer to which it originally belongs.
If this is the case, you need to address that deficiency
instead of overlaying the include file.
For example, consider how support plug-ins for the Qt 4
database are configured.
The Source Directory does not have MySQL or PostgreSQL.
However, OpenEmbedded's layer meta-oe
does.
Consequently, meta-oe uses
.bbappend files to modify the
QT_SQL_DRIVER_FLAGS variable to
enable the appropriate plug-ins.
This variable was added to the qt4.inc
include file in the Source Directory specifically to allow
the meta-oe layer to be able to control
which plug-ins are built.
Proper use of overrides within append files and placement of machine-specific files within your layer can ensure that a build is not using the wrong Metadata and negatively impacting a build for a different machine. Following are some examples:
Modifying Variables to Support a Different Machine: Suppose you have a layer named
meta-onethat adds support for building machine "one". To do so, you use an append file namedbase-files.bbappendand create a dependency on "foo" by altering theDEPENDSvariable:DEPENDS = "foo"The dependency is created during any build that includes the layer
meta-one. However, you might not want this dependency for all machines. For example, suppose you are building for machine "two" but yourbblayers.conffile has themeta-onelayer included. During the build, thebase-filesfor machine "two" will also have the dependency onfoo.To make sure your changes apply only when building machine "one", use a machine override with the
DEPENDSstatement:DEPENDS_one = "foo"You should follow the same strategy when using
_appendand_prependoperations:DEPENDS_append_one = " foo" DEPENDS_prepend_one = "foo "Note
Avoiding "+=" and "=+" and using machine-specific_appendand_prependoperations is recommended as well.Place Machine-Specific Files in Machine-Specific Locations: When you have a base recipe, such as
base-files.bb, that contains aSRC_URIstatement to a file, you can use an append file to cause the build to use your own version of the file. For example, an append file in your layer atmeta-one/recipes-core/base-files/base-files.bbappendcould extendFILESPATHusingFILESEXTRAPATHSas follows:FILESEXTRAPATHS_prepend := "${THISDIR}/${BPN}:"The build for machine "one" will pick up your machine-specific file as long as you have the file in
meta-one/recipes-core/base-files/base-files/. However, if you are building for a different machine and thebblayers.conffile includes themeta-onelayer and the location of your machine-specific file is the first location where that file is found according toFILESPATH, builds for all machines will also use that machine-specific file.You can make sure that a machine-specific file is used for a particular machine by putting the file in a subdirectory specific to the machine. For example, rather than placing the file in
meta-one/recipes-core/base-files/base-files/as shown above, put it inmeta-one/recipes-core/base-files/base-files/one/. Not only does this make sure the file is used only when building for machine "one" but the build process locates the file more quickly.In summary, you need to place all files referenced from
SRC_URIin a machine-specific subdirectory within the layer in order to restrict those files to machine-specific builds.
We also recommend the following:
Store custom layers in a Git repository that uses the
meta-<layer_name>format.Clone the repository alongside other
metadirectories in the Source Directory.
Following these recommendations keeps your Source Directory and its configuration entirely inside the Yocto Project's core base.
Before the OpenEmbedded build system can use your new layer,
you need to enable it.
To enable your layer, simply add your layer's path to the
BBLAYERS
variable in your conf/bblayers.conf file,
which is found in the
Build Directory.
The following example shows how to enable a layer named
meta-mylayer:
LCONF_VERSION = "6"
BBPATH = "${TOPDIR}"
BBFILES ?= ""
BBLAYERS ?= " \
$HOME/poky/meta \
$HOME/poky/meta-yocto \
$HOME/poky/meta-yocto-bsp \
$HOME/poky/meta-mylayer \
"
BBLAYERS_NON_REMOVABLE ?= " \
$HOME/poky/meta \
$HOME/poky/meta-yocto \
"
BitBake parses each conf/layer.conf file
as specified in the BBLAYERS variable
within the conf/bblayers.conf file.
During the processing of each
conf/layer.conf file, BitBake adds the
recipes, classes and configurations contained within the
particular layer to the source directory.
Recipes used to append Metadata to other recipes are called
BitBake append files.
BitBake append files use the .bbappend file
type suffix, while the corresponding recipes to which Metadata
is being appended use the .bb file type
suffix.
A .bbappend file allows your layer to make
additions or changes to the content of another layer's recipe
without having to copy the other recipe into your layer.
Your .bbappend file resides in your layer,
while the main .bb recipe file to
which you are appending Metadata resides in a different layer.
Append files must have the same root names as their corresponding
recipes.
For example, the append file
someapp_1.5.4.bbappend must apply to
someapp_1.5.4.bb.
This means the original recipe and append file names are version
number-specific.
If the corresponding recipe is renamed to update to a newer
version, the corresponding .bbappend file must
be renamed (and possibly updated) as well.
During the build process, BitBake displays an error on starting
if it detects a .bbappend file that does
not have a corresponding recipe with a matching name.
See the
BB_DANGLINGAPPENDS_WARNONLY
variable for information on how to handle this error.
Being able to append information to an existing recipe not only avoids duplication, but also automatically applies recipe changes in a different layer to your layer. If you were copying recipes, you would have to manually merge changes as they occur.
As an example, consider the main formfactor recipe and a
corresponding formfactor append file both from the
Source Directory.
Here is the main formfactor recipe, which is named
formfactor_0.0.bb and located in the
"meta" layer at
meta/recipes-bsp/formfactor:
DESCRIPTION = "Device formfactor information"
SECTION = "base"
LICENSE = "MIT"
LIC_FILES_CHKSUM = "file://${COREBASE}/LICENSE;md5=3f40d7994397109285ec7b81fdeb3b58 \
file://${COREBASE}/meta/COPYING.MIT;md5=3da9cfbcb788c80a0384361b4de20420"
PR = "r41"
SRC_URI = "file://config file://machconfig"
S = "${WORKDIR}"
PACKAGE_ARCH = "${MACHINE_ARCH}"
INHIBIT_DEFAULT_DEPS = "1"
do_install() {
# Only install file if it has a contents
install -d ${D}${sysconfdir}/formfactor/
install -m 0644 ${S}/config ${D}${sysconfdir}/formfactor/
if [ -s "${S}/machconfig" ]; then
install -m 0644 ${S}/machconfig ${D}${sysconfdir}/formfactor/
fi
}
In the main recipe, note the
SRC_URI
variable, which tells the OpenEmbedded build system where to
find files during the build.
Following is the append file, which is named
formfactor_0.0.bbappend and is from the
Crown Bay BSP Layer named
meta-intel/meta-crownbay.
The file is in recipes-bsp/formfactor:
FILESEXTRAPATHS_prepend := "${THISDIR}/${PN}:"
By default, the build system uses the
FILESPATH
variable to locate files.
This append file extends the locations by setting the
FILESEXTRAPATHS
variable.
Setting this variable in the .bbappend
file is the most reliable and recommended method for adding
directories to the search path used by the build system
to find files.
The statement in this example extends the directories to include
${THISDIR}/${PN},
which resolves to a directory named
formfactor in the same directory
in which the append file resides (i.e.
meta-intel/meta-crownbay/recipes-bsp/formfactor/formfactor.
This implies that you must have the supporting directory
structure set up that will contain any files or patches you
will be including from the layer.
Using the immediate expansion assignment operator
:= is important because of the reference to
THISDIR.
The trailing colon character is important as it ensures that
items in the list remain colon-separated.
Note
BitBake automatically defines the
THISDIR variable.
You should never set this variable yourself.
Using _prepend ensures your path will
be searched prior to other paths in the final list.
Also, not all append files add extra files.
Many append files simply exist to add build options
(e.g. systemd).
For these cases, it is not necessary to use the
"_prepend" part of the statement.
Each layer is assigned a priority value.
Priority values control which layer takes precedence if there
are recipe files with the same name in multiple layers.
For these cases, the recipe file from the layer with a higher
priority number takes precedence.
Priority values also affect the order in which multiple
.bbappend files for the same recipe are
applied.
You can either specify the priority manually, or allow the
build system to calculate it based on the layer's dependencies.
To specify the layer's priority manually, use the
BBFILE_PRIORITY
variable.
For example:
BBFILE_PRIORITY_mylayer = "1"
Note
It is possible for a recipe with a lower version number
PV
in a layer that has a higher priority to take precedence.
Also, the layer priority does not currently affect the
precedence order of .conf
or .bbclass files.
Future versions of BitBake might address this.
You can use the BitBake layer management tool to provide a view
into the structure of recipes across a multi-layer project.
Being able to generate output that reports on configured layers
with their paths and priorities and on
.bbappend files and their applicable
recipes can help to reveal potential problems.
Use the following form when running the layer management tool.
$ bitbake-layers <command> [arguments]
The following list describes the available commands:
help:Displays general help or help on a specified command.show-layers:Shows the current configured layers.show-recipes:Lists available recipes and the layers that provide them.show-overlayed:Lists overlayed recipes. A recipe is overlayed when a recipe with the same name exists in another layer that has a higher layer priority.show-appends:Lists.bbappendfiles and the recipe files to which they apply.show-cross-depends:Lists dependency relationships between recipes that cross layer boundaries.flatten:Flattens the layer configuration into a separate output directory. Flattening your layer configuration builds a "flattened" directory that contains the contents of all layers, with any overlayed recipes removed and any.bbappendfiles appended to the corresponding recipes. You might have to perform some manual cleanup of the flattened layer as follows:Non-recipe files (such as patches) are overwritten. The flatten command shows a warning for these files.
Anything beyond the normal layer setup has been added to the
layer.conffile. Only the lowest priority layer'slayer.confis used.Overridden and appended items from
.bbappendfiles need to be cleaned up. The contents of each.bbappendend up in the flattened recipe. However, if there are appended or changed variable values, you need to tidy these up yourself. Consider the following example. Here, thebitbake-layerscommand adds the line#### bbappended ...so that you know where the following lines originate:... DESCRIPTION = "A useful utility" ... EXTRA_OECONF = "--enable-something" ... #### bbappended from meta-anotherlayer #### DESCRIPTION = "Customized utility" EXTRA_OECONF += "--enable-somethingelse"Ideally, you would tidy up these utilities as follows:
... DESCRIPTION = "Customized utility" ... EXTRA_OECONF = "--enable-something --enable-somethingelse" ...
The yocto-layer script simplifies
creating a new general layer.
Note
For information on BSP layers, see the "BSP Layers" section in the Yocto Project Board Specific (BSP) Developer's Guide.The default mode of the script's operation is to prompt you for information needed to generate the layer:
The layer priority
Whether or not to create a sample recipe.
Whether or not to create a sample append file.
Use the yocto-layer create sub-command
to create a new general layer.
In its simplest form, you can create a layer as follows:
$ yocto-layer create mylayer
The previous example creates a layer named
meta-mylayer in the current directory.
As the yocto-layer create command runs,
default values for the prompts appear in brackets.
Pressing enter without supplying anything for the prompts
or pressing enter and providing an invalid response causes the
script to accept the default value.
Once the script completes, the new layer
is created in the current working directory.
The script names the layer by prepending
meta- to the name you provide.
Minimally, the script creates the following within the layer:
The
confdirectory: This directory contains the layer's configuration file. The root name for the file is the same as the root name your provided for the layer (e.g.<layer>.conf).The
COPYING.MITfile: The copyright and use notice for the software.The
READMEfile: A file describing the contents of your new layer.
If you choose to generate a sample recipe file, the script
prompts you for the name for the recipe and then creates it
in <layer>/recipes-example/example/.
The script creates a .bb file and a
directory, which contains a sample
helloworld.c source file, along with
a sample patch file.
If you do not provide a recipe name, the script uses
"example".
If you choose to generate a sample append file, the script
prompts you for the name for the file and then creates it
in <layer>/recipes-example-bbappend/example-bbappend/.
The script creates a .bbappend file and a
directory, which contains a sample patch file.
If you do not provide a recipe name, the script uses
"example".
The script also prompts you for the version of the append file.
The version should match the recipe to which the append file
is associated.
The easiest way to see how the yocto-layer
script works is to experiment with the script.
You can also read the usage information by entering the
following:
$ yocto-layer help
Once you create your general layer, you must add it to your
bblayers.conf file.
Here is an example where a layer named
meta-mylayer is added:
BBLAYERS = ?" \
/usr/local/src/yocto/meta \
/usr/local/src/yocto/meta-yocto \
/usr/local/src/yocto/meta-yocto-bsp \
/usr/local/src/yocto/meta-mylayer \
"
BBLAYERS_NON_REMOVABLE ?= " \
/usr/local/src/yocto/meta \
/usr/local/src/yocto/meta-yocto \
"
Adding the layer to this file enables the build system to locate the layer during the build.
You can customize images to satisfy particular requirements. This section describes several methods and provides guidelines for each.
Probably the easiest way to customize an image is to add a
package by way of the local.conf
configuration file.
Because it is limited to local use, this method generally only
allows you to add packages and is not as flexible as creating
your own customized image.
When you add packages using local variables this way, you need
to realize that these variable changes affect all images at
the same time and might not be what you require.
To add a package to your image using the local configuration
file, use the
IMAGE_INSTALL
variable with the _append operator:
IMAGE_INSTALL_append = " strace"
Use of the syntax is important - specifically, the space between
the quote and the package name, which is
strace in this example.
This space is required since the _append
operator does not add the space.
Furthermore, you must use _append instead
of the += operator if you want to avoid
ordering issues.
The reason for this is because doing so unconditionally appends
to the variable and avoids ordering problems due to the
variable being set in image recipes and
.bbclass files with operators like
?=.
Using _append ensures the operation takes
affect.
As shown in its simplest use,
IMAGE_INSTALL_append affects all images.
It is possible to extend the syntax so that the variable
applies to a specific image only.
Here is an example:
IMAGE_INSTALL_append_pn-core-image-minimal = " strace"
This example adds strace to
core-image-minimal only.
You can add packages using a similar approach through the
CORE_IMAGE_EXTRA_INSTALL
variable.
If you use this variable, only
core-image-* images are affected.
Another method for customizing your image is to enable or
disable high-level image features by using the
IMAGE_FEATURES
and EXTRA_IMAGE_FEATURES
variables.
Although the functions for both variables are nearly equivalent,
best practices dictate using IMAGE_FEATURES
from within a recipe and using
EXTRA_IMAGE_FEATURES from within
your local.conf file, which is found in the
Build Directory.
To understand how these features work, the best reference is
meta/classes/core-image.bbclass.
In summary, the file looks at the contents of the
IMAGE_FEATURES variable and then maps
those contents into a set of package groups.
Based on this information, the build system automatically
adds the appropriate packages to the
IMAGE_INSTALL
variable.
Effectively, you are enabling extra features by extending the
class or creating a custom class for use with specialized image
.bb files.
Use the EXTRA_IMAGE_FEATURES variable
from within your local configuration file.
Using a separate area from which to enable features with
this variable helps you avoid overwriting the features in the
image recipe that are enabled with
IMAGE_FEATURES.
The value of EXTRA_IMAGE_FEATURES is added
to IMAGE_FEATURES within
meta/conf/bitbake.conf.
To illustrate how you can use these variables to modify your
image, consider an example that selects the SSH server.
The Yocto Project ships with two SSH servers you can use
with your images: Dropbear and OpenSSH.
Dropbear is a minimal SSH server appropriate for
resource-constrained environments, while OpenSSH is a
well-known standard SSH server implementation.
By default, the core-image-sato image
is configured to use Dropbear.
The core-image-basic and
core-image-lsb images both
include OpenSSH.
The core-image-minimal image does not
contain an SSH server.
You can customize your image and change these defaults.
Edit the IMAGE_FEATURES variable
in your recipe or use the
EXTRA_IMAGE_FEATURES in your
local.conf file so that it configures the
image you are working with to include
ssh-server-dropbear or
ssh-server-openssh.
Note
See the "Images" section in the Yocto Project Reference Manual for a complete list of image features that ship with the Yocto Project.You can also customize an image by creating a custom recipe that defines additional software as part of the image. The following example shows the form for the two lines you need:
IMAGE_INSTALL = "packagegroup-core-x11-base package1 package2"
inherit core-image
Defining the software using a custom recipe gives you total
control over the contents of the image.
It is important to use the correct names of packages in the
IMAGE_INSTALL
variable.
You must use the OpenEmbedded notation and not the Debian notation for the names
(e.g. eglibc-dev instead of libc6-dev).
The other method for creating a custom image is to base it on an existing image.
For example, if you want to create an image based on core-image-sato
but add the additional package strace to the image,
copy the meta/recipes-sato/images/core-image-sato.bb to a
new .bb and add the following line to the end of the copy:
IMAGE_INSTALL += "strace"
For complex custom images, the best approach for customizing
an image is to create a custom package group recipe that is
used to build the image or images.
A good example of a package group recipe is
meta/recipes-core/packagegroups/packagegroup-core-boot.bb.
