Yocto Project Reference Manual
Copyright © 2010-2019 Linux Foundation
Permission is granted to copy, distribute and/or modify this document under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 2.0 UK: England & Wales as published by Creative Commons.
Manual Notes
This version of the Yocto Project Reference Manual is for the 2.6.1 release of the Yocto Project. To be sure you have the latest version of the manual for this release, go to the Yocto Project documentation page and select the manual from that site. Manuals from the site are more up-to-date than manuals derived from the Yocto Project released TAR files.
If you located this manual through a web search, the version of the manual might not be the one you want (e.g. the search might have returned a manual much older than the Yocto Project version with which you are working). You can see all Yocto Project major releases by visiting the Releases page. If you need a version of this manual for a different Yocto Project release, visit the Yocto Project documentation page and select the manual set by using the "ACTIVE RELEASES DOCUMENTATION" or "DOCUMENTS ARCHIVE" pull-down menus.
To report any inaccuracies or problems with this manual, send an email to the Yocto Project discussion group at
yocto@yoctoproject.comor log into the freenode#yoctochannel.
| Revision History | |
|---|---|
| Revision 4.0+git | 24 November 2010 |
| Released with the Yocto Project 0.9 Release | |
| Revision 1.0 | 6 April 2011 |
| Released with the Yocto Project 1.0 Release. | |
| Revision 1.0.1 | 23 May 2011 |
| Released with the Yocto Project 1.0.1 Release. | |
| Revision 1.1 | 6 October 2011 |
| Released with the Yocto Project 1.1 Release. | |
| Revision 1.2 | April 2012 |
| Released with the Yocto Project 1.2 Release. | |
| Revision 1.3 | October 2012 |
| Released with the Yocto Project 1.3 Release. | |
| Revision 1.4 | April 2013 |
| Released with the Yocto Project 1.4 Release. | |
| Revision 1.5 | October 2013 |
| Released with the Yocto Project 1.5 Release. | |
| Revision 1.5.1 | January 2014 |
| Released with the Yocto Project 1.5.1 Release. | |
| Revision 1.6 | April 2014 |
| Released with the Yocto Project 1.6 Release. | |
| Revision 1.7 | October 2014 |
| Released with the Yocto Project 1.7 Release. | |
| Revision 1.8 | April 2015 |
| Released with the Yocto Project 1.8 Release. | |
| Revision 2.0 | October 2015 |
| Released with the Yocto Project 2.0 Release. | |
| Revision 2.1 | April 2016 |
| Released with the Yocto Project 2.1 Release. | |
| Revision 2.2 | October 2016 |
| Released with the Yocto Project 2.2 Release. | |
| Revision 2.3 | May 2017 |
| Released with the Yocto Project 2.3 Release. | |
| Revision 2.4 | October 2017 |
| Released with the Yocto Project 2.4 Release. | |
| Revision 2.5 | May 2018 |
| Released with the Yocto Project 2.5 Release. | |
| Revision 2.6 | November 2018 |
| Released with the Yocto Project 2.6 Release. | |
| Revision 2.6.1 | February 2019 |
| Released with the Yocto Project 2.6.1 Release. | |
Table of Contents
- 1. System Requirements
- 2. Yocto Project Terms
- 3. Yocto Project Releases and the Stable Release Process
- 4. Migrating to a Newer Yocto Project Release
- 4.1. General Migration Considerations
- 4.2. Moving to the Yocto Project 1.3 Release
- 4.3. Moving to the Yocto Project 1.4 Release
- 4.4. Moving to the Yocto Project 1.5 Release
- 4.4.1. Host Dependency Changes
- 4.4.2.
atom-pcBoard Support Package (BSP) - 4.4.3. BitBake
- 4.4.4. QA Warnings
- 4.4.5. Directory Layout Changes
- 4.4.6. Shortened Git
SRCREVValues - 4.4.7.
IMAGE_FEATURES - 4.4.8.
/run - 4.4.9. Removal of Package Manager Database Within Image Recipes
- 4.4.10. Images Now Rebuild Only on Changes Instead of Every Time
- 4.4.11. Task Recipes
- 4.4.12. BusyBox
- 4.4.13. Automated Image Testing
- 4.4.14. Build History
- 4.4.15.
udev - 4.4.16. Removed and Renamed Recipes
- 4.4.17. Other Changes
- 4.5. Moving to the Yocto Project 1.6 Release
- 4.5.1.
archiverClass - 4.5.2. Packaging Changes
- 4.5.3. BitBake
- 4.5.4. Changes to Variables
- 4.5.5. Package Test (ptest)
- 4.5.6. Build Changes
- 4.5.7.
qemu-native - 4.5.8.
core-image-basic - 4.5.9. Licensing
- 4.5.10.
CFLAGSOptions - 4.5.11. Custom Image Output Types
- 4.5.12. Tasks
- 4.5.13.
update-alternativeProvider - 4.5.14.
virtclassOverrides - 4.5.15. Removed and Renamed Recipes
- 4.5.16. Removed Classes
- 4.5.17. Reference Board Support Packages (BSPs)
- 4.5.1.
- 4.6. Moving to the Yocto Project 1.7 Release
- 4.6.1. Changes to Setting QEMU
PACKAGECONFIGOptions inlocal.conf - 4.6.2. Minimum Git version
- 4.6.3. Autotools Class Changes
- 4.6.4. Binary Configuration Scripts Disabled
- 4.6.5.
eglibc 2.19Replaced withglibc 2.20 - 4.6.6. Kernel Module Autoloading
- 4.6.7. QA Check Changes
- 4.6.8. Removed Recipes
- 4.6.9. Miscellaneous Changes
- 4.6.1. Changes to Setting QEMU
- 4.7. Moving to the Yocto Project 1.8 Release
- 4.8. Moving to the Yocto Project 2.0 Release
- 4.8.1. GCC 5
- 4.8.2. Gstreamer 0.10 Removed
- 4.8.3. Removed Recipes
- 4.8.4. BitBake datastore improvements
- 4.8.5. Shell Message Function Changes
- 4.8.6. Extra Development/Debug Package Cleanup
- 4.8.7. Recipe Maintenance Tracking Data Moved to OE-Core
- 4.8.8. Automatic Stale Sysroot File Cleanup
- 4.8.9.
linux-yoctoKernel Metadata Repository Now Split from Source - 4.8.10. Additional QA checks
- 4.8.11. Miscellaneous Changes
- 4.9. Moving to the Yocto Project 2.1 Release
- 4.9.1. Variable Expansion in Python Functions
- 4.9.2. Overrides Must Now be Lower-Case
- 4.9.3. Expand Parameter to
getVar()andgetVarFlag()is Now Mandatory - 4.9.4. Makefile Environment Changes
- 4.9.5.
libexecdirReverted to${prefix}/libexec - 4.9.6.
ac_cv_sizeof_off_tis No Longer Cached in Site Files - 4.9.7. Image Generation is Now Split Out from Filesystem Generation
- 4.9.8. Removed Recipes
- 4.9.9. Class Changes
- 4.9.10. Build System User Interface Changes
- 4.9.11. ADT Removed
- 4.9.12. Poky Reference Distribution Changes
- 4.9.13. Packaging Changes
- 4.9.14. Tuning File Changes
- 4.9.15. Supporting GObject Introspection
- 4.9.16. Miscellaneous Changes
- 4.10. Moving to the Yocto Project 2.2 Release
- 4.10.1. Minimum Kernel Version
- 4.10.2. Staging Directories in Sysroot Has Been Simplified
- 4.10.3. Removal of Old Images and Other Files in
tmp/deployNow Enabled - 4.10.4. Python Changes
- 4.10.5. uClibc Replaced by musl
- 4.10.6.
${B}No Longer Default Working Directory for Tasks - 4.10.7.
runqemuPorted to Python - 4.10.8. Default Linker Hash Style Changed
- 4.10.9.
KERNEL_IMAGE_BASE_NAMEno Longer UsesKERNEL_IMAGETYPE - 4.10.10. BitBake Changes
- 4.10.11. Swabber has Been Removed
- 4.10.12. Removed Recipes
- 4.10.13. Removed Classes
- 4.10.14. Minor Packaging Changes
- 4.10.15. Miscellaneous Changes
- 4.11. Moving to the Yocto Project 2.3 Release
- 4.11.1. Recipe-specific Sysroots
- 4.11.2.
PATHVariable - 4.11.3. Changes to Scripts
- 4.11.4. Changes to Functions
- 4.11.5. BitBake Changes
- 4.11.6. Absolute Symbolic Links
- 4.11.7. GPLv2 Versions of GPLv3 Recipes Moved
- 4.11.8. Package Management Changes
- 4.11.9. Removed Recipes
- 4.11.10. Wic Changes
- 4.11.11. QA Changes
- 4.11.12. Miscellaneous Changes
- 4.12. Moving to the Yocto Project 2.4 Release
- 4.13. Moving to the Yocto Project 2.5 Release
- 4.14. Moving to the Yocto Project 2.6 Release
- 4.14.1. GCC 8.2 is Now Used by Default
- 4.14.2. Removed Recipes
- 4.14.3. Packaging Changes
- 4.14.4. XOrg Protocol dependencies
- 4.14.5.
distutilsanddistutils3Now Prevent Fetching Dependencies During thedo_configureTask - 4.14.6.
linux-yoctoConfiguration Audit Issues Now Correctly Reported - 4.14.7. Image/Kernel Artifact Naming Changes
- 4.14.8.
SERIAL_CONSOLEDeprecated - 4.14.9. Configure Script Reports Unknown Options as Errors
- 4.14.10. Override Changes
- 4.14.11.
systemdConfiguration is Now Split Intosystemd-conf - 4.14.12. Automatic Testing Changes
- 4.14.13. OpenSSL Changes
- 4.14.14. BitBake Changes
- 4.14.15. Security Changes
- 4.14.16. Post Installation Changes
- 4.14.17. Python 3 Profile-Guided Optimization
- 4.14.18. Miscellaneous Changes
- 5. Source Directory Structure
- 5.1. Top-Level Core Components
- 5.2. The Build Directory -
build/ - 5.2.1.
build/buildhistory - 5.2.2.
build/conf/local.conf - 5.2.3.
build/conf/bblayers.conf - 5.2.4.
build/conf/sanity_info - 5.2.5.
build/downloads/ - 5.2.6.
build/sstate-cache/ - 5.2.7.
build/tmp/ - 5.2.8.
build/tmp/buildstats/ - 5.2.9.
build/tmp/cache/ - 5.2.10.
build/tmp/deploy/ - 5.2.11.
build/tmp/deploy/deb/ - 5.2.12.
build/tmp/deploy/rpm/ - 5.2.13.
build/tmp/deploy/ipk/ - 5.2.14.
build/tmp/deploy/licenses/ - 5.2.15.
build/tmp/deploy/images/ - 5.2.16.
build/tmp/deploy/sdk/ - 5.2.17.
build/tmp/sstate-control/ - 5.2.18.
build/tmp/sysroots-components/ - 5.2.19.
build/tmp/sysroots/ - 5.2.20.
build/tmp/stamps/ - 5.2.21.
build/tmp/log/ - 5.2.22.
build/tmp/work/ - 5.2.23.
build/tmp/work/tunearch/recipename/version/ - 5.2.24.
build/tmp/work-shared/
- 5.2.1.
- 5.3. The Metadata -
meta/ - 5.3.1.
meta/classes/ - 5.3.2.
meta/conf/ - 5.3.3.
meta/conf/machine/ - 5.3.4.
meta/conf/distro/ - 5.3.5.
meta/conf/machine-sdk/ - 5.3.6.
meta/files/ - 5.3.7.
meta/lib/ - 5.3.8.
meta/recipes-bsp/ - 5.3.9.
meta/recipes-connectivity/ - 5.3.10.
meta/recipes-core/ - 5.3.11.
meta/recipes-devtools/ - 5.3.12.
meta/recipes-extended/ - 5.3.13.
meta/recipes-gnome/ - 5.3.14.
meta/recipes-graphics/ - 5.3.15.
meta/recipes-kernel/ - 5.3.16.
meta/recipes-lsb4/ - 5.3.17.
meta/recipes-multimedia/ - 5.3.18.
meta/recipes-rt/ - 5.3.19.
meta/recipes-sato/ - 5.3.20.
meta/recipes-support/ - 5.3.21.
meta/site/ - 5.3.22.
meta/recipes.txt
- 5.3.1.
- 6. Classes
- 6.1.
allarch.bbclass - 6.2.
archiver.bbclass - 6.3.
autotools*.bbclass - 6.4.
base.bbclass - 6.5.
bash-completion.bbclass - 6.6.
bin_package.bbclass - 6.7.
binconfig.bbclass - 6.8.
binconfig-disabled.bbclass - 6.9.
blacklist.bbclass - 6.10.
bluetooth.bbclass - 6.11.
bugzilla.bbclass - 6.12.
buildhistory.bbclass - 6.13.
buildstats.bbclass - 6.14.
buildstats-summary.bbclass - 6.15.
ccache.bbclass - 6.16.
chrpath.bbclass - 6.17.
clutter.bbclass - 6.18.
cmake.bbclass - 6.19.
cml1.bbclass - 6.20.
compress_doc.bbclass - 6.21.
copyleft_compliance.bbclass - 6.22.
copyleft_filter.bbclass - 6.23.
core-image.bbclass - 6.24.
cpan*.bbclass - 6.25.
cross.bbclass - 6.26.
cross-canadian.bbclass - 6.27.
crosssdk.bbclass - 6.28.
debian.bbclass - 6.29.
deploy.bbclass - 6.30.
devshell.bbclass - 6.31.
devupstream.bbclass - 6.32.
distro_features_check.bbclass - 6.33.
distrodata.bbclass - 6.34.
distutils*.bbclass - 6.35.
distutils3*.bbclass - 6.36.
externalsrc.bbclass - 6.37.
extrausers.bbclass - 6.38.
fontcache.bbclass - 6.39.
fs-uuid.bbclass - 6.40.
gconf.bbclass - 6.41.
gettext.bbclass - 6.42.
gnome.bbclass - 6.43.
gnomebase.bbclass - 6.44.
gobject-introspection.bbclass - 6.45.
grub-efi.bbclass - 6.46.
gsettings.bbclass - 6.47.
gtk-doc.bbclass - 6.48.
gtk-icon-cache.bbclass - 6.49.
gtk-immodules-cache.bbclass - 6.50.
gzipnative.bbclass - 6.51.
icecc.bbclass - 6.52.
image.bbclass - 6.53.
image-buildinfo.bbclass - 6.54.
image_types.bbclass - 6.55.
image-live.bbclass - 6.56.
image-mklibs.bbclass - 6.57.
image-prelink.bbclass - 6.58.
insane.bbclass - 6.59.
insserv.bbclass - 6.60.
kernel.bbclass - 6.61.
kernel-arch.bbclass - 6.62.
kernel-devicetree.bbclass - 6.63.
kernel-fitimage.bbclass - 6.64.
kernel-grub.bbclass - 6.65.
kernel-module-split.bbclass - 6.66.
kernel-uboot.bbclass - 6.67.
kernel-uimage.bbclass - 6.68.
kernel-yocto.bbclass - 6.69.
kernelsrc.bbclass - 6.70.
lib_package.bbclass - 6.71.
libc*.bbclass - 6.72.
license.bbclass - 6.73.
linux-kernel-base.bbclass - 6.74.
linuxloader.bbclass - 6.75.
logging.bbclass - 6.76.
meta.bbclass - 6.77.
metadata_scm.bbclass - 6.78.
migrate_localcount.bbclass - 6.79.
mime.bbclass - 6.80.
mirrors.bbclass - 6.81.
module.bbclass - 6.82.
module-base.bbclass - 6.83.
multilib*.bbclass - 6.84.
native.bbclass - 6.85.
nativesdk.bbclass - 6.86.
nopackages.bbclass - 6.87.
npm.bbclass - 6.88.
oelint.bbclass - 6.89.
own-mirrors.bbclass - 6.90.
package.bbclass - 6.91.
package_deb.bbclass - 6.92.
package_ipk.bbclass - 6.93.
package_rpm.bbclass - 6.94.
package_tar.bbclass - 6.95.
packagedata.bbclass - 6.96.
packagegroup.bbclass - 6.97.
patch.bbclass - 6.98.
perlnative.bbclass - 6.99.
pixbufcache.bbclass - 6.100.
pkgconfig.bbclass - 6.101.
populate_sdk.bbclass - 6.102.
populate_sdk_*.bbclass - 6.103.
prexport.bbclass - 6.104.
primport.bbclass - 6.105.
prserv.bbclass - 6.106.
ptest.bbclass - 6.107.
ptest-gnome.bbclass - 6.108.
python-dir.bbclass - 6.109.
python3native.bbclass - 6.110.
pythonnative.bbclass - 6.111.
qemu.bbclass - 6.112.
recipe_sanity.bbclass - 6.113.
relocatable.bbclass - 6.114.
remove-libtool.bbclass - 6.115.
report-error.bbclass - 6.116.
rm_work.bbclass - 6.117.
rootfs*.bbclass - 6.118.
sanity.bbclass - 6.119.
scons.bbclass - 6.120.
sdl.bbclass - 6.121.
setuptools.bbclass - 6.122.
setuptools3.bbclass - 6.123.
sign_rpm.bbclass - 6.124.
sip.bbclass - 6.125.
siteconfig.bbclass - 6.126.
siteinfo.bbclass - 6.127.
spdx.bbclass - 6.128.
sstate.bbclass - 6.129.
staging.bbclass - 6.130.
syslinux.bbclass - 6.131.
systemd.bbclass - 6.132.
systemd-boot.bbclass - 6.133.
terminal.bbclass - 6.134.
testimage*.bbclass - 6.135.
testsdk.bbclass - 6.136.
texinfo.bbclass - 6.137.
tinderclient.bbclass - 6.138.
toaster.bbclass - 6.139.
toolchain-scripts.bbclass - 6.140.
typecheck.bbclass - 6.141.
uboot-config.bbclass - 6.142.
uninative.bbclass - 6.143.
update-alternatives.bbclass - 6.144.
update-rc.d.bbclass - 6.145.
useradd*.bbclass - 6.146.
utility-tasks.bbclass - 6.147.
utils.bbclass - 6.148.
vala.bbclass - 6.149.
waf.bbclass
- 6.1.
- 7. Tasks
- 7.1. Normal Recipe Build Tasks
- 7.1.1.
do_build - 7.1.2.
do_compile - 7.1.3.
do_compile_ptest_base - 7.1.4.
do_configure - 7.1.5.
do_configure_ptest_base - 7.1.6.
do_deploy - 7.1.7.
do_distrodata - 7.1.8.
do_fetch - 7.1.9.
do_image - 7.1.10.
do_image_complete - 7.1.11.
do_install - 7.1.12.
do_install_ptest_base - 7.1.13.
do_package - 7.1.14.
do_package_qa - 7.1.15.
do_package_write_deb - 7.1.16.
do_package_write_ipk - 7.1.17.
do_package_write_rpm - 7.1.18.
do_package_write_tar - 7.1.19.
do_packagedata - 7.1.20.
do_patch - 7.1.21.
do_populate_lic - 7.1.22.
do_populate_sdk - 7.1.23.
do_populate_sysroot - 7.1.24.
do_prepare_recipe_sysroot - 7.1.25.
do_rm_work - 7.1.26.
do_unpack
- 7.1.1.
- 7.2. Manually Called Tasks
- 7.3. Image-Related Tasks
- 7.4. Kernel-Related Tasks
- 7.4.1.
do_compile_kernelmodules - 7.4.2.
do_diffconfig - 7.4.3.
do_kernel_checkout - 7.4.4.
do_kernel_configcheck - 7.4.5.
do_kernel_configme - 7.4.6.
do_kernel_menuconfig - 7.4.7.
do_kernel_metadata - 7.4.8.
do_menuconfig - 7.4.9.
do_savedefconfig - 7.4.10.
do_shared_workdir - 7.4.11.
do_sizecheck - 7.4.12.
do_strip - 7.4.13.
do_validate_branches
- 7.4.1.
- 7.5. Miscellaneous Tasks
- 8.
devtoolQuick Reference - 8.1. Getting Help
- 8.2. The Workspace Layer Structure
- 8.3. Adding a New Recipe to the Workspace Layer
- 8.4. Extracting the Source for an Existing Recipe
- 8.5. Synchronizing a Recipe's Extracted Source Tree
- 8.6. Modifying an Existing Recipe
- 8.7. Edit an Existing Recipe
- 8.8. Updating a Recipe
- 8.9. Upgrading a Recipe
- 8.10. Resetting a Recipe
- 8.11. Building Your Recipe
- 8.12. Building Your Image
- 8.13. Deploying Your Software on the Target Machine
- 8.14. Removing Your Software from the Target Machine
- 8.15. Creating the Workspace Layer in an Alternative Location
- 8.16. Get the Status of the Recipes in Your Workspace
- 8.17. Search for Available Target Recipes
- 9. OpenEmbedded Kickstart (
.wks) Reference - 10. QA Error and Warning Messages
- 11. Images
- 12. Features
- 13. Variables Glossary
- 14. Variable Context
- 15. FAQ
- 16. Contributions and Additional Information
Chapter 1. System Requirements¶
Table of Contents
Welcome to the Yocto Project Reference Manual! This manual provides reference information for the current release of the Yocto Project. The manual is best used after you have an understanding of the basics of the Yocto Project. The manual is neither meant to be read as a starting point to the Yocto Project nor read from start to finish. Use this manual to find variable definitions, class descriptions, and so forth as needed during the course of using the Yocto Project.
For introductory information on the Yocto Project, see the Yocto Project Website and the "Yocto Project Development Environment" chapter in the Yocto Project Overview and Concepts Manual.
If you want to use the Yocto Project to quickly build an image without having to understand concepts, work through the Yocto Project Quick Build document. You can find "how-to" information in the Yocto Project Development Tasks Manual. You can find Yocto Project overview and conceptual information in the Yocto Project Overview and Concepts Manual.
Tip
For more information about the Yocto Project Documentation set, see the "Links and Related Documentation" section.
1.1. Supported Linux Distributions¶
Currently, the Yocto Project is supported on the following distributions:
Notes
Yocto Project releases are tested against the stable Linux distributions in the following list. The Yocto Project should work on other distributions but validation is not performed against them.
In particular, the Yocto Project does not support and currently has no plans to support rolling-releases or development distributions due to their constantly changing nature. We welcome patches and bug reports, but keep in mind that our priority is on the supported platforms listed below.
The Yocto Project is not compatible with the Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL). You cannot use a build host that is running WSL.
If you encounter problems, please go to Yocto Project Bugzilla and submit a bug. We are interested in hearing about your experience. For information on how to submit a bug, see the Yocto Project Bugzilla wiki page and the "Submitting a Defect Against the Yocto Project" section in the Yocto Project Development Tasks Manual.