The
PACKAGES
variable lists the package group packages you wish to produce.
inherit packagegroup sets appropriate
default values and automatically adds -dev,
-dbg, and -ptest
complementary packages for every package specified in
PACKAGES.
Note that the inherit line should be towards
the top of the recipe, certainly before you set
PACKAGES.
For each package you specify in PACKAGES,
you can use
RDEPENDS
and
RRECOMMENDS
entries to provide a list of packages the parent task package
should contain.
Following is an example:
DESCRIPTION = "My Custom Package Groups"
inherit packagegroup
PACKAGES = "\
packagegroup-custom-apps \
packagegroup-custom-tools \
"
RDEPENDS_packagegroup-custom-apps = "\
dropbear \
portmap \
psplash"
RDEPENDS_packagegroup-custom-tools = "\
oprofile \
oprofileui-server \
lttng-control \
lttng-viewer"
RRECOMMENDS_packagegroup-custom-tools = "\
kernel-module-oprofile"
In the previous example, two package group packages are created with their dependencies and their
recommended package dependencies listed: packagegroup-custom-apps, and
packagegroup-custom-tools.
To build an image using these package group packages, you need to add
packagegroup-custom-apps and/or
packagegroup-custom-tools to
IMAGE_INSTALL.
For other forms of image dependencies see the other areas of this section.
Recipes let you define packages you can add to your image.
Writing a recipe means creating a .bb file that sets some
variables.
For information on variables that are useful for recipes and for information about recipe naming
issues, see the
"Required"
section of the Yocto Project Reference Manual.
Before writing a recipe from scratch, it is often useful to check whether someone else has written one already. OpenEmbedded is a good place to look as it has a wider scope and range of packages. Because the Yocto Project aims to be compatible with OpenEmbedded, most recipes you find there should work for you.
For new packages, the simplest way to add a recipe is to base it on a similar pre-existing recipe. The sections that follow provide some examples that show how to add standard types of packages.
Note
When writing shell functions, you need to be aware of BitBake's curly brace parsing. If a recipe uses a closing curly brace within the function and the character has no leading spaces, BitBake produces a parsing error. If you use a pair of curly brace in a shell function, the closing curly brace must not be located at the start of the line without leading spaces.
Here is an example that causes BitBake to produce a parsing error:
fakeroot create_shar() {
cat << "EOF" > ${SDK_DEPLOY}/${TOOLCHAIN_OUTPUTNAME}.sh
usage()
{
echo "test"
###### The following "}" at the start of the line causes a parsing error ######
}
EOF
}
Writing the recipe this way avoids the error:
fakeroot create_shar() {
cat << "EOF" > ${SDK_DEPLOY}/${TOOLCHAIN_OUTPUTNAME}.sh
usage()
{
echo "test"
######The following "}" with a leading space at the start of the line avoids the error ######
}
EOF
}
Building an application from a single file that is stored locally (e.g. under
files/) requires a recipe that has the file listed in
the
SRC_URI
variable.
Additionally, you need to manually write the do_compile and
do_install tasks.
The S
variable defines the
directory containing the source code, which is set to
WORKDIR in this case - the directory BitBake uses for the build.
DESCRIPTION = "Simple helloworld application"
SECTION = "examples"
LICENSE = "MIT"
LIC_FILES_CHKSUM = "file://${COMMON_LICENSE_DIR}/MIT;md5=0835ade698e0bcf8506ecda2f7b4f302"
PR = "r0"
SRC_URI = "file://helloworld.c"
S = "${WORKDIR}"
do_compile() {
${CC} helloworld.c -o helloworld
}
do_install() {
install -d ${D}${bindir}
install -m 0755 helloworld ${D}${bindir}
}
By default, the helloworld, helloworld-dbg,
and helloworld-dev packages are built.
For information on how to customize the packaging process, see the
"Splitting an Application
into Multiple Packages" section.
Applications that use Autotools such as autoconf and
automake require a recipe that has a source archive listed in
SRC_URI and
also inherits Autotools, which instructs BitBake to use the
autotools.bbclass file, which contains the definitions of all the steps
needed to build an Autotool-based application.
The result of the build is automatically packaged.
And, if the application uses NLS for localization, packages with local information are
generated (one package per language).
Following is one example: (hello_2.3.bb)
DESCRIPTION = "GNU Helloworld application"
SECTION = "examples"
LICENSE = "GPLv2+"
LIC_FILES_CHKSUM = "file://COPYING;md5=751419260aa954499f7abaabaa882bbe"
PR = "r0"
SRC_URI = "${GNU_MIRROR}/hello/hello-${PV}.tar.gz"
inherit autotools gettext
The variable
LIC_FILES_CHKSUM
is used to track source license changes as described in the
"Tracking License Changes" section.
You can quickly create Autotool-based recipes in a manner similar to the previous example.
Applications that use GNU make also require a recipe that has
the source archive listed in
SRC_URI.
You do not need to add a do_compile step since by default BitBake
starts the make command to compile the application.
If you need additional make options, you should store them in the
EXTRA_OEMAKE
variable.
BitBake passes these options into the make GNU invocation.
Note that a do_install task is still required.
Otherwise, BitBake runs an empty do_install task by default.
Some applications might require extra parameters to be passed to the compiler.
For example, the application might need an additional header path.
You can accomplish this by adding to the
CFLAGS variable.
The following example shows this:
CFLAGS_prepend = "-I ${S}/include "
In the following example, mtd-utils is a makefile-based package:
DESCRIPTION = "Tools for managing memory technology devices."
SECTION = "base"
DEPENDS = "zlib lzo e2fsprogs util-linux"
HOMEPAGE = "http://www.linux-mtd.infradead.org/"
LICENSE = "GPLv2+"
LIC_FILES_CHKSUM = "file://COPYING;md5=0636e73ff0215e8d672dc4c32c317bb3 \
file://include/common.h;beginline=1;endline=17;md5=ba05b07912a44ea2bf81ce409380049c"
SRC_URI = "git://git.infradead.org/mtd-utils.git;protocol=git;tag=995cfe51b0a3cf32f381c140bf72b21bf91cef1b \
file://add-exclusion-to-mkfs-jffs2-git-2.patch"
S = "${WORKDIR}/git/"
PR = "r1"
EXTRA_OEMAKE = "'CC=${CC}' 'RANLIB=${RANLIB}' 'AR=${AR}' \
'CFLAGS=${CFLAGS} -I${S}/include -DWITHOUT_XATTR' 'BUILDDIR=${S}'"
do_install () {
oe_runmake install DESTDIR=${D} SBINDIR=${sbindir} MANDIR=${mandir} \
INCLUDEDIR=${includedir}
install -d ${D}${includedir}/mtd/
for f in ${S}/include/mtd/*.h; do
install -m 0644 $f ${D}${includedir}/mtd/
done
}
PARALLEL_MAKE = ""
BBCLASSEXTEND = "native"
If your sources are available as a tarball instead of a Git repository, you
will need to provide the URL to the tarball as well as an
md5 or sha256 sum of
the download.
Here is an example:
SRC_URI="ftp://ftp.infradead.org/pub/mtd-utils/mtd-utils-1.4.9.tar.bz2"
SRC_URI[md5sum]="82b8e714b90674896570968f70ca778b"
You can generate the md5 or sha256 sums
by using the md5sum or sha256sum commands
with the target file as the only argument.
Here is an example:
$ md5sum mtd-utils-1.4.9.tar.bz2
82b8e714b90674896570968f70ca778b mtd-utils-1.4.9.tar.bz2
You can use the variables
PACKAGES and
FILES
to split an application into multiple packages.
Following is an example that uses the libXpm recipe.
By default, this recipe generates a single package that contains the library along
with a few binaries.
You can modify the recipe to split the binaries into separate packages:
require xorg-lib-common.inc
DESCRIPTION = "X11 Pixmap library"
LICENSE = "X-BSD"
LIC_FILES_CHKSUM = "file://COPYING;md5=3e07763d16963c3af12db271a31abaa5"
DEPENDS += "libxext libsm libxt"
PR = "r3"
PE = "1"
XORG_PN = "libXpm"
PACKAGES =+ "sxpm cxpm"
FILES_cxpm = "${bindir}/cxpm"
FILES_sxpm = "${bindir}/sxpm"
In the previous example, we want to ship the sxpm
and cxpm binaries in separate packages.
Since bindir would be packaged into the main
PN
package by default, we prepend the PACKAGES
variable so additional package names are added to the start of list.
This results in the extra FILES_*
variables then containing information that define which files and
directories go into which packages.
Files included by earlier packages are skipped by latter packages.
Thus, the main PN package
does not include the above listed files.
To add a post-installation script to a package, add a
pkg_postinst_PACKAGENAME() function to the
.bb file and use
PACKAGENAME as the name of the package you want to attach to the
postinst script.
Normally,
PN
can be used, which automatically expands to PACKAGENAME.
A post-installation function has the following structure:
pkg_postinst_PACKAGENAME () {
#!/bin/sh -e
# Commands to carry out
}
The script defined in the post-installation function is called when the root filesystem is created. If the script succeeds, the package is marked as installed. If the script fails, the package is marked as unpacked and the script is executed when the image boots again.
Sometimes it is necessary for the execution of a post-installation script to be delayed until the first boot. For example, the script might need to be executed on the device itself. To delay script execution until boot time, use the following structure in the post-installation script:
pkg_postinst_PACKAGENAME () {
#!/bin/sh -e
if [ x"$D" = "x" ]; then
# Actions to carry out on the device go here
else
exit 1
fi
}
The previous example delays execution until the image boots again because the
D
variable points
to the directory containing the image when the root filesystem is created at build time but
is unset when executed on the first boot.
Adding a new machine to the Yocto Project is a straightforward process.
This section provides information that gives you an idea of the changes you must make.
The information covers adding machines similar to those the Yocto Project already supports.
Although well within the capabilities of the Yocto Project, adding a totally new architecture
might require
changes to gcc/eglibc and to the site information, which is
beyond the scope of this manual.
For a complete example that shows how to add a new machine, see the "Creating a New BSP Layer Using the yocto-bsp Script" in the Yocto Project Board Support Package (BSP) Developer's Guide.
To add a machine configuration, you need to add a .conf file
with details of the device being added to the conf/machine/ file.
The name of the file determines the name the OpenEmbedded build system
uses to reference the new machine.
The most important variables to set in this file are as follows:
TARGET_ARCH(e.g. "arm")PREFERRED_PROVIDER_virtual/kernel(see below)MACHINE_FEATURES(e.g. "apm screen wifi")
You might also need these variables:
SERIAL_CONSOLES(e.g. "115200;ttyS0 115200;ttyS1")KERNEL_IMAGETYPE(e.g. "zImage")IMAGE_FSTYPES(e.g. "tar.gz jffs2")
You can find full details on these variables in the reference section.
You can leverage many existing machine .conf files from
meta/conf/machine/.
The OpenEmbedded build system needs to be able to build a kernel for the machine.
You need to either create a new kernel recipe for this machine, or extend an
existing recipe.
You can find several kernel examples in the
Source Directory at meta/recipes-kernel/linux
that you can use as references.
If you are creating a new recipe, normal recipe-writing rules apply for setting
up a
SRC_URI.
Thus, you need to specify any necessary patches and set
S to point at the source code.
You need to create a configure task that configures the
unpacked kernel with a defconfig.
You can do this by using a make defconfig command or,
more commonly, by copying in a suitable defconfig file and then running
make oldconfig.
By making use of inherit kernel and potentially some of the
linux-*.inc files, most other functionality is
centralized and the defaults of the class normally work well.
If you are extending an existing kernel, it is usually a matter of adding a
suitable defconfig file.
The file needs to be added into a location similar to defconfig files
used for other machines in a given kernel.
A possible way to do this is by listing the file in the
SRC_URI and adding the machine to the expression in
COMPATIBLE_MACHINE:
COMPATIBLE_MACHINE = '(qemux86|qemumips)'
A formfactor configuration file provides information about the target hardware for which the image is being built and information that the build system cannot obtain from other sources such as the kernel. Some examples of information contained in a formfactor configuration file include framebuffer orientation, whether or not the system has a keyboard, the positioning of the keyboard in relation to the screen, and the screen resolution.
The build system uses reasonable defaults in most cases.
However, if customization is
necessary, you need to create a machconfig file
in the meta/recipes-bsp/formfactor/files
directory.
This directory contains directories for specific machines such as
qemuarm and qemux86.
For information about the settings available and the defaults, see the
meta/recipes-bsp/formfactor/files/config file found in the
same area.
Following is an example for qemuarm:
HAVE_TOUCHSCREEN=1
HAVE_KEYBOARD=1
DISPLAY_CAN_ROTATE=0
DISPLAY_ORIENTATION=0
#DISPLAY_WIDTH_PIXELS=640
#DISPLAY_HEIGHT_PIXELS=480
#DISPLAY_BPP=16
DISPLAY_DPI=150
DISPLAY_SUBPIXEL_ORDER=vrgb
Libraries are an integral part of your system. This section describes some common practices you might find helpful when working with libraries to build your system:
If you are building a library and the library offers static linking, you can control
which static library files (*.a files) get included in the
built library.
The PACKAGES
and FILES_*
variables in the
meta/conf/bitbake.conf configuration file define how files installed
by the do_install task are packaged.
By default, the PACKAGES variable contains
${PN}-staticdev, which includes all static library files.
Note
Some previously released versions of the Yocto Project defined the static library files through${PN}-dev.
Following, is part of the BitBake configuration file. You can see where the static library files are defined:
PACKAGES = "${PN}-dbg ${PN} ${PN}-doc ${PN}-dev ${PN}-staticdev ${PN}-locale"
PACKAGES_DYNAMIC = "${PN}-locale-*"
FILES = ""
FILES_${PN} = "${bindir}/* ${sbindir}/* ${libexecdir}/* ${libdir}/lib*${SOLIBS} \
${sysconfdir} ${sharedstatedir} ${localstatedir} \
${base_bindir}/* ${base_sbindir}/* \
${base_libdir}/*${SOLIBS} \
${datadir}/${BPN} ${libdir}/${BPN}/* \
${datadir}/pixmaps ${datadir}/applications \
${datadir}/idl ${datadir}/omf ${datadir}/sounds \
${libdir}/bonobo/servers"
FILES_${PN}-doc = "${docdir} ${mandir} ${infodir} ${datadir}/gtk-doc \
${datadir}/gnome/help"
SECTION_${PN}-doc = "doc"
FILES_${PN}-dev = "${includedir} ${libdir}/lib*${SOLIBSDEV} ${libdir}/*.la \
${libdir}/*.o ${libdir}/pkgconfig ${datadir}/pkgconfig \
${datadir}/aclocal ${base_libdir}/*.o"
SECTION_${PN}-dev = "devel"
ALLOW_EMPTY_${PN}-dev = "1"
RDEPENDS_${PN}-dev = "${PN} (= ${EXTENDPKGV})"
FILES_${PN}-staticdev = "${libdir}/*.a ${base_libdir}/*.a"
SECTION_${PN}-staticdev = "devel"
RDEPENDS_${PN}-staticdev = "${PN}-dev (= ${EXTENDPKGV})"
The build system offers the ability to build libraries with different target optimizations or architecture formats and combine these together into one system image. You can link different binaries in the image against the different libraries as needed for specific use cases. This feature is called "Multilib."
An example would be where you have most of a system compiled in 32-bit mode using 32-bit libraries, but you have something large, like a database engine, that needs to be a 64-bit application and uses 64-bit libraries. Multilib allows you to get the best of both 32-bit and 64-bit libraries.
While the Multilib feature is most commonly used for 32 and 64-bit differences, the approach the build system uses facilitates different target optimizations. You could compile some binaries to use one set of libraries and other binaries to use other different sets of libraries. The libraries could differ in architecture, compiler options, or other optimizations.
This section overviews the Multilib process only. For more details on how to implement Multilib, see the Multilib wiki page.
Aside from this wiki page, several examples exist in the
meta-skeleton
layer found in the
Source Directory:
conf/multilib-example.confconfiguration fileconf/multilib-example2.confconfiguration filerecipes-multilib/images/core-image-multilib-example.bbrecipe
User-specific requirements drive the Multilib feature. Consequently, there is no one "out-of-the-box" configuration that likely exists to meet your needs.
In order to enable Multilib, you first need to ensure your recipe is
extended to support multiple libraries.
Many standard recipes are already extended and support multiple libraries.
You can check in the meta/conf/multilib.conf
configuration file in the
Source Directory to see how this is
done using the
BBCLASSEXTEND
variable.
Eventually, all recipes will be covered and this list will be unneeded.
For the most part, the Multilib class extension works automatically to
extend the package name from ${PN} to
${MLPREFIX}${PN}, where MLPREFIX
is the particular multilib (e.g. "lib32-" or "lib64-").
Standard variables such as
DEPENDS,
RDEPENDS,
RPROVIDES,
RRECOMMENDS,
PACKAGES,
and PACKAGES_DYNAMIC are automatically extended by the system.