Ubuntu 16.04 (LTS)
Ubuntu 18.04
Fedora 28
CentOS 7.x
Debian GNU/Linux 8.x (Jessie)
Debian GNU/Linux 9.x (Stretch)
OpenSUSE 42.3
Note
While the Yocto Project Team attempts to ensure all Yocto Project releases are one hundred percent compatible with each officially supported Linux distribution, instances might exist where you encounter a problem while using the Yocto Project on a specific distribution.1.2. Required Packages for the Build Host¶
The list of packages you need on the host development system can be large when covering all build scenarios using the Yocto Project. This section provides required packages according to Linux distribution and function.
1.2.1. Ubuntu and Debian¶
The following list shows the required packages by function given a supported Ubuntu or Debian Linux distribution:
Note
If your build system has theoss4-dev package installed, you
might experience QEMU build failures due to the package
installing its own custom
/usr/include/linux/soundcard.h on
the Debian system.
If you run into this situation, either of the following
solutions exist:
$ sudo apt-get build-dep qemu
$ sudo apt-get remove oss4-dev
Essentials: Packages needed to build an image on a headless system:
$ sudo apt-get install gawk wget git-core diffstat unzip texinfo gcc-multilib \ build-essential chrpath socat cpio python python3 python3-pip python3-pexpect \ xz-utils debianutils iputils-pingGraphical and Eclipse Plug-In Extras: Packages recommended if the host system has graphics support or if you are going to use the Eclipse IDE:
$ sudo apt-get install libsdl1.2-dev xtermDocumentation: Packages needed if you are going to build out the Yocto Project documentation manuals:
$ sudo apt-get install make xsltproc docbook-utils fop dblatex xmltoOpenEmbedded Self-Test (
oe-selftest): Packages needed if you are going to runoe-selftest:$ sudo apt-get install python-git
1.2.2. Fedora Packages¶
The following list shows the required packages by function given a supported Fedora Linux distribution:
Essentials: Packages needed to build an image for a headless system:
$ sudo dnf install gawk make wget tar bzip2 gzip python3 unzip perl patch \ diffutils diffstat git cpp gcc gcc-c++ glibc-devel texinfo chrpath \ ccache perl-Data-Dumper perl-Text-ParseWords perl-Thread-Queue perl-bignum socat \ python3-pexpect findutils which file cpio python python3-pip xzGraphical and Eclipse Plug-In Extras: Packages recommended if the host system has graphics support or if you are going to use the Eclipse IDE:
$ sudo dnf install SDL-devel xtermDocumentation: Packages needed if you are going to build out the Yocto Project documentation manuals:
$ sudo dnf install make docbook-style-dsssl docbook-style-xsl \ docbook-dtds docbook-utils fop libxslt dblatex xmltoOpenEmbedded Self-Test (
oe-selftest): Packages needed if you are going to runoe-selftest:$ sudo dnf install python3-GitPython
1.2.3. openSUSE Packages¶
The following list shows the required packages by function given a supported openSUSE Linux distribution:
Essentials: Packages needed to build an image for a headless system:
$ sudo zypper install python gcc gcc-c++ git chrpath make wget python-xml \ diffstat makeinfo python-curses patch socat python3 python3-curses tar python3-pip \ python3-pexpect xz whichGraphical and Eclipse Plug-In Extras: Packages recommended if the host system has graphics support or if you are going to use the Eclipse IDE:
$ sudo zypper install libSDL-devel xtermDocumentation: Packages needed if you are going to build out the Yocto Project documentation manuals:
$ sudo zypper install make dblatex xmltoOpenEmbedded Self-Test (
oe-selftest): Packages needed if you are going to runoe-selftest:$ sudo zypper install python-GitPython
Note
Sanity testing, through the testimage classes, does not work on systems using the Wicked network manager.
1.2.4. CentOS Packages¶
The following list shows the required packages by function given a supported CentOS Linux distribution:
Essentials: Packages needed to build an image for a headless system:
$ sudo yum install -y epel-release $ sudo yum makecache $ sudo yum install gawk make wget tar bzip2 gzip python unzip perl patch \ diffutils diffstat git cpp gcc gcc-c++ glibc-devel texinfo chrpath socat \ perl-Data-Dumper perl-Text-ParseWords perl-Thread-Queue python34-pip xz \ which SDL-devel xtermNotes
Extra Packages for Enterprise Linux (i.e.
epel-release) is a collection of packages from Fedora built on RHEL/CentOS for easy installation of packages not included in enterprise Linux by default. You need to install these packages separately.The
makecachecommand consumes additional Metadata fromepel-release.
Graphical and Eclipse Plug-In Extras: Packages recommended if the host system has graphics support or if you are going to use the Eclipse IDE:
$ sudo yum install SDL-devel xtermDocumentation: Packages needed if you are going to build out the Yocto Project documentation manuals:
$ sudo yum install make docbook-style-dsssl docbook-style-xsl \ docbook-dtds docbook-utils fop libxslt dblatex xmltoOpenEmbedded Self-Test (
oe-selftest): Packages needed if you are going to runoe-selftest:$ sudo yum install GitPython
1.3. Required Git, tar, and Python Versions¶
In order to use the build system, your host development system must meet the following version requirements for Git, tar, and Python:
Git 1.8.3.1 or greater
tar 1.27 or greater
Python 3.4.0 or greater
If your host development system does not meet all these requirements,
you can resolve this by installing a buildtools
tarball that contains these tools.
You can get the tarball one of two ways: download a pre-built
tarball or use BitBake to build the tarball.
1.3.1. Downloading a Pre-Built buildtools Tarball¶
Downloading and running a pre-built buildtools installer is the easiest of the two methods by which you can get these tools:
Locate and download the
*.shat http://downloads.yoctoproject.org/releases/yocto/yocto-2.6.1/buildtools/.Execute the installation script. Here is an example:
$ sh ~/Downloads/x86_64-buildtools-nativesdk-standalone-2.6.1.shDuring execution, a prompt appears that allows you to choose the installation directory. For example, you could choose the following:
/home/your-username/buildtoolsSource the tools environment setup script by using a command like the following:
$ source /home/your_username/buildtools/environment-setup-i586-poky-linuxOf course, you need to supply your installation directory and be sure to use the right file (i.e. i585 or x86-64).
After you have sourced the setup script, the tools are added to
PATHand any other environment variables required to run the tools are initialized. The results are working versions versions of Git, tar, Python andchrpath.
1.3.2. Building Your Own buildtools Tarball¶
Building and running your own buildtools installer applies
only when you have a build host that can already run BitBake.
In this case, you use that machine to build the
.sh file and then
take steps to transfer and run it on a
machine that does not meet the minimal Git, tar, and Python
requirements.
Here are the steps to take to build and run your own buildtools installer:
On the machine that is able to run BitBake, be sure you have set up your build environment with the setup script (
oe-init-build-env).Run the BitBake command to build the tarball:
$ bitbake buildtools-tarballNote
TheSDKMACHINEvariable in yourlocal.conffile determines whether you build tools for a 32-bit or 64-bit system.Once the build completes, you can find the
.shfile that installs the tools in thetmp/deploy/sdksubdirectory of the Build Directory. The installer file has the string "buildtools" in the name.Transfer the
.shfile from the build host to the machine that does not meet the Git, tar, or Python requirements.On the machine that does not meet the requirements, run the
.shfile to install the tools. Here is an example:$ sh ~/Downloads/x86_64-buildtools-nativesdk-standalone-2.6.1.shDuring execution, a prompt appears that allows you to choose the installation directory. For example, you could choose the following:
/home/your_username/buildtoolsSource the tools environment setup script by using a command like the following:
$ source /home/your_username/buildtools/environment-setup-i586-poky-linuxOf course, you need to supply your installation directory and be sure to use the right file (i.e. i585 or x86-64).
After you have sourced the setup script, the tools are added to
PATHand any other environment variables required to run the tools are initialized. The results are working versions versions of Git, tar, Python andchrpath.
Chapter 2. Yocto Project Terms¶
Following is a list of terms and definitions users new to the Yocto Project development environment might find helpful. While some of these terms are universal, the list includes them just in case:
Append Files: Files that append build information to a recipe file. Append files are known as BitBake append files and
.bbappendfiles. The OpenEmbedded build system expects every append file to have a corresponding recipe (.bb) file. Furthermore, the append file and corresponding recipe file must use the same root filename. The filenames can differ only in the file type suffix used (e.g.formfactor_0.0.bbandformfactor_0.0.bbappend).Information in append files extends or overrides the information in the similarly-named recipe file. For an example of an append file in use, see the "Using .bbappend Files in Your Layer" section in the Yocto Project Development Tasks Manual.
When you name an append file, you can use the "
%" wildcard character to allow for matching recipe names. For example, suppose you have an append file named as follows:busybox_1.21.%.bbappendThat append file would match any
busybox_1.21.x.bbversion of the recipe. So, the append file would match the following recipe names:busybox_1.21.1.bb busybox_1.21.2.bb busybox_1.21.3.bbImportant
The use of the "%" character is limited in that it only works directly in front of the.bbappendportion of the append file's name. You cannot use the wildcard character in any other location of the name.BitBake: The task executor and scheduler used by the OpenEmbedded build system to build images. For more information on BitBake, see the BitBake User Manual.
Board Support Package (BSP): A group of drivers, definitions, and other components that provide support for a specific hardware configuration. For more information on BSPs, see the Yocto Project Board Support Package (BSP) Developer's Guide.
Build Directory: This term refers to the area used by the OpenEmbedded build system for builds. The area is created when you
sourcethe setup environment script that is found in the Source Directory (i.e.oe-init-build-env). TheTOPDIRvariable points to the Build Directory.You have a lot of flexibility when creating the Build Directory. Following are some examples that show how to create the directory. The examples assume your Source Directory is named
poky:Create the Build Directory inside your Source Directory and let the name of the Build Directory default to
build:$ cd $HOME/poky $ source oe-init-build-envCreate the Build Directory inside your home directory and specifically name it
test-builds:$ cd $HOME $ source poky/oe-init-build-env test-buildsProvide a directory path and specifically name the Build Directory. Any intermediate folders in the pathname must exist. This next example creates a Build Directory named
YP-21.0.1in your home directory within the existing directorymybuilds:$cd $HOME $ source $HOME/poky/oe-init-build-env $HOME/mybuilds/YP-21.0.1
Note
By default, the Build Directory containsTMPDIR, which is a temporary directory the build system uses for its work.TMPDIRcannot be under NFS. Thus, by default, the Build Directory cannot be under NFS. However, if you need the Build Directory to be under NFS, you can set this up by settingTMPDIRin yourlocal.conffile to use a local drive. Doing so effectively separatesTMPDIRfromTOPDIR, which is the Build Directory.Build Host: The system used to build images in a Yocto Project Development environment. The build system is sometimes referred to as the development host.
Classes: Files that provide for logic encapsulation and inheritance so that commonly used patterns can be defined once and then easily used in multiple recipes. For reference information on the Yocto Project classes, see the "Classes" chapter. Class files end with the
.bbclassfilename extension.Configuration File: Files that hold global definitions of variables, user-defined variables, and hardware configuration information. These files tell the OpenEmbedded build system what to build and what to put into the image to support a particular platform.
Configuration files end with a
.conffilename extension. Theconf/local.confconfiguration file in the Build Directory contains user-defined variables that affect every build. Themeta-poky/conf/distro/poky.confconfiguration file defines Yocto "distro" configuration variables used only when building with this policy. Machine configuration files, which are located throughout the Source Directory, define variables for specific hardware and are only used when building for that target (e.g. themachine/beaglebone.confconfiguration file defines variables for the Texas Instruments ARM Cortex-A8 development board).Container Layer: Layers that hold other layers. An example of a container layer is the
meta-intellayer. This layer contains BSP layers for the Intel-core2-32 Intel® Common Core (Intel-core2-32) and the Intel-corei7-64 Intel® Common Core (Intel-corei7-64). themeta-intellayer also contains thecommon/directory, which contains common content across those layers.Cross-Development Toolchain: In general, a cross-development toolchain is a collection of software development tools and utilities that run on one architecture and allow you to develop software for a different, or targeted, architecture. These toolchains contain cross-compilers, linkers, and debuggers that are specific to the target architecture.
The Yocto Project supports two different cross-development toolchains:
A toolchain only used by and within BitBake when building an image for a target architecture.
A relocatable toolchain used outside of BitBake by developers when developing applications that will run on a targeted device.
Creation of these toolchains is simple and automated. For information on toolchain concepts as they apply to the Yocto Project, see the "Cross-Development Toolchain Generation" section in the Yocto Project Overview and Concepts Manual. You can also find more information on using the relocatable toolchain in the Yocto Project Application Development and the Extensible Software Development Kit (eSDK) manual.
Extensible Software Development Kit (eSDK): A custom SDK for application developers. This eSDK allows developers to incorporate their library and programming changes back into the image to make their code available to other application developers.
For information on the eSDK, see the Yocto Project Application Development and the Extensible Software Development Kit (eSDK) manual.
Image: An image is an artifact of the BitBake build process given a collection of recipes and related Metadata. Images are the binary output that run on specific hardware or QEMU and are used for specific use-cases. For a list of the supported image types that the Yocto Project provides, see the "Images" chapter.
Layer: A collection of related recipes. Layers allow you to consolidate related metadata to customize your build. Layers also isolate information used when building for multiple architectures. Layers are hierarchical in their ability to override previous specifications. You can include any number of available layers from the Yocto Project and customize the build by adding your layers after them. You can search the Layer Index for layers used within Yocto Project.
For introductory information on layers, see the "The Yocto Project Layer Model" section in the Yocto Project Overview and Concepts Manual. For more detailed information on layers, see the "Understanding and Creating Layers" section in the Yocto Project Development Tasks Manual. For a discussion specifically on BSP Layers, see the "BSP Layers" section in the Yocto Project Board Support Packages (BSP) Developer's Guide.
Metadata: A key element of the Yocto Project is the Metadata that is used to construct a Linux distribution and is contained in the files that the OpenEmbedded build system parses when building an image. In general, Metadata includes recipes, configuration files, and other information that refers to the build instructions themselves, as well as the data used to control what things get built and the effects of the build. Metadata also includes commands and data used to indicate what versions of software are used, from where they are obtained, and changes or additions to the software itself (patches or auxiliary files) that are used to fix bugs or customize the software for use in a particular situation. OpenEmbedded-Core is an important set of validated metadata.
In the context of the kernel ("kernel Metadata"), the term refers to the kernel config fragments and features contained in the
yocto-kernel-cacheGit repository.OpenEmbedded-Core (OE-Core): OE-Core is metadata comprised of foundational recipes, classes, and associated files that are meant to be common among many different OpenEmbedded-derived systems, including the Yocto Project. OE-Core is a curated subset of an original repository developed by the OpenEmbedded community that has been pared down into a smaller, core set of continuously validated recipes. The result is a tightly controlled and an quality-assured core set of recipes.
You can see the Metadata in the
metadirectory of the Yocto Project Source Repositories.OpenEmbedded Build System: The build system specific to the Yocto Project. The OpenEmbedded build system is based on another project known as "Poky", which uses BitBake as the task executor. Throughout the Yocto Project documentation set, the OpenEmbedded build system is sometimes referred to simply as "the build system". If other build systems, such as a host or target build system are referenced, the documentation clearly states the difference.
Note
For some historical information about Poky, see the Poky term.Package: In the context of the Yocto Project, this term refers to a recipe's packaged output produced by BitBake (i.e. a "baked recipe"). A package is generally the compiled binaries produced from the recipe's sources. You "bake" something by running it through BitBake.
It is worth noting that the term "package" can, in general, have subtle meanings. For example, the packages referred to in the "Required Packages for the Build Host" section are compiled binaries that, when installed, add functionality to your Linux distribution.
Another point worth noting is that historically within the Yocto Project, recipes were referred to as packages - thus, the existence of several BitBake variables that are seemingly mis-named, (e.g.
PR,PV, andPE).Package Groups: Arbitrary groups of software Recipes. You use package groups to hold recipes that, when built, usually accomplish a single task. For example, a package group could contain the recipes for a company’s proprietary or value-add software. Or, the package group could contain the recipes that enable graphics. A package group is really just another recipe. Because package group files are recipes, they end with the
.bbfilename extension.Poky: Poky, which is pronounced Pock-ee, is a reference embedded distribution and a reference test configuration. Poky provides the following:
A base-level functional distro used to illustrate how to customize a distribution.
A means by which to test the Yocto Project components (i.e. Poky is used to validate the Yocto Project).
A vehicle through which you can download the Yocto Project.
Poky is not a product level distro. Rather, it is a good starting point for customization.
Note
Poky began an open-source project initially developed by OpenedHand. OpenedHand developed Poky from the existing OpenEmbedded build system to create a commercially supportable build system for embedded Linux. After Intel Corporation acquired OpenedHand, the poky project became the basis for the Yocto Project's build system.Recipe: A set of instructions for building packages. A recipe describes where you get source code, which patches to apply, how to configure the source, how to compile it and so on. Recipes also describe dependencies for libraries or for other recipes. Recipes represent the logical unit of execution, the software to build, the images to build, and use the
.bbfile extension.Reference Kit: A working example of a system, which includes a BSP as well as a build host and other components, that can work on specific hardware.
Source Directory: This term refers to the directory structure created as a result of creating a local copy of the
pokyGit repositorygit://git.yoctoproject.org/pokyor expanding a releasedpokytarball.Note
Creating a local copy of thepokyGit repository is the recommended method for setting up your Source Directory.Sometimes you might hear the term "poky directory" used to refer to this directory structure.
Note
The OpenEmbedded build system does not support file or directory names that contain spaces. Be sure that the Source Directory you use does not contain these types of names.The Source Directory contains BitBake, Documentation, Metadata and other files that all support the Yocto Project. Consequently, you must have the Source Directory in place on your development system in order to do any development using the Yocto Project.
When you create a local copy of the Git repository, you can name the repository anything you like. Throughout much of the documentation, "poky" is used as the name of the top-level folder of the local copy of the poky Git repository. So, for example, cloning the
pokyGit repository results in a local Git repository whose top-level folder is also named "poky".While it is not recommended that you use tarball expansion to set up the Source Directory, if you do, the top-level directory name of the Source Directory is derived from the Yocto Project release tarball. For example, downloading and unpacking
poky-thud-21.0.1.tar.bz2results in a Source Directory whose root folder is namedpoky-thud-21.0.1.It is important to understand the differences between the Source Directory created by unpacking a released tarball as compared to cloning
git://git.yoctoproject.org/poky. When you unpack a tarball, you have an exact copy of the files based on the time of release - a fixed release point. Any changes you make to your local files in the Source Directory are on top of the release and will remain local only. On the other hand, when you clone thepokyGit repository, you have an active development repository with access to the upstream repository's branches and tags. In this case, any local changes you make to the local Source Directory can be later applied to active development branches of the upstreampokyGit repository.For more information on concepts related to Git repositories, branches, and tags, see the "Repositories, Tags, and Branches" section in the Yocto Project Overview and Concepts Manual.
Task: A unit of execution for BitBake (e.g.
do_compile,do_fetch,do_patch, and so forth).Toaster: A web interface to the Yocto Project's OpenEmbedded Build System. The interface enables you to configure and run your builds. Information about builds is collected and stored in a database. For information on Toaster, see the Toaster User Manual.
Upstream: A reference to source code or repositories that are not local to the development system but located in a master area that is controlled by the maintainer of the source code. For example, in order for a developer to work on a particular piece of code, they need to first get a copy of it from an "upstream" source.
Chapter 3. Yocto Project Releases and the Stable Release Process¶
Table of Contents
The Yocto Project release process is predictable and consists of both major and minor (point) releases. This brief chapter provides information on how releases are named, their life cycle, and their stability.
3.1. Major and Minor Release Cadence¶
The Yocto Project delivers major releases (e.g. 2.6.1) using a six month cadence roughly timed each April and October of the year. Following are examples of some major YP releases with their codenames also shown. See the "Major Release Codenames" section for information on codenames used with major releases.
2.2 (Morty)
2.1 (Krogoth)
2.0 (Jethro)
While the cadence is never perfect, this timescale facilitates regular releases that have strong QA cycles while not overwhelming users with too many new releases. The cadence is predictable and avoids many major holidays in various geographies.
The Yocto project delivers minor (point) releases on an unscheduled basis and are usually driven by the accumulation of enough significant fixes or enhancements to the associated major release. Following are some example past point releases:
2.1.1
2.1.2
2.2.1
The point release indicates a point in the major release branch where a full QA cycle and release process validates the content of the new branch.
Note
Realize that there can be patches merged onto the stable release branches as and when they become available.
3.2. Major Release Codenames¶
Each major release receives a codename that identifies the release in the Yocto Project Source Repositories. The concept is that branches of Metadata with the same codename are likely to be compatible and thus work together.
Note
Codenames are associated with major releases because a Yocto Project release number (e.g. 2.6.1) could conflict with a given layer or company versioning scheme. Codenames are unique, interesting, and easily identifiable.Releases are given a nominal release version as well but the codename is used in repositories for this reason. You can find information on Yocto Project releases and codenames at https://wiki.yoctoproject.org/wiki/Releases.
3.3. Stable Release Process¶
Once released, the release enters the stable release process at which time a person is assigned as the maintainer for that stable release. This maintainer monitors activity for the release by investigating and handling nominated patches and backport activity. Only fixes and enhancements that have first been applied on the "master" branch (i.e. the current, in-development branch) are considered for backporting to a stable release.
Note
The current Yocto Project policy regarding backporting is to consider bug fixes and security fixes only. Policy dictates that features are not backported to a stable release. This policy means generic recipe version upgrades are unlikely to be accepted for backporting. The exception to this policy occurs when a strong reason exists such as the fix happens to also be the preferred upstream approach.
Stable release branches have strong maintenance for about a year after their initial release. Should significant issues be found for any release regardless of its age, fixes could be backported to older releases. For issues that are not backported given an older release, Community LTS trees and branches exist where community members share patches for older releases. However, these types of patches do not go through the same release process as do point releases. You can find more information about stable branch maintenance at https://wiki.yoctoproject.org/wiki/Stable_branch_maintenance.
3.4. Testing and Quality Assurance¶
Part of the Yocto Project development and release process is quality assurance through the execution of test strategies. Test strategies provide the Yocto Project team a way to ensure a release is validated. Additionally, because the test strategies are visible to you as a developer, you can validate your projects. This section overviews the available test infrastructure used in the Yocto Project. For information on how to run available tests on your projects, see the "Performing Automated Runtime Testing" section in the Yocto Project Development Tasks Manual.
The QA/testing infrastructure is woven into the project to the point where core developers take some of it for granted. The infrastructure consists of the following pieces:
bitbake-selftest: A standalone command that runs unit tests on key pieces of BitBake and its fetchers.sanity.bbclass: This automatically included class checks the build environment for missing tools (e.g.gcc) or common misconfigurations such asMACHINEset incorrectly.insane.bbclass: This class checks the generated output from builds for sanity. For example, if building for an ARM target, did the build produce ARM binaries. If, for example, the build produced PPC binaries then there is a problem.testimage.bbclass: This class performs runtime testing of images after they are built. The tests are usually used with QEMU to boot the images and check the combined runtime result boot operation and functions. However, the test can also use the IP address of a machine to test.ptest: Runs tests against packages produced during the build for a given piece of software. The test allows the packages to be be run within a target image.oe-selftest: Tests combination BitBake invocations. These tests operate outside the OpenEmbedded build system itself. Theoe-selftestcan run all tests by default or can run selected tests or test suites.Note
Runningoe-selftestrequires host packages beyond the "Essential" grouping. See the "Required Packages for the Build Host" section for more information.