If you are extending any manual code in the recipe, you can use the
${MLPREFIX} variable to ensure those names are extended
correctly.
This automatic extension code resides in multilib.bbclass.
After you have set up the recipes, you need to define the actual
combination of multiple libraries you want to build.
You accomplish this through your local.conf
configuration file in the
Build Directory.
An example configuration would be as follows:
MACHINE = "qemux86-64"
require conf/multilib.conf
MULTILIBS = "multilib:lib32"
DEFAULTTUNE_virtclass-multilib-lib32 = "x86"
IMAGE_INSTALL = "lib32-connman"
This example enables an
additional library named lib32 alongside the
normal target packages.
When combining these "lib32" alternatives, the example uses "x86" for tuning.
For information on this particular tuning, see
meta/conf/machine/include/ia32/arch-ia32.inc.
The example then includes lib32-connman
in all the images, which illustrates one method of including a
multiple library dependency.
You can use a normal image build to include this dependency,
for example:
$ bitbake core-image-sato
You can also build Multilib packages specifically with a command like this:
$ bitbake lib32-connman
Different packaging systems have different levels of native Multilib support. For the RPM Package Management System, the following implementation details exist:
A unique architecture is defined for the Multilib packages, along with creating a unique deploy folder under
tmp/deploy/rpmin the Build Directory. For example, considerlib32in aqemux86-64image. The possible architectures in the system are "all", "qemux86_64", "lib32_qemux86_64", and "lib32_x86".The
${MLPREFIX}variable is stripped from${PN}during RPM packaging. The naming for a normal RPM package and a Multilib RPM package in aqemux86-64system resolves to something similar tobash-4.1-r2.x86_64.rpmandbash-4.1.r2.lib32_x86.rpm, respectively.When installing a Multilib image, the RPM backend first installs the base image and then installs the Multilib libraries.
The build system relies on RPM to resolve the identical files in the two (or more) Multilib packages.
For the IPK Package Management System, the following implementation details exist:
The
${MLPREFIX}is not stripped from${PN}during IPK packaging. The naming for a normal RPM package and a Multilib IPK package in aqemux86-64system resolves to something likebash_4.1-r2.x86_64.ipkandlib32-bash_4.1-rw_x86.ipk, respectively.The IPK deploy folder is not modified with
${MLPREFIX}because packages with and without the Multilib feature can exist in the same folder due to the${PN}differences.IPK defines a sanity check for Multilib installation using certain rules for file comparison, overridden, etc.
Situations can exist where you need to install and use multiple versions of the same library on the same system at the same time. These situations almost always exist when a library API changes and you have multiple pieces of software that depend on the separate versions of the library. To accommodate these situations, you can install multiple versions of the same library in parallel on the same system.
The process is straight forward as long as the libraries use
proper versioning.
With properly versioned libraries, all you need to do to
individually specify the libraries is create separate,
appropriately named recipes where the
PN part of the
name includes a portion that differentiates each library version
(e.g.the major part of the version number).
Thus, instead of having a single recipe that loads one version
of a library (e.g. clutter), you provide
multiple recipes that result in different versions
of the libraries you want.
As an example, the following two recipes would allow the
two separate versions of the clutter
library to co-exist on the same system:
clutter-1.6_1.6.20.bb
clutter-1.8_1.8.4.bb
Additionally, if you have other recipes that depend on a given
library, you need to use the
DEPENDS
variable to create the dependency.
Continuing with the same example, if you want to have a recipe
depend on the 1.8 version of the clutter
library, use the following in your recipe:
DEPENDS = "clutter-1.8"
Creating an image for a particular hardware target using the OpenEmbedded build system does not necessarily mean you can boot that image as is on your device. Physical devices accept and boot images in various ways depending on the specifics of the device. Usually, information about the hardware can tell you what image format the device requires. Should your device require multiple partitions on an SD card, flash, or an HDD, you can use the OpenEmbedded Image Creator to create the properly partitioned image.
The wic command generates partitioned images
from existing OpenEmbedded build artifacts.
Image generation is driven by partitioning commands contained
in an Openembedded kickstart file (.wks)
specified either directly on the command-line or as one of a
selection of canned .wks files as shown
with the wic list images command in the
"Using a Provided Kickstart File"
section.
When applied to a given set of build artifacts, the result is an
image or set of images that can be directly written onto media and
used on a particular system.
This section provides some background information on
wic, describes what you need to have in
place to run the tool, provides instruction on how to use
wic, and provides several examples.
This section provides some background on the
wic utility.
While none of this information is required to use
wic, you might find it interesting.
The name "wic" is derived from OpenEmbedded Image Creator (oeic). The "oe" diphthong in "oeic" was promoted to the letter "w", because "oeic" is both difficult to remember and pronounce.
wicis loosely based on the Meego Image Creator (mic) framework. Thewicimplementation has been heavily modified to make direct use of OpenEmbedded build artifacts instead of package installation and configuration, which are already incorporated within the OpenEmbedded artifacts.wicis a completely independent standalone utility that initially provides easier-to-use and more flexible replacements for a couple bits of existing functionality in OE Core'sdirectdisk.bbclassandmkefidisk.shscript. The replaced scripts are implemented by a general-purpose partitioning language based on Red Hat kickstart syntax. Underlying code forwicsucceeded from several projects over time.
In order to use the wic utility with the
OpenEmbedded Build system, you need to meet the following
requirements:
The Linux distribution on your development host must support the Yocto Project. See the "Supported Linux Distributions" section in the Yocto Project Reference Manual for this list of distributions.
The standard system utilities, such as
cp, must be installed on your development host system.The GNU Parted package must be installed on your development host system.
Have the build artifacts already available. You must already have created an image using the Openembedded build system (e.g.
core-image-minimal. It might seem redundant to generate an image in order to create an image usingwic, but the artifacts are needed and they are generated with the build system.You must have sourced one of the build environment setup scripts (i.e.
oe-init-build-envoroe-init-build-env-memres) found in the Build Directory.
You can get general help for the wic
by entering the wic command by itself
or by entering the command with a help argument as follows:
$ wic -h
$ wic --help
Currently, wic supports two commands:
create and list.
You can get help for these commands as follows:
$ wic help <command>
You can find more out about the images
wic creates using the provided
kickstart files with the following form of the command:
$ wic list <image> help
Where <image> is either
directdisk or
mkefidisk.
You can run wic in two modes: Raw and
Cooked:
Raw Mode: You explicitly specify build artifacts through command-line arguments.
Cooked Mode: The current
MACHINEsetting and image name are used to automatically locate and provide the build artifacts.
Regardless of the mode you use, you need to have the build
artifacts ready and available.
Additionally, the environment must be set up using the
oe-init-build-env
or
oe-init-build-env-memres
script found in the
Build Directory.
The general form of the 'wic' command in raw mode is:
$ wic create image_name.wks [options] [...]
Where:
image_name.wks
An an OpenEmbedded kickstart file. You can provide
your own custom file or use a file from a set of
provided files as described by further options.
-o OUTDIR, --outdir=OUTDIR
The name of a directory in which to create image.
-i PROPERTIES_FILE, --infile=PROPERTIES_FILE
The name of a file containing the values for image
properties as a JSON file.
-e IMAGE_NAME, --image-name=IMAGE_NAME
The name of the image from which to use the artifacts
(e.g. core-image-sato).
-r ROOTFS_DIR, --rootfs-dir=ROOTFS_DIR
The path to the /rootfs directory to use as the
.wks rootfs source.
-b BOOTIMG_DIR, --bootimg-dir=BOOTIMG_DIR
The path to the directory containing the boot artifacts
(e.g. /EFI or /syslinux) to use as the .wks bootimg
source.
-k KERNEL_DIR, --kernel-dir=KERNEL_DIR
The path to the directory containing the kernel to use
in the .wks boot image.
-n NATIVE_SYSROOT, --native-sysroot=NATIVE_SYSROOT
The path to the native sysroot containing the tools to use
to build the image.
-p, --skip-build-check
Skips the build check.
-D, --debug
Output debug information.
Note
You do not need root privileges to runwic.
In fact, you should not run as root when using the
utility.
The general form of the wic command
using Cooked Mode is:
$ wic create kickstart_file -e image_name
Where:
kickstart_file
An OpenEmbedded kickstart file. You can provide your own
custom file or supplied file.
image_name
Specifies the image built using the OpenEmbedded build
system.
This form is the simplest and most user-friendly, as it
does not require specifying all individual parameters.
All you need to provide is your own
.wks file or one provided with the
release.
If you do not want to create your own
.wks file, you can use a provided
file.
Use the following command to list the available files:
$ wic list images
directdisk Create a 'pcbios' direct disk image
mkefidisk Create an EFI disk image
When you use a provided file, you do not have to use the
.wks extension.
Here is an example in Raw Mode that uses the
directdisk file:
$ wic create directdisk -r rootfs_dir -b bootimg_dir \
-k kernel_dir -n native_sysroot
Here are the actual partition language commands
used in the mkefidisk.wks file to generate
an image:
# short-description: Create an EFI disk image
# long-description: Creates a partitioned EFI disk image that the user
# can directly dd to boot media.
part /boot ‐‐source bootimg-efi ‐‐ondisk sda ‐‐fstype=efi ‐‐active
part / ‐‐source rootfs ‐‐ondisk sda ‐‐fstype=ext3 ‐‐label platform
part swap ‐‐ondisk sda ‐‐size 44 ‐‐label swap1 ‐‐fstype=swap
bootloader ‐‐timeout=10 ‐‐append="rootwait console=ttyPCH0,115200"
This section provides several examples that show how to use
the wic utility.
All the examples assume the list of requirements in the
"Requirements" section
have been met.
The examples assume the previously generated image is
core-image-minimal.
This example runs in Cooked Mode and uses the
mkefidisk kickstart file:
$ wic create mkefidisk -e core-image-minimal
Checking basic build environment...
Done.
Creating image(s)...
Info: The new image(s) can be found here:
/var/tmp/wic/build/mkefidisk-201310230946-sda.direct
The following build artifacts were used to create the image(s):
ROOTFS_DIR: /home/trz/yocto/yocto-image/build/tmp/work/minnow-poky-linux/core-image-minimal/1.0-r0/rootfs
BOOTIMG_DIR: /home/trz/yocto/yocto-image/build/tmp/work/minnow-poky-linux/core-image-minimal/1.0-r0/core-image-minimal-1.0/hddimg
KERNEL_DIR: /home/trz/yocto/yocto-image/build/tmp/sysroots/minnow/usr/src/kernel
NATIVE_SYSROOT: /home/trz/yocto/yocto-image/build/tmp/sysroots/x86_64-linux
The image(s) were created using OE kickstart file:
/home/trz/yocto/yocto-image/scripts/lib/image/canned-wks/mkefidisk.wks
This example shows the easiest way to create an image
by running in Cooked Mode and using the
-e option with a provided kickstart
file.
All that is necessary is to specify the image used to
generate the artifacts.
Your local.conf needs to have the
MACHINE
variable set to the machine you are using, which is
"minnow" in this example.
The output specifies exactly which image was
created as well as where it was created.
The output also names the artifacts used and the exact
.wks script that was used to generate
the image.
Note
You should always verify the details provided in the output to make sure that the image was indeed created exactly as expected.
Continuing with the example, you can now directly
dd the image to a USB stick, or
whatever media for which you built your image,
and boot the resulting media:
$ sudo dd if=/var/tmp/wic/build/mkefidisk-201310230946-sda.direct of=/dev/sdb
[sudo] password for trz:
182274+0 records in
182274+0 records out
93324288 bytes (93 MB) copied, 14.4777 s, 6.4 MB/s
[trz@empanada ~]$ sudo eject /dev/sdb
Because wic image creation is driven
by the kickstart file, it is easy to affect image creation
by changing the parameters in the file.
This next example demonstrates that through modification
of the directdisk kickstart file.
As mentioned earlier, you can use the command
wic list images to show the list
of provided kickstart files.
The directory in which these files reside is
scripts/lib/image/canned-wks/
located in the
Source Directory.
Because the available files reside in this directory, you
can create and add your own custom files to the directory.
Subsequent use of the wic list images
command would then include your kickstart files.
In this example, the existing
directdisk file already does most
of what is needed.
However, for the hardware in this example, the image will
need to boot from sdb instead of
sda, which is what the
directdisk kickstart file uses.
The example begins by making a copy of the
directdisk.wks file in the
scripts/lib/image/canned-wks
directory and then changing the lines that specify the
target disk from which to boot.
$ cp /home/trz/yocto/yocto-image/scripts/lib/image/canned-wks/directdisk.wks \
/home/trz/yocto/yocto-image/scripts/lib/image/canned-wks/directdisksdb.wks
Next, the example modifies the
directdisksdb.wks file and changes all
instances of "--ondisk sda"
to "--ondisk sdb".
The example changes the following two lines and leaves the
remaining lines untouched:
part /boot --source bootimg --ondisk sdb --fstype=msdos --label boot --active --align 1024
part / --source rootfs --ondisk sdb --fstype=ext3 --label platform --align 1024
Once the lines are changed, the example generates the
directdisksdb image.
The command points the process at the
core-image-minimal artifacts for the
Next Unit of Computing (nuc)
MACHINE
the local.conf.
$ wic create directdisksdb -e core-image-minimal
Checking basic build environment...
Done.
Creating image(s)...
Info: The new image(s) can be found here:
/var/tmp/wic/build/directdisksdb-201310231131-sdb.direct
The following build artifacts were used to create the image(s):
ROOTFS_DIR: /home/trz/yocto/yocto-image/build/tmp/work/nuc-poky-linux/core-image-minimal/1.0-r0/rootfs
BOOTIMG_DIR: /home/trz/yocto/yocto-image/build/tmp/sysroots/nuc/usr/share
KERNEL_DIR: /home/trz/yocto/yocto-image/build/tmp/sysroots/nuc/usr/src/kernel
NATIVE_SYSROOT: /home/trz/yocto/yocto-image/build/tmp/sysroots/x86_64-linux
The image(s) were created using OE kickstart file:
/home/trz/yocto/yocto-image/scripts/lib/image/canned-wks/directdisksdb.wks
Continuing with the example, you can now directly
dd the image to a USB stick, or
whatever media for which you built your image,
and boot the resulting media:
$ sudo dd if=/var/tmp/wic/build/directdisksdb-201310231131-sdb.direct of=/dev/sdb
86018+0 records in
86018+0 records out
44041216 bytes (44 MB) copied, 13.0734 s, 3.4 MB/s
[trz@empanada tmp]$ sudo eject /dev/sdb
This example creates an image based on
core-image-minimal and a
crownbay-noemgd
MACHINE
that works right out of the box.
$ wic create directdisk -e core-image-minimal
Checking basic build environment...
Done.
Creating image(s)...
Info: The new image(s) can be found here:
/var/tmp/wic/build/directdisk-201309252350-sda.direct
The following build artifacts were used to create the image(s):
ROOTFS_DIR: /home/trz/yocto/yocto-image/build/tmp/work/crownbay_noemgd-poky-linux/core-image-minimal/1.0-r0/rootfs
BOOTIMG_DIR: /home/trz/yocto/yocto-image/build/tmp/sysroots/crownbay-noemgd/usr/share
KERNEL_DIR: /home/trz/yocto/yocto-image/build/tmp/sysroots/crownbay-noemgd/usr/src/kernel
NATIVE_SYSROOT: /home/trz/yocto/yocto-image/build/tmp/sysroots/crownbay-noemgd/usr/src/kernel
The image(s) were created using OE kickstart file:
/home/trz/yocto/yocto-image/scripts/lib/image/canned-wks/directdisk.wks
This next example manually specifies each build artifact
(runs in Raw Mode) and uses a modified kickstart file.
The example also uses the -o option
to cause wic to create the output
somewhere other than the default
/var/tmp/wic directory:
$ wic create ~/test.wks -o /home/trz/testwic --rootfs-dir \
/home/trz/yocto/yocto-image/build/tmp/work/crownbay_noemgd-poky-linux/core-image-minimal/1.0-r0/rootfs \
--bootimg-dir /home/trz/yocto/yocto-image/build/tmp/sysroots/crownbay-noemgd/usr/share \
--kernel-dir /home/trz/yocto/yocto-image/build/tmp/sysroots/crownbay-noemgd/usr/src/kernel \
--native-sysroot /home/trz/yocto/yocto-image/build/tmp/sysroots/x86_64-linux
Creating image(s)...
Info: The new image(s) can be found here:
/home/trz/testwic/build/test-201309260032-sda.direct
The following build artifacts were used to create the image(s):
ROOTFS_DIR: /home/trz/yocto/yocto-image/build/tmp/work/crownbay_noemgd-poky-linux/core-image-minimal/1.0-r0/rootfs
BOOTIMG_DIR: /home/trz/yocto/yocto-image/build/tmp/sysroots/crownbay-noemgd/usr/share
KERNEL_DIR: /home/trz/yocto/yocto-image/build/tmp/sysroots/crownbay-noemgd/usr/src/kernel
NATIVE_SYSROOT: /home/trz/yocto/yocto-image/build/tmp/sysroots/crownbay-noemgd/usr/src/kernel
The image(s) were created using OE kickstart file:
/home/trz/test.wks
For this example,
MACHINE
did not have to be specified in the
local.conf file since the artifact is
manually specified.
The current wic implementation supports
only the basic kickstart partitioning commands:
partition (or part
for short) and bootloader.
Following is a listing of the commands, their syntax, and
meanings.
The commands are based on the Fedora kickstart documentation
but with modifications to reflect wic
capabilities.
http://fedoraproject.org/wiki/Anaconda/Kickstart#part_or_partition
http://fedoraproject.org/wiki/Anaconda/Kickstart#bootloader
This command creates a partition on the system and uses the following syntax:
part <mntpoint>
The <mntpoint> is where the
partition will be mounted and must be of one of the
following forms:
/<path>: For example,/,/usr, and/homeswap: The partition will be used as swap space.
Following are the supported options:
--size: The minimum partition size in MBytes. Specify an integer value such as 500. Do not append the number with "MB". You do not need this option if you use--source.--source: This option is a wic-specific option that can currently have one of two values, "bootimg" or "rootfs".If
--source rootfsis used, it tells thewiccommand to create a partition as large as needed to fill with the contents of the root filesystem (specified by the-rwicoption) and to fill it with the contents of/rootfs.If
--source bootimgis used, it tells thewiccommand to create a partition as large as needed to fill with the contents of the boot partition (specified by the-bwicoption). Exactly what those contents are depend on the value of the--fstypeoption for that partition. If--fstype=efiis specified, the boot artifacts contained in HDDDIR are used, and if--fstype=msdosis specified, the boot artifacts found inSTAGING_DATADIRare used.--ondiskor--ondrive: Forces the partition to be created on a particular disk.--fstype: Sets the file system type for the partition. Valid values are:msdosefiext4ext3ext2btrfsswap
--label label: Specifies the label to give to the filesystem to be made on the partition. If the given label is already in use by another filesystem, a new label is created for the partition.--active: Marks the partition as active.--align (in KBytes): This option is specific to the Meego Image Creator (mic) that says to start a partition on an x KBytes boundary.
This command specifies how the boot loader should be and supports the following options:
--timeout: Specifies the number of seconds before the bootloader times out and boots the default option.--append: Specifies kernel parameters. These will be added to the syslinuxAPPENDorgrubkernel command line.The boot type is determined by the fstype of the
/bootmountpoint. If the fstype is "msdos" the boot type is "pcbios", otherwise it is the fstype, which is currently "efi" (more to be added later).If the boot type is "efi", the image will use
gruband has one menuentry: "boot".If the boot type is "pcbios", the image will use syslinux and has one menu label: "boot".
Future updates will implement more options. If you use anything that is not specifically supported, results can be unpredictable.
Configuring the Yocto Project kernel consists of making sure the .config
file has all the right information in it for the image you are building.
You can use the menuconfig tool and configuration fragments to
make sure your .config file is just how you need it.
This section describes how to use menuconfig, create and use
configuration fragments, and how to interactively tweak your .config
file to create the leanest kernel configuration file possible.
For more information on kernel configuration, see the "Changing the Configuration" section in the Yocto Project Linux Kernel Development Manual.
The easiest way to define kernel configurations is to set them through the
menuconfig tool.
This tool provides an interactive method with which
to set kernel configurations.
For general information on menuconfig, see
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Menuconfig.
To use the menuconfig tool in the Yocto Project development
environment, you must launch it using BitBake.
Thus, the environment must be set up using the
oe-init-build-env
or
oe-init-build-env-memres
script found in the
Build Directory.
The following commands run menuconfig assuming the
Source Directory
top-level folder is ~/poky:
$ cd poky
$ source oe-init-build-env
$ bitbake linux-yocto -c menuconfig
Once menuconfig comes up, its standard interface allows you to
interactively examine and configure all the kernel configuration parameters.
After making your changes, simply exit the tool and save your changes to
create an updated version of the .config configuration file.
Consider an example that configures the linux-yocto-3.4
kernel.
The OpenEmbedded build system recognizes this kernel as
linux-yocto.
Thus, the following commands from the shell in which you previously sourced the
environment initialization script cleans the shared state cache and the
WORKDIR
directory and then runs menuconfig:
$ bitbake linux-yocto -c menuconfig
Once menuconfig launches, use the interface
to navigate through the selections to find the configuration settings in
which you are interested.
For example, consider the CONFIG_SMP configuration setting.
You can find it at Processor Type and Features under
the configuration selection Symmetric Multi-processing Support.
After highlighting the selection, use the arrow keys to select or deselect
the setting.
When you are finished with all your selections, exit out and save them.
Saving the selections updates the .config configuration file.
This is the file that the OpenEmbedded build system uses to configure the
kernel during the build.
You can find and examine this file in the Build Directory in
tmp/work/.
The actual .config is located in the area where the
specific kernel is built.
For example, if you were building a Linux Yocto kernel based on the
Linux 3.4 kernel and you were building a QEMU image targeted for
x86 architecture, the
.config file would be located here:
poky/build/tmp/work/qemux86-poky-linux/linux-yocto-3.4.11+git1+84f...
...656ed30-r1/linux-qemux86-standard-build
Note
The previous example directory is artificially split and many of the characters in the actual filename are omitted in order to make it more readable. Also, depending on the kernel you are using, the exact pathname forlinux-yocto-3.4... might differ.
Within the .config file, you can see the kernel settings.
For example, the following entry shows that symmetric multi-processor support
is not set:
# CONFIG_SMP is not set
A good method to isolate changed configurations is to use a combination of the
menuconfig tool and simple shell commands.
Before changing configurations with menuconfig, copy the
existing .config and rename it to something else,
use menuconfig to make
as many changes an you want and save them, then compare the renamed configuration
file against the newly created file.
You can use the resulting differences as your base to create configuration fragments
to permanently save in your kernel layer.
Note
Be sure to make a copy of the.config and don't just
rename it.
The build system needs an existing .config
from which to work.
Configuration fragments are simply kernel options that appear in a file
placed where the OpenEmbedded build system can find and apply them.
Syntactically, the configuration statement is identical to what would appear
in the .config file, which is in the
Build Directory in
tmp/work/<arch>-poky-linux/linux-yocto-<release-specific-string>/linux-<arch>-<build-type>.
It is simple to create a configuration fragment.
For example, issuing the following from the shell creates a configuration fragment
file named my_smp.cfg that enables multi-processor support
within the kernel:
$ echo "CONFIG_SMP=y" >> my_smp.cfg
Note
All configuration files must use the.cfg extension in order
for the OpenEmbedded build system to recognize them as a configuration fragment.
Where do you put your configuration files?
You can place these configuration files in the same area pointed to by
SRC_URI.
The OpenEmbedded build system will pick up the configuration and add it to the
kernel's configuration.
For example, suppose you had a set of configuration options in a file called
myconfig.cfg.
If you put that file inside a directory named linux-yocto
that resides in the same directory as the kernel's append file and then add
a SRC_URI statement such as the following to the kernel's append file,
those configuration options will be picked up and applied when the kernel is built.
SRC_URI += "file://myconfig.cfg"
As mentioned earlier, you can group related configurations into multiple files and
name them all in the SRC_URI statement as well.
For example, you could group separate configurations specifically for Ethernet and graphics
into their own files and add those by using a SRC_URI statement like the
following in your append file:
SRC_URI += "file://myconfig.cfg \
file://eth.cfg \
file://gfx.cfg"
You can make sure the .config file is as lean or efficient as
possible by reading the output of the kernel configuration fragment audit,
noting any issues, making changes to correct the issues, and then repeating.
As part of the kernel build process, the
kernel_configcheck task runs.
This task validates the kernel configuration by checking the final
.config file against the input files.
During the check, the task produces warning messages for the following
issues:
Requested options that did not make the final
.configfile.Configuration items that appear twice in the same configuration fragment.
Configuration items tagged as "required" that were overridden.
A board overrides a non-board specific option.
Listed options not valid for the kernel being processed. In other words, the option does not appear anywhere.
Note
Thekernel_configcheck task can also optionally report
if an option is overridden during processing.
For each output warning, a message points to the file that contains a list of the options and a pointer to the config fragment that defines them. Collectively, the files are the key to streamlining the configuration.
To streamline the configuration, do the following:
Start with a full configuration that you know works - it builds and boots successfully. This configuration file will be your baseline.
Separately run the
configmeandkernel_configchecktasks.Take the resulting list of files from the
kernel_configchecktask warnings and do the following:Drop values that are redefined in the fragment but do not change the final
.configfile.Analyze and potentially drop values from the
.configfile that override required configurations.Analyze and potentially remove non-board specific options.
Remove repeated and invalid options.
After you have worked through the output of the kernel configuration audit, you can re-run the
configmeandkernel_configchecktasks to see the results of your changes. If you have more issues, you can deal with them as described in the previous step.
Iteratively working through steps two through four eventually yields
a minimal, streamlined configuration file.
Once you have the best .config, you can build the Linux
Yocto kernel.
Patching the kernel involves changing or adding configurations to an existing kernel, changing or adding recipes to the kernel that are needed to support specific hardware features, or even altering the source code itself.
Note
You can use theyocto-kernel script
found in the Source Directory
under scripts to manage kernel patches and configuration.
See the "Managing kernel Patches and Config Items with yocto-kernel"
section in the Yocto Project Board Support Packages (BSP) Developer's Guide for
more information.
This example creates a simple patch by adding some QEMU emulator console
output at boot time through printk statements in the kernel's
calibrate.c source code file.
Applying the patch and booting the modified image causes the added
messages to appear on the emulator's console.
The example assumes a clean build exists for the qemux86
machine in a Source Directory named poky.
Furthermore, the Build Directory is
build and is located in poky and
the kernel is based on the Linux 3.4 kernel.
For general information on how to configure the most efficient build, see the
"Building an Image" section
in the Yocto Project Quick Start.
Also, for more information on patching the kernel, see the "Applying Patches" section in the Yocto Project Linux Kernel Development Manual.
The first step is to create a layer so you can isolate your changes:
$ cd ~/poky
$ mkdir meta-mylayer
Creating a directory that follows the Yocto Project layer naming conventions sets up the layer for your changes. The layer is where you place your configuration files, append files, and patch files. To learn more about creating a layer and filling it with the files you need, see the "Understanding and Creating Layers" section.
Each time you build a kernel image, the kernel source code is fetched and unpacked into the following directory:
${S}/linux
See the "Finding the Temporary Source Code"
section and the
S variable
for more information about where source is kept during a build.
For this example, we are going to patch the
init/calibrate.c file
by adding some simple console printk statements that we can
see when we boot the image using QEMU.
Two methods exist by which you can create the patch: Git workflow and Quilt workflow. For kernel patches, the Git workflow is more appropriate. This section assumes the Git workflow and shows the steps specific to this example.
Change the working directory: Change to where the kernel source code is before making your edits to the
calibrate.cfile:$ cd ~/poky/build/tmp/work/qemux86-poky-linux/linux-yocto-${PV}-${PR}/linuxBecause you are working in an established Git repository, you must be in this directory in order to commit your changes and create the patch file.
Edit the source file: Edit the
init/calibrate.cfile to have the following changes:void calibrate_delay(void) { unsigned long lpj; static bool printed; int this_cpu = smp_processor_id(); printk("*************************************\n"); printk("* *\n"); printk("* HELLO YOCTO KERNEL *\n"); printk("* *\n"); printk("*************************************\n"); if (per_cpu(cpu_loops_per_jiffy, this_cpu)) { . . .Stage and commit your changes: These Git commands display the modified file, stage it, and then commit the file:
$ git status $ git add init/calibrate.c $ git commit -m "calibrate: Add printk example"Generate the patch file: This Git command creates the a patch file named
0001-calibrate-Add-printk-example.patchin the current directory.$ git format-patch -1
These steps get your layer set up for the build:
Create additional structure: Create the additional layer structure:
$ cd ~/poky/meta-mylayer $ mkdir conf $ mkdir recipes-kernel $ mkdir recipes-kernel/linux $ mkdir recipes-kernel/linux/linux-yoctoThe
confdirectory holds your configuration files, while therecipes-kerneldirectory holds your append file and your patch file.Create the layer configuration file: Move to the
meta-mylayer/confdirectory and create thelayer.conffile as follows:# We have a conf and classes directory, add to BBPATH BBPATH .= ":${LAYERDIR}" # We have recipes-* directories, add to BBFILES BBFILES += "${LAYERDIR}/recipes-*/*/*.bb \ ${LAYERDIR}/recipes-*/*/*.bbappend" BBFILE_COLLECTIONS += "mylayer" BBFILE_PATTERN_mylayer = "^${LAYERDIR}/" BBFILE_PRIORITY_mylayer = "5"Notice
mylayeras part of the last three statements.Create the kernel recipe append file: Move to the
meta-mylayer/recipes-kernel/linuxdirectory and create thelinux-yocto_3.4.bbappendfile as follows:FILESEXTRAPATHS_prepend := "${THISDIR}/${PN}:" SRC_URI += "file://0001-calibrate-Add-printk-example.patch" PRINC := "${@int(PRINC) + 1}"The
FILESEXTRAPATHSandSRC_URIstatements enable the OpenEmbedded build system to find the patch file. For more information on using append files, see the "Using .bbappend Files" section.Put the patch file in your layer: Move the
0001-calibrate-Add-printk-example.patchfile to themeta-mylayer/recipes-kernel/linux/linux-yoctodirectory.
Do the following to make sure the build parameters are set up for the example. Once you set up these build parameters, they do not have to change unless you change the target architecture of the machine you are building:
Build for the correct target architecture: Your selected
MACHINEdefinition within thelocal.conffile in the Build Directory specifies the target architecture used when building the Linux kernel. By default,MACHINEis set toqemux86, which specifies a 32-bit Intel® Architecture target machine suitable for the QEMU emulator.Identify your
meta-mylayerlayer: TheBBLAYERSvariable in thebblayers.conffile found in thepoky/build/confdirectory needs to have the path to your localmeta-mylayerlayer. By default, theBBLAYERSvariable contains paths tometa,meta-yocto, andmeta-yocto-bspin thepokyGit repository. Add the path to yourmeta-mylayerlocation:BBLAYERS ?= " \ $HOME/poky/meta \ $HOME/poky/meta-yocto \ $HOME/poky/meta-yocto-bsp \ $HOME/poky/meta-mylayer \ " BBLAYERS_NON_REMOVABLE ?= " \ $HOME/poky/meta \ $HOME/poky/meta-yocto \ "
The following steps build your modified kernel image:
Be sure your build environment is initialized: Your environment should be set up since you previously sourced the
oe-init-build-envscript. If it is not, source the script again frompoky.$ cd ~/poky $ source oe-init-build-envClean up: Be sure to clean the shared state out by running the
cleansstateBitBake task as follows from your Build Directory:$ bitbake -c cleansstate linux-yoctoNote
Never remove any files by hand from thetmp/deploydirectory inside the Build Directory. Always use the various BitBake clean tasks to clear out previous build artifacts.Build the image: Next, build the kernel image using this command:
$ bitbake -k linux-yocto
These steps boot the image and allow you to see the changes
Boot the image: Boot the modified image in the QEMU emulator using this command:
$ runqemu qemux86Verify the changes: Log into the machine using
rootwith no password and then use the following shell command to scroll through the console's boot output.# dmesg | lessYou should see the results of your
printkstatements as part of the output.
When you build an image using the Yocto Project and do not alter any distribution Metadata, you are creating a Poky distribution. If you wish to gain more control over package alternative selections, compile-time options, and other low-level configurations, you can create your own distribution.