Originally, much of this testing was done manually. However, significant effort has been made to automate the tests so that more people can use them and the Yocto Project development team can run them faster and more efficiently.
The Yocto Project's main Autobuilder
(autobuilder.yoctoproject.org) publicly tests
each Yocto Project release's code in the
OE-Core, Poky, and BitBake
repositories.
The testing occurs for both the current state of the
"master" branch and also for submitted patches.
Testing for submitted patches usually occurs in the
"ross/mut" branch in the poky-contrib repository
(i.e. the master-under-test branch) or in the "master-next" branch
in the poky repository.
Note
You can find all these branches in the Yocto Project Source Repositories.Testing within these public branches ensures in a publicly visible way that all of the main supposed architectures and recipes in OE-Core successfully build and behave properly.
Various features such as multilib, sub
architectures (e.g. x32,
poky-tiny, musl,
no-x11 and and so forth),
bitbake-selftest, and
oe-selftest are tested as part of
the QA process of a release.
Complete testing and validation for a release takes the Autobuilder
workers several hours.
Note
The Autobuilder workers are non-homogeneous, which means regular testing across a variety of Linux distributions occurs. The Autobuilder is limited to only testing QEMU-based setups and not real hardware.
Finally, in addition to the Autobuilder's tests, the Yocto Project QA team also performs testing on a variety of platforms, which includes actual hardware, to ensure expected results.
Chapter 4. Migrating to a Newer Yocto Project Release¶
Table of Contents
- 4.1. General Migration Considerations
- 4.2. Moving to the Yocto Project 1.3 Release
- 4.3. Moving to the Yocto Project 1.4 Release
- 4.4. Moving to the Yocto Project 1.5 Release
- 4.4.1. Host Dependency Changes
- 4.4.2.
atom-pcBoard Support Package (BSP) - 4.4.3. BitBake
- 4.4.4. QA Warnings
- 4.4.5. Directory Layout Changes
- 4.4.6. Shortened Git
SRCREVValues - 4.4.7.
IMAGE_FEATURES - 4.4.8.
/run - 4.4.9. Removal of Package Manager Database Within Image Recipes
- 4.4.10. Images Now Rebuild Only on Changes Instead of Every Time
- 4.4.11. Task Recipes
- 4.4.12. BusyBox
- 4.4.13. Automated Image Testing
- 4.4.14. Build History
- 4.4.15.
udev - 4.4.16. Removed and Renamed Recipes
- 4.4.17. Other Changes
- 4.5. Moving to the Yocto Project 1.6 Release
- 4.5.1.
archiverClass - 4.5.2. Packaging Changes
- 4.5.3. BitBake
- 4.5.4. Changes to Variables
- 4.5.5. Package Test (ptest)
- 4.5.6. Build Changes
- 4.5.7.
qemu-native - 4.5.8.
core-image-basic - 4.5.9. Licensing
- 4.5.10.
CFLAGSOptions - 4.5.11. Custom Image Output Types
- 4.5.12. Tasks
- 4.5.13.
update-alternativeProvider - 4.5.14.
virtclassOverrides - 4.5.15. Removed and Renamed Recipes
- 4.5.16. Removed Classes
- 4.5.17. Reference Board Support Packages (BSPs)
- 4.5.1.
- 4.6. Moving to the Yocto Project 1.7 Release
- 4.6.1. Changes to Setting QEMU
PACKAGECONFIGOptions inlocal.conf - 4.6.2. Minimum Git version
- 4.6.3. Autotools Class Changes
- 4.6.4. Binary Configuration Scripts Disabled
- 4.6.5.
eglibc 2.19Replaced withglibc 2.20 - 4.6.6. Kernel Module Autoloading
- 4.6.7. QA Check Changes
- 4.6.8. Removed Recipes
- 4.6.9. Miscellaneous Changes
- 4.6.1. Changes to Setting QEMU
- 4.7. Moving to the Yocto Project 1.8 Release
- 4.8. Moving to the Yocto Project 2.0 Release
- 4.8.1. GCC 5
- 4.8.2. Gstreamer 0.10 Removed
- 4.8.3. Removed Recipes
- 4.8.4. BitBake datastore improvements
- 4.8.5. Shell Message Function Changes
- 4.8.6. Extra Development/Debug Package Cleanup
- 4.8.7. Recipe Maintenance Tracking Data Moved to OE-Core
- 4.8.8. Automatic Stale Sysroot File Cleanup
- 4.8.9.
linux-yoctoKernel Metadata Repository Now Split from Source - 4.8.10. Additional QA checks
- 4.8.11. Miscellaneous Changes
- 4.9. Moving to the Yocto Project 2.1 Release
- 4.9.1. Variable Expansion in Python Functions
- 4.9.2. Overrides Must Now be Lower-Case
- 4.9.3. Expand Parameter to
getVar()andgetVarFlag()is Now Mandatory - 4.9.4. Makefile Environment Changes
- 4.9.5.
libexecdirReverted to${prefix}/libexec - 4.9.6.
ac_cv_sizeof_off_tis No Longer Cached in Site Files - 4.9.7. Image Generation is Now Split Out from Filesystem Generation
- 4.9.8. Removed Recipes
- 4.9.9. Class Changes
- 4.9.10. Build System User Interface Changes
- 4.9.11. ADT Removed
- 4.9.12. Poky Reference Distribution Changes
- 4.9.13. Packaging Changes
- 4.9.14. Tuning File Changes
- 4.9.15. Supporting GObject Introspection
- 4.9.16. Miscellaneous Changes
- 4.10. Moving to the Yocto Project 2.2 Release
- 4.10.1. Minimum Kernel Version
- 4.10.2. Staging Directories in Sysroot Has Been Simplified
- 4.10.3. Removal of Old Images and Other Files in
tmp/deployNow Enabled - 4.10.4. Python Changes
- 4.10.5. uClibc Replaced by musl
- 4.10.6.
${B}No Longer Default Working Directory for Tasks - 4.10.7.
runqemuPorted to Python - 4.10.8. Default Linker Hash Style Changed
- 4.10.9.
KERNEL_IMAGE_BASE_NAMEno Longer UsesKERNEL_IMAGETYPE - 4.10.10. BitBake Changes
- 4.10.11. Swabber has Been Removed
- 4.10.12. Removed Recipes
- 4.10.13. Removed Classes
- 4.10.14. Minor Packaging Changes
- 4.10.15. Miscellaneous Changes
- 4.11. Moving to the Yocto Project 2.3 Release
- 4.11.1. Recipe-specific Sysroots
- 4.11.2.
PATHVariable - 4.11.3. Changes to Scripts
- 4.11.4. Changes to Functions
- 4.11.5. BitBake Changes
- 4.11.6. Absolute Symbolic Links
- 4.11.7. GPLv2 Versions of GPLv3 Recipes Moved
- 4.11.8. Package Management Changes
- 4.11.9. Removed Recipes
- 4.11.10. Wic Changes
- 4.11.11. QA Changes
- 4.11.12. Miscellaneous Changes
- 4.12. Moving to the Yocto Project 2.4 Release
- 4.13. Moving to the Yocto Project 2.5 Release
- 4.14. Moving to the Yocto Project 2.6 Release
- 4.14.1. GCC 8.2 is Now Used by Default
- 4.14.2. Removed Recipes
- 4.14.3. Packaging Changes
- 4.14.4. XOrg Protocol dependencies
- 4.14.5.
distutilsanddistutils3Now Prevent Fetching Dependencies During thedo_configureTask - 4.14.6.
linux-yoctoConfiguration Audit Issues Now Correctly Reported - 4.14.7. Image/Kernel Artifact Naming Changes
- 4.14.8.
SERIAL_CONSOLEDeprecated - 4.14.9. Configure Script Reports Unknown Options as Errors
- 4.14.10. Override Changes
- 4.14.11.
systemdConfiguration is Now Split Intosystemd-conf - 4.14.12. Automatic Testing Changes
- 4.14.13. OpenSSL Changes
- 4.14.14. BitBake Changes
- 4.14.15. Security Changes
- 4.14.16. Post Installation Changes
- 4.14.17. Python 3 Profile-Guided Optimization
- 4.14.18. Miscellaneous Changes
This chapter provides information you can use to migrate work to a newer Yocto Project release. You can find the same information in the release notes for a given release.
4.1. General Migration Considerations¶
Some considerations are not tied to a specific Yocto Project release. This section presents information you should consider when migrating to any new Yocto Project release.
Dealing with Customized Recipes: Issues could arise if you take older recipes that contain customizations and simply copy them forward expecting them to work after you migrate to new Yocto Project metadata. For example, suppose you have a recipe in your layer that is a customized version of a core recipe copied from the earlier release, rather than through the use of an append file. When you migrate to a newer version of Yocto Project, the metadata (e.g. perhaps an include file used by the recipe) could have changed in a way that would break the build. Say, for example, a function is removed from an include file and the customized recipe tries to call that function.
You could "forward-port" all your customizations in your recipe so that everything works for the new release. However, this is not the optimal solution as you would have to repeat this process with each new release if changes occur that give rise to problems.
The better solution (where practical) is to use append files (
*.bbappend) to capture any customizations you want to make to a recipe. Doing so, isolates your changes from the main recipe making them much more manageable. However, sometimes it is not practical to use an append file. A good example of this is when introducing a newer or older version of a recipe in another layer.Updating Append Files: Since append files generally only contain your customizations, they often do not need to be adjusted for new releases. However, if the
.bbappendfile is specific to a particular version of the recipe (i.e. its name does not use the % wildcard) and the version of the recipe to which it is appending has changed, then you will at a minimum need to rename the append file to match the name of the recipe file. A mismatch between an append file and its corresponding recipe file (.bb) will trigger an error during parsing.Depending on the type of customization the append file applies, other incompatibilities might occur when you upgrade. For example, if your append file applies a patch and the recipe to which it is appending is updated to a newer version, the patch might no longer apply. If this is the case and assuming the patch is still needed, you must modify the patch file so that it does apply.
4.2. Moving to the Yocto Project 1.3 Release¶
This section provides migration information for moving to the Yocto Project 1.3 Release from the prior release.
4.2.1. Local Configuration¶
Differences include changes for
SSTATE_MIRRORS
and bblayers.conf.
4.2.1.1. SSTATE_MIRRORS¶
The shared state cache (sstate-cache), as pointed to by
SSTATE_DIR,
by default now has two-character subdirectories to prevent
issues arising from too many files in the same directory.
Also, native sstate-cache packages, which are built to run
on the host system, will go into a subdirectory named using
the distro ID string.
If you copy the newly structured sstate-cache to a mirror
location (either local or remote) and then point to it in
SSTATE_MIRRORS,
you need to append "PATH" to the end of the mirror URL so that
the path used by BitBake before the mirror substitution is
appended to the path used to access the mirror.
Here is an example:
SSTATE_MIRRORS = "file://.* http://someserver.tld/share/sstate/PATH"
4.2.1.2. bblayers.conf¶
The meta-yocto layer consists of two parts
that correspond to the Poky reference distribution and the
reference hardware Board Support Packages (BSPs), respectively:
meta-yocto and
meta-yocto-bsp.
When running BitBake for the first time after upgrading,
your conf/bblayers.conf file will be
updated to handle this change and you will be asked to
re-run or restart for the changes to take effect.
4.2.2. Recipes¶
Differences include changes for the following:
Python function whitespace
proto=inSRC_URInativesdkTask recipes
IMAGE_FEATURESRemoved recipes
4.2.2.1. Python Function Whitespace¶
All Python functions must now use four spaces for indentation.
Previously, an inconsistent mix of spaces and tabs existed,
which made extending these functions using
_append or _prepend
complicated given that Python treats whitespace as
syntactically significant.
If you are defining or extending any Python functions (e.g.
populate_packages, do_unpack,
do_patch and so forth) in custom recipes
or classes, you need to ensure you are using consistent
four-space indentation.
4.2.2.2. proto= in SRC_URI¶
Any use of proto= in
SRC_URI
needs to be changed to protocol=.
In particular, this applies to the following URIs:
svn://bzr://hg://osc://
Other URIs were already using protocol=.
This change improves consistency.
4.2.2.3. nativesdk¶
The suffix nativesdk is now implemented
as a prefix, which simplifies a lot of the packaging code for
nativesdk recipes.
All custom nativesdk recipes, which are
relocatable packages that are native to
SDK_ARCH,
and any references need to be updated to use
nativesdk-* instead of
*-nativesdk.
4.2.2.4. Task Recipes¶
"Task" recipes are now known as "Package groups" and have
been renamed from task-*.bb to
packagegroup-*.bb.
Existing references to the previous task-*
names should work in most cases as there is an automatic
upgrade path for most packages.
However, you should update references in your own recipes and
configurations as they could be removed in future releases.
You should also rename any custom task-*
recipes to packagegroup-*, and change
them to inherit packagegroup instead of
task, as well as taking the opportunity
to remove anything now handled by
packagegroup.bbclass, such as providing
-dev and -dbg
packages, setting
LIC_FILES_CHKSUM,
and so forth.
See the
"packagegroup.bbclass"
section for further details.
4.2.2.5. IMAGE_FEATURES¶
Image recipes that previously included "apps-console-core"
in IMAGE_FEATURES
should now include "splash" instead to enable the boot-up
splash screen.
Retaining "apps-console-core" will still include the splash
screen but generates a warning.
The "apps-x11-core" and "apps-x11-games"
IMAGE_FEATURES features have been removed.
4.2.2.6. Removed Recipes¶
The following recipes have been removed. For most of them, it is unlikely that you would have any references to them in your own Metadata. However, you should check your metadata against this list to be sure:
libx11-trim: Replaced bylibx11, which has a negligible size difference with modern Xorg.xserver-xorg-lite: Usexserver-xorg, which has a negligible size difference when DRI and GLX modules are not installed.xserver-kdrive: Effectively unmaintained for many years.mesa-xlib: No longer serves any purpose.galago: Replaced by telepathy.gail: Functionality was integrated into GTK+ 2.13.eggdbus: No longer needed.gcc-*-intermediate: The build has been restructured to avoid the need for this step.libgsmd: Unmaintained for many years. Functionality now provided byofonoinstead.contacts, dates, tasks, eds-tools: Largely unmaintained PIM application suite. It has been moved to
meta-gnomeinmeta-openembedded.
In addition to the previously listed changes, the
meta-demoapps directory has also been removed
because the recipes in it were not being maintained and many
had become obsolete or broken.
Additionally, these recipes were not parsed in the default configuration.
Many of these recipes are already provided in an updated and
maintained form within the OpenEmbedded community layers such as
meta-oe and meta-gnome.
For the remainder, you can now find them in the
meta-extras repository, which is in the
Yocto Project
Source Repositories.
4.2.3. Linux Kernel Naming¶
The naming scheme for kernel output binaries has been changed to
now include
PE as part of the
filename:
KERNEL_IMAGE_BASE_NAME ?= "${KERNEL_IMAGETYPE}-${PE}-${PV}-${PR}-${MACHINE}-${DATETIME}"
Because the PE variable is not set by default,
these binary files could result with names that include two dash
characters.
Here is an example:
bzImage--3.10.9+git0+cd502a8814_7144bcc4b8-r0-qemux86-64-20130830085431.bin
4.3. Moving to the Yocto Project 1.4 Release¶
This section provides migration information for moving to the Yocto Project 1.4 Release from the prior release.
4.3.1. BitBake¶
Differences include the following:
Comment Continuation: If a comment ends with a line continuation (\) character, then the next line must also be a comment. Any instance where this is not the case, now triggers a warning. You must either remove the continuation character, or be sure the next line is a comment.
Package Name Overrides: The runtime package specific variables
RDEPENDS,RRECOMMENDS,RSUGGESTS,RPROVIDES,RCONFLICTS,RREPLACES,FILES,ALLOW_EMPTY, and the pre, post, install, and uninstall script functionspkg_preinst,pkg_postinst,pkg_prerm, andpkg_postrmshould always have a package name override. For example, useRDEPENDS_${PN}for the main package instead ofRDEPENDS. BitBake uses more strict checks when it parses recipes.
4.3.2. Build Behavior¶
Differences include the following:
Shared State Code: The shared state code has been optimized to avoid running unnecessary tasks. For example, the following no longer populates the target sysroot since that is not necessary:
$ bitbake -c rootfssome-imageInstead, the system just needs to extract the output package contents, re-create the packages, and construct the root filesystem. This change is unlikely to cause any problems unless you have missing declared dependencies.
Scanning Directory Names: When scanning for files in
SRC_URI, the build system now usesFILESOVERRIDESinstead ofOVERRIDESfor the directory names. In general, the values previously inOVERRIDESare now inFILESOVERRIDESas well. However, if you relied upon an additional value you previously added toOVERRIDES, you might now need to add it toFILESOVERRIDESunless you are already adding it through theMACHINEOVERRIDESorDISTROOVERRIDESvariables, as appropriate. For more related changes, see the "Variables" section.
4.3.3. Proxies and Fetching Source¶
A new oe-git-proxy script has been added to
replace previous methods of handling proxies and fetching source
from Git.
See the meta-yocto/conf/site.conf.sample file
for information on how to use this script.
4.3.4. Custom Interfaces File (netbase change)¶
If you have created your own custom
etc/network/interfaces file by creating
an append file for the netbase recipe,
you now need to create an append file for the
init-ifupdown recipe instead, which you can
find in the
Source Directory
at meta/recipes-core/init-ifupdown.
For information on how to use append files, see the
"Using .bbappend Files"
section in the Yocto Project Development Tasks Manual.
4.3.5. Remote Debugging¶
Support for remote debugging with the Eclipse IDE is now
separated into an image feature
(eclipse-debug) that corresponds to the
packagegroup-core-eclipse-debug package group.
Previously, the debugging feature was included through the
tools-debug image feature, which corresponds
to the packagegroup-core-tools-debug
package group.
4.3.6. Variables¶
The following variables have changed:
SANITY_TESTED_DISTROS: This variable now uses a distribution ID, which is composed of the host distributor ID followed by the release. Previously,SANITY_TESTED_DISTROSwas composed of the description field. For example, "Ubuntu 12.10" becomes "Ubuntu-12.10". You do not need to worry about this change if you are not specifically setting this variable, or if you are specifically setting it to "".SRC_URI: The${PN},${PF},${P}, andFILE_DIRNAMEdirectories have been dropped from the default value of theFILESPATHvariable, which is used as the search path for finding files referred to inSRC_URI. If you have a recipe that relied upon these directories, which would be unusual, then you will need to add the appropriate paths within the recipe or, alternatively, rearrange the files. The most common locations are still covered by${BP},${BPN}, and "files", which all remain in the default value ofFILESPATH.
4.3.7. Target Package Management with RPM¶
If runtime package management is enabled and the RPM backend is selected, Smart is now installed for package download, dependency resolution, and upgrades instead of Zypper. For more information on how to use Smart, run the following command on the target:
smart --help
4.3.8. Recipes Moved¶
The following recipes were moved from their previous locations because they are no longer used by anything in the OpenEmbedded-Core:
clutter-box2d: Now resides in themeta-oelayer.evolution-data-server: Now resides in themeta-gnomelayer.gthumb: Now resides in themeta-gnomelayer.gtkhtml2: Now resides in themeta-oelayer.gupnp: Now resides in themeta-multimedialayer.gypsy: Now resides in themeta-oelayer.libcanberra: Now resides in themeta-gnomelayer.libgdata: Now resides in themeta-gnomelayer.libmusicbrainz: Now resides in themeta-multimedialayer.metacity: Now resides in themeta-gnomelayer.polkit: Now resides in themeta-oelayer.zeroconf: Now resides in themeta-networkinglayer.
4.3.9. Removals and Renames¶
The following list shows what has been removed or renamed:
evieext: Removed because it has been removed fromxserversince 2008.Gtk+ DirectFB: Removed support because upstream Gtk+ no longer supports it as of version 2.18.
libxfontcache / xfontcacheproto: Removed because they were removed from the Xorg server in 2008.libxp / libxprintapputil / libxprintutil / printproto: Removed because the XPrint server was removed from Xorg in 2008.libxtrap / xtrapproto: Removed because their functionality was broken upstream.linux-yocto 3.0 kernel: Removed with linux-yocto 3.8 kernel being added. The linux-yocto 3.2 and linux-yocto 3.4 kernels remain as part of the release.
lsbsetup: Removed with functionality now provided bylsbtest.matchbox-stroke: Removed because it was never more than a proof-of-concept.matchbox-wm-2 / matchbox-theme-sato-2: Removed because they are not maintained. However,matchbox-wmandmatchbox-theme-satoare still provided.mesa-dri: Renamed tomesa.mesa-xlib: Removed because it was no longer useful.mutter: Removed because nothing ever uses it and the recipe is very old.orinoco-conf: Removed because it has become obsolete.update-modules: Removed because it is no longer used. The kernel modulepostinstallandpostrmscripts can now do the same task without the use of this script.web: Removed because it is not maintained. Superseded byweb-webkit.xf86bigfontproto: Removed because upstream it has been disabled by default since 2007. Nothing usesxf86bigfontproto.xf86rushproto: Removed because its dependency inxserverwas spurious and it was removed in 2005.zypper / libzypp / sat-solver: Removed and been functionally replaced with Smart (python-smartpm) when RPM packaging is used and package management is enabled on the target.
4.4. Moving to the Yocto Project 1.5 Release¶
This section provides migration information for moving to the Yocto Project 1.5 Release from the prior release.
4.4.1. Host Dependency Changes¶
The OpenEmbedded build system now has some additional requirements on the host system:
Python 2.7.3+
Tar 1.24+
Git 1.7.8+
Patched version of Make if you are using 3.82. Most distributions that provide Make 3.82 use the patched version.
If the Linux distribution you are using on your build host does not provide packages for these, you can install and use the Buildtools tarball, which provides an SDK-like environment containing them.
For more information on this requirement, see the "Required Git, tar, and Python Versions" section.
4.4.2. atom-pc Board Support Package (BSP)¶
The atom-pc hardware reference BSP has been
replaced by a genericx86 BSP.
This BSP is not necessarily guaranteed to work on all x86
hardware, but it will run on a wider range of systems than the
atom-pc did.
Note
Additionally, agenericx86-64 BSP has
been added for 64-bit Atom systems.
4.4.3. BitBake¶
The following changes have been made that relate to BitBake:
BitBake now supports a
_removeoperator. The addition of this operator means you will have to rename any items in recipe space (functions, variables) whose names currently contain_remove_or end with_removeto avoid unexpected behavior.BitBake's global method pool has been removed. This method is not particularly useful and led to clashes between recipes containing functions that had the same name.
The "none" server backend has been removed. The "process" server backend has been serving well as the default for a long time now.