To create your own distribution, the basic steps consist of creating your own distribution layer, creating your own distribution configuration file, and then adding any needed code and Metadata to the layer. The following steps provide some more detail:
Create a layer for your new distro: Create your distribution layer so that you can keep your Metadata and code for the distribution separate. It is strongly recommended that you create and use your own layer for configuration and code. Using your own layer as compared to just placing configurations in a
local.confconfiguration file makes it easier to reproduce the same build configuration when using multiple build machines. See the "Creating a General Layer Using the yocto-layer Script" section for information on how to quickly set up a layer.Create the distribution configuration file: The distribution configuration file needs to be created in the
conf/distrodirectory of your layer. You need to name it using your distribution name (e.g.mydistro.conf).You can split out parts of your configuration file into include files and then "require" them from within your distribution configuration file. Be sure to place the include files in the
conf/distro/includedirectory of your layer. A common example usage of include files would be to separate out the selection of desired version and revisions for individual recipes.Your configuration file needs to set the following required variables:
DISTRO_NAME[required]DISTRO_VERSION[required]These following variables are optional and you typically set them from the distribution configuration file:
DISTRO_FEATURES[optional]DISTRO_EXTRA_RDEPENDS[optional]DISTRO_EXTRA_RRECOMMENDS[optional]TCLIBC[optional]Tip
If you want to base your distribution configuration file on the very basic configuration from OE-Core, you can useconf/distro/defaultsetup.confas a reference and just include variables that differ as compared todefaultsetup.conf. Alternatively, you can create a distribution configuration file from scratch using thedefaultsetup.conffile or configuration files from other distributions such as Poky or Angstrom as references.Provide miscellaneous variables: Be sure to define any other variables for which you want to create a default or enforce as part of the distribution configuration. You can include nearly any variable from the
local.conffile. The variables you use are not limited to the list in the previous bulleted item.Point to Your distribution configuration file: In your
local.conffile in the Build Directory, set yourDISTROvariable to point to your distribution's configuration file. For example, if your distribution's configuration file is namedmydistro.conf, then you point to it as follows:DISTRO = "mydistro"Add more to the layer if necessary: Use your layer to hold other information needed for the distribution:
Add recipes for installing distro-specific configuration files that are not already installed by another recipe. If you have distro-specific configuration files that are included by an existing recipe, you should add a
.bbappendfor those. For general information and recommendations on how to add recipes to your layer, see the "Creating Your Own Layer" and "Best Practices to Follow When Creating Layers" sections.Add any image recipes that are specific to your distribution.
Add a
psplashappend file for a branded splash screen. For information on append files, see the "Using .bbappend Files" section.Add any other append files to make custom changes that are specific to individual recipes.
Very small distributions have some significant advantages such as requiring less on-die or in-package memory (cheaper), better performance through efficient cache usage, lower power requirements due to less memory, faster boot times, and reduced development overhead. Some real-world examples where a very small distribution gives you distinct advantages are digital cameras, medical devices, and small headless systems.
This section presents information that shows you how you can
trim your distribution to even smaller sizes than the
poky-tiny distribution, which is around
5 Mbytes, that can be built out-of-the-box using the Yocto Project.
The following list presents the overall steps you need to consider and perform to create distributions with smaller root filesystems, achieve faster boot times, maintain your critical functionality, and avoid initial RAM disks:
Determine your goals and guiding principles.
Understand what contributes to your image size.
Reduce the size of the root filesystem.
Reduce the size of the kernel.
Eliminate packaging requirements.
Look for other ways to minimize size.
Iterate on the process.
Before you can reach your destination, you need to know where you are going. Here is an example list that you can use as a guide when creating very small distributions:
Determine how much space you need (e.g. a kernel that is 1 Mbyte or less and a root filesystem that is 3 Mbytes or less).
Find the areas that are currently taking 90% of the space and concentrate on reducing those areas.
Do not create any difficult "hacks" to achieve your goals.
Leverage the device-specific options.
Work in a separate layer so that you keep changes isolated. For information on how to create layers, see the "Understanding and Creating Layers" section.
It is easiest to have something to start with when creating
your own distribution.
You can use the Yocto Project out-of-the-box to create the
poky-tiny distribution.
Ultimately, you will want to make changes in your own
distribution that are likely modeled after
poky-tiny.
Note
To usepoky-tiny in your build,
set the
DISTRO
variable in your
local.conf file to "poky-tiny"
as described in the
"Creating Your Own Distribution"
section.
Understanding some memory concepts will help you reduce the
system size.
Memory consists of static, dynamic, and temporary memory.
Static memory is the TEXT (code), DATA (initialized data
in the code), and BSS (uninitialized data) sections.
Dynamic memory represents memory that is allocated at runtime:
stacks, hash tables, and so forth.
Temporary memory is recovered after the boot process.
This memory consists of memory used for decompressing
the kernel and for the __init__
functions.
To help you see where you currently are with kernel and root
filesystem sizes, you can use two tools found in the
Source Directory in
the scripts/tiny/ directory:
ksize.py: Reports component sizes for the kernel build objects.dirsize.py: Reports component sizes for the root filesystem.
This next tool and command helps you organize configuration fragments and view file dependencies in a human-readable form:
merge_config.sh: Helps you manage configuration files and fragments within the kernel. With this tool, you can merge individual configuration fragments together. The tool allows you to make overrides and warns you of any missing configuration options. The tool is ideal for allowing you to iterate on configurations, create minimal configurations, and create configuration files for different machines without having to duplicate your process.The
merge_config.shscript is part of the Linux Yocto kernel Git repository in thescripts/kconfigdirectory.For more information on configuration fragments, see the "Generating Configuration Files" section of the Yocto Project Linux Kernel Development Manual and the "Creating Configuration Fragments" section, which is in this manual.
bitbake -u depexp -g <bitbake_target>: Using the BitBake command with these options brings up a Dependency Explorer from which you can view file dependencies. Understanding these dependencies allows you to make informed decisions when cutting out various pieces of the kernel and root filesystem.
The root filesystem is made up of packages for booting, libraries, and applications. To change things, you can configure how the packaging happens, which changes the way you build them. You can also tweak the filesystem itself or select a different filesystem.
First, find out what is hogging your root filesystem by running the
dirsize.py script from your root directory:
$ cd <root-directory-of-image>
$ dirsize.py 100000 > dirsize-100k.log
$ cat dirsize-100k.log
You can apply a filter to the script to ignore files under a certain size. The previous example filters out any files below 100 Kbytes. The sizes reported by the tool are uncompressed, and thus will be smaller by a relatively constant factor in a compressed root filesystem. When you examine your log file, you can focus on areas of the root filesystem that take up large amounts of memory.
You need to be sure that what you eliminate does not cripple the functionality you need. One way to see how packages relate to each other is by using the Dependency Explorer UI with the BitBake command:
$ cd <image-directory>
$ bitbake -u depexp -g <image>
Use the interface to select potential packages you wish to eliminate and see their dependency relationships.
When deciding how to reduce the size, get rid of packages that
result in minimal impact on the feature set.
For example, you might not need a VGA display.
Or, you might be able to get by with devtmpfs
and mdev instead of
udev.
Use your local.conf file to make changes.
For example, to eliminate udev and
glib, set the following in the
local configuration file:
VIRTUAL-RUNTIME_dev_manager = ""
Finally, you should consider exactly the type of root
filesystem you need to meet your needs while also reducing
its size.
For example, consider cramfs,
squashfs, ubifs,
ext2, or an initramfs
using initramfs.
Be aware that ext3 requires a 1 Mbyte
journal.
If you are okay with running read-only, you do not need this
journal.
Note
After each round of elimination, you need to rebuild your system and then use the tools to see the effects of your reductions.The kernel is built by including policies for hardware-independent aspects. What subsystems do you enable? For what architecture are you building? Which drivers do you build by default?
Note
You can modify the kernel source if you want to help with boot time.
Run the ksize.py script from the top-level
Linux build directory to get an idea of what is making up
the kernel:
$ cd <top-level-linux-build-directory>
$ ksize.py > ksize.log
$ cat ksize.log
When you examine the log, you will see how much space is
taken up with the built-in .o files for
drivers, networking, core kernel files, filesystem, sound,
and so forth.
The sizes reported by the tool are uncompressed, and thus
will be smaller by a relatively constant factor in a compressed
kernel image.
Look to reduce the areas that are large and taking up around
the "90% rule."
To examine, or drill down, into any particular area, use the
-d option with the script:
$ ksize.py -d > ksize.log
Using this option breaks out the individual file information for each area of the kernel (e.g. drivers, networking, and so forth).
Use your log file to see what you can eliminate from the kernel based on features you can let go. For example, if you are not going to need sound, you do not need any drivers that support sound.
After figuring out what to eliminate, you need to reconfigure
the kernel to reflect those changes during the next build.
You could run menuconfig and make all your
changes at once.
However, that makes it difficult to see the effects of your
individual eliminations and also makes it difficult to replicate
the changes for perhaps another target device.
A better method is to start with no configurations using
allnoconfig, create configuration
fragments for individual changes, and then manage the
fragments into a single configuration file using
merge_config.sh.
The tool makes it easy for you to iterate using the
configuration change and build cycle.
Each time you make configuration changes, you need to rebuild the kernel and check to see what impact your changes had on the overall size.
Packaging requirements add size to the image. One way to reduce the size of the image is to remove all the packaging requirements from the image. This reduction includes both removing the package manager and its unique dependencies as well as removing the package management data itself.
To eliminate all the packaging requirements for an image, follow these steps:
Put the following line in your main recipe for the image to remove package management data files:
ROOTFS_POSTPROCESS_COMMAND += "remove_packaging_data_files ;For example, the recipe for the
core-image-minimalimage contains this line. You can also add the line to thelocal.confconfiguration file.Be sure that "package-management" is not part of your
IMAGE_FEATURESstatement for the image. When you remove this feature, you are removing the package manager as well as its dependencies from the root filesystem.
Depending on your particular circumstances, other areas that you can trim likely exist. The key to finding these areas is through tools and methods described here combined with experimentation and iteration. Here are a couple of areas to experiment with:
eglibc: In general, follow this process:Remove
eglibcfeatures fromDISTRO_FEATURESthat you think you do not need.Build your distribution.
If the build fails due to missing symbols in a package, determine if you can reconfigure the package to not need those features. For example, change the configuration to not support wide character support as is done for
ncurses. Or, if support for those characters is needed, determine whateglibcfeatures provide the support and restore the configuration.Rebuild and repeat the process.
busybox: For BusyBox, use a process similar as described foreglibc. A difference is you will need to boot the resulting system to see if you are able to do everything you expect from the running system. You need to be sure to integrate configuration fragments into Busybox because BusyBox handles its own core features and then allows you to add configuration fragments on top.
If you have not reached your goals on system size, you need to iterate on the process. The process is the same. Use the tools and see just what is taking up 90% of the root filesystem and the kernel. Decide what you can eliminate without limiting your device beyond what you need.
Depending on your system, a good place to look might be Busybox, which provides a stripped down version of Unix tools in a single, executable file. You might be able to drop virtual terminal services or perhaps ipv6.
This section describes a few tasks that involve packages:
Excluding packages from an image
Incrementing a package revision number
Handling a package name alias
Handling optional module packaging
Using Runtime Package Management
Setting up and running package test (ptest)
You might find it necessary to prevent specific packages from being installed into an image. If so, you can use several variables to direct the build system to essentially ignore installing recommended packages or to not install a package at all.
The following list introduces variables you can use to
prevent packages from being installed into your image.
Each of these variables only works with IPK and RPM
package types.
Support for Debian packages does not exist.
Also, you can use these variables from your
local.conf file or attach them to a
specific image recipe by using a recipe name override.
For more detail on the variables, see the descriptions in the
Yocto Project Reference Manual's glossary chapter.
BAD_RECOMMENDATIONS: Use this variable to specify "recommended-only" packages that you do not want installed.NO_RECOMMENDATIONS: Use this variable to prevent all "recommended-only" packages from being installed.PACKAGE_EXCLUDE: Use this variable to prevent specific packages from being installed regardless of whether they are "recommended-only" or not. You need to realize that the build process could fail with an error when you prevent the installation of a package whose presence is required by an installed package.
If a committed change results in changing the package output,
then the value of the
PR
variable needs to be increased (or "bumped").
Increasing PR occurs one of two ways:
Automatically using a Package Revision Service (PR Service).
Manually incrementing the
PRvariable.
Given that one of the challenges any build system and its users face is how to maintain a package feed that is compatible with existing package manager applications such as RPM, APT, and OPKG, using an automated system is much preferred over a manual system. In either system, the main requirement is that version numbering increases in a linear fashion and that a number of version components exist that support that linear progression.
The following two sections provide information on the PR Service
and on manual PR bumping.
As mentioned, attempting to maintain revision numbers in the Metadata is error prone, inaccurate and causes problems for people submitting recipes. Conversely, the PR Service automatically generates increasing numbers, particularly the revision field, which removes the human element.
Note
For additional information on using a PR Service, you can see the PR Service wiki page.
The Yocto Project uses variables in order of
decreasing priority to facilitate revision numbering (i.e.
PE,
PV, and
PR
for epoch, version and revision, respectively).
The values are highly dependent on the policies and
procedures of a given distribution and package feed.
Because the OpenEmbedded build system uses
"signatures",
which are unique to a given build, the build system
knows when to rebuild packages.
All the inputs into a given task are represented by a
signature, which can trigger a rebuild when different.
Thus, the build system itself does not rely on the
PR numbers to trigger a rebuild.
The signatures, however, can be used to generate
PR values.
The PR Service works with both
OEBasic and
OEBasicHash generators.
The value of PR bumps when the
checksum changes and the different generator mechanisms
change signatures under different circumstances.
As implemented, the build system includes values from
the PR Service into the PR field as
an addition using the form ".x" so
r0 becomes r0.1,
r0.2 and so forth.
This scheme allows existing PR values
to be used for whatever reasons, which include manual
PR bumps should it be necessary.
By default, the PR Service is not enabled or running. Thus, the packages generated are just "self consistent". The build system adds and removes packages and there are no guarantees about upgrade paths but images will be consistent and correct with the latest changes.
The simplest form for a PR Service is for it to exist
for a single host development system that builds the
package feed (building system).
For this scenario, you can enable a local PR Service by
setting
PRSERV_HOST
in your local.conf file in the
Build Directory:
PRSERV_HOST = "localhost:0"
Once the service is started, packages will automatically
get increasing PR values and
BitBake will take care of starting and stopping the server.
If you have a more complex setup where multiple host
development systems work against a common, shared package
feed, you have a single PR Service running and it is
connected to each building system.
For this scenario, you need to start the PR Service using
the bitbake-prserv command:
bitbake-prserv ‐‐host <ip> ‐‐port <port> ‐‐start
In addition to hand-starting the service, you need to
update the local.conf file of each
building system as described earlier so each system
points to the server and port.
It is also recommended you use Build History, which adds
some sanity checks to package versions, in conjunction with
the server that is running the PR Service.
To enable build history, add the following to each building
system's local.conf file:
# It is recommended to activate "buildhistory" for testing the PR service
INHERIT += "buildhistory"
BUILDHISTORY_COMMIT = "1"
For information on Build History, see the "Maintaining Build Output Quality" section in the Yocto Project Reference Manual.
Note
The OpenEmbedded build system does not maintain
PR information as part of the
shared state (sstate) packages.
If you maintain an sstate feed, its expected that either
all your building systems that contribute to the sstate
feed use a shared PR Service, or you do not run a PR
Service on any of your building systems.
Having some systems use a PR Service while others do
not leads to obvious problems.
For more information on shared state, see the "Shared State Cache" section in the Yocto Project Reference Manual.
The alternative to setting up a PR Service is to manually
bump the
PR
variable.
If a committed change results in changing the package output,
then the value of the PR variable needs to be increased
(or "bumped") as part of that commit.
For new recipes you should add the PR
variable and set its initial value equal to "r0", which is the default.
Even though the default value is "r0", the practice of adding it to a new recipe makes
it harder to forget to bump the variable when you make changes
to the recipe in future.
If you are sharing a common .inc file with multiple recipes,
you can also use the
INC_PR
variable to ensure that
the recipes sharing the .inc file are rebuilt when the
.inc file itself is changed.
The .inc file must set INC_PR
(initially to "r0"), and all recipes referring to it should set PR
to "$(INC_PR).0" initially, incrementing the last number when the recipe is changed.
If the .inc file is changed then its
INC_PR should be incremented.
When upgrading the version of a package, assuming the
PV
changes, the PR variable should be
reset to "r0" (or "$(INC_PR).0" if you are using
INC_PR).
Usually, version increases occur only to packages.
However, if for some reason PV changes but does not
increase, you can increase the
PE
variable (Package Epoch).
The PE variable defaults to "0".
Version numbering strives to follow the Debian Version Field Policy Guidelines. These guidelines define how versions are compared and what "increasing" a version means.
Sometimes a package name you are using might exist under an alias or as a similarly named
package in a different distribution.
The OpenEmbedded build system implements a distro_check
task that automatically connects to major distributions
and checks for these situations.
If the package exists under a different name in a different distribution, you get a
distro_check mismatch.
You can resolve this problem by defining a per-distro recipe name alias using the
DISTRO_PN_ALIAS
variable.
Following is an example that shows how you specify the DISTRO_PN_ALIAS
variable:
DISTRO_PN_ALIAS_pn-PACKAGENAME = "distro1=package_name_alias1 \
distro2=package_name_alias2 \
distro3=package_name_alias3 \
..."
If you have more than one distribution alias, separate them with a space.
Note that the build system currently automatically checks the
Fedora, OpenSUSE, Debian, Ubuntu,
and Mandriva distributions for source package recipes without having to specify them
using the DISTRO_PN_ALIAS variable.
For example, the following command generates a report that lists the Linux distributions
that include the sources for each of the recipes.
$ bitbake world -f -c distro_check
The results are stored in the build/tmp/log/distro_check-${DATETIME}.results
file found in the
Source Directory.
Many pieces of software split functionality into optional modules (or plug-ins) and the plug-ins that are built might depend on configuration options. To avoid having to duplicate the logic that determines what modules are available in your recipe or to avoid having to package each module by hand, the OpenEmbedded build system provides functionality to handle module packaging dynamically.
To handle optional module packaging, you need to do two things:
Ensure the module packaging is actually done
Ensure that any dependencies on optional modules from other recipes are satisfied by your recipe
To ensure the module packaging actually gets done, you use
the do_split_packages function within
the populate_packages Python function
in your recipe.
The do_split_packages function
searches for a pattern of files or directories under a
specified path and creates a package for each one it finds
by appending to the
PACKAGES
variable and setting the appropriate values for
FILES_packagename,
RDEPENDS_packagename,
DESCRIPTION_packagename, and so forth.
Here is an example from the lighttpd
recipe:
python populate_packages_prepend () {
lighttpd_libdir = d.expand('${libdir}')
do_split_packages(d, lighttpd_libdir, '^mod_(.*)\.so$',
'lighttpd-module-%s', 'Lighttpd module for %s',
extra_depends='')
}
The previous example specifies a number of things in the
call to do_split_packages.
A directory within the files installed by your recipe through
do_installin which to search.A regular expression to match module files in that directory. In the example, note the parentheses () that mark the part of the expression from which the module name should be derived.
A pattern to use for the package names.
A description for each package.
An empty string for
extra_depends, which disables the default dependency on the mainlighttpdpackage. Thus, if a file in${libdir}calledmod_alias.sois found, a package calledlighttpd-module-aliasis created for it and theDESCRIPTIONis set to "Lighttpd module for alias".
Often, packaging modules is as simple as the previous
example.
However, more advanced options exist that you can use
within do_split_packages to modify its
behavior.
And, if you need to, you can add more logic by specifying
a hook function that is called for each package.
It is also perfectly acceptable to call
do_split_packages multiple times if
you have more than one set of modules to package.
For more examples that show how to use
do_split_packages, see the
connman.inc file in the
meta/recipes-connectivity/connman/
directory of the poky
source repository.
You can also find examples in
meta/classes/kernel.bbclass.
Following is a reference that shows
do_split_packages mandatory and
optional arguments:
Mandatory arguments
root
The path in which to search
file_regex
Regular expression to match searched files.
Use parentheses () to mark the part of this
expression that should be used to derive the
module name (to be substituted where %s is
used in other function arguments as noted below)
output_pattern
Pattern to use for the package names. Must
include %s.
description
Description to set for each package. Must
include %s.
Optional arguments
postinst
Postinstall script to use for all packages
(as a string)
recursive
True to perform a recursive search - default
False
hook
A hook function to be called for every match.
The function will be called with the following
arguments (in the order listed):
f
Full path to the file/directory match
pkg
The package name
file_regex
As above
output_pattern
As above
modulename
The module name derived using file_regex
extra_depends
Extra runtime dependencies (RDEPENDS) to be
set for all packages. The default value of None
causes a dependency on the main package
(${PN}) - if you do not want this, pass empty
string '' for this parameter.
aux_files_pattern
Extra item(s) to be added to FILES for each
package. Can be a single string item or a list
of strings for multiple items. Must include %s.
postrm
postrm script to use for all packages (as a
string)
allow_dirs
True to allow directories to be matched -
default False
prepend
If True, prepend created packages to PACKAGES
instead of the default False which appends them
match_path
match file_regex on the whole relative path to
the root rather than just the file name
aux_files_pattern_verbatim
Extra item(s) to be added to FILES for each
package, using the actual derived module name
rather than converting it to something legal
for a package name. Can be a single string item
or a list of strings for multiple items. Must
include %s.
allow_links
True to allow symlinks to be matched - default
False
The second part for handling optional module packaging
is to ensure that any dependencies on optional modules
from other recipes are satisfied by your recipe.
You can be sure these dependencies are satisfied by
using the
PACKAGES_DYNAMIC variable.
Here is an example that continues with the
lighttpd recipe shown earlier:
PACKAGES_DYNAMIC = "lighttpd-module-.*"
The name specified in the regular expression can of
course be anything.
In this example, it is lighttpd-module-
and is specified as the prefix to ensure that any
RDEPENDS
and RRECOMMENDS
on a package name starting with the prefix are satisfied
during build time.
If you are using do_split_packages
as described in the previous section, the value you put in
PACKAGES_DYNAMIC should correspond to
the name pattern specified in the call to
do_split_packages.
During a build, BitBake always transforms a recipe into one or
more packages.
For example, BitBake takes the bash recipe
and currently produces the bash-dbg,
bash-staticdev,
bash-dev, bash-doc,
bash-locale, and
bash packages.
Not all generated packages are included in an image.
In several situations, you might need to update, add, remove, or query the packages on a target device at runtime (i.e. without having to generate a new image). Examples of such situations include:
You want to provide in-the-field updates to deployed devices (e.g. security updates).
You want to have a fast turn-around development cycle for one or more applications that run on your device.
You want to temporarily install the "debug" packages of various applications on your device so that debugging can be greatly improved by allowing access to symbols and source debugging.
You want to deploy a more minimal package selection of your device but allow in-the-field updates to add a larger selection for customization.
In all these situations, you have something similar to a more traditional Linux distribution in that in-field devices are able to receive pre-compiled packages from a server for installation or update. Being able to install these packages on a running, in-field device is what is termed "runtime package management".
In order to use runtime package management, you need a host/server machine that serves up the pre-compiled packages plus the required metadata. You also need package manipulation tools on the target. The build machine is a likely candidate to act as the server. However, that machine does not necessarily have to be the package server. The build machine could push its artifacts to another machine that acts as the server (e.g. Internet-facing).
A simple build that targets just one device produces
more than one package database.
In other words, the packages produced by a build are separated
out into a couple of different package groupings based on
criteria such as the target's CPU architecture, the target
board, or the C library used on the target.
For example, a build targeting the qemuarm
device produces the following three package databases:
all, armv5te, and
qemuarm.
If you wanted your qemuarm device to be
aware of all the packages that were available to it,
you would need to point it to each of these databases
individually.
In a similar way, a traditional Linux distribution usually is
configured to be aware of a number of software repositories
from which it retrieves packages.
Using runtime package management is completely optional and not required for a successful build or deployment in any way. But if you want to make use of runtime package management, you need to do a couple things above and beyond the basics. The remainder of this section describes what you need to do.
This section describes build considerations that you need to be aware of in order to provide support for runtime package management.
When BitBake generates packages it needs to know
what format(s) to use.
In your configuration, you use the
PACKAGE_CLASSES
variable to specify the format.
Note
You can choose to have more than one format but you must provide at least one.
If you would like your image to start off with a basic
package database of the packages in your current build
as well as have the relevant tools available on the
target for runtime package management, you can include
"package-management" in the
IMAGE_FEATURES
variable.
Including "package-management" in this
configuration variable ensures that when the image
is assembled for your target, the image includes
the currently-known package databases as well as
the target-specific tools required for runtime
package management to be performed on the target.
However, this is not strictly necessary.
You could start your image off without any databases
but only include the required on-target package
tool(s).
As an example, you could include "opkg" in your
IMAGE_INSTALL
variable if you are using the IPK package format.
You can then initialize your target's package database(s)
later once your image is up and running.
Whenever you perform any sort of build step that can potentially generate a package or modify an existing package, it is always a good idea to re-generate the package index with:
$ bitbake package-index
Realize that it is not sufficient to simply do the following:
$ bitbake <some-package> package-index
This is because BitBake does not properly schedule the
package-index target fully after any
other target has completed.
Thus, be sure to run the package update step separately.
As described below in the
"Using IPK"
section, if you are using IPK as your package format, you
can make use of the
distro-feed-configs recipe provided
by meta-oe in order to configure your
target to use your IPK databases.
When your build is complete, your packages reside in the
${TMPDIR}/deploy/<package-format>
directory.
For example, if ${TMPDIR}
is tmp and your selected package type
is IPK, then your IPK packages are available in
tmp/deploy/ipk.
Typically, packages are served from a server using HTTP. However, other protocols are possible. If you want to use HTTP, then setup and configure a web server, such as Apache 2 or lighttpd, on the machine serving the packages.
As previously mentioned, the build machine can act as the package server. In the following sections that describe server machine setups, the build machine is assumed to also be the server.
This example assumes you are using the Apache 2 server:
Add the directory to your Apache configuration, which you can find at
/etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf. Use commands similar to these on the development system. These example commands assume a top-level Source Directory namedpokyin your home directory. The example also assumes an RPM package type. If you are using a different package type, such as IPK, use "ipk" in the pathnames:<VirtualHost *:80> .... Alias /rpm ~/poky/build/tmp/deploy/rpm <Directory "~/poky/build/tmp/deploy/rpm"> Options +Indexes </Directory> </VirtualHost>Reload the Apache configuration as described in this step. For all commands, be sure you have root privileges.
If your development system is using Fedora or CentOS, use the following:
# service httpd reloadFor Ubuntu and Debian, use the following:
# /etc/init.d/apache2 reloadFor OpenSUSE, use the following:
# /etc/init.d/apache2 reloadIf you are using Security-Enhanced Linux (SELinux), you need to label the files as being accessible through Apache. Use the following command from the development host. This example assumes RPM package types:
# chcon -R -h -t httpd_sys_content_t tmp/deploy/rpm
If you are using lighttpd, all you need
to do is to provide a link from your
${TMPDIR}/deploy/<package-format>
directory to lighttpd's document-root.
You can determine the specifics of your lighttpd
installation by looking through its configuration file,
which is usually found at:
/etc/lighttpd/lighttpd.conf.
For example, if you are using IPK, lighttpd's
document-root is set to
/var/www/lighttpd, and you had
packages for a target named "BOARD",
then you might create a link from your build location
to lighttpd's document-root as follows:
# ln -s $(PWD)/tmp/deploy/ipk /var/www/lighttpd/BOARD-dir
At this point, you need to start the lighttpd server. The method used to start the server varies by distribution. However, one basic method that starts it by hand is:
# lighttpd -f /etc/lighttpd/lighttpd.conf
Setting up the target differs depending on the package management system. This section provides information for RPM and IPK.
The application for performing runtime package
management of RPM packages on the target is called
smart.
On the target machine, you need to inform
smart of every package database
you want to use.
As an example, suppose your target device can use the
following three package databases from a server named
server.name:
all, i586,
and qemux86.
Given this example, issue the following commands on the
target:
# smart channel --add all type=rpm-md baseurl=http://server.name/rpm/all
# smart channel --add i585 type=rpm-md baseurl=http://server.name/rpm/i586
# smart channel --add qemux86 type=rpm-md baseurl=http://server.name/rpm/qemux86
Also from the target machine, fetch the repository information using this command:
# smart update
You can now use the smart query
and smart install commands to
find and install packages from the repositories.
The application for performing runtime package
management of IPK packages on the target is called
opkg.
In order to inform opkg of the
package databases you want to use, simply create one
or more *.conf files in the
/etc/opkg directory on the target.
The opkg application uses them
to find its available package databases.
As an example, suppose you configured your HTTP server
on your machine named
www.mysite.com to serve files
from a BOARD-dir directory under
its document-root.
In this case, you might create a configuration
file on the target called
/etc/opkg/base-feeds.conf that
contains:
src/gz all http://www.mysite.com/BOARD-dir/all
src/gz armv7a http://www.mysite.com/BOARD-dir/armv7a
src/gz beagleboard http://www.mysite.com/BOARD-dir/beagleboard
As a way of making it easier to generate and make
these IPK configuration files available on your
target, simply define
FEED_DEPLOYDIR_BASE_URI
to point to your server and the location within the
document-root which contains the databases.
For example: if you are serving your packages over
HTTP, your server's IP address is 192.168.7.1, and
your databases are located in a directory called
BOARD-dir underneath your HTTP
server's document-root, you need to set
FEED_DEPLOYDIR_BASE_URI to
http://192.168.7.1/BOARD-dir and
a set of configuration files will be generated for you
in your target to work with this feed.
On the target machine, fetch (or refresh) the repository information using this command:
# opkg update
You can now use the opkg list and
opkg install commands to find and
install packages from the repositories.
A Package Test (ptest) runs tests against packages built
by the OpenEmbedded build system on the target machine.
A ptest contains at least two items: the actual test, and
a shell script (run-ptest) that starts
the test.
The shell script that starts the test must not contain
the actual test, the script only starts it.
On the other hand, the test can be anything from a simple
shell script that runs a binary and checks the output to
an elaborate system of test binaries and data files.
The test generates output in the format used by Automake:
<result>: <testname>
where the result can be PASS,
FAIL, or SKIP,
and the testname can be any identifying string.
Note
A recipe is "ptest-enabled" if it inherits ptest.
To add package testing to your build, add the
DISTRO_FEATURES
and EXTRA_IMAGE_FEATURES
variables to your local.conf file,
which is found in the
Build Directory:
DISTRO_FEATURES_append = " ptest"
EXTRA_IMAGE_FEATURES += "ptest-pkgs"
Once your build is complete, the ptest files are installed
into the /usr/lib/<package>/ptest
directory within the image, where
<package> is the name of the
package.
The ptest-runner package installs a
shell script that loops through all installed ptest test
suites and runs them in sequence.
Consequently, you might want to add this package to
your image.
In order to enable a recipe to run installed ptests on target hardware, you need to prepare the recipes that build the packages you want to test. Here is what you have to do for each recipe:
Be sure the recipe inherits ptest: Include the following line in each recipe:
inherit ptestCreate
run-ptest: This script starts your test. Locate the script where you will refer to it usingSRC_URI. Here is an example that starts a test fordbus:#!/bin/sh cd test make -k runtest-TESTSEnsure dependencies are met: If the test adds build or runtime dependencies that normally do not exist for the package (such as requiring "make" to run the test suite), use the
DEPENDSandRDEPENDSvariables in your recipe in order for the package to meet the dependencies. Here is an example where the package has a runtime dependency on "make":RDEPENDS_${PN}-ptest += "make"Add a function to build the test suite: Not many packages support cross-compilation of their test suites. Consequently, you usually need to add a cross-compilation function to the package.
Many packages based on Automake compile and run the test suite by using a single command such as
make check. However, the nativemake checkbuilds and runs on the same computer, while cross-compiling requires that the package is built on the host but executed on the target. The built version of Automake that ships with the Yocto Project includes a patch that separates building and execution. Consequently, packages that use the unaltered, patched version ofmake checkautomatically cross-compiles.However, you still must add a
do_compile_ptestfunction to build the test suite. Add a function similar to the following to your recipe:do_compile_ptest() { oe_runmake buildtest-TESTS }Ensure special configurations are set: If the package requires special configurations prior to compiling the test code, you must insert a
do_configure_ptestfunction into the recipe.Install the test suite: The
ptest.bbclassclass automatically copies the filerun-ptestto the target and then runs makeinstall-ptestto run the tests. If this is not enough, you need to create ado_install_ptestfunction and make sure it gets called after the "make install-ptest" completes.
By default, the OpenEmbedded build system uses the Build Directory to build source code. The build process involves fetching the source files, unpacking them, and then patching them if necessary before the build takes place.
Situations exist where you might want to build software from source
files that are external to and thus outside of the
OpenEmbedded build system.
For example, suppose you have a project that includes a new BSP with
a heavily customized kernel.
And, you want to minimize exposing the build system to the
development team so that they can focus on their project and
maintain everyone's workflow as much as possible.
In this case, you want a kernel source directory on the development
machine where the development occurs.
You want the recipe's
SRC_URI
variable to point to the external directory and use it as is, not
copy it.
To build from software that comes from an external source, all you
need to do is inherit
externalsrc.bbclass
and then set the
EXTERNALSRC
variable to point to your external source code.
Here are the statements to put in your
local.conf file:
INHERIT += "externalsrc"
EXTERNALSRC_pn-myrecipe = "/some/path/to/your/source/tree"
By default, externalsrc.bbclass builds
the source code in a directory separate from the external source
directory as specified by
EXTERNALSRC.
If you need to have the source built in the same directory in
which it resides, or some other nominated directory, you can set
EXTERNALSRC_BUILD
to point to that directory:
EXTERNALSRC_BUILD_pn-myrecipe = "/path/to/my/source/tree"
By default, the Yocto Project uses
SysVinit as the initialization manager.
However, support also exists for systemd,
which is a full replacement for init with
parallel starting of services, reduced shell overhead and other
features that are used by many distributions.
If you want to use sysvinit, you do
not have to do anything.
But, if you want to use systemd, you must
take some steps as described in the following sections.