The
bitbake-runtaskscript has been removed.${P}and${PF}are no longer added toPROVIDESby default inbitbake.conf. These version-specificPROVIDESitems were seldom used. Attempting to use them could result in two versions being built simultaneously rather than just one version due to the way BitBake resolves dependencies.
4.4.4. QA Warnings¶
The following changes have been made to the package QA checks:
If you have customized
ERROR_QAorWARN_QAvalues in your configuration, check that they contain all of the issues that you wish to be reported. Previous Yocto Project versions contained a bug that meant that any item not mentioned inERROR_QAorWARN_QAwould be treated as a warning. Consequently, several important items were not already in the default value ofWARN_QA. All of the possible QA checks are now documented in the "insane.bbclass" section.An additional QA check has been added to check if
/usr/share/info/diris being installed. Your recipe should delete this file withindo_installif "make install" is installing it.If you are using the buildhistory class, the check for the package version going backwards is now controlled using a standard QA check. Thus, if you have customized your
ERROR_QAorWARN_QAvalues and still wish to have this check performed, you should add "version-going-backwards" to your value for one or the other variables depending on how you wish it to be handled. See the documented QA checks in the "insane.bbclass" section.
4.4.5. Directory Layout Changes¶
The following directory changes exist:
Output SDK installer files are now named to include the image name and tuning architecture through the
SDK_NAMEvariable.Images and related files are now installed into a directory that is specific to the machine, instead of a parent directory containing output files for multiple machines. The
DEPLOY_DIR_IMAGEvariable continues to point to the directory containing images for the currentMACHINEand should be used anywhere there is a need to refer to this directory. Therunqemuscript now uses this variable to find images and kernel binaries and will use BitBake to determine the directory. Alternatively, you can set theDEPLOY_DIR_IMAGEvariable in the external environment.When buildhistory is enabled, its output is now written under the Build Directory rather than
TMPDIR. Doing so makes it easier to deleteTMPDIRand preserve the build history. Additionally, data for produced SDKs is now split byIMAGE_NAME.The
pkgdatadirectory produced as part of the packaging process has been collapsed into a single machine-specific directory. This directory is located undersysrootsand uses a machine-specific name (i.e.tmp/sysroots/).machine/pkgdata
4.4.6. Shortened Git SRCREV Values¶
BitBake will now shorten revisions from Git repositories from the
normal 40 characters down to 10 characters within
SRCPV
for improved usability in path and file names.
This change should be safe within contexts where these revisions
are used because the chances of spatially close collisions
is very low.
Distant collisions are not a major issue in the way
the values are used.
4.4.7. IMAGE_FEATURES¶
The following changes have been made that relate to
IMAGE_FEATURES:
The value of
IMAGE_FEATURESis now validated to ensure invalid feature items are not added. Some users mistakenly add package names to this variable instead of usingIMAGE_INSTALLin order to have the package added to the image, which does not work. This change is intended to catch those kinds of situations. ValidIMAGE_FEATURESare drawn fromPACKAGE_GROUPdefinitions,COMPLEMENTARY_GLOBand a new "validitems" varflag onIMAGE_FEATURES. The "validitems" varflag change allows additional features to be added if they are not provided using the previous two mechanisms.The previously deprecated "apps-console-core"
IMAGE_FEATURESitem is no longer supported. Add "splash" toIMAGE_FEATURESif you wish to have the splash screen enabled, since this is all that apps-console-core was doing.
4.4.8. /run¶
The /run directory from the Filesystem
Hierarchy Standard 3.0 has been introduced.
You can find some of the implications for this change
here.
The change also means that recipes that install files to
/var/run must be changed.
You can find a guide on how to make these changes
here.
4.4.9. Removal of Package Manager Database Within Image Recipes¶
The image core-image-minimal no longer adds
remove_packaging_data_files to
ROOTFS_POSTPROCESS_COMMAND.
This addition is now handled automatically when "package-management"
is not in
IMAGE_FEATURES.
If you have custom image recipes that make this addition,
you should remove the lines, as they are not needed and might
interfere with correct operation of postinstall scripts.
4.4.10. Images Now Rebuild Only on Changes Instead of Every Time¶
The
do_rootfs
and other related image
construction tasks are no longer marked as "nostamp".
Consequently, they will only be re-executed when their inputs have
changed.
Previous versions of the OpenEmbedded build system always rebuilt
the image when requested rather when necessary.
4.4.11. Task Recipes¶
The previously deprecated task.bbclass has
now been dropped.
For recipes that previously inherited from this class, you should
rename them from task-* to
packagegroup-* and inherit packagegroup
instead.
For more information, see the
"packagegroup.bbclass"
section.
4.4.12. BusyBox¶
By default, we now split BusyBox into two binaries:
one that is suid root for those components that need it, and
another for the rest of the components.
Splitting BusyBox allows for optimization that eliminates the
tinylogin recipe as recommended by upstream.
You can disable this split by setting
BUSYBOX_SPLIT_SUID
to "0".
4.4.13. Automated Image Testing¶
A new automated image testing framework has been added
through the
testimage.bbclass
class.
This framework replaces the older
imagetest-qemu framework.
You can learn more about performing automated image tests in the "Performing Automated Runtime Testing" section in the Yocto Project Development Tasks Manual.
4.4.14. Build History¶
Following are changes to Build History:
Installed package sizes:
installed-package-sizes.txtfor an image now records the size of the files installed by each package instead of the size of each compressed package archive file.The dependency graphs (
depends*.dot) now use the actual package names instead of replacing dashes, dots and plus signs with underscores.The
buildhistory-diffandbuildhistory-collect-srcrevsutilities have improved command-line handling. Use the--helpoption for each utility for more information on the new syntax.
For more information on Build History, see the "Maintaining Build Output Quality" section in the Yocto Project Development Tasks Manual.
4.4.15. udev¶
Following are changes to udev:
udevno longer brings inudev-extraconfautomatically throughRRECOMMENDS, since this was originally intended to be optional. If you need the extra rules, then addudev-extraconfto your image.udevno longer brings inpciutils-idsorusbutils-idsthroughRRECOMMENDS. These are not needed byudevitself and removing them saves around 350KB.
4.4.16. Removed and Renamed Recipes¶
The
linux-yocto3.2 kernel has been removed.libtool-nativesdkhas been renamed tonativesdk-libtool.tinyloginhas been removed. It has been replaced by a suid portion of Busybox. See the "BusyBox" section for more information.external-python-tarballhas been renamed tobuildtools-tarball.web-webkithas been removed. It has been functionally replaced bymidori.imakehas been removed. It is no longer needed by any other recipe.transfig-nativehas been removed. It is no longer needed by any other recipe.anjuta-remote-runhas been removed. Anjuta IDE integration has not been officially supported for several releases.
4.4.17. Other Changes¶
Following is a list of short entries describing other changes:
run-postinsts: Make this generic.base-files: Remove the unnecessarymedia/xxxdirectories.alsa-state: Provide an emptyasound.confby default.classes/image: EnsureBAD_RECOMMENDATIONSsupports pre-renamed package names.classes/rootfs_rpm: ImplementBAD_RECOMMENDATIONSfor RPM.systemd: Removesystemd_unitdirifsystemdis not inDISTRO_FEATURES.systemd: Removeinit.ddir ifsystemdunit file is present andsysvinitis not a distro feature.libpam: Deny all services for theOTHERentries.image.bbclass: Moveruntime_mapping_renameto avoid conflict withmultilib. SeeYOCTO #4993in Bugzilla for more information.linux-dtb: Use kernel build system to generate thedtbfiles.kern-tools: Switch from guilt to newkgit-s2qtool.
4.5. Moving to the Yocto Project 1.6 Release¶
This section provides migration information for moving to the Yocto Project 1.6 Release from the prior release.
4.5.1. archiver Class¶
The
archiver
class has been rewritten and its configuration has been simplified.
For more details on the source archiver, see the
"Maintaining Open Source License Compliance During Your Product's Lifecycle"
section in the Yocto Project Development Tasks Manual.
4.5.2. Packaging Changes¶
The following packaging changes have been made:
The
binutilsrecipe no longer produces abinutils-symlinkspackage.update-alternativesis now used to handle the preferredbinutilsvariant on the target instead.The tc (traffic control) utilities have been split out of the main
iproute2package and put into theiproute2-tcpackage.The
gtk-enginesschemas have been moved to a dedicatedgtk-engines-schemaspackage.The
armv7awith thumb package architecture suffix has changed. The suffix for these packages with the thumb optimization enabled is "t2" as it should be. Use of this suffix was not the case in the 1.5 release. Architecture names will change within package feeds as a result.
4.5.3. BitBake¶
The following changes have been made to BitBake.
4.5.3.1. Matching Branch Requirement for Git Fetching¶
When fetching source from a Git repository using
SRC_URI,
BitBake will now validate the
SRCREV
value against the branch.
You can specify the branch using the following form:
SRC_URI = "git://server.name/repository;branch=branchname"
If you do not specify a branch, BitBake looks in the default "master" branch.
Alternatively, if you need to bypass this check (e.g.
if you are fetching a revision corresponding to a tag that
is not on any branch), you can add ";nobranch=1" to
the end of the URL within SRC_URI.
4.5.3.2. Python Definition substitutions¶
BitBake had some previously deprecated Python definitions
within its bb module removed.
You should use their sub-module counterparts instead:
bb.MalformedUrl: Usebb.fetch.MalformedUrl.bb.encodeurl: Usebb.fetch.encodeurl.bb.decodeurl: Usebb.fetch.decodeurlbb.mkdirhier: Usebb.utils.mkdirhier.bb.movefile: Usebb.utils.movefile.bb.copyfile: Usebb.utils.copyfile.bb.which: Usebb.utils.which.bb.vercmp_string: Usebb.utils.vercmp_string.bb.vercmp: Usebb.utils.vercmp.
4.5.3.3. SVK Fetcher¶
The SVK fetcher has been removed from BitBake.
4.5.3.4. Console Output Error Redirection¶
The BitBake console UI will now output errors to
stderr instead of
stdout.
Consequently, if you are piping or redirecting the output of
bitbake to somewhere else, and you wish
to retain the errors, you will need to add
2>&1 (or something similar) to the
end of your bitbake command line.
4.5.3.5. task-taskname Overrides¶
task-taskname overrides have been
adjusted so that tasks whose names contain underscores have the
underscores replaced by hyphens for the override so that they
now function properly.
For example, the task override for
do_populate_sdk
is task-populate-sdk.
4.5.4. Changes to Variables¶
The following variables have changed. For information on the OpenEmbedded build system variables, see the "Variables Glossary" Chapter.
4.5.4.1. TMPDIR¶
TMPDIR
can no longer be on an NFS mount.
NFS does not offer full POSIX locking and inode consistency
and can cause unexpected issues if used to store
TMPDIR.
The check for this occurs on startup.
If TMPDIR is detected on an NFS mount,
an error occurs.
4.5.4.2. PRINC¶
The PRINC
variable has been deprecated and triggers a warning if
detected during a build.
For
PR
increments on changes, use the PR service instead.
You can find out more about this service in the
"Working With a PR Service"
section in the Yocto Project Development Tasks Manual.
4.5.4.3. IMAGE_TYPES¶
The "sum.jffs2" option for
IMAGE_TYPES
has been replaced by the "jffs2.sum" option, which fits the
processing order.
4.5.4.4. COPY_LIC_MANIFEST¶
The
COPY_LIC_MANIFEST
variable must
now be set to "1" rather than any value in order to enable
it.
4.5.4.5. COPY_LIC_DIRS¶
The
COPY_LIC_DIRS
variable must
now be set to "1" rather than any value in order to enable
it.
4.5.4.6. PACKAGE_GROUP¶
The
PACKAGE_GROUP
variable has been renamed to
FEATURE_PACKAGES
to more accurately reflect its purpose.
You can still use PACKAGE_GROUP but
the OpenEmbedded build system produces a warning message when
it encounters the variable.
4.5.4.7. Preprocess and Post Process Command Variable Behavior¶
The following variables now expect a semicolon separated list of functions to call and not arbitrary shell commands:
ROOTFS_PREPROCESS_COMMAND
ROOTFS_POSTPROCESS_COMMAND
SDK_POSTPROCESS_COMMAND
POPULATE_SDK_POST_TARGET_COMMAND
POPULATE_SDK_POST_HOST_COMMAND
IMAGE_POSTPROCESS_COMMAND
IMAGE_PREPROCESS_COMMAND
ROOTFS_POSTUNINSTALL_COMMAND
ROOTFS_POSTINSTALL_COMMAND
For migration purposes, you can simply wrap shell commands in a shell function and then call the function. Here is an example:
my_postprocess_function() {
echo "hello" > ${IMAGE_ROOTFS}/hello.txt
}
ROOTFS_POSTPROCESS_COMMAND += "my_postprocess_function; "
4.5.5. Package Test (ptest)¶
Package Tests (ptest) are built but not installed by default.
For information on using Package Tests, see the
"Testing Packages with ptest"
section in the Yocto Project Development Tasks Manual.
For information on the ptest class, see the
"ptest.bbclass"
section.
4.5.6. Build Changes¶
Separate build and source directories have been enabled
by default for selected recipes where it is known to work
(a whitelist) and for all recipes that inherit the
cmake
class.
In future releases the
autotools
class will enable a separate build directory by default as
well.
Recipes building Autotools-based
software that fails to build with a separate build directory
should be changed to inherit from the
autotools-brokensep
class instead of the autotools or
autotools_stageclasses.
4.5.7. qemu-native¶
qemu-native now builds without
SDL-based graphical output support by default.
The following additional lines are needed in your
local.conf to enable it:
PACKAGECONFIG_pn-qemu-native = "sdl"
ASSUME_PROVIDED += "libsdl-native"
Note
The defaultlocal.conf
contains these statements.
Consequently, if you are building a headless system and using
a default local.conf file, you will need
comment these two lines out.
4.5.8. core-image-basic¶
core-image-basic has been renamed to
core-image-full-cmdline.
In addition to core-image-basic being renamed,
packagegroup-core-basic has been renamed to
packagegroup-core-full-cmdline to match.
4.5.9. Licensing¶
The top-level LICENSE file has been changed
to better describe the license of the various components of
OE-Core.
However, the licensing itself remains unchanged.
Normally, this change would not cause any side-effects.
However, some recipes point to this file within
LIC_FILES_CHKSUM
(as ${COREBASE}/LICENSE) and thus the
accompanying checksum must be changed from
3f40d7994397109285ec7b81fdeb3b58 to
4d92cd373abda3937c2bc47fbc49d690.
A better alternative is to have
LIC_FILES_CHKSUM point to a file
describing the license that is distributed with the source
that the recipe is building, if possible, rather than pointing
to ${COREBASE}/LICENSE.
4.5.10. CFLAGS Options¶
The "-fpermissive" option has been removed from the default
CFLAGS
value.
You need to take action on individual recipes that fail when
building with this option.
You need to either patch the recipes to fix the issues reported by
the compiler, or you need to add "-fpermissive" to
CFLAGS in the recipes.
4.5.11. Custom Image Output Types¶
Custom image output types, as selected using
IMAGE_FSTYPES,
must declare their dependencies on other image types (if any) using
a new
IMAGE_TYPEDEP
variable.
4.5.12. Tasks¶
The do_package_write task has been removed.
The task is no longer needed.
4.5.13. update-alternative Provider¶
The default update-alternatives provider has
been changed from opkg to
opkg-utils.
This change resolves some troublesome circular dependencies.
The runtime package has also been renamed from
update-alternatives-cworth
to update-alternatives-opkg.
4.5.14. virtclass Overrides¶
The virtclass overrides are now deprecated.
Use the equivalent class overrides instead (e.g.
virtclass-native becomes
class-native.)
4.5.15. Removed and Renamed Recipes¶
The following recipes have been removed:
packagegroup-toolset-native- This recipe is largely unused.linux-yocto-3.8- Support for the Linux yocto 3.8 kernel has been dropped. Support for the 3.10 and 3.14 kernels have been added with thelinux-yocto-3.10andlinux-yocto-3.14recipes.ocf-linux- This recipe has been functionally replaced usingcryptodev-linux.genext2fs-genext2fsis no longer used by the build system and is unmaintained upstream.js- This provided an ancient version of Mozilla's javascript engine that is no longer needed.zaurusd- The recipe has been moved to themeta-handheldlayer.eglibc 2.17- Replaced by theeglibc 2.19recipe.gcc 4.7.2- Replaced by the now stablegcc 4.8.2.external-sourcery-toolchain- this recipe is now maintained in themeta-sourcerylayer.linux-libc-headers-yocto 3.4+git- Now using version 3.10 of thelinux-libc-headersby default.meta-toolchain-gmae- This recipe is obsolete.packagegroup-core-sdk-gmae- This recipe is obsolete.packagegroup-core-standalone-gmae-sdk-target- This recipe is obsolete.
4.5.16. Removed Classes¶
The following classes have become obsolete and have been removed:
module_strippkg_metainfopkg_distributeimage-empty
4.5.17. Reference Board Support Packages (BSPs)¶
The following reference BSPs changes occurred:
The BeagleBoard (
beagleboard) ARM reference hardware has been replaced by the BeagleBone (beaglebone) hardware.The RouterStation Pro (
routerstationpro) MIPS reference hardware has been replaced by the EdgeRouter Lite (edgerouter) hardware.
The previous reference BSPs for the
beagleboard and
routerstationpro machines are still available
in a new meta-yocto-bsp-old layer in the
Source Repositories
at
http://git.yoctoproject.org/cgit/cgit.cgi/meta-yocto-bsp-old/.
4.6. Moving to the Yocto Project 1.7 Release¶
This section provides migration information for moving to the Yocto Project 1.7 Release from the prior release.
4.6.1. Changes to Setting QEMU PACKAGECONFIG Options in local.conf¶
The QEMU recipe now uses a number of
PACKAGECONFIG
options to enable various optional features.
The method used to set defaults for these options means that
existing
local.conf files will need to be be
modified to append to PACKAGECONFIG for
qemu-native and
nativesdk-qemu instead of setting it.
In other words, to enable graphical output for QEMU, you should
now have these lines in local.conf:
PACKAGECONFIG_append_pn-qemu-native = " sdl"
PACKAGECONFIG_append_pn-nativesdk-qemu = " sdl"
4.6.2. Minimum Git version¶
The minimum
Git version
required on the build host is now 1.7.8 because the
--list option is now required by
BitBake's Git fetcher.
As always, if your host distribution does not provide a version of
Git that meets this requirement, you can use the
buildtools-tarball that does.
See the
"Required Git, tar, and Python Versions"
section for more information.
4.6.3. Autotools Class Changes¶
The following
autotools
class changes occurred:
A separate build directory is now used by default: The
autotoolsclass has been changed to use a directory for building (B), which is separate from the source directory (S). This is commonly referred to asB != S, or an out-of-tree build.If the software being built is already capable of building in a directory separate from the source, you do not need to do anything. However, if the software is not capable of being built in this manner, you will need to either patch the software so that it can build separately, or you will need to change the recipe to inherit the
autotools-brokensepclass instead of theautotoolsorautotools_stageclasses.The
--foreignoption is no longer passed toautomakewhen runningautoconf: This option tellsautomakethat a particular software package does not follow the GNU standards and therefore should not be expected to distribute certain files such asChangeLog,AUTHORS, and so forth. Because the majority of upstream software packages already tellautomaketo enable foreign mode themselves, the option is mostly superfluous. However, some recipes will need patches for this change. You can easily make the change by patchingconfigure.acso that it passes "foreign" toAM_INIT_AUTOMAKE(). See this commit for an example showing how to make the patch.
4.6.4. Binary Configuration Scripts Disabled¶
Some of the core recipes that package binary configuration scripts
now disable the scripts due to the
scripts previously requiring error-prone path substitution.
Software that links against these libraries using these scripts
should use the much more robust pkg-config
instead.
The list of recipes changed in this version (and their
configuration scripts) is as follows:
directfb (directfb-config)
freetype (freetype-config)
gpgme (gpgme-config)
libassuan (libassuan-config)
libcroco (croco-6.0-config)
libgcrypt (libgcrypt-config)
libgpg-error (gpg-error-config)
libksba (ksba-config)
libpcap (pcap-config)
libpcre (pcre-config)
libpng (libpng-config, libpng16-config)
libsdl (sdl-config)
libusb-compat (libusb-config)
libxml2 (xml2-config)
libxslt (xslt-config)
ncurses (ncurses-config)
neon (neon-config)
npth (npth-config)
pth (pth-config)
taglib (taglib-config)
Additionally, support for pkg-config has been
added to some recipes in the previous list in the rare cases
where the upstream software package does not already provide
it.
4.6.5. eglibc 2.19 Replaced with glibc 2.20¶
Because eglibc and
glibc were already fairly close, this
replacement should not require any significant changes to other
software that links to eglibc.
However, there were a number of minor changes in
glibc 2.20 upstream that could require
patching some software (e.g. the removal of the
_BSD_SOURCE feature test macro).
glibc 2.20 requires version 2.6.32 or greater
of the Linux kernel.
Thus, older kernels will no longer be usable in conjunction with it.
For full details on the changes in glibc 2.20,
see the upstream release notes
here.
4.6.6. Kernel Module Autoloading¶
The
module_autoload_*
variable is now deprecated and a new
KERNEL_MODULE_AUTOLOAD
variable should be used instead.
Also,
module_conf_*
must now be used in conjunction with a new
KERNEL_MODULE_PROBECONF
variable.
The new variables no longer require you to specify the module name
as part of the variable name.
This change not only simplifies usage but also allows the values
of these variables to be appropriately incorporated into task
signatures and thus trigger the appropriate tasks to re-execute
when changed.
You should replace any references to
module_autoload_* with
KERNEL_MODULE_AUTOLOAD, and add any modules
for which module_conf_* is specified to
KERNEL_MODULE_PROBECONF.
4.6.7. QA Check Changes¶
The following changes have occurred to the QA check process:
Additional QA checks
file-rdepsandbuild-depshave been added in order to verify that file dependencies are satisfied (e.g. package contains a script requiring/bin/bash) and build-time dependencies are declared, respectively. For more information, please see the "QA Error and Warning Messages" chapter.Package QA checks are now performed during a new
do_package_qatask rather than being part of thedo_packagetask. This allows more parallel execution. This change is unlikely to be an issue except for highly customized recipes that disable packaging tasks themselves by marking them asnoexec. For those packages, you will need to disable thedo_package_qatask as well.Files being overwritten during the
do_populate_sysroottask now trigger an error instead of a warning. Recipes should not be overwriting files written to the sysroot by other recipes. If you have these types of recipes, you need to alter them so that they do not overwrite these files.You might now receive this error after changes in configuration or metadata resulting in orphaned files being left in the sysroot. If you do receive this error, the way to resolve the issue is to delete your
TMPDIRor to move it out of the way and then re-start the build. Anything that has been fully built up to that point and does not need rebuilding will be restored from the shared state cache and the rest of the build will be able to proceed as normal.