Set the following variables in your distribution configuration file as follows:
DISTRO_FEATURES_append = " systemd"
VIRTUAL-RUNTIME_init_manager = "systemd"
You can also prevent the sysvinit
distribution feature from
being automatically enabled as follows:
DISTRO_FEATURES_BACKFILL_CONSIDERED = "sysvinit"
Doing so removes any redundant sysvinit
scripts.
For information on the backfill variable, see
DISTRO_FEATURES_BACKFILL_CONSIDERED
in the Yocto Project Reference Manual.
Set the following variables in your distribution configuration file as follows:
DISTRO_FEATURES_append = " systemd"
VIRTUAL-RUNTIME_init_manager = "systemd"
Doing so causes your main image to use the
packagegroup-core-boot.bb recipe and
systemd.
The rescue/minimal image cannot use this package group.
However, it can install sysvinit
and the appropriate packages will have support for both
systemd and sysvinit.
You might find that there are groups of recipes or append files
that you want to filter out of the build process.
Usually, this is not necessary.
However, on rare occasions where you might want to use a
layer but exclude parts that are causing problems, such
as introducing a different version of a recipe, you can
use
BBMASK
to exclude the recipe.
It is possible to filter or mask out .bb and
.bbappend files.
You can do this by providing an expression with the
BBMASK variable.
Here is one example:
BBMASK = "/meta-mymachine/recipes-maybe/"
Here, all .bb and
.bbappend files in the directory that match
the expression are ignored during the build process.
Note
The value you provide is passed to Python's regular expression compiler. The expression is compared against the full paths to the files. For complete syntax information, see Python's documentation at http://docs.python.org/release/2.3/lib/re-syntax.html.If you're working on a recipe that pulls from an external Source Code Manager (SCM), it is possible to have the OpenEmbedded build system notice new recipe changes added to the SCM and then build the resulting package that depends on the new recipes by using the latest versions. This only works for SCMs from which it is possible to get a sensible revision number for changes. Currently, you can do this with Apache Subversion (SVN), Git, and Bazaar (BZR) repositories.
To enable this behavior, simply add the following to the local.conf
configuration file found in the
Build Directory:
SRCREV_pn-<PN> = "${AUTOREV}"
where PN
is the name of the recipe for which you want to enable automatic source
revision updating.
In fact, the Yocto Project provides a distribution named
poky-bleeding, whose configuration
file contains the line:
require conf/distro/include/poky-floating-revisions.inc
This line pulls in the listed include file that contains numerous lines of exactly that form:
SRCREV_pn-gconf-dbus ?= "${AUTOREV}"
SRCREV_pn-matchbox-common ?= "${AUTOREV}"
SRCREV_pn-matchbox-config-gtk ?= "${AUTOREV}"
SRCREV_pn-matchbox-desktop ?= "${AUTOREV}"
SRCREV_pn-matchbox-keyboard ?= "${AUTOREV}"
SRCREV_pn-matchbox-panel ?= "${AUTOREV}"
SRCREV_pn-matchbox-panel-2 ?= "${AUTOREV}"
SRCREV_pn-matchbox-themes-extra ?= "${AUTOREV}"
SRCREV_pn-matchbox-terminal ?= "${AUTOREV}"
SRCREV_pn-matchbox-wm ?= "${AUTOREV}"
SRCREV_pn-matchbox-wm-2 ?= "${AUTOREV}"
SRCREV_pn-settings-daemon ?= "${AUTOREV}"
SRCREV_pn-screenshot ?= "${AUTOREV}"
SRCREV_pn-libfakekey ?= "${AUTOREV}"
SRCREV_pn-oprofileui ?= "${AUTOREV}"
.
.
.
These lines allow you to experiment with building a distribution that tracks the latest development source for numerous packages.
Caution
Thepoky-bleeding distribution
is not tested on a regular basis.
Keep this in mind if you use it.
Suppose, for security reasons, you need to disable your target device's root filesystem's write permissions (i.e. you need a read-only root filesystem). Or, perhaps you are running the device's operating system from a read-only storage device. For either case, you can customize your image for that behavior.
Note
Supporting a read-only root filesystem requires that the system and applications do not try to write to the root filesystem. You must configure all parts of the target system to write elsewhere, or to gracefully fail in the event of attempting to write to the root filesystem.
To create the read-only root filesystem, simply add the
read-only-rootfs feature to your image.
Using either of the following statements in your
image recipe or from within the
local.conf file found in the
Build Directory
causes the build system to create a read-only root filesystem:
IMAGE_FEATURES = "read-only-rootfs"
or
EXTRA_IMAGE_FEATURES += "read-only-rootfs"
For more information on how to use these variables, see the
"Customizing Images Using Custom IMAGE_FEATURES and EXTRA_IMAGE_FEATURES"
section.
For information on the variables, see
IMAGE_FEATURES
and EXTRA_IMAGE_FEATURES.
It is very important that you make sure all
post-Installation (pkg_postinst) scripts
for packages that are installed into the image can be run
at the time when the root filesystem is created during the
build on the host system.
These scripts cannot attempt to run during first-boot on the
target device.
With the read-only-rootfs feature enabled,
the build system checks during root filesystem creation to make
sure all post-installation scripts succeed.
If any of these scripts still need to be run after the root
filesystem is created, the build immediately fails.
These checks during build time ensure that the build fails
rather than the target device fails later during its
initial boot operation.
Most of the common post-installation scripts generated by the build system for the out-of-the-box Yocto Project are engineered so that they can run during root filesystem creation (e.g. post-installation scripts for caching fonts). However, if you create and add custom scripts, you need to be sure they can be run during file system creation.
Here are some common problems that prevent post-installation scripts from running during root filesystem creation:
Not using $D in front of absolute paths: The build system defines
$Dat root filesystem creation time, and it is blank when run on the target device. This implies two purposes for$D: ensuring paths are valid in both the host and target environments, and checking to determine which environment is being used as a method for taking appropriate actions.Attempting to run processes that are specific to or dependent on the target architecture: You can work around these attempts by using native tools to accomplish the same tasks, or by alternatively running the processes under QEMU, which has the
qemu_run_binaryfunction. For more information, see themeta/classes/qemu.bbclassclass in the Source Directory.
With the read-only-rootfs feature enabled,
any attempt by the target to write to the root filesystem at
runtime fails.
Consequently, you must make sure that you configure processes
and applications that attempt these types of writes do so
to directories with write access (e.g.
/tmp or /var/run).
The OpenEmbedded build system makes available a series of automated tests for images to verify runtime functionality.
Note
Currently, there is only support for running these tests under QEMU.
These tests are written in Python making use of the
unittest module, and the majority of them
run commands on the target system over
ssh.
This section describes how you set up the environment to use these
tests, run available tests, and write and add your own tests.
In order to run tests, you need to do the following:
Set up to avoid interaction with
sudofor networking: To accomplish this, you must do one of the following:Add
NOPASSWDfor your user in/etc/sudoerseither for ALL commands or just forrunqemu-ifup. You must provide the full path as that can change if you are using multiple clones of the source repository.Note
On some distributions, you also need to comment out "Defaults requiretty" in/etc/sudoers.Manually configure a tap interface for your system.
Run as root the script in
scripts/runqemu-gen-tapdevs, which should generate a list of tap devices. This is the option typically chosen for Autobuilder-type environments.
Set the
DISPLAYvariable: You need to set this variable so that you have an X server available (e.g. startvncserverfor a headless machine).Be sure your host's firewall accepts incoming connections from 192.168.7.0/24: Some of the tests (in particular smart tests) start a HTTP server on a random high number port, which is used to serve files to the target. The smart module serves
${DEPLOY_DIR}/rpmso it can run smart channel commands. That means your host's firewall must accept incoming connections from 192.168.7.0/24, which is the default IP range used for tap devices byrunqemu.
Note
Regardless of how you initiate the tests, if you built your image usingrm_work,
most of the tests will fail with errors because they rely on
${WORKDIR}/installed_pkgs.txt.
You can start the tests automatically or manually:
Automatically Running Tests: To run the tests automatically after the OpenEmbedded build system successfully creates an image, first set the
TEST_IMAGEvariable to "1" in yourlocal.conffile in the Build Directory:TEST_IMAGE = "1"Next, simply build your image. If the image successfully builds, the tests will be run:
bitbake core-image-satoManually Running Tests: To manually run the tests, first globally inherit
testimage.classby editing yourlocal.conffile:INHERIT += "testimage"Next, use BitBake to run the tests:
bitbake -c testimage <image>
Regardless of how you run the tests, once they start, the following happens:
A copy of the root filesystem is written to
${WORKDIR}/testimage.The image is booted under QEMU using the standard
runqemuscript.A default timeout of 500 seconds occurs to allow for the boot process to reach the login prompt. You can change the timeout period by setting
TEST_QEMUBOOT_TIMEOUTin thelocal.conffile.Once the boot process is reached and the login prompt appears, the tests run. The full boot log is written to
${WORKDIR}/testimage/qemu_boot_log.Each test module loads in the order found in
TEST_SUITES. You can find the full output of the commands run oversshin${WORKDIR}/testimgage/ssh_target_log.If no failures occur, the task running the tests ends successfully. You can find the output from the
unittestin the task log at${WORKDIR}/temp/log.do_testimage.
All test files reside in
meta/lib/oeqa/runtime in the
Source Directory.
A test name maps directly to a Python module.
Each test module may contain a number of individual tests.
Tests are usually grouped together by the area
tested (e.g tests for systemd reside in
meta/lib/oeqa/runtime/systemd.py).
You can add tests to any layer provided you place them in the
proper area and you extend
BBPATH
in the local.conf file as normal.
Be sure that tests reside in
<layer>/lib/oeqa/runtime.
Note
Be sure that module names do not collide with module names used in the default set of test modules inmeta/lib/oeqa/runtime.
You can change the set of tests run by appending or overriding
TEST_SUITES
variable in local.conf.
Each name in TEST_SUITES represents a
required test for the image.
Test modules named within TEST_SUITES
cannot be skipped even if a test is not suitable for an image
(e.g. running the rpm tests on an image without
rpm).
Appending "auto" to TEST_SUITES causes the
build system to try to run all tests that are suitable for the
image (i.e. each test module may elect to skip itself).
The order you list tests in TEST_SUITES
is important.
The order influences test dependencies.
Consequently, tests that depend on other tests should be added
after the test on which they depend.
For example, since ssh depends on the
ping test, ssh
needs to come after ping in the list.
The test class provides no re-ordering or dependency handling.
Note
Each module can have multiple classes with multiple test methods. And, Pythonunittest rules apply.
Here are some things to keep in mind when running tests:
The default tests for the image are defined as:
DEFAULT_TEST_SUITES_pn-<image> = "ping ssh df connman syslog xorg scp vnc date rpm smart dmesg"Add your own test to the list of the by using the following:
TEST_SUITES_append = " mytest"Run a specific list of tests as follows:
TEST_SUITES = "test1 test2 test3"Remember, order is important. Be sure to place a test that is dependent on another test later in the order.
As mentioned previously, all new test files need to be in the
proper place for the build system to find them.
New tests for additional functionality outside of the core
should be added to the layer that adds the functionality, in
<layer>/lib/oeqa/runtime (as
long as
BBPATH
is extended in the layer's
layer.conf file as normal).
Just remember that filenames need to map directly to test
(module) names and that you do not use module names that
collide with existing core tests.
To create a new test, start by copying an existing module
(e.g. syslog.py or
gcc.py are good ones to use).
Test modules can use code from
meta/lib/oeqa/utils, which are helper
classes.
Note
Structure shell commands such that you rely on them and they return a single code for success. Be aware that sometimes you will need to parse the output. See thedf.py and
date.py modules for examples.
You will notice that all test classes inherit
oeRuntimeTest, which is found in
meta/lib/oetest.py.
This base class offers some helper attributes, which are
described in the following sections:
Class methods are as follows:
hasPackage(pkg): Returns "True" ifpkgis in the installed package list of the image, which is based on${WORKDIR}/installed_pkgs.txtthat is generated during thedo.rootfstask.hasFeature(feature): Returns "True" if the feature is inIMAGE_FEATURESorDISTRO_FEATURES.restartTarget(params): Restarts the QEMU image optionally passingparamsto therunqemuscript'sqemuparamslist (e.g "-m 1024" for more memory).
Class attributes are as follows:
pscmd: Equals "ps -ef" ifprocpsis installed in the image. Otherwise,pscmdequals "ps" (busybox).tc: The called text context, which gives access to the following attributes:d: The BitBake data store, which allows you to use stuff such asoeRuntimeTest.tc.d.getVar("VIRTUAL-RUNTIME_init_manager").testslistandtestsrequired: Used internally. The tests do not need these.filesdir: The absolute path tometa/lib/oeqa/runtime/files, which contains helper files for tests meant for copying on the target such as small files written in C for compilation.qemu: Provides access to theQemuRunnerobject, which is the class that boots the image. Theqemuattribute provides the following useful attributes:ip: The machine's IP address.host_ip: The host IP address, which is only used by smart tests.
target: TheSSHControlobject, which is used for running the following commands on the image:host: Used internally. The tests do not use this command.timeout: A global timeout for commands run on the target for the instance of a test. The default is 300 seconds.run(cmd, timeout=None): The single, most used method. This command is a wrapper for:ssh root@host "cmd". The command returns a tuple: (status, output), which are what their names imply - the return code of 'cmd' and whatever output it produces. The optional timeout argument represents the number of seconds the test should wait for 'cmd' to return. If the argument is "None", the test uses the default instance's timeout period, which is 300 seconds. If the argument is "0", the test runs until the command returns.copy_to(localpath, remotepath):scp localpath root@ip:remotepath.copy_from(remotepath, localpath):scp root@host:remotepath localpath.
A single instance attribute exists, which is
target.
The target instance attribute is
identical to the class attribute of the same name, which
is described in the previous section.
This attribute exists as both an instance and class
attribute so tests can use
self.target.run(cmd) in instance
methods instead of
oeRuntimeTest.tc.target.run(cmd).
GDB allows you to examine running programs, which in turn helps you to understand and fix problems. It also allows you to perform post-mortem style analysis of program crashes. GDB is available as a package within the Yocto Project and is installed in SDK images by default. See the "Images" chapter in the Yocto Project Reference Manual for a description of these images. You can find information on GDB at http://sourceware.org/gdb/.
Tip
For best results, install-dbg packages for
the applications you are going to debug.
Doing so makes extra debug symbols available that give you more
meaningful output.
Sometimes, due to memory or disk space constraints, it is not possible to use GDB directly on the remote target to debug applications. These constraints arise because GDB needs to load the debugging information and the binaries of the process being debugged. Additionally, GDB needs to perform many computations to locate information such as function names, variable names and values, stack traces and so forth - even before starting the debugging process. These extra computations place more load on the target system and can alter the characteristics of the program being debugged.
To help get past the previously mentioned constraints, you can use Gdbserver. Gdbserver runs on the remote target and does not load any debugging information from the debugged process. Instead, a GDB instance processes the debugging information that is run on a remote computer - the host GDB. The host GDB then sends control commands to Gdbserver to make it stop or start the debugged program, as well as read or write memory regions of that debugged program. All the debugging information loaded and processed as well as all the heavy debugging is done by the host GDB. Offloading these processes gives the Gdbserver running on the target a chance to remain small and fast.
Because the host GDB is responsible for loading the debugging information and for doing the necessary processing to make actual debugging happen, the user has to make sure the host can access the unstripped binaries complete with their debugging information and also be sure the target is compiled with no optimizations. The host GDB must also have local access to all the libraries used by the debugged program. Because Gdbserver does not need any local debugging information, the binaries on the remote target can remain stripped. However, the binaries must also be compiled without optimization so they match the host's binaries.
To remain consistent with GDB documentation and terminology, the binary being debugged on the remote target machine is referred to as the "inferior" binary. For documentation on GDB see the GDB site.
The remainder of this section describes the steps you need to take to debug using the GNU project debugger.
Before you can initiate a remote debugging session, you need to be sure you have set up the cross-development environment, toolchain, and sysroot. The "Preparing for Application Development" chapter of the Yocto Project Application Developer's Guide describes this process. Be sure you have read that chapter and have set up your environment.
Make sure Gdbserver is installed on the target.
If it is not, install the package
gdbserver, which needs the
libthread-db1 package.
Here is an example that when entered from the host
connects to the target and launches Gdbserver in order to
"debug" a binary named helloworld:
$ gdbserver localhost:2345 /usr/bin/helloworld
Gdbserver should now be listening on port 2345 for debugging commands coming from a remote GDB process that is running on the host computer. Communication between Gdbserver and the host GDB are done using TCP. To use other communication protocols, please refer to the Gdbserver documentation.
Running GDB on the host computer takes a number of stages, which this section describes.
A suitable GDB cross-binary is required that runs on your
host computer but also knows about the the ABI of the
remote target.
You can get this binary from the
Cross-Development Toolchain.