4.6.8. Removed Recipes¶
The following recipes have been removed:
x-load: This recipe has been superseded by U-boot SPL for all Cortex-based TI SoCs. For legacy boards, themeta-tilayer, which contains a maintained recipe, should be used instead.ubootchart: This recipe is obsolete. Abootchart2recipe has been added to functionally replace it.linux-yocto 3.4: Support for the linux-yocto 3.4 kernel has been dropped. Support for the 3.10 and 3.14 kernels remains, while support for version 3.17 has been added.eglibchas been removed in favor ofglibc. See the "eglibc 2.19Replaced withglibc 2.20" section for more information.
4.6.9. Miscellaneous Changes¶
The following miscellaneous change occurred:
The build history feature now writes
build-id.txtinstead ofbuild-id. Additionally,build-id.txtnow contains the full build header as printed by BitBake upon starting the build. You should manually remove old "build-id" files from your existing build history repositories to avoid confusion. For information on the build history feature, see the "Maintaining Build Output Quality" section in the Yocto Project Development Tasks Manual.
4.7. Moving to the Yocto Project 1.8 Release¶
This section provides migration information for moving to the Yocto Project 1.8 Release from the prior release.
4.7.1. Removed Recipes¶
The following recipes have been removed:
owl-video: Functionality replaced bygst-player.gaku: Functionality replaced bygst-player.gnome-desktop: This recipe is now available inmeta-gnomeand is no longer needed.gsettings-desktop-schemas: This recipe is now available inmeta-gnomeand is no longer needed.python-argparse: Theargparsemodule is already provided in the default Python distribution in a package namedpython-argparse. Consequently, the separatepython-argparserecipe is no longer needed.telepathy-python, libtelepathy, telepathy-glib, telepathy-idle, telepathy-mission-control: All these recipes have moved tometa-oeand are consequently no longer needed by any recipes in OpenEmbedded-Core.linux-yocto_3.10andlinux-yocto_3.17: Support for the linux-yocto 3.10 and 3.17 kernels has been dropped. Support for the 3.14 kernel remains, while support for 3.19 kernel has been added.poky-feed-config-opkg: This recipe has become obsolete and is no longer needed. Usedistro-feed-configfrommeta-oeinstead.libav 0.8.x:libav 9.xis now used.sed-native: No longer needed. A working version ofsedis expected to be provided by the host distribution.
4.7.2. BlueZ 4.x / 5.x Selection¶
Proper built-in support for selecting BlueZ 5.x in preference
to the default of 4.x now exists.
To use BlueZ 5.x, simply add "bluez5" to your
DISTRO_FEATURES
value.
If you had previously added append files
(*.bbappend) to make this selection, you can
now remove them.
Additionally, a
bluetooth
class has been added to make selection of the appropriate bluetooth
support within a recipe a little easier.
If you wish to make use of this class in a recipe, add something
such as the following:
inherit bluetooth
PACKAGECONFIG ??= "${@bb.utils.contains('DISTRO_FEATURES', 'bluetooth', '${BLUEZ}', '', d)}
PACKAGECONFIG[bluez4] = "--enable-bluetooth,--disable-bluetooth,bluez4"
PACKAGECONFIG[bluez5] = "--enable-bluez5,--disable-bluez5,bluez5"
4.7.3. Kernel Build Changes¶
The kernel build process was changed to place the source
in a common shared work area and to place build artifacts
separately in the source code tree.
In theory, migration paths have been provided for most common
usages in kernel recipes but this might not work in all cases.
In particular, users need to ensure that
${S} (source files) and
${B} (build artifacts) are used
correctly in functions such as
do_configure
and
do_install.
For kernel recipes that do not inherit from
kernel-yocto or include
linux-yocto.inc, you might wish to
refer to the linux.inc file in the
meta-oe layer for the kinds of changes you
need to make.
For reference, here is the
commit
where the linux.inc file in
meta-oe was updated.
Recipes that rely on the kernel source code and do not inherit
the module classes might need to add explicit dependencies on
the do_shared_workdir kernel task, for example:
do_configure[depends] += "virtual/kernel:do_shared_workdir"
4.7.4. SSL 3.0 is Now Disabled in OpenSSL¶
SSL 3.0 is now disabled when building OpenSSL.
Disabling SSL 3.0 avoids any lingering instances of the POODLE
vulnerability.
If you feel you must re-enable SSL 3.0, then you can add an
append file (*.bbappend) for the
openssl recipe to remove "-no-ssl3"
from
EXTRA_OECONF.
4.7.5. Default Sysroot Poisoning¶
gcc's default sysroot and include directories
are now "poisoned".
In other words, the sysroot and include directories are being
redirected to a non-existent location in order to catch when
host directories are being used due to the correct options not
being passed.
This poisoning applies both to the cross-compiler used within the
build and to the cross-compiler produced in the SDK.
If this change causes something in the build to fail, it almost certainly means the various compiler flags and commands are not being passed correctly to the underlying piece of software. In such cases, you need to take corrective steps.
4.7.6. Rebuild Improvements¶
Changes have been made to the
base,
autotools,
and
cmake
classes to clean out generated files when the
do_configure
task needs to be re-executed.
One of the improvements is to attempt to run "make clean" during
the do_configure task if a
Makefile exists.
Some software packages do not provide a working clean target
within their make files.
If you have such recipes, you need to set
CLEANBROKEN
to "1" within the recipe, for example:
CLEANBROKEN = "1"
4.7.7. QA Check and Validation Changes¶
The following QA Check and Validation Changes have occurred:
Usage of
PRINCpreviously triggered a warning. It now triggers an error. You should remove any remaining usage ofPRINCin any recipe or append file.An additional QA check has been added to detect usage of
${D}inFILESvalues whereDvalues should not be used at all. The same check ensures that$Dis used inpkg_preinst/pkg_postinst/pkg_prerm/pkg_postrmfunctions instead of${D}.Snow needs to be set to a valid value within a recipe. IfSis not set in the recipe, the directory is not automatically created. IfSdoes not point to a directory that exists at the time thedo_unpacktask finishes, a warning will be shown.LICENSEis now validated for correct formatting of multiple licenses. If the format is invalid (e.g. multiple licenses are specified with no operators to specify how the multiple licenses interact), then a warning will be shown.
4.7.8. Miscellaneous Changes¶
The following miscellaneous changes have occurred:
The
send-error-reportscript now expects a "-s" option to be specified before the server address. This assumes a server address is being specified.The
oe-pkgdata-utilscript now expects a "-p" option to be specified before thepkgdatadirectory, which is now optional. If thepkgdatadirectory is not specified, the script will run BitBake to queryPKGDATA_DIRfrom the build environment.
4.8. Moving to the Yocto Project 2.0 Release¶
This section provides migration information for moving to the Yocto Project 2.0 Release from the prior release.
4.8.1. GCC 5¶
The default compiler is now GCC 5.2. This change has required fixes for compilation errors in a number of other recipes.
One important example is a fix for when the Linux kernel freezes at
boot time on ARM when built with GCC 5.
If you are using your own kernel recipe or source tree and
building for ARM, you will likely need to apply this
patch.
The standard linux-yocto kernel source tree
already has a workaround for the same issue.
For further details, see https://gcc.gnu.org/gcc-5/changes.html and the porting guide at https://gcc.gnu.org/gcc-5/porting_to.html.
Alternatively, you can switch back to GCC 4.9 or 4.8 by
setting GCCVERSION in your configuration,
as follows:
GCCVERSION = "4.9%"
4.8.2. Gstreamer 0.10 Removed¶
Gstreamer 0.10 has been removed in favor of Gstreamer 1.x.
As part of the change, recipes for Gstreamer 0.10 and related
software are now located
in meta-multimedia.
This change results in Qt4 having Phonon and Gstreamer
support in QtWebkit disabled by default.
4.8.3. Removed Recipes¶
The following recipes have been moved or removed:
bluez4: The recipe is obsolete and has been moved due tobluez5becoming fully integrated. Thebluez4recipe now resides inmeta-oe.gamin: The recipe is obsolete and has been removed.gnome-icon-theme: The recipe's functionally has been replaced byadwaita-icon-theme.Gstreamer 0.10 Recipes: Recipes for Gstreamer 0.10 have been removed in favor of the recipes for Gstreamer 1.x.
insserv: The recipe is obsolete and has been removed.libunique: The recipe is no longer used and has been moved tometa-oe.midori: The recipe's functionally has been replaced byepiphany.python-gst: The recipe is obsolete and has been removed since it only contains bindings for Gstreamer 0.10.qt-mobility: The recipe is obsolete and has been removed since it requiresGstreamer 0.10, which has been replaced.subversion: All 1.6.x versions of this recipe have been removed.webkit-gtk: The older 1.8.3 version of this recipe has been removed in favor ofwebkitgtk.
4.8.4. BitBake datastore improvements¶
The method by which BitBake's datastore handles overrides has
changed.
Overrides are now applied dynamically and
bb.data.update_data() is now a no-op.
Thus, bb.data.update_data() is no longer
required in order to apply the correct overrides.
In practice, this change is unlikely to require any changes to
Metadata.
However, these minor changes in behavior exist:
All potential overrides are now visible in the variable history as seen when you run the following:
$ bitbake -ed.delVar('VARNAME')andd.setVar('VARNAME', None)result in the variable and all of its overrides being cleared out. Before the change, only the non-overridden values were cleared.
4.8.5. Shell Message Function Changes¶
The shell versions of the BitBake message functions (i.e.
bbdebug, bbnote,
bbwarn, bbplain,
bberror, and bbfatal)
are now connected through to their BitBake equivalents
bb.debug(), bb.note(),
bb.warn(), bb.plain(),
bb.error(), and
bb.fatal(), respectively.
Thus, those message functions that you would expect to be printed
by the BitBake UI are now actually printed.
In practice, this change means two things:
If you now see messages on the console that you did not previously see as a result of this change, you might need to clean up the calls to
bbwarn,bberror, and so forth. Or, you might want to simply remove the calls.The
bbfatalmessage function now suppresses the full error log in the UI, which means any calls tobbfatalwhere you still wish to see the full error log should be replaced bydieorbbfatal_log.
4.8.6. Extra Development/Debug Package Cleanup¶
The following recipes have had extra
dev/dbg packages removed:
aclapmdaspellattraugeasbzip2coglcurlelfutilsgcc-targetlibgcclibtoollibxmuopkgpciutilsrpmsysfsutilstiffxz
All of the above recipes now conform to the standard packaging
scheme where a single -dev,
-dbg, and -staticdev
package exists per recipe.
4.8.7. Recipe Maintenance Tracking Data Moved to OE-Core¶
Maintenance tracking data for recipes that was previously part
of meta-yocto has been moved to
OE-Core.
The change includes package_regex.inc and
distro_alias.inc, which are typically enabled
when using the
distrodata
class.
Additionally, the contents of
upstream_tracking.inc has now been split out
to the relevant recipes.
4.8.8. Automatic Stale Sysroot File Cleanup¶
Stale files from recipes that no longer exist in the current
configuration are now automatically removed from
sysroot as well as removed from
any other place managed by shared state.
This automatic cleanup means that the build system now properly
handles situations such as renaming the build system side of
recipes, removal of layers from
bblayers.conf, and
DISTRO_FEATURES
changes.
Additionally, work directories for old versions of recipes are now pruned. If you wish to disable pruning old work directories, you can set the following variable in your configuration:
SSTATE_PRUNE_OBSOLETEWORKDIR = "0"
4.8.9. linux-yocto Kernel Metadata Repository Now Split from Source¶
The linux-yocto tree has up to now been a
combined set of kernel changes and configuration (meta) data
carried in a single tree.
While this format is effective at keeping kernel configuration and
source modifications synchronized, it is not always obvious to
developers how to manipulate the Metadata as compared to the
source.
Metadata processing has now been removed from the
kernel-yocto
class and the external Metadata repository
yocto-kernel-cache, which has always been used
to seed the linux-yocto "meta" branch.
This separate linux-yocto cache repository
is now the primary location for this data.
Due to this change, linux-yocto is no longer
able to process combined trees.
Thus, if you need to have your own combined kernel repository,
you must do the split there as well and update your recipes
accordingly.
See the meta/recipes-kernel/linux/linux-yocto_4.1.bb
recipe for an example.
4.8.10. Additional QA checks¶
The following QA checks have been added:
Added a "host-user-contaminated" check for ownership issues for packaged files outside of
/home. The check looks for files that are incorrectly owned by the user that ran BitBake instead of owned by a valid user in the target system.Added an "invalid-chars" check for invalid (non-UTF8) characters in recipe metadata variable values (i.e.
DESCRIPTION,SUMMARY,LICENSE, andSECTION). Some package managers do not support these characters.Added an "invalid-packageconfig" check for any options specified in
PACKAGECONFIGthat do not match anyPACKAGECONFIGoption defined for the recipe.
4.8.11. Miscellaneous Changes¶
These additional changes exist:
gtk-update-icon-cachehas been renamed togtk-icon-utils.The
tools-profileIMAGE_FEATURESitem as well as its corresponding packagegroup andpackagegroup-core-tools-profileno longer bring inoprofile. Bringing inoprofilewas originally added to aid compilation on resource-constrained targets. However, this aid has not been widely used and is not likely to be used going forward due to the more powerful target platforms and the existence of better cross-compilation tools.The
IMAGE_FSTYPESvariable's default value now specifiesext4instead ofext3.All support for the
PRINCvariable has been removed.The
packagegroup-core-full-cmdlinepackagegroup no longer brings inlighttpddue to the fact that bringing inlighttpdis not really in line with the packagegroup's purpose, which is to add full versions of command-line tools that by default are provided bybusybox.
4.9. Moving to the Yocto Project 2.1 Release¶
This section provides migration information for moving to the Yocto Project 2.1 Release from the prior release.
4.9.1. Variable Expansion in Python Functions¶
Variable expressions, such as
${VARNAME}
no longer expand automatically within Python functions.
Suppressing expansion was done to allow Python functions to
construct shell scripts or other code for situations in which you
do not want such expressions expanded.
For any existing code that relies on these expansions, you need to
change the expansions to expand the value of individual
variables through d.getVar().
To alternatively expand more complex expressions,
use d.expand().
4.9.2. Overrides Must Now be Lower-Case¶
The convention for overrides has always been for them to be
lower-case characters.
This practice is now a requirement as BitBake's datastore now
assumes lower-case characters in order to give a slight performance
boost during parsing.
In practical terms, this requirement means that anything that ends
up in
OVERRIDES
must now appear in lower-case characters (e.g. values for
MACHINE, TARGET_ARCH,
DISTRO, and also recipe names if
_pn-recipename
overrides are to be effective).
4.9.3. Expand Parameter to getVar() and
getVarFlag() is Now Mandatory¶
The expand parameter to getVar() and
getVarFlag() previously defaulted to
False if not specified.
Now, however, no default exists so one must be specified.
You must change any getVar() calls that
do not specify the final expand parameter to calls that do specify
the parameter.
You can run the following sed command at the
base of a layer to make this change:
sed -e 's:\(\.getVar([^,()]*\)):\1, False):g' -i `grep -ril getVar *`
sed -e 's:\(\.getVarFlag([^,()]*, [^,()]*\)):\1, False):g' -i `grep -ril getVarFlag *`
Note
The reason for this change is that it prepares the way for changing the default to True in a future Yocto Project release. This future change is a much more sensible default than False. However, the change needs to be made gradually as a sudden change of the default would potentially cause side-effects that would be difficult to detect.
4.9.4. Makefile Environment Changes¶
EXTRA_OEMAKE
now defaults to "" instead of "-e MAKEFLAGS=".
Setting EXTRA_OEMAKE to "-e MAKEFLAGS=" by
default was a historical accident that has required many classes
(e.g. autotools, module)
and recipes to override this default in order to work with
sensible build systems.
When upgrading to the release, you must edit any recipe that
relies upon this old default by either setting
EXTRA_OEMAKE back to "-e MAKEFLAGS=" or by
explicitly setting any required variable value overrides using
EXTRA_OEMAKE, which is typically only needed
when a Makefile sets a default value for a variable that is
inappropriate for cross-compilation using the "=" operator rather
than the "?=" operator.
4.9.5. libexecdir Reverted to ${prefix}/libexec¶
The use of ${libdir}/${BPN} as
libexecdir is different as compared to all
other mainstream distributions, which either uses
${prefix}/libexec or
${libdir}.
The use is also contrary to the GNU Coding Standards
(i.e. https://www.gnu.org/prep/standards/html_node/Directory-Variables.html)
that suggest ${prefix}/libexec and also
notes that any package-specific nesting should be done by the
package itself.
Finally, having libexecdir change between
recipes makes it very difficult for different recipes to invoke
binaries that have been installed into
libexecdir.
The Filesystem Hierarchy Standard
(i.e. http://refspecs.linuxfoundation.org/FHS_3.0/fhs/ch04s07.html)
now recognizes the use of ${prefix}/libexec/,
giving distributions the choice between
${prefix}/lib or
${prefix}/libexec without breaking FHS.
4.9.6. ac_cv_sizeof_off_t is No Longer Cached in Site Files¶
For recipes inheriting the
autotools
class, ac_cv_sizeof_off_t is no longer cached
in the site files for autoconf.
The reason for this change is because the
ac_cv_sizeof_off_t value is not necessarily
static per architecture as was previously assumed.
Rather, the value changes based on whether large file support is
enabled.
For most software that uses autoconf, this
change should not be a problem.
However, if you have a recipe that bypasses the standard
do_configure
task from the autotools class and the software
the recipe is building uses a very old version of
autoconf, the recipe might be incapable of
determining the correct size of off_t during
do_configure.
The best course of action is to patch the software as necessary
to allow the default implementation from the
autotools class to work such that
autoreconf succeeds and produces a working
configure script, and to remove the
overridden do_configure task such that the
default implementation does get used.
4.9.7. Image Generation is Now Split Out from Filesystem Generation¶
Previously, for image recipes the
do_rootfs
task assembled the filesystem and then from that filesystem
generated images.
With this Yocto Project release, image generation is split into
separate
do_image_*
tasks for clarity both in operation and in the code.
For most cases, this change does not present any problems.
However, if you have made customizations that directly modify the
do_rootfs task or that mention
do_rootfs, you might need to update those
changes.
In particular, if you had added any tasks after
do_rootfs, you should make edits so that
those tasks are after the
do_image_complete
task rather than after do_rootfs
so that the your added tasks
run at the correct time.
A minor part of this restructuring is that the post-processing
definitions and functions have been moved from the
image
class to the
rootfs-postcommands
class.
Functionally, however, they remain unchanged.
4.9.8. Removed Recipes¶
The following recipes have been removed in the 2.1 release:
gccversion 4.8: Versions 4.9 and 5.3 remain.qt4: All support for Qt 4.x has been moved out to a separatemeta-qt4layer because Qt 4 is no longer supported upstream.x11vnc: Moved to themeta-oelayer.linux-yocto-3.14: No longer supported.linux-yocto-3.19: No longer supported.libjpeg: Replaced by thelibjpeg-turborecipe.pth: Became obsolete.liboil: Recipe is no longer needed and has been moved to themeta-multimedialayer.gtk-theme-torturer: Recipe is no longer needed and has been moved to themeta-gnomelayer.gnome-mime-data: Recipe is no longer needed and has been moved to themeta-gnomelayer.udev: Replaced by theeudevrecipe for compatibility when usingsysvinitwith newer kernels.python-pygtk: Recipe became obsolete.adt-installer: Recipe became obsolete. See the "ADT Removed" section for more information.
4.9.9. Class Changes¶
The following classes have changed:
autotools_stage: Removed because theautotoolsclass now provides its functionality. Recipes that inherited fromautotools_stageshould now inherit fromautotoolsinstead.boot-directdisk: Merged into theimage-vmclass. Theboot-directdiskclass was rarely directly used. Consequently, this change should not cause any issues.bootimg: Merged into theimage-liveclass. Thebootimgclass was rarely directly used. Consequently, this change should not cause any issues.packageinfo: Removed due to its limited use by the Hob UI, which has itself been removed.
4.9.10. Build System User Interface Changes¶
The following changes have been made to the build system user interface:
Hob GTK+-based UI: Removed because it is unmaintained and based on the outdated GTK+ 2 library. The Toaster web-based UI is much more capable and is actively maintained. See the "Using the Toaster Web Interface" section in the Toaster User Manual for more information on this interface.
"puccho" BitBake UI: Removed because is unmaintained and no longer useful.
4.9.11. ADT Removed¶
The Application Development Toolkit (ADT) has been removed because its functionality almost completely overlapped with the standard SDK and the extensible SDK. For information on these SDKs and how to build and use them, see the Yocto Project Application Development and the Extensible Software Development Kit (eSDK) manual.
Note
The Yocto Project Eclipse IDE Plug-in is still supported and is not affected by this change.
4.9.12. Poky Reference Distribution Changes¶
The following changes have been made for the Poky distribution:
The
meta-yoctolayer has been renamed tometa-pokyto better match its purpose, which is to provide the Poky reference distribution. Themeta-yocto-bsplayer retains its original name since it provides reference machines for the Yocto Project and it is otherwise unrelated to Poky. References tometa-yoctoin yourconf/bblayers.confshould automatically be updated, so you should not need to change anything unless you are relying on this naming elsewhere.The
uninativeclass is now enabled by default in Poky. This class attempts to isolate the build system from the host distribution's C library and makes re-use of native shared state artifacts across different host distributions practical. With this class enabled, a tarball containing a pre-built C library is downloaded at the start of the build.The
uninativeclass is enabled through themeta/conf/distro/include/yocto-uninative.incfile, which for those not using the Poky distribution, can include to easily enable the same functionality.Alternatively, if you wish to build your own
uninativetarball, you can do so by building theuninative-tarballrecipe, making it available to your build machines (e.g. over HTTP/HTTPS) and setting a similar configuration as the one set byyocto-uninative.inc.Static library generation, for most cases, is now disabled by default in the Poky distribution. Disabling this generation saves some build time as well as the size used for build output artifacts.
Disabling this library generation is accomplished through a
meta/conf/distro/include/no-static-libs.inc, which for those not using the Poky distribution can easily include to enable the same functionality.Any recipe that needs to opt-out of having the "--disable-static" option specified on the configure command line either because it is not a supported option for the configure script or because static libraries are needed should set the following variable:
DISABLE_STATIC = ""The separate
poky-tinydistribution now uses the musl C library instead of a heavily pared downglibc. Using musl results in a smaller distribution and facilitates much greater maintainability because musl is designed to have a small footprint.If you have used
poky-tinyand have customized theglibcconfiguration you will need to redo those customizations with musl when upgrading to the new release.
4.9.13. Packaging Changes¶
The following changes have been made to packaging:
The
runuserandmountpointbinaries, which were previously in the mainutil-linuxpackage, have been split out into theutil-linux-runuserandutil-linux-mountpointpackages, respectively.The
python-elementtreepackage has been merged into thepython-xmlpackage.
4.9.14. Tuning File Changes¶
The following changes have been made to the tuning files:
The "no-thumb-interwork" tuning feature has been dropped from the ARM tune include files. Because interworking is required for ARM EABI, attempting to disable it through a tuning feature no longer makes sense.
Note
Support for ARM OABI was deprecated in gcc 4.7.The
tune-cortexm*.incandtune-cortexr4.incfiles have been removed because they are poorly tested. Until the OpenEmbedded build system officially gains support for CPUs without an MMU, these tuning files would probably be better maintained in a separate layer if needed.
4.9.15. Supporting GObject Introspection¶
This release supports generation of GLib Introspective Repository (GIR) files through GObject introspection, which is the standard mechanism for accessing GObject-based software from runtime environments. You can enable, disable, and test the generation of this data. See the "Enabling GObject Introspection Support" section in the Yocto Project Development Tasks Manual for more information.
4.9.16. Miscellaneous Changes¶
These additional changes exist:
The minimum Git version has been increased to 1.8.3.1. If your host distribution does not provide a sufficiently recent version, you can install the buildtools, which will provide it. See the "Required Git, tar, and Python Versions" section for more information on the buildtools tarball.
The buggy and incomplete support for the RPM version 4 package manager has been removed. The well-tested and maintained support for RPM version 5 remains.
Previously, the following list of packages were removed if package-management was not in
IMAGE_FEATURES, regardless of any dependencies:update-rc.d base-passwd shadow update-alternatives run-postinstsWith the Yocto Project 2.1 release, these packages are only removed if "read-only-rootfs" is in
IMAGE_FEATURES, since they might still be needed for a read-write image even in the absence of a package manager (e.g. if users need to be added, modified, or removed at runtime).The
devtool modifycommand now defaults to extracting the source since that is most commonly expected. The "-x" or "--extract" options are now no-ops. If you wish to provide your own existing source tree, you will now need to specify either the "-n" or "--no-extract" options when runningdevtool modify.If the formfactor for a machine is either not supplied or does not specify whether a keyboard is attached, then the default is to assume a keyboard is attached rather than assume no keyboard. This change primarily affects the Sato UI.
The
.debugdirectory packaging is now automatic. If your recipe builds software that installs binaries into directories other than the standard ones, you no longer need to take care of settingFILES_${PN}-dbgto pick up the resulting.debugdirectories as these directories are automatically found and added.Inaccurate disk and CPU percentage data has been dropped from
buildstatsoutput. This data has been replaced withgetrusage()data and corrected IO statistics. You will probably need to update any custom code that reads thebuildstatsdata.The
meta/conf/distro/include/package_regex.incis now deprecated. The contents of this file have been moved to individual recipes.Tip
Because this file will likely be removed in a future Yocto Project release, it is suggested that you remove any references to the file that might be in your configuration.The
v86d/uvesafbhas been removed from thegenericx86andgenericx86-64reference machines, which are provided by themeta-yocto-bsplayer. Most modern x86 boards do not rely on this file and it only adds kernel error messages during startup. If you do still need to supportuvesafb, you can simply addv86dto your image.Build sysroot paths are now removed from debug symbol files. Removing these paths means that remote GDB using an unstripped build system sysroot will no longer work (although this was never documented to work). The supported method to accomplish something similar is to set
IMAGE_GEN_DEBUGFSto "1", which will generate a companion debug image containing unstripped binaries and associated debug sources alongside the image.
4.10. Moving to the Yocto Project 2.2 Release¶
This section provides migration information for moving to the Yocto Project 2.2 Release from the prior release.
4.10.1. Minimum Kernel Version¶
The minimum kernel version for the target system and for SDK
is now 3.2.0, due to the upgrade
to glibc 2.24.
Specifically, for AArch64-based targets the version is
3.14.
For Nios II-based targets, the minimum kernel version is 3.19.
Note
For x86 and x86_64, you can resetOLDEST_KERNEL
to anything down to 2.6.32 if desired.
4.10.2. Staging Directories in Sysroot Has Been Simplified¶
The way directories are staged in sysroot has been simplified and
introduces the new
SYSROOT_DIRS,
SYSROOT_DIRS_NATIVE,
and
SYSROOT_DIRS_BLACKLIST.
See the
v2 patch series on the OE-Core Mailing List
for additional information.
4.10.3. Removal of Old Images and Other Files in tmp/deploy Now Enabled¶
Removal of old images and other files in
tmp/deploy/ is now enabled by default due
to a new staging method used for those files.
As a result of this change, the
RM_OLD_IMAGE variable is now redundant.
4.10.4. Python Changes¶
The following changes for Python occurred:
4.10.4.1. BitBake Now Requires Python 3.4+¶
BitBake requires Python 3.4 or greater.
4.10.4.2. UTF-8 Locale Required on Build Host¶
A UTF-8 locale is required on the build host due to Python 3. Since C.UTF-8 is not a standard, the default is en_US.UTF-8.
4.10.4.3. Metadata Must Now Use Python 3 Syntax¶
The metadata is now required to use Python 3 syntax. For help preparing metadata, see any of the many Python 3 porting guides available. Alternatively, you can reference the conversion commits for Bitbake and you can use OE-Core as a guide for changes. Following are particular areas of interest:
* subprocess command-line pipes needing locale decoding
* the syntax for octal values changed
* the iter*() functions changed name
* iterators now return views, not lists
* changed names for Python modules
4.10.4.4. Target Python Recipes Switched to Python 3¶
Most target Python recipes have now been switched to Python 3. Unfortunately, systems using RPM as a package manager and providing online package-manager support through SMART still require Python 2.
Note
Python 2 and recipes that use it can still be built for the target as with previous versions.
4.10.4.5. buildtools-tarball Includes Python 3¶
buildtools-tarball now includes Python 3.
4.10.5. uClibc Replaced by musl¶
uClibc has been removed in favor of musl. Musl has matured, is better maintained, and is compatible with a wider range of applications as compared to uClibc.
4.10.6. ${B} No Longer Default Working Directory for Tasks¶
${B}
is no longer the default working directory for tasks.
Consequently, any custom tasks you define now need to either
have the
[dirs] flag set, or the task needs to change into the
appropriate working directory manually (e.g using
cd for a shell task).
Note
The preferred method is to use the[dirs] flag.
4.10.7. runqemu Ported to Python¶
runqemu has been ported to Python and has
changed behavior in some cases.
Previous usage patterns continue to be supported.
The new runqemu is a Python script.
Machine knowledge is no longer hardcoded into
runqemu.
You can choose to use the qemuboot
configuration file to define the BSP's own arguments and to make
it bootable with runqemu.
If you use a configuration file, use the following form:
image-name-machine.qemuboot.conf
The configuration file enables fine-grained tuning of options
passed to QEMU without the runqemu script
hard-coding any knowledge about different machines.
Using a configuration file is particularly convenient when trying
to use QEMU with machines other than the
qemu* machines in
OE-Core.
The qemuboot.conf file is generated by the
qemuboot
class when the root filesystem is being build (i.e.
build rootfs).
QEMU boot arguments can be set in BSP's configuration file and
the qemuboot class will save them to
qemuboot.conf.
If you want to use runqemu without a
configuration file, use the following command form:
$ runqemu machine rootfs kernel [options]
Supported machines are as follows:
qemuarm
qemuarm64
qemux86
qemux86-64
qemuppc
qemumips
qemumips64
qemumipsel
qemumips64el
Consider the following example, which uses the
qemux86-64 machine,
provides a root filesystem, provides an image, and uses
the nographic option:
$ runqemu qemux86-64 tmp/deploy/images/qemux86-64/core-image-minimal-qemux86-64.ext4 tmp/deploy/images/qemux86-64/bzImage nographic
Following is a list of variables that can be set in configuration
files such as bsp.conf to enable the BSP
to be booted by runqemu:
Note
"QB" means "QEMU Boot".
QB_SYSTEM_NAME: QEMU name (e.g. "qemu-system-i386")
QB_OPT_APPEND: Options to append to QEMU (e.g. "-show-cursor")
QB_DEFAULT_KERNEL: Default kernel to boot (e.g. "bzImage")
QB_DEFAULT_FSTYPE: Default FSTYPE to boot (e.g. "ext4")
QB_MEM: Memory (e.g. "-m 512")
QB_MACHINE: QEMU machine (e.g. "-machine virt")
QB_CPU: QEMU cpu (e.g. "-cpu qemu32")
QB_CPU_KVM: Similar to QB_CPU except used for kvm support (e.g. "-cpu kvm64")
QB_KERNEL_CMDLINE_APPEND: Options to append to the kernel's -append
option (e.g. "console=ttyS0 console=tty")
QB_DTB: QEMU dtb name
QB_AUDIO_DRV: QEMU audio driver (e.g. "alsa", set it when support audio)
QB_AUDIO_OPT: QEMU audio option (e.g. "-soundhw ac97,es1370"), which is used
when QB_AUDIO_DRV is set.
QB_KERNEL_ROOT: Kernel's root (e.g. /dev/vda)
QB_TAP_OPT: Network option for 'tap' mode (e.g.
"-netdev tap,id=net0,ifname=@TAP@,script=no,downscript=no -device virtio-net-device,netdev=net0").
runqemu will replace "@TAP@" with the one that is used, such as tap0, tap1 ...
QB_SLIRP_OPT: Network option for SLIRP mode (e.g. "-netdev user,id=net0 -device virtio-net-device,netdev=net0")
QB_ROOTFS_OPT: Used as rootfs (e.g.
"-drive id=disk0,file=@ROOTFS@,if=none,format=raw -device virtio-blk-device,drive=disk0").
runqemu will replace "@ROOTFS@" with the one which is used, such as
core-image-minimal-qemuarm64.ext4.
QB_SERIAL_OPT: Serial port (e.g. "-serial mon:stdio")
QB_TCPSERIAL_OPT: tcp serial port option (e.g.
" -device virtio-serial-device -chardev socket,id=virtcon,port=@PORT@,host=127.0.0.1 -device virtconsole,chardev=virtcon"
runqemu will replace "@PORT@" with the port number which is used.
To use runqemu, set
IMAGE_CLASSES
as follows and run runqemu:
Note
For command-line syntax, userunqemu help.
IMAGE_CLASSES += "qemuboot"
4.10.8. Default Linker Hash Style Changed¶
The default linker hash style for gcc-cross
is now "sysv" in order to catch recipes that are building software
without using the OpenEmbedded
LDFLAGS.
This change could result in seeing some "No GNU_HASH in the elf
binary" QA issues when building such recipes.
You need to fix these recipes so that they use the expected
LDFLAGS.
Depending on how the software is built, the build system used by
the software (e.g. a Makefile) might need to be patched.
However, sometimes making this fix is as simple as adding the
following to the recipe:
TARGET_CC_ARCH += "${LDFLAGS}"
4.10.9. KERNEL_IMAGE_BASE_NAME no Longer Uses KERNEL_IMAGETYPE¶
The
KERNEL_IMAGE_BASE_NAME
variable no longer uses the
KERNEL_IMAGETYPE
variable to create the image's base name.
Because the OpenEmbedded build system can now build multiple kernel
image types, this part of the kernel image base name as been
removed leaving only the following:
KERNEL_IMAGE_BASE_NAME ?= "${PKGE}-${PKGV}-${PKGR}-${MACHINE}-${DATETIME}
If you have recipes or classes that use
KERNEL_IMAGE_BASE_NAME directly, you might
need to update the references to ensure they continue to work.
4.10.10. BitBake Changes¶
The following changes took place for BitBake:
The "goggle" UI and standalone image-writer tool have been removed as they both require GTK+ 2.0 and were not being maintained.
The Perforce fetcher now supports
SRCREVfor specifying the source revision to use, be it${AUTOREV}, changelist number, p4date, or label, in preference to separateSRC_URIparameters to specify these. This change is more in-line with how the other fetchers work for source control systems. Recipes that fetch from Perforce will need to be updated to useSRCREVin place of specifying the source revision withinSRC_URI.Some of BitBake's internal code structures for accessing the recipe cache needed to be changed to support the new multi-configuration functionality. These changes will affect external tools that use BitBake's tinfoil module. For information on these changes, see the changes made to the scripts supplied with OpenEmbedded-Core: 1 and 2.
The task management code has been rewritten to avoid using ID indirection in order to improve performance. This change is unlikely to cause any problems for most users. However, the setscene verification function as pointed to by
BB_SETSCENE_VERIFY_FUNCTIONneeded to change signature. Consequently, a new variable namedBB_SETSCENE_VERIFY_FUNCTION2has been added allowing multiple versions of BitBake to work with suitably written metadata, which includes OpenEmbedded-Core and Poky. Anyone with custom BitBake task scheduler code might also need to update the code to handle the new structure.
4.10.11. Swabber has Been Removed¶
Swabber, a tool that was intended to detect host contamination in the build process, has been removed, as it has been unmaintained and unused for some time and was never particularly effective. The OpenEmbedded build system has since incorporated a number of mechanisms including enhanced QA checks that mean that there is less of a need for such a tool.
4.10.12. Removed Recipes¶
The following recipes have been removed:
augeas: No longer needed and has been moved tometa-oe.directfb: Unmaintained and has been moved tometa-oe.gcc: Removed 4.9 version. Versions 5.4 and 6.2 are still present.gnome-doc-utils: No longer needed.gtk-doc-stub: Replaced bygtk-doc.gtk-engines: No longer needed and has been moved tometa-gnome.gtk-sato-engine: Became obsolete.libglade: No longer needed and has been moved tometa-oe.libmad: Unmaintained and functionally replaced bylibmpg123.libmadhas been moved tometa-oe.libowl: Became obsolete.libxsettings-client: No longer needed.oh-puzzles: Functionally replaced bypuzzles.oprofileui: Became obsolete. OProfile has been largely supplanted by perf.packagegroup-core-directfb.bb: Removed.core-image-directfb.bb: Removed.pointercal: No longer needed and has been moved tometa-oe.python-imaging: No longer needed and moved tometa-pythonpython-pyrex: No longer needed and moved tometa-python.sato-icon-theme: Became obsolete.swabber-native: Swabber has been removed. See the entry on Swabber.tslib: No longer needed and has been moved tometa-oe.uclibc: Removed in favor of musl.xtscal: No longer needed and moved tometa-oe
4.10.13. Removed Classes¶
The following classes have been removed:
distutils-native-base: No longer needed.distutils3-native-base: No longer needed.sdl: Only setDEPENDSandSECTION, which are better set within the recipe instead.sip: Mostly unused.swabber: See the entry on Swabber.
4.10.14. Minor Packaging Changes¶
The following minor packaging changes have occurred:
grub: Splitgrub-editenvinto its own package.systemd: Split container and vm related units into a new package, systemd-container.util-linux: Movedprlimitto a separateutil-linux-prlimitpackage.
4.10.15. Miscellaneous Changes¶
The following miscellaneous changes have occurred:
package_regex.inc: Removed because the definitionspackage_regex.incpreviously contained have been moved to their respective recipes.Both
devtool addandrecipetool createnow use a fixedSRCREVby default when fetching from a Git repository. You can override this in either case to use${AUTOREV}instead by using the-aor‐‐autorevcommand-line optiondistcc: GTK+ UI is now disabled by default.packagegroup-core-tools-testapps: Removed Piglit.image.bbclass: Renamed COMPRESS(ION) to CONVERSION. This change means thatCOMPRESSIONTYPES,COMPRESS_DEPENDSandCOMPRESS_CMDare deprecated in favor ofCONVERSIONTYPES,CONVERSION_DEPENDSandCONVERSION_CMD. TheCOMPRESS*variable names will still work in the 2.2 release but metadata that does not need to be backwards-compatible should be changed to use the new names as theCOMPRESS*ones will be removed in a future release.gtk-doc: A full version ofgtk-docis now made available. However, some old software might not be capable of using the current version ofgtk-docto build documentation. You need to change recipes that build such software so that they explicitly disable building documentation withgtk-doc.
4.11. Moving to the Yocto Project 2.3 Release¶
This section provides migration information for moving to the Yocto Project 2.3 Release from the prior release.
4.11.1. Recipe-specific Sysroots¶
The OpenEmbedded build system now uses one sysroot per recipe to resolve long-standing issues with configuration script auto-detection of undeclared dependencies. Consequently, you might find that some of your previously written custom recipes are missing declared dependencies, particularly those dependencies that are incidentally built earlier in a typical build process and thus are already likely to be present in the shared sysroot in previous releases.
Consider the following:
Declare Build-Time Dependencies: Because of this new feature, you must explicitly declare all build-time dependencies for your recipe. If you do not declare these dependencies, they are not populated into the sysroot for the recipe.
Specify Pre-Installation and Post-Installation Native Tool Dependencies: You must specifically specify any special native tool dependencies of
pkg_preinstandpkg_postinstscripts by using thePACKAGE_WRITE_DEPSvariable. Specifying these dependencies ensures that these tools are available if these scripts need to be run on the build host during thedo_rootfstask.As an example, see the
dbusrecipe. You will see that this recipe has apkg_postinstthat callssystemctlif "systemd" is inDISTRO_FEATURES. In the example,systemd-systemctl-nativeis added toPACKAGE_WRITE_DEPS, which is also conditional on "systemd" being inDISTRO_FEATURES.Examine Recipes that Use
SSTATEPOSTINSTFUNCS: You need to examine any recipe that usesSSTATEPOSTINSTFUNCSand determine steps to take.Functions added to
SSTATEPOSTINSTFUNCSare still called as they were in previous Yocto Project releases. However, since a separate sysroot is now being populated for every recipe and if existing functions being called throughSSTATEPOSTINSTFUNCSare doing relocation, then you will need to change these to use a post-installation script that is installed by a function added toSYSROOT_PREPROCESS_FUNCS.For an example, see the
pixbufcacheclass inmeta/classes/in the Yocto Project Source Repositories.Note
TheSSTATEPOSTINSTFUNCSvariable itself is now deprecated in favor of thedo_populate_sysroot[postfuncs]task. Consequently, if you do still have any function or functions that need to be called after the sysroot component is created for a recipe, then you would be well advised to take steps to use a post installation script as described previously. Taking these steps prepares your code for whenSSTATEPOSTINSTFUNCSis removed in a future Yocto Project release.Specify the Sysroot when Using Certain External Scripts: Because the shared sysroot is now gone, the scripts
oe-find-native-sysrootandoe-run-nativehave been changed such that you need to specify which recipe'sSTAGING_DIR_NATIVEis used.
Note
You can find more information on how recipe-specific sysroots work in the "staging.bbclass"
section.
4.11.2. PATH Variable¶
Within the environment used to run build tasks, the environment
variable PATH is now sanitized such that
the normal native binary paths
(/bin, /sbin,
/usr/bin and so forth) are
removed and a directory containing symbolic links linking only
to the binaries from the host mentioned in the
HOSTTOOLS
and
HOSTTOOLS_NONFATAL
variables is added to PATH.
Consequently, any native binaries provided by the host that you need to call needs to be in one of these two variables at the configuration level.
Alternatively, you can add a native recipe (i.e.
-native) that provides the
binary to the recipe's
DEPENDS
value.
Note
PATH is not sanitized in the same way
within devshell.
If it were, you would have difficulty running host tools for
development and debugging within the shell.
4.11.3. Changes to Scripts¶
The following changes to scripts took place:
oe-find-native-sysroot: The usage for theoe-find-native-sysrootscript has changed to the following:$ . oe-find-native-sysrootrecipeYou must now supply a recipe for
recipeas part of the command. Prior to the Yocto Project 2.6.1 release, it was not necessary to provide the script with the command.oe-run-native: The usage for theoe-run-nativescript has changed to the following:$ oe-run-nativenative_recipetoolYou must supply the name of the native recipe and the tool you want to run as part of the command. Prior to the Yocto Project 2.6.1 release, it was not necessary to provide the native recipe with the command.
cleanup-workdir: Thecleanup-workdirscript has been removed because the script was found to be deleting files it should not have, which lead to broken build trees. Rather than trying to delete portions ofTMPDIRand getting it wrong, it is recommended that you deleteTMPDIRand have it restored from shared state (sstate) on subsequent builds.wipe-sysroot: Thewipe-sysrootscript has been removed as it is no longer needed with recipe-specific sysroots.
4.11.4. Changes to Functions¶
The previously deprecated
bb.data.getVar(),
bb.data.setVar(), and
related functions have been removed in favor of
d.getVar(),
d.setVar(), and so forth.
You need to fix any references to these old functions.
4.11.5. BitBake Changes¶
The following changes took place for BitBake:
BitBake's Graphical Dependency Explorer UI Replaced: BitBake's graphical dependency explorer UI
depexpwas replaced bytaskexp("Task Explorer"), which provides a graphical way of exploring thetask-depends.dotfile. The data presented by Task Explorer is much more accurate than the data that was presented bydepexp. Being able to visualize the data is an often requested feature as standard*.dotfile viewers cannot usual cope with the size of thetask-depends.dotfile.BitBake "-g" Output Changes: The
package-depends.dotandpn-depends.dotfiles as previously generated using thebitbake -gcommand have been removed. Arecipe-depends.dotfile is now generated as a collapsed version oftask-depends.dotinstead.The reason for this change is because
package-depends.dotandpn-depends.dotlargely date back to a time before task-based execution and do not take into account task-level dependencies between recipes, which could be misleading.Mirror Variable Splitting Changes: Mirror variables including
MIRRORS,PREMIRRORS, andSSTATE_MIRRORScan now separate values entirely with spaces. Consequently, you no longer need "\\n". BitBake looks for pairs of values, which simplifies usage. There should be no change required to existing mirror variable values themselves.The Subversion (SVN) Fetcher Uses an "ssh" Parameter and Not an "rsh" Parameter: The SVN fetcher now takes an "ssh" parameter instead of an "rsh" parameter. This new optional parameter is used when the "protocol" parameter is set to "svn+ssh". You can only use the new parameter to specify the
sshprogram used by SVN. The SVN fetcher passes the new parameter through theSVN_SSHenvironment variable during thedo_fetchtask.See the "Subversion (SVN) Fetcher (svn://)" section in the BitBake User Manual for additional information.
BB_SETSCENE_VERIFY_FUNCTIONandBB_SETSCENE_VERIFY_FUNCTION2Removed: Because the mechanism they were part of is no longer necessary with recipe-specific sysroots, theBB_SETSCENE_VERIFY_FUNCTIONandBB_SETSCENE_VERIFY_FUNCTION2variables have been removed.
4.11.6. Absolute Symbolic Links¶
Absolute symbolic links (symlinks) within staged files are no
longer permitted and now trigger an error.
Any explicit creation of symlinks can use the
lnr script, which is a replacement for
ln -r.
If the build scripts in the software that the recipe is building
are creating a number of absolute symlinks that need to be
corrected, you can inherit
relative_symlinks within the recipe to turn
those absolute symlinks into relative symlinks.
4.11.7. GPLv2 Versions of GPLv3 Recipes Moved¶
Older GPLv2 versions of GPLv3 recipes have moved to a
separate meta-gplv2 layer.
If you use
INCOMPATIBLE_LICENSE
to exclude GPLv3 or set
PREFERRED_VERSION
to substitute a GPLv2 version of a GPLv3 recipe, then you must add
the meta-gplv2 layer to your configuration.
Note
You can findmeta-gplv2 layer in the
OpenEmbedded layer index at
https://layers.openembedded.org/layerindex/branch/master/layer/meta-gplv2/.
These relocated GPLv2 recipes do not receive the same level of maintenance as other core recipes. The recipes do not get security fixes and upstream no longer maintains them. In fact, the upstream community is actively hostile towards people that use the old versions of the recipes. Moving these recipes into a separate layer both makes the different needs of the recipes clearer and clearly identifies the number of these recipes.