Here is an example where the toolchain has been installed
in the default directory
/opt/poky/1.5.4:
/opt/poky/1.4/sysroots/i686-pokysdk-linux/usr/bin/armv7a-vfp-neon-poky-linux-gnueabi/arm-poky-linux-gnueabi-gdb
where arm is the target architecture
and linux-gnueabi is the target ABI.
Alternatively, you can use BitBake to build the
gdb-cross binary.
Here is an example:
$ bitbake gdb-cross
Once the binary is built, you can find it here:
tmp/sysroots/<host-arch>/usr/bin/<target-platform>/<target-abi>-gdb
Aside from the GDB cross-binary, you also need a GDB
initialization file in the same top directory in which
your binary resides.
When you start GDB on your host development system, GDB
finds this initialization file and executes all the
commands within.
For information on the .gdbinit, see
"Debugging with GDB",
which is maintained by
sourceware.org.
You need to add a statement in the
.gdbinit file that points to your
root filesystem.
Here is an example that points to the root filesystem for
an ARM-based target device:
set sysroot /home/jzhang/sysroot_arm
Before launching the host GDB, you need to be sure
you have sourced the cross-debugging environment script,
which if you installed the root filesystem in the default
location is at /opt/poky/1.5.4
and begins with the string "environment-setup".
For more information, see the
"Setting Up the Cross-Development Environment"
section in the Yocto Project Application Developer's
Guide.
Finally, switch to the directory where the binary resides
and run the cross-gdb binary.
Provide the binary file you are going to debug.
For example, the following command continues with the
example used in the previous section by loading
the helloworld binary as well as the
debugging information:
$ arm-poky-linux-gnuabi-gdb helloworld
The commands in your .gdbinit execute
and the GDB prompt appears.
From the target, you need to connect to the remote GDB server that is running on the host. You need to specify the remote host and port. Here is the command continuing with the example:
target remote 192.168.7.2:2345
You can now proceed with debugging as normal - as if you were debugging on the local machine. For example, to instruct GDB to break in the "main" function and then continue with execution of the inferior binary use the following commands from within GDB:
(gdb) break main
(gdb) continue
For more information about using GDB, see the project's online documentation at http://sourceware.org/gdb/download/onlinedocs/.
Toaster is an Application Programming Interface (API) and
web-based interface to the OpenEmbedded build system, which uses
BitBake.
Both interfaces are based on a Representational State Transfer
(REST) API that queries for and returns build information using
GET and JSON.
These types of search operations retrieve sets of objects from
a data store used to collect build information.
The results contain all the data for the objects being returned.
You can order the results of the search by key and the search
parameters are consistent for all object types.
Using the interfaces you can do the following:
See information about the tasks executed and reused during the build.
See what is built (recipes and packages) and what packages were installed into the final image.
See performance-related information such as build time, CPU usage, and disk I/O.
Examine error, warning and trace messages to aid in debugging.
Note
This release of Toaster provides you with information about a BitBake run. The tool does not allow you to configure and launch a build. However, future development includes plans to integrate the configuration and build launching capabilities of Hob.
For more information on using Hob to build an image, see the "Image Development Using Hob" section.
The remainder of this section describes what you need to have in place to use Toaster, how to start it, use it, and stop it. For additional information on installing and running Toaster, see the "Installation and Running" section of the "Toaster" wiki page. For complete information on the API and its search operation URI, parameters, and responses, see the REST API Contracts Wiki page.
Getting set up to use and start Toaster is simple. First, be sure you have met the following requirements:
You have set up your Source Directory by cloning the upstream
pokyrepository. See the Yocto Project Release item for information on how to set up the Source Directory.You have checked out the
dora-toasterbranch:$ cd poky $ git checkout -b dora-toaster origin/dora-toasterBe sure your build machine has Django version 1.4.5 installed.
Make sure that port 8000 and 8200 are free (i.e. they have no servers on them).
Once you have met the requirements, follow these steps to start Toaster running in the background of your shell:
Note
The Toaster must be started and running in order for it to collect data.Set up your build environment: Source a build environment script (i.e.
oe-init-build-envoroe-init-build-env-memres).Prepare your local configuration file: Toaster needs the Toaster class enabled in Bitbake in order to record target image package information. You can enable it by adding the following line to your
conf/local.conffile:INHERIT += "toaster"Toaster also needs Build History enabled in Bitbake in order to record target image package information. You can enable this by adding the following two lines to your
conf/local.conffile:INHERIT += "buildhistory" BUILDHISTORY_COMMIT = "1"Start Toaster: Start the Toaster service using this command from within your build directory:
$ source toaster start
When Toaster starts, it creates some additional files in your Build Directory. Deleting these files will cause you to lose data or interrupt Toaster:
toaster.sqlite: Toaster's database file.toaster_web.log: The log file of the web server.toaster_ui.log: The log file of the user interface component.toastermain.pid: The PID of the web server.toasterui.pid: The PID of the DSI data bridge.bitbake-cookerdaemon.log: The BitBake server's log file.
Once Toaster is running, it logs information for any BitBake run from your Build Directory. This logging is automatic. All you need to do is access and use the information.
You access the information one of two ways:
Open a Browser and type enter in the
http://localhost:8000URL.Use the
xdg-opentool from the shell and pass it the same URL.
Either method opens the home page for the Toaster interface, which is temporary for this release.
The Toaster database is persistent regardless of whether you start or stop the service.
Toaster's interface shows you a list of builds (successful and unsuccessful) for which it has data. You can click on any build to see related information. This information includes configuration details, information about tasks, all recipes and packages built and their dependencies, packages installed in your final image, execution time, CPU usage and disk I/O per task.
OProfile is a statistical profiler well suited for finding performance bottlenecks in both user-space software and in the kernel. This profiler provides answers to questions like "Which functions does my application spend the most time in when doing X?" Because the OpenEmbedded build system is well integrated with OProfile, it makes profiling applications on target hardware straightforward.
Note
For more information on how to set up and run OProfile, see the "OProfile" section in the Yocto Project Profiling and Tracing Manual.
To use OProfile, you need an image that has OProfile installed.
The easiest way to do this is with tools-profile in the
IMAGE_FEATURES variable.
You also need debugging symbols to be available on the system where the analysis
takes place.
You can gain access to the symbols by using dbg-pkgs in the
IMAGE_FEATURES variable or by
installing the appropriate -dbg packages.
For successful call graph analysis, the binaries must preserve the frame
pointer register and should also be compiled with the
-fno-omit-framepointer flag.
You can achieve this by setting the
SELECTED_OPTIMIZATION
variable with the following options:
-fexpensive-optimizations
-fno-omit-framepointer
-frename-registers
-O2
You can also achieve it by setting the
DEBUG_BUILD
variable to "1" in the local.conf configuration file.
If you use the DEBUG_BUILD variable,
you also add extra debugging information that can make the debug
packages large.
Using OProfile you can perform all the profiling work on the target device. A simple OProfile session might look like the following:
# opcontrol --reset
# opcontrol --start --separate=lib --no-vmlinux -c 5
.
.
[do whatever is being profiled]
.
.
# opcontrol --stop
$ opreport -cl
In this example, the reset command clears any previously profiled data.
The next command starts OProfile.
The options used when starting the profiler separate dynamic library data
within applications, disable kernel profiling, and enable callgraphing up to
five levels deep.
Note
To profile the kernel, you would specify the--vmlinux=/path/to/vmlinux option.
The vmlinux file is usually in the source directory in the
/boot/ directory and must match the running kernel.
After you perform your profiling tasks, the next command stops the profiler.
After that, you can view results with the opreport command with options
to see the separate library symbols and callgraph information.
Callgraphing logs information about time spent in functions and about a function's calling function (parent) and called functions (children). The higher the callgraphing depth, the more accurate the results. However, higher depths also increase the logging overhead. Consequently, you should take care when setting the callgraphing depth.
Note
On ARM, binaries need to have the frame pointer enabled for callgraphing to work. To accomplish this use the-fno-omit-framepointer option
with gcc.
For more information on using OProfile, see the OProfile online documentation at http://oprofile.sourceforge.net/docs/.
A graphical user interface for OProfile is also available. You can download and build this interface from the Yocto Project at http://git.yoctoproject.org/cgit.cgi/oprofileui/. If the "tools-profile" image feature is selected, all necessary binaries are installed onto the target device for OProfileUI interaction. For a list of image features that ship with the Yocto Project, see the "Image Features" section in the Yocto Project Reference Manual.
Even though the source directory usually includes all needed patches on the target device, you might find you need other OProfile patches for recent OProfileUI features. If so, see the OProfileUI README for the most recent information.
Using OProfile in online mode assumes a working network connection with the target hardware. With this connection, you just need to run "oprofile-server" on the device. By default, OProfile listens on port 4224.
Note
You can change the port using the--port command-line
option.
The client program is called oprofile-viewer and its UI is relatively
straightforward.
You access key functionality through the buttons on the toolbar, which
are duplicated in the menus.
Here are the buttons:
Connect: Connects to the remote host. You can also supply the IP address or hostname.
Disconnect: Disconnects from the target.
Start: Starts profiling on the device.
Stop: Stops profiling on the device and downloads the data to the local host. Stopping the profiler generates the profile and displays it in the viewer.
Download: Downloads the data from the target and generates the profile, which appears in the viewer.
Reset: Resets the sample data on the device. Resetting the data removes sample information collected from previous sampling runs. Be sure you reset the data if you do not want to include old sample information.
Save: Saves the data downloaded from the target to another directory for later examination.
Open: Loads previously saved data.
The client downloads the complete 'profile archive' from
the target to the host for processing.
This archive is a directory that contains the sample data, the object files,
and the debug information for the object files.
The archive is then converted using the oparchconv script, which is
included in this distribution.
The script uses opimport to convert the archive from
the target to something that can be processed on the host.
Downloaded archives reside in the
Build Directory in
tmp and are cleared up when they are no longer in use.
If you wish to perform kernel profiling, you need to be sure
a vmlinux file that matches the running kernel is available.
In the source directory, that file is usually located in
/boot/vmlinux-KERNELVERSION, where
KERNEL-version is the version of the kernel.
The OpenEmbedded build system generates separate vmlinux
packages for each kernel it builds.
Thus, it should just be a question of making sure a matching package is
installed (e.g. opkg install kernel-vmlinux).
The files are automatically installed into development and profiling images
alongside OProfile.
A configuration option exists within the OProfileUI settings page that you can use to
enter the location of the vmlinux file.
Waiting for debug symbols to transfer from the device can be slow, and it is not always necessary to actually have them on the device for OProfile use. All that is needed is a copy of the filesystem with the debug symbols present on the viewer system. The "Launch GDB on the Host Computer" section covers how to create such a directory with the Source Directory and how to use the OProfileUI Settings Dialog to specify the location. If you specify the directory, it will be used when the file checksums match those on the system you are profiling.
If network access to the target is unavailable, you can generate
an archive for processing in oprofile-viewer as follows:
# opcontrol --reset
# opcontrol --start --separate=lib --no-vmlinux -c 5
.
.
[do whatever is being profiled]
.
.
# opcontrol --stop
# oparchive -o my_archive
In the above example, my_archive is the name of the
archive directory where you would like the profile archive to be kept.
After the directory is created, you can copy it to another host and load it
using oprofile-viewer open functionality.
If necessary, the archive is converted.
One of the concerns for a development organization using open source software is how to maintain compliance with various open source licensing during the lifecycle of the product. While this section does not provide legal advice or comprehensively cover all scenarios, it does present methods that you can use to assist you in meeting the compliance requirements during a software release.
With hundreds of different open source licenses that the Yocto Project tracks, it is difficult to know the requirements of each and every license. However, we can begin to cover the requirements of the major FLOSS licenses, by assuming that there are three main areas of concern:
Source code must be provided.
License text for the software must be provided.
Compilation scripts and modifications to the source code must be provided.
There are other requirements beyond the scope of these three and the methods described in this section (e.g. the mechanism through which source code is distributed).
As different organizations have different methods of complying with open source licensing, this section is not meant to imply that there is only one single way to meet your compliance obligations, but rather to describe one method of achieving compliance. The remainder of this section describes methods supported to meet the previously mentioned three requirements. Once you take steps to meet these requirements, and prior to releasing images, sources, and the build system, you should audit all artifacts to ensure completeness.
Note
The Yocto Project generates a license manifest during image creation that is located in${DEPLOY_DIR}/licenses/<image_name-datestamp>
to assist with any audits.
Compliance activities should begin before you generate the final image. The first thing you should look at is the requirement that tops the list for most compliance groups - providing the source. The Yocto Project has a few ways of meeting this requirement.
One of the easiest ways to meet this requirement is
to provide the entire
DL_DIR
used by the build.
This method, however, has a few issues.
The most obvious is the size of the directory since it includes
all sources used in the build and not just the source used in
the released image.
It will include toolchain source, and other artifacts, which
you would not generally release.
However, the more serious issue for most companies is accidental
release of proprietary software.
The Yocto Project provides an archiver class to help avoid
some of these concerns.
See the
"Archiving Sources - archive*.bbclass"
section in the Yocto Project Reference Manual for information
on this class.
Before you employ DL_DIR or the
archiver class, you need to decide how you choose to
provide source.
The source archiver class can generate tarballs and SRPMs
and can create them with various levels of compliance in mind.
One way of doing this (but certainly not the only way) is to
release just the original source as a tarball.
You can do this by adding the following to the
local.conf file found in the
Build Directory:
ARCHIVER_MODE ?= "original"
ARCHIVER_CLASS = "${@'archive-${ARCHIVER_MODE}-source' if ARCHIVER_MODE != 'none' else ''}"
INHERIT += "${ARCHIVER_CLASS}"
SOURCE_ARCHIVE_PACKAGE_TYPE = "tar"
During the creation of your image, the source from all
recipes that deploy packages to the image is placed within
subdirectories of
DEPLOY_DIR/sources based on the
LICENSE
for each recipe.
Releasing the entire directory enables you to comply with
requirements concerning providing the unmodified source.
It is important to note that the size of the directory can
get large.
A way to help mitigate the size issue is to only release tarballs for licenses that require the release of source. Let's assume you are only concerned with GPL code as identified with the following:
$ cd poky/build/tmp/deploy/sources
$ mkdir ~/gpl_source_release
$ for dir in */*GPL*; do cp -r $dir ~/gpl_source_release; done
At this point, you could create a tarball from the
gpl_source_release directory and
provide that to the end user.
This method would be a step toward achieving compliance
with section 3a of GPLv2 and with section 6 of GPLv3.
One requirement that is often overlooked is inclusion
of license text.
This requirement also needs to be dealt with prior to
generating the final image.
Some licenses require the license text to accompany
the binary.
You can achieve this by adding the following to your
local.conf file:
COPY_LIC_MANIFEST = "1"
COPY_LIC_DIRS = "1"
Adding these statements to the configuration file ensures that the licenses collected during package generation are included on your image. As the source archiver has already archived the original unmodified source that contains the license files, you would have already met the requirements for inclusion of the license information with source as defined by the GPL and other open source licenses.
At this point, we have addressed all we need to address prior to generating the image. The next two requirements are addressed during the final packaging of the release.
By releasing the version of the OpenEmbedded build system and the layers used during the build, you will be providing both compilation scripts and the source code modifications in one step.
If the deployment team has a BSP layer and a distro layer, and those those layers are used to patch, compile, package, or modify (in any way) any open source software included in your released images, you may be required to to release those layers under section 3 of GPLv2 or section 1 of GPLv3. One way of doing that is with a clean checkout of the version of the Yocto Project and layers used during your build. Here is an example:
# We built using the dora branch of the poky repo
$ git clone -b dora git://git.yoctoproject.org/poky
$ cd poky
# We built using the release_branch for our layers
$ git clone -b release_branch git://git.mycompany.com/meta-my-bsp-layer
$ git clone -b release_branch git://git.mycompany.com/meta-my-software-layer
# clean up the .git repos
$ find . -name ".git" -type d -exec rm -rf {} \;
One thing a development organization might want to consider
for end-user convenience is to modify
meta-yocto/conf/bblayers.conf.sample to
ensure that when the end user utilizes the released build
system to build an image, the development organization's
layers are included in the bblayers.conf
file automatically:
# LAYER_CONF_VERSION is increased each time build/conf/bblayers.conf
# changes incompatibly
LCONF_VERSION = "6"
BBPATH = "${TOPDIR}"
BBFILES ?= ""
BBLAYERS ?= " \
##OEROOT##/meta \
##OEROOT##/meta-yocto \
##OEROOT##/meta-yocto-bsp \
##OEROOT##/meta-mylayer \
"
BBLAYERS_NON_REMOVABLE ?= " \
##OEROOT##/meta \
##OEROOT##/meta-yocto \
"
Creating and providing an archive of the Metadata layers (recipes, configuration files, and so forth) enables you to meet your requirements to include the scripts to control compilation as well as any modifications to the original source.