Note
The long-term solution might be to move to BSD-licensed replacements of the GPLv3 components for those that need to exclude GPLv3-licensed components from the target system. This solution will be investigated for future Yocto Project releases.
4.11.8. Package Management Changes¶
The following package management changes took place:
Smart package manager is replaced by DNF package manager. Smart has become unmaintained upstream, is not ported to Python 3.x. Consequently, Smart needed to be replaced. DNF is the only feasible candidate.
The change in functionality is that the on-target runtime package management from remote package feeds is now done with a different tool that has a different set of command-line options. If you have scripts that call the tool directly, or use its API, they need to be fixed.
For more information, see the DNF Documentation.
Rpm 5.x is replaced with Rpm 4.x. This is done for two major reasons:
DNF is API-incompatible with Rpm 5.x and porting it and maintaining the port is non-trivial.
Rpm 5.x itself has limited maintenance upstream, and the Yocto Project is one of the very few remaining users.
Berkeley DB 6.x is removed and Berkeley DB 5.x becomes the default:
Version 6.x of Berkeley DB has largely been rejected by the open source community due to its AGPLv3 license. As a result, most mainstream open source projects that require DB are still developed and tested with DB 5.x.
In OE-core, the only thing that was requiring DB 6.x was Rpm 5.x. Thus, no reason exists to continue carrying DB 6.x in OE-core.
createrepois replaced withcreaterepo_c.createrepo_cis the current incarnation of the tool that generates remote repository metadata. It is written in C as compared tocreaterepo, which is written in Python.createrepo_cis faster and is maintained.Architecture-independent RPM packages are "noarch" instead of "all".
This change was made because too many places in DNF/RPM4 stack already make that assumption. Only the filenames and the architecture tag has changed. Nothing else has changed in OE-core system, particularly in the
allarch.bbclassclass.Signing of remote package feeds using
PACKAGE_FEED_SIGNis not currently supported. This issue will be fully addressed in a future Yocto Project release. See defect 11209 for more information on a solution to package feed signing with RPM in the Yocto Project 2.3 release.OPKG now uses the libsolv backend for resolving package dependencies by default. This is vastly superior to OPKG's internal ad-hoc solver that was previously used. This change does have a small impact on disk (around 500 KB) and memory footprint.
Note
For further details on this change, see the commit message.
4.11.9. Removed Recipes¶
The following recipes have been removed:
linux-yocto 4.8:Version 4.8 has been removed. Versions 4.1 (LTSI), 4.4 (LTS), 4.9 (LTS/LTSI) and 4.10 are now present.python-smartpm:Functionally replaced bydnf.createrepo:Replaced by thecreaterepo-crecipe.rpmresolve:No longer needed with the move to RPM 4 as RPM itself is used instead.gstreamer:Removed the GStreamer Git version recipes as they have been stale.1.10.xrecipes are still present.alsa-conf-base:Merged intoalsa-confsincelibasounddepended on both. Essentially, no way existed to install only one of these.tremor:Moved tometa-multimedia. Fixed-integer Vorbis decoding is not needed by current hardware. Thus, GStreamer's ivorbis plugin has been disabled by default eliminating the need for thetremorrecipe in OE-Core.gummiboot:Replaced bysystemd-boot.
4.11.10. Wic Changes¶
The following changes have been made to Wic:
Note
For more information on Wic, see the "Creating Partitioned Images Using Wic" section in the Yocto Project Development Tasks Manual.
Default Output Directory Changed: Wic's default output directory is now the current directory by default instead of the unusual
/var/tmp/wic.The "-o" and "--outdir" options remain unchanged and are used to specify your preferred output directory if you do not want to use the default directory.
fsimage Plug-in Removed: The Wic fsimage plug-in has been removed as it duplicates functionality of the rawcopy plug-in.
4.11.11. QA Changes¶
The following QA checks have changed:
unsafe-references-in-binaries: Theunsafe-references-in-binariesQA check, which was disabled by default, has now been removed. This check was intended to detect binaries in/binthat link to libraries in/usr/liband have the case where the user has/usron a separate filesystem to/.The removed QA check was buggy. Additionally,
/usrresiding on a separate partition from/is now a rare configuration. Consequently,unsafe-references-in-binarieswas removed.file-rdeps: Thefile-rdepsQA check is now an error by default instead of a warning. Because it is an error instead of a warning, you need to address missing runtime dependencies.For additional information, see the
insaneclass and the "Errors and Warnings" section.
4.11.12. Miscellaneous Changes¶
The following miscellaneous changes have occurred:
In this release, a number of recipes have been changed to ignore the
largefileDISTRO_FEATURESitem, enabling large file support unconditionally. This feature has always been enabled by default. Disabling the feature has not been widely tested.Note
Future releases of the Yocto Project will remove entirely the ability to disable thelargefilefeature, which would make it unconditionally enabled everywhere.If the
DISTRO_VERSIONvalue contains the value of theDATEvariable, which is the default between Poky releases, theDATEvalue is explicitly excluded from/etc/issueand/etc/issue.net, which is displayed at the login prompt, in order to avoid conflicts with Multilib enabled. Regardless, theDATEvalue is inaccurate if thebase-filesrecipe is restored from shared state (sstate) rather than rebuilt.If you need the build date recorded in
/etc/issue*or anywhere else in your image, a better method is to define a post-processing function to do it and have the function called fromROOTFS_POSTPROCESS_COMMAND. Doing so ensures the value is always up-to-date with the created image.Dropbear's
initscript now disables DSA host keys by default. This change is in line with the systemd service file, which supports RSA keys only, and with recent versions of OpenSSH, which deprecates DSA host keys.The
buildhistoryclass now correctly uses tabs as separators between all columns ininstalled-package-sizes.txtin order to aid import into other tools.The
USE_LDCONFIGvariable has been replaced with the "ldconfig"DISTRO_FEATURESfeature. Distributions that previously set:USE_LDCONFIG = "0"should now instead use the following:
DISTRO_FEATURES_BACKFILL_CONSIDERED_append = " ldconfig"The default value of
COPYLEFT_LICENSE_INCLUDEnow includes all versions of AGPL licenses in addition to GPL and LGPL.Note
The default list is not intended to be guaranteed as a complete safe list. You should seek legal advice based on what you are distributing if you are unsure.Kernel module packages are now suffixed with the kernel version in order to allow module packages from multiple kernel versions to co-exist on a target system. If you wish to return to the previous naming scheme that does not include the version suffix, use the following:
KERNEL_MODULE_PACKAGE_SUFFIX to ""Removal of
libtool*.lafiles is now enabled by default. The*.lafiles are not actually needed on Linux and relocating them is an unnecessary burden.If you need to preserve these
.lafiles (e.g. in a custom distribution), you must changeINHERIT_DISTROsuch that "remove-libtool" is not included in the value.Extensible SDKs built for GCC 5+ now refuse to install on a distribution where the host GCC version is 4.8 or 4.9. This change resulted from the fact that the installation is known to fail due to the way the
uninativeshared state (sstate) package is built. See theuninativeclass for additional information.All native and nativesdk recipes now use a separate
DISTRO_FEATURESvalue instead of sharing the value used by recipes for the target, in order to avoid unnecessary rebuilds.The
DISTRO_FEATURESfornativerecipes isDISTRO_FEATURES_NATIVEadded to an intersection ofDISTRO_FEATURESandDISTRO_FEATURES_FILTER_NATIVE.For nativesdk recipes, the corresponding variables are
DISTRO_FEATURES_NATIVESDKandDISTRO_FEATURES_FILTER_NATIVESDK.The
FILESDIRvariable, which was previously deprecated and rarely used, has now been removed. You should change any recipes that setFILESDIRto setFILESPATHinstead.The
MULTIMACH_HOST_SYSvariable has been removed as it is no longer needed with recipe-specific sysroots.
4.12. Moving to the Yocto Project 2.4 Release¶
This section provides migration information for moving to the Yocto Project 2.4 Release from the prior release.
4.12.1. Memory Resident Mode¶
A persistent mode is now available in BitBake's default operation,
replacing its previous "memory resident mode" (i.e.
oe-init-build-env-memres).
Now you only need to set
BB_SERVER_TIMEOUT
to a timeout (in seconds) and BitBake's server stays resident for
that amount of time between invocations.
The oe-init-build-env-memres script has been
removed since a separate environment setup script is no longer
needed.
4.12.2. Packaging Changes¶
This section provides information about packaging changes that have ocurred:
python3Changes:The main "python3" package now brings in all of the standard Python 3 distribution rather than a subset. This behavior matches what is expected based on traditional Linux distributions. If you wish to install a subset of Python 3, specify
python-coreplus one or more of the individual packages that are still produced.python3: Thebz2.py,lzma.py, and_compression.pyscripts have been moved from thepython3-miscpackage to thepython3-compressionpackage.
binutils: Thelibbfdlibrary is now packaged in a separate "libbfd" package. This packaging saves space when certain tools (e.g.perf) are installed. In such cases, the tools only needlibbfdrather than all the packages inbinutils.util-linuxChanges:The
suprogram is now packaged in a separate "util-linux-su" package, which is only built when "pam" is listed in theDISTRO_FEATURESvariable.util-linuxshould not be installed unless it is needed becausesuis normally provided through the shadow file format. The mainutil-linuxpackage has runtime dependencies (i.e.RDEPENDS) on theutil-linux-supackage when "pam" is inDISTRO_FEATURES.The
switch_rootprogram is now packaged in a separate "util-linux-switch-root" package for small initramfs images that do not need the wholeutil-linuxpackage or the busybox binary, which are both much larger thanswitch_root. The mainutil-linuxpackage has a recommended runtime dependency (i.e.RRECOMMENDS) on theutil-linux-switch-rootpackage.The
ioniceprogram is now packaged in a separate "util-linux-ionice" package. The mainutil-linuxpackage has a recommended runtime dependency (i.e.RRECOMMENDS) on theutil-linux-ionicepackage.
initscripts: Thesushellprogram is now packaged in a separate "initscripts-sushell" package. This packaging change allows systems to pullsushellin whenselinuxis enabled. The change also eliminates needing to pull in the entireinitscriptspackage. The maininitscriptspackage has a runtime dependency (i.e.RDEPENDS) on thesushellpackage when "selinux" is inDISTRO_FEATURES.glib-2.0: Theglib-2.0package now has a recommended runtime dependency (i.e.RRECOMMENDS) on theshared-mime-infopackage, since large portions of GIO are not useful without the MIME database. You can remove the dependency by using theBAD_RECOMMENDATIONSvariable ifshared-mime-infois too large and is not required.Go Standard Runtime: The Go standard runtime has been split out from the main
gorecipe into a separatego-runtimerecipe.
4.12.3. Removed Recipes¶
The following recipes have been removed:
acpitests: This recipe is not maintained.autogen-native: No longer required by Grub, oe-core, or meta-oe.bdwgc: Nothing in OpenEmbedded-Core requires this recipe. It has moved to meta-oe.byacc: This recipe was only needed by rpm 5.x and has moved to meta-oe.gcc (5.4): The 5.4 series dropped the recipe in favor of 6.3 / 7.2.gnome-common: Deprecated upstream and no longer needed.go-bootstrap-native: Go 1.9 does its own bootstrapping so this recipe has been removed.guile: This recipe was only needed byautogen-nativeandremake. The recipe is no longer needed by either of these programs.libclass-isa-perl: This recipe was previously needed for LSB 4, no longer needed.libdumpvalue-perl: This recipe was previously needed for LSB 4, no longer needed.libenv-perl: This recipe was previously needed for LSB 4, no longer needed.libfile-checktree-perl: This recipe was previously needed for LSB 4, no longer needed.libi18n-collate-perl: This recipe was previously needed for LSB 4, no longer needed.libiconv: This recipe was only needed foruclibc, which was removed in the previous release.glibcandmuslhave their own implementations.meta-mingwstill needslibiconv, so it has been moved tometa-mingw.libpng12: This recipe was previously needed for LSB. The currentlibpngis 1.6.x.libpod-plainer-perl: This recipe was previously needed for LSB 4, no longer needed.linux-yocto (4.1): This recipe was removed in favor of 4.4, 4.9, 4.10 and 4.12.mailx: This recipe was previously only needed for LSB compatibility, and upstream is defunct.mesa (git version only): The git version recipe was stale with respect to the release version.ofono (git version only): The git version recipe was stale with respect to the release version.portmap: This recipe is obsolete and is superseded byrpcbind.python3-pygpgme: This recipe is old and unmaintained. It was previously required bydnf, which has switched to officialgpgmePython bindings.python-async: This recipe has been removed in favor of the Python 3 version.python-gitdb: This recipe has been removed in favor of the Python 3 version.python-git: This recipe was removed in favor of the Python 3 version.python-mako: This recipe was removed in favor of the Python 3 version.python-pexpect: This recipe was removed in favor of the Python 3 version.python-ptyprocess: This recipe was removed in favor of Python the 3 version.python-pycurl: Nothing is using this recipe in OpenEmbedded-Core (i.e.meta-oe).python-six: This recipe was removed in favor of the Python 3 version.python-smmap: This recipe was removed in favor of the Python 3 version.remake: Usingremakeas the provider ofvirtual/makeis broken. Consequently, this recipe is not needed in OpenEmbedded-Core.
4.12.4. Kernel Device Tree Move¶
Kernel Device Tree support is now easier to enable in a kernel
recipe.
The Device Tree code has moved to a
kernel-devicetree
class.
Functionality is automatically enabled for any recipe that inherits
the
kernel
class and sets the
KERNEL_DEVICETREE
variable.
The previous mechanism for doing this,
meta/recipes-kernel/linux/linux-dtb.inc,
is still available to avoid breakage, but triggers a
deprecation warning.
Future releases of the Yocto Project will remove
meta/recipes-kernel/linux/linux-dtb.inc.
It is advisable to remove any require
statements that request
meta/recipes-kernel/linux/linux-dtb.inc
from any custom kernel recipes you might have.
This will avoid breakage in post 2.4 releases.
4.12.5. Package QA Changes¶
The following package QA changes took place:
The "unsafe-references-in-scripts" QA check has been removed.
If you refer to
${COREBASE}/LICENSEwithinLIC_FILES_CHKSUMyou receive a warning because this file is a description of the license for OE-Core. Use${COMMON_LICENSE_DIR}/MITif your recipe is MIT-licensed and you cannot use the preferred method of referring to a file within the source tree.
4.12.6. README File Changes¶
The following are changes to README files:
The main Poky
READMEfile has been moved to themeta-pokylayer and has been renamedREADME.poky. A symlink has been created so that references to the old location work.The
README.hardwarefile has been moved tometa-yocto-bsp. A symlink has been created so that references to the old location work.A
README.qemufile has been created with coverage of theqemu*machines.
4.12.7. Miscellaneous Changes¶
The following are additional changes:
The
ROOTFS_PKGMANAGE_BOOTSTRAPvariable and any references to it have been removed. You should remove this variable from any custom recipes.The
meta-yoctodirectory has been removed.Note
In the Yocto Project 2.1 releasemeta-yoctowas renamed tometa-pokyand themeta-yoctosubdirectory remained to avoid breaking existing configurations.The
maintainers.incfile, which tracks maintainers by listing a primary person responsible for each recipe in OE-Core, has been moved frommeta-pokyto OE-Core (i.e. frommeta-poky/conf/distro/includetometa/conf/distro/include).The
buildhistoryclass now makes a single commit per build rather than one commit per subdirectory in the repository. This behavior assumes the commits are enabled withBUILDHISTORY_COMMIT= "1", which is typical. Previously, thebuildhistoryclass made one commit per subdirectory in the repository in order to make it easier to see the changes for a particular subdirectory. To view a particular change, specify that subdirectory as the last parameter on thegit showorgit diffcommands.The
x86-base.incfile, which is included by all x86-based machine configurations, now setsIMAGE_FSTYPESusing?=to "live" rather than appending with+=. This change makes the default easier to override.BitBake fires multiple "BuildStarted" events when multiconfig is enabled (one per configuration). For more information, see the "Events" section in the BitBake User Manual.
By default, the
security_flags.incfile sets aGCCPIEvariable with an option to enable Position Independent Executables (PIE) withingcc. Enabling PIE in the GNU C Compiler (GCC), makes Return Oriented Programming (ROP) attacks much more difficult to execute.OE-Core now provides a
bitbake-layersplugin that implements a "create-layer" subcommand. The implementation of this subcommand has resulted in theyocto-layerscript being deprecated and will likely be removed in the next Yocto Project release.The
vmdk,vdi, andqcow2image file types are now used in conjunction with the "wic" image type throughCONVERSION_CMD. Consequently, the equivalent image types are nowwic.vmdk,wic.vdi, andwic.qcow2, respectively.do_image_<type>[depends]has replacedIMAGE_DEPENDS_<type>. If you have your own classes that implement custom image types, then you need to update them.OpenSSL 1.1 has been introduced. However, the default is still 1.0.x through the
PREFERRED_VERSIONvariable. This preference is set is due to the remaining compatibility issues with other software. ThePROVIDESvariable in the openssl 1.0 recipe now includes "openssl10" as a marker that can be used inDEPENDSwithin recipes that build software that still depend on OpenSSL 1.0.To ensure consistent behavior, BitBake's "-r" and "-R" options (i.e. prefile and postfile), which are used to read or post-read additional configuration files from the command line, now only affect the current BitBake command. Before these BitBake changes, these options would "stick" for future executions.
4.13. Moving to the Yocto Project 2.5 Release¶
This section provides migration information for moving to the Yocto Project 2.5 Release from the prior release.
4.13.1. Packaging Changes¶
This section provides information about packaging changes that have occurred:
bind-libs: The libraries packaged by the bind recipe are in a separatebind-libspackage.libfm-gtk: ThelibfmGTK+ bindings are split into a separatelibfm-gtkpackage.flex-libfl: The flex recipe splits out libfl into a separateflex-libflpackage to avoid too many dependencies being pulled in where only the library is needed.grub-efi: Thegrub-eficonfiguration is split into a separategrub-bootconfrecipe. However, the dependency relationship fromgrub-efiis through a virtual/grub-bootconf provider making it possible to have your own recipe provide the dependency. Alternatively, you can use a BitBake append file to bring the configuration back into thegrub-efirecipe.armv7a Legacy Package Feed Support: Legacy support is removed for transitioning from
armv7atoarmv7a-vfp-neonin package feeds, which was previously enabled by settingPKGARCHCOMPAT_ARMV7A. This transition occurred in 2011 and active package feeds should by now be updated to the new naming.
4.13.2. Removed Recipes¶
The following recipes have been removed:
gcc: The version 6.4 recipes are replaced by 7.x.gst-player: Renamed togst-examplesas per upstream.hostap-utils: This software package is obsolete.latencytop: This recipe is no longer maintained upstream. The last release was in 2009.libpfm4: The only file that requires this recipe isoprofile, which has been removed.linux-yocto: The version 4.4, 4.9, and 4.10 recipes have been removed. Versions 4.12, 4.14, and 4.15 remain.man: This recipe has been replaced by modernman-dbmkelfimage: This tool has been removed in the upstream coreboot project, and is no longer needed with the removal of the ELF image type.nativesdk-postinst-intercept: This recipe is not maintained.neon: This software package is no longer maintained upstream and is no longer needed by anything in OpenEmbedded-Core.oprofile: The functionality of this recipe is replaced byperfand keeping compatibility on an ongoing basis withmuslis difficult.pax: This software package is obsolete.stat: This software package is not maintained upstream.coreutilsprovides a modern stat binary.zisofs-tools-native: This recipe is no longer needed because the compressed ISO image feature has been removed.
4.13.3. Scripts and Tools Changes¶
The following are changes to scripts and tools:
yocto-bsp,yocto-kernel, andyocto-layer: Theyocto-bsp,yocto-kernel, andyocto-layerscripts previously shipped with poky but not in OpenEmbedded-Core have been removed. These scripts are not maintained and are outdated. In many cases, they are also limited in scope. Thebitbake-layers create-layercommand is a direct replacement foryocto-layer. See the documentation to create a BSP or kernel recipe in the "BSP Kernel Recipe Example" section.devtool finish:devtool finishnow exits with an error if there are uncommitted changes or a rebase/am in progress in the recipe's source repository. If this error occurs, there might be uncommitted changes that will not be included in updates to the patches applied by the recipe. A -f/--force option is provided for situations that the uncommitted changes are inconsequential and you want to proceed regardless.scripts/oe-setup-rpmreposcript: The functionality ofscripts/oe-setup-rpmrepois replaced bybitbake package-index.scripts/test-dependencies.shscript: The script is largely made obsolete by the recipe-specific sysroots functionality introduced in the previous release.
4.13.4. BitBake Changes¶
The following are BitBake changes:
The
--runalloption has changed. There are two different behaviors people might want:Behavior A: For a given target (or set of targets) look through the task graph and run task X only if it is present and will be built.
Behavior B: For a given target (or set of targets) look through the task graph and run task X if any recipe in the taskgraph has such a target, even if it is not in the original task graph.
The
--runalloption now performs "Behavior B". Previously--runallbehaved like "Behavior A". A--runonlyoption has been added to retain the ability to perform "Behavior A".Several explicit "run this task for all recipes in the dependency tree" tasks have been removed (e.g.
fetchall,checkuriall, and the*alltasks provided by thedistrodataandarchiverclasses). There is a BitBake option to complete this for any arbitrary task. For example:bitbake <target> -c fetchallshould now be replaced with:
bitbake <target> --runall=fetch
4.13.5. Python and Python 3 Changes¶
The following are auto-packaging changes to Python and Python 3:
The script-managed python-*-manifest.inc files
that were previously used to generate Python and Python 3
packages have been replaced with a JSON-based file that is
easier to read and maintain.
A new task is available for maintainers of the Python recipes to
update the JSON file when upgrading to new Python versions.
You can now edit the file directly instead of having to edit a
script and run it to update the file.
One particular change to note is that the Python recipes no longer
have build-time provides for their packages.
This assumes python-foo is one of the packages
provided by the Python recipe.
You can no longer run bitbake python-foo or
have a DEPENDS on
python-foo, but doing either of the following
causes the package to work as expected:
IMAGE_INSTALL_append = " python-foo"
or
RDEPENDS_${PN} = "python-foo"
The earlier build-time provides behavior was a quirk of the way the Python manifest file was created. For more information on this change please see this commit.
4.13.6. Miscellaneous Changes¶
The following are additional changes:
The
kernelclass supports building packages for multiple kernels. If your kernel recipe or.bbappendfile mentions packaging at all, you should replace references to the kernel in package names with${KERNEL_PACKAGE_NAME}. For example, if you disable automatic installation of the kernel image usingRDEPENDS_kernel-base = ""you can avoid warnings usingRDEPENDS_${KERNEL_PACKAGE_NAME}-base = ""instead.The
buildhistoryclass commits changes to the repository by default so you no longer need to setBUILDHISTORY_COMMIT = "1". If you want to disable commits you need to setBUILDHISTORY_COMMIT = "0"in your configuration.The
beaglebonereference machine has been renamed tobeaglebone-yocto. Thebeaglebone-yoctoBSP is a reference implementation using only mainline components available in OpenEmbedded-Core andmeta-yocto-bsp, whereas Texas Instruments maintains a full-featured BSP in themeta-tilayer. This rename avoids the previous name clash that existed between the two BSPs.The
update-alternativesclass no longer works with SysVinitscripts because this usage has been problematic. Also, thesysklogdrecipe no longer usesupdate-alternativesbecause it is incompatible with other implementations.By default, the
cmakeclass usesninjainstead ofmakefor building. This improves build performance. If a recipe is broken withninja, then the recipe can setOECMAKE_GENERATOR = "Unix Makefiles"to change back tomake.The previously deprecated
base_*functions have been removed in favor of their replacements inmeta/lib/oeandbitbake/lib/bb. These are typically used from recipes and classes. Any references to the old functions must be updated. The following table shows the removed functions and their replacements:Removed Replacement ============================ ============================ base_path_join() oe.path.join() base_path_relative() oe.path.relative() base_path_out() oe.path.format_display() base_read_file() oe.utils.read_file() base_ifelse() oe.utils.ifelse() base_conditional() oe.utils.conditional() base_less_or_equal() oe.utils.less_or_equal() base_version_less_or_equal() oe.utils.version_less_or_equal() base_contains() bb.utils.contains() base_both_contain() oe.utils.both_contain() base_prune_suffix() oe.utils.prune_suffix() oe_filter() oe.utils.str_filter() oe_filter_out() oe.utils.str_filter_out() (or use the _remove operator).Using
exit 1to explicitly defer a postinstall script until first boot is now deprecated since it is not an obvious mechanism and can mask actual errors. If you want to explicitly defer a postinstall to first boot on the target rather than atrootfscreation time, usepkg_postinst_ontarget()or callpostinst-intercepts defer_to_first_bootfrompkg_postinst(). Any failure of apkg_postinst()script (includingexit 1) will trigger a warning duringdo_rootfs.For more information, see the "Post-Installation Scripts" section in the Yocto Project Development Tasks Manual.
The
elfimage type has been removed. This image type was removed because themkelfimagetool that was required to create it is no longer provided by coreboot upstream and required updating every timebinutilsupdated.Support for .iso image compression (previously enabled through
COMPRESSISO = "1") has been removed. The userspace tools (zisofs-tools) are unmaintained andsquashfsprovides better performance and compression. In order to build a live image with squashfs+lz4 compression enabled you should now setLIVE_ROOTFS_TYPE = "squashfs-lz4"and ensure thatliveis inIMAGE_FSTYPES.Recipes with an unconditional dependency on
libpamare only buildable withpaminDISTRO_FEATURES. If the dependency is truly optional then it is recommended that the dependency be conditional uponpambeing inDISTRO_FEATURES.For EFI-based machines, the bootloader (
grub-efiby default) is installed into the image at /boot. Wic can be used to split the bootloader into separate boot and rootfs partitions if necessary.Patches whose context does not match exactly (i.e. where patch reports "fuzz" when applying) will generate a warning. For an example of this see this commit.
Layers are expected to set
LAYERSERIES_COMPAT_layernameto match the version(s) of OpenEmbedded-Core they are compatible with. This is specified as codenames using spaces to separate multiple values (e.g. "rocko sumo"). If a layer does not setLAYERSERIES_COMPAT_layername, a warning will is shown. If a layer sets a value that does not include the current version ("sumo" for the 2.5 release), then an error will be produced.The
TZenvironment variable is set to "UTC" within the build environment in order to fix reproducibility problems in some recipes.
4.14. Moving to the Yocto Project 2.6 Release¶
This section provides migration information for moving to the Yocto Project 2.6 Release from the prior release.
4.14.1. GCC 8.2 is Now Used by Default¶
The GNU Compiler Collection version 8.2 is now used by default for compilation. For more information on what has changed in the GCC 8.x release, see https://gcc.gnu.org/gcc-8/changes.html.
If you still need to compile with version 7.x, GCC 7.3 is
also provided.
You can select this version by setting the
and can be selected by setting the
GCCVERSION
variable to "7.%" in your configuration.
4.14.2. Removed Recipes¶
The following recipes have been removed:
beecrypt: No longer needed since moving to RPM 4.
bigreqsproto: Replaced by xorgproto.
calibrateproto: Removed in favor of xinput.
compositeproto: Replaced by xorgproto.
damageproto: Replaced by xorgproto.
dmxproto: Replaced by xorgproto.
dri2proto: Replaced by xorgproto.
dri3proto: Replaced by xorgproto.
eee-acpi-scripts: Became obsolete.
fixesproto: Replaced by xorgproto.
fontsproto: Replaced by xorgproto.
fstests: Became obsolete.
gccmakedep: No longer used.
glproto: Replaced by xorgproto.
gnome-desktop3: No longer needed. This recipe has moved to meta-oe.
icon-naming-utils: No longer used since the Sato theme was removed in 2016.
inputproto: Replaced by xorgproto.
kbproto: Replaced by xorgproto.
libusb-compat: Became obsolete.
libuser: Became obsolete.
libnfsidmap: No longer an external requirement since nfs-utils 2.2.1. libnfsidmap is now integrated.
libxcalibrate: No longer needed with xinput
mktemp: Became obsolete. The mktemp command is provided by both busybox and coreutils.
ossp-uuid: Is not being maintained and has mostly been replaced by uuid.h in util-linux.
pax-utils: No longer needed. Previous QA tests that did use this recipe are now done at build time.
pcmciautils: Became obsolete.
pixz: No longer needed. xz now supports multi-threaded compression.
presentproto: Replaced by xorgproto.
randrproto: Replaced by xorgproto.
recordproto: Replaced by xorgproto.
renderproto: Replaced by xorgproto.
resourceproto: Replaced by xorgproto.
scrnsaverproto: Replaced by xorgproto.
trace-cmd: Became obsolete. perf replaced this recipe's functionally.
videoproto: Replaced by xorgproto.
wireless-tools: Became obsolete. Superseded by iw.
xcmiscproto: Replaced by xorgproto.
xextproto: Replaced by xorgproto.
xf86dgaproto: Replaced by xorgproto.
xf86driproto: Replaced by xorgproto.
xf86miscproto: Replaced by xorgproto.
xf86-video-omapfb: Became obsolete. Use kernel modesetting driver instead.
xf86-video-omap: Became obsolete. Use kernel modesetting driver instead.
xf86vidmodeproto: Replaced by xorgproto.
xineramaproto: Replaced by xorgproto.
xproto: Replaced by xorgproto.
yasm: No longer needed since previous usages are now satisfied by nasm.
4.14.3. Packaging Changes¶
The following packaging changes have been made:
cmake:cmake.m4andtoolchainfiles have been moved to the main package.iptables: Theiptablesmodules have been split into separate packages.alsa-lib:libasoundis now in the mainalsa-libpackage instead oflibasound.glibc:libnss-dbis now in its own package along with a/var/db/makedbs.shscript to update databases.pythonandpython3: The main package has been removed from the recipe. You must install specific packages orpython-modules/python3-modulesfor everything.systemtap: Movedsystemtap-exporterinto its own package.
4.14.4. XOrg Protocol dependencies¶
The "*proto" upstream repositories have been combined into one
"xorgproto" repository.
Thus, the corresponding recipes have also been combined into a
single xorgproto recipe.
Any recipes that depend upon the older *proto
recipes need to be changed to depend on the newer
xorgproto recipe instead.
For names of recipes removed because of this repository change, see the Removed Recipes section.
4.14.5. distutils and distutils3 Now Prevent Fetching Dependencies During the do_configure Task¶
Previously, it was possible for Python recipes that inherited
the
distutils
and
distutils3
classes to fetch code during the
do_configure
task to satisfy dependencies mentioned in
setup.py if those dependencies were not
provided in the sysroot (i.e. recipes providing the dependencies
were missing from
DEPENDS).
Note
This change affects classes beyond just the two mentioned (i.e.distutils and
distutils3).
Any recipe that inherits distutils*
classes are affected.
For example, the setuptools and
setuptools3 recipes are affected since
they inherit the distutils* classes.
Fetching these types of dependencies that are not provided in the
sysroot negatively affects the ability to reproduce builds.
This type of fetching is now explicitly disabled.
Consequently, any missing dependencies in Python recipes that
use these classes now result in an error during the
do_configure task.
4.14.6. linux-yocto Configuration Audit Issues Now Correctly Reported¶
Due to a bug, the kernel configuration audit functionality was
not writing out any resulting warnings during the build.
This issue is now corrected.
You might notice these warnings now if you have a custom kernel
configuration with a linux-yocto style
kernel recipe.
4.14.7. Image/Kernel Artifact Naming Changes¶
The following changes have been made:
Name variables (e.g.
IMAGE_NAME) use a newIMAGE_VERSION_SUFFIXvariable instead ofDATETIME. UsingIMAGE_VERSION_SUFFIXallows easier and more direct changes.The
IMAGE_VERSION_SUFFIXvariable is set in thebitbake.confconfiguration file as follows:IMAGE_VERSION_SUFFIX = "-${DATETIME}"Several variables have changed names for consistency:
Old Variable Name New Variable Name ======================================================== KERNEL_IMAGE_BASE_NAME KERNEL_IMAGE_NAME KERNEL_IMAGE_SYMLINK_NAME KERNEL_IMAGE_LINK_NAME MODULE_TARBALL_BASE_NAME MODULE_TARBALL_NAME MODULE_TARBALL_SYMLINK_NAME MODULE_TARBALL_LINK_NAME INITRAMFS_BASE_NAME INITRAMFS_NAMEThe
MODULE_IMAGE_BASE_NAMEvariable has been removed. The module tarball name is now controlled directly with theMODULE_TARBALL_NAMEvariable.The
KERNEL_DTB_NAMEandKERNEL_DTB_LINK_NAMEvariables have been introduced to control kernel Device Tree Binary (DTB) artifact names instead of manglingKERNEL_IMAGE_*variables.The
KERNEL_FIT_NAMEandKERNEL_FIT_LINK_NAMEvariables have been introduced to specify the name of flattened image tree (FIT) kernel images similar to other deployed artifacts.The
MODULE_TARBALL_NAMEandMODULE_TARBALL_LINK_NAMEvariable values no longer include the "module-" prefix or ".tgz" suffix. These parts are now hardcoded so that the values are consistent with other artifact naming variables.Added the
INITRAMFS_LINK_NAMEvariable so that the symlink can be controlled similarly to other artifact types.INITRAMFS_NAMEnow uses "${PKGE}-${PKGV}-${PKGR}-${MACHINE}${IMAGE_VERSION_SUFFIX}" instead of "${PV}-${PR}-${MACHINE}-${DATETIME}", which makes it consistent with other variables.
4.14.8. SERIAL_CONSOLE Deprecated¶
The
SERIAL_CONSOLE
variable has been functionally replaced by the
SERIAL_CONSOLES
variable for some time.
With the Yocto Project 2.6 release,
SERIAL_CONSOLE has been officially deprecated.
SERIAL_CONSOLE will continue to work as
before for the 2.6 release.
However, for the sake of future compatibility, it is recommended
that you replace all instances of
SERIAL_CONSOLE with
SERIAL_CONSOLES.
Note
The only difference in usage is thatSERIAL_CONSOLES expects entries to be
separated using semicolons as compared to
SERIAL_CONSOLE, which expects spaces.
4.14.9. Configure Script Reports Unknown Options as Errors¶
If the configure script reports an unknown option, this now triggers a QA error instead of a warning. Any recipes that previously got away with specifying such unknown options now need to be fixed.
4.14.10. Override Changes¶
The following changes have occurred:
The
virtclass-nativeandvirtclass-nativesdkOverrides Have Been Removed: Thevirtclass-nativeandvirtclass-nativesdkoverrides have been deprecated since 2012 in favor ofclass-nativeandclass-nativesdk, respectively. Bothvirtclass-nativeandvirtclass-nativesdkare now dropped.Note
Thevirtclass-multilib-overrides for multilib are still valid.The
forcevariableOverride Now Has a Higher Priority ThanlibcOverrides: Theforcevariableoverride is documented to be the highest priority override. However, due to a long-standing quirk of howOVERRIDESis set, thelibcoverrides (e.g.libc-glibc,libc-musl, and so forth) erroneously had a higher priority. This issue is now corrected.It is likely this change will not cause any problems. However, it is possible with some unusual configurations that you might see a change in behavior if you were relying on the previous behavior. Be sure to check how you use
forcevariableandlibc-*overrides in your custom layers and configuration files to ensure they make sense.The
build-${BUILD_OS}Override Has Been Removed: Thebuild-${BUILD_OS}, which is typicallybuild-linux, override has been removed because building on a host operating system other than a recent version of Linux is neither supported nor recommended. Dropping the override avoids giving the impression that other host operating systems might be supported.The "_remove" operator now preserves whitespace. Consequently, when specifying list items to remove, be aware that leading and trailing whitespace resulting from the removal is retained.
See the "Removal (Override Style Syntax)" section in the BitBake User Manual for a detailed example.
4.14.11. systemd Configuration is Now Split Into systemd-conf¶
The configuration for the systemd recipe
has been moved into a system-conf recipe.
Moving this configuration to a separate recipe avoids the
systemd recipe from becoming machine-specific
for cases where machine-specific configurations need to be applied
(e.g. for qemu* machines).
Currently, the new recipe packages the following files:
${sysconfdir}/machine-id
${sysconfdir}/systemd/coredump.conf
${sysconfdir}/systemd/journald.conf
${sysconfdir}/systemd/logind.conf
${sysconfdir}/systemd/system.conf
${sysconfdir}/systemd/user.conf
If you previously used bbappend files to append the
systemd recipe to change any of the
listed files, you must do so for the
systemd-conf recipe instead.
4.14.12. Automatic Testing Changes¶
This section provides information about automatic testing changes:
TEST_IMAGEVariable Removed: Prior to this release, you set theTEST_IMAGEvariable to "1" to enable automatic testing for successfully built images. TheTEST_IMAGEvariable no longer exists and has been replaced by theTESTIMAGE_AUTOvariable.Inheriting the
testimageandtestsdkClasses: Best practices now dictate that you use theIMAGE_CLASSESvariable rather than theINHERITvariable when you inherit thetestimageandtestsdkclasses used for automatic testing.
4.14.13. OpenSSL Changes¶
OpenSSL has been upgraded from 1.0 to 1.1. By default, this upgrade could cause problems for recipes that have both versions in their dependency chains. The problem is that both versions cannot be installed together at build time.
Note
It is possible to have both versions of the library at runtime.
4.14.14. BitBake Changes¶
The server logfile bitbake-cookerdaemon.log is
now always placed in the
Build Directory
instead of the current directory.
4.14.15. Security Changes¶
The Poky distribution now uses security compiler flags by default. Inclusion of these flags could cause new failures due to stricter checking for various potential security issues in code.
4.14.16. Post Installation Changes¶
You must explicitly mark post installs to defer to the target.
If you want to explicitly defer a postinstall to first boot on
the target rather than at rootfs creation time, use
pkg_postinst_ontarget() or call
postinst-intercepts defer_to_first_boot from
pkg_postinst().
Any failure of a pkg_postinst() script
(including exit 1) triggers an error during the
do_rootfs task.
For more information on post-installation behavior, see the "Post-Installation Scripts" section in the Yocto Project Development Tasks Manual.
4.14.17. Python 3 Profile-Guided Optimization¶
The python3 recipe now enables profile-guided
optimization.
Using this optimization requires a little extra build time in
exchange for improved performance on the target at runtime.
Additionally, the optimization is only enabled if the current
MACHINE
has support for user-mode emulation in QEMU (i.e. "qemu-usermode"
is in
MACHINE_FEATURES,
which it is by default).
If you wish to disable Python profile-guided optimization
regardless of the value of
MACHINE_FEATURES, then ensure that
PACKAGECONFIG
for the python3 recipe does not contain "pgo".
You could accomplish the latter using the following at the
configuration level:
PACKAGECONFIG_remove_pn-python3 = "pgo"
Alternatively, you can set
PACKAGECONFIG using an append file for the
python3 recipe.
4.14.18. Miscellaneous Changes¶
The following miscellaneous changes occurred:
Default to using the Thumb-2 instruction set for armv7a and above. If you have any custom recipes that build software that needs to be built with the ARM instruction set, change the recipe to set the instruction set as follows:
ARM_INSTRUCTION_SET = "arm"run-postinstsno longer uses/etc/*-postinstsfordpkg/opkgin favor of built-in postinst support. RPM behavior remains unchanged.The
NOISOandNOHDDvariables are no longer used. You now control building*.isoand*.hddimgimage types directly by using theIMAGE_FSTYPESvariable.The
scripts/contrib/mkefidisk.shhas been removed in favor of Wic.kernel-moduleshas been removed fromRRECOMMENDSforqemumipsandqemumips64machines. Removal also impacts thex86-base.incfile.Note
genericx86andgenericx86-64retainkernel-modulesas part of theRRECOMMENDSvariable setting.The
LGPLv2_WHITELIST_GPL-3.0variable has been removed. If you are setting this variable in your configuration, set or append it to theWHITELIST_GPL-3.0variable instead.${ASNEEDED}is now included in theTARGET_LDFLAGSvariable directly. The remaining definitions frommeta/conf/distro/include/as-needed.inchave been moved to corresponding recipes.Support for DSA host keys has been dropped from the OpenSSH recipes. If you are still using DSA keys, you must switch over to a more secure algorithm as recommended by OpenSSH upstream.
The
dhcprecipe now uses thedhcpd6.confconfiguration file indhcpd6.servicefor IPv6 DHCP rather than re-usingdhcpd.conf, which is now reserved for IPv4.
Chapter 5. Source Directory Structure¶
Table of Contents
- 5.1. Top-Level Core Components
- 5.2. The Build Directory -
build/ - 5.2.1.
build/buildhistory - 5.2.2.
build/conf/local.conf - 5.2.3.
build/conf/bblayers.conf - 5.2.4.
build/conf/sanity_info - 5.2.5.
build/downloads/ - 5.2.6.
build/sstate-cache/ - 5.2.7.
build/tmp/ - 5.2.8.
build/tmp/buildstats/ - 5.2.9.
build/tmp/cache/ - 5.2.10.
build/tmp/deploy/ - 5.2.11.
build/tmp/deploy/deb/ - 5.2.12.
build/tmp/deploy/rpm/ - 5.2.13.
build/tmp/deploy/ipk/ - 5.2.14.
build/tmp/deploy/licenses/ - 5.2.15.
build/tmp/deploy/images/ - 5.2.16.
build/tmp/deploy/sdk/ - 5.2.17.
build/tmp/sstate-control/ - 5.2.18.
build/tmp/sysroots-components/ - 5.2.19.
build/tmp/sysroots/ - 5.2.20.
build/tmp/stamps/ - 5.2.21.
build/tmp/log/ - 5.2.22.
build/tmp/work/ - 5.2.23.
build/tmp/work/tunearch/recipename/version/ - 5.2.24.
build/tmp/work-shared/
- 5.2.1.
- 5.3. The Metadata -
meta/ - 5.3.1.
meta/classes/ - 5.3.2.
meta/conf/ - 5.3.3.
meta/conf/machine/ - 5.3.4.
meta/conf/distro/ - 5.3.5.
meta/conf/machine-sdk/ - 5.3.6.
meta/files/ - 5.3.7.
meta/lib/ - 5.3.8.
meta/recipes-bsp/ - 5.3.9.
meta/recipes-connectivity/ - 5.3.10.
meta/recipes-core/ - 5.3.11.
meta/recipes-devtools/ - 5.3.12.
meta/recipes-extended/ - 5.3.13.
meta/recipes-gnome/ - 5.3.14.
meta/recipes-graphics/ - 5.3.15.
meta/recipes-kernel/ - 5.3.16.
meta/recipes-lsb4/ - 5.3.17.
meta/recipes-multimedia/ - 5.3.18.
meta/recipes-rt/ - 5.3.19.
meta/recipes-sato/ - 5.3.20.
meta/recipes-support/ - 5.3.21.
meta/site/ - 5.3.22.
meta/recipes.txt
- 5.3.1.
The Source Directory consists of several components. Understanding them and knowing where they are located is key to using the Yocto Project well. This chapter describes the Source Directory and gives information about the various files and directories.
For information on how to establish a local Source Directory on your development system, see the "Locating Yocto Project Source Files" section in the Yocto Project Development Tasks Manual.
Note
The OpenEmbedded build system does not support file or directory names that contain spaces. Be sure that the Source Directory you use does not contain these types of names.5.1. Top-Level Core Components¶
This section describes the top-level components of the Source Directory.
5.1.1. bitbake/¶
This directory includes a copy of BitBake for ease of use. The copy usually matches the current stable BitBake release from the BitBake project. BitBake, a Metadata interpreter, reads the Yocto Project Metadata and runs the tasks defined by that data. Failures are usually from the Metadata and not from BitBake itself. Consequently, most users do not need to worry about BitBake.
When you run the bitbake command, the
main BitBake executable, which resides in the
bitbake/bin/ directory, starts.
Sourcing the environment setup script (i.e.
oe-init-build-env)
places the scripts and
bitbake/bin directories (in that order) into
the shell's PATH environment variable.
For more information on BitBake, see the BitBake User Manual.
5.1.2. build/¶
This directory contains user configuration files and the output
generated by the OpenEmbedded build system in its standard configuration where
the source tree is combined with the output.
The
Build Directory
is created initially when you source
the OpenEmbedded build environment setup script
(i.e.
oe-init-build-env).
It is also possible to place output and configuration
files in a directory separate from the
Source Directory
by providing a directory name when you source
the setup script.
For information on separating output from your local
Source Directory files, see the
"oe-init-build-env"
section.
5.1.3. documentation/¶
This directory holds the source for the Yocto Project documentation
as well as templates and tools that allow you to generate PDF and HTML
versions of the manuals.
Each manual is contained in a sub-folder.
For example, the files for this manual reside in
the ref-manual/ directory.
5.1.4. meta/¶
This directory contains the OpenEmbedded-Core metadata.
The directory holds recipes, common classes, and machine
configuration for emulated targets (qemux86,
qemuarm, and so forth.)
5.1.5. meta-poky/¶
This directory contains the configuration for the Poky reference distribution.
5.1.6. meta-yocto-bsp/¶
This directory contains the Yocto Project reference hardware Board Support Packages (BSPs). For more information on BSPs, see the Yocto Project Board Support Package (BSP) Developer's Guide.
5.1.7. meta-selftest/¶
This directory adds additional recipes and append files used by the OpenEmbedded selftests to verify the behavior of the build system.
You do not have to add this layer to your
bblayers.conf file unless you want to run the
selftests.
5.1.8. meta-skeleton/¶
This directory contains template recipes for BSP and kernel development.
5.1.9. scripts/¶
This directory contains various integration scripts that implement
extra functionality in the Yocto Project environment (e.g. QEMU scripts).
The oe-init-build-env
script appends this directory to the shell's
PATH environment variable.
The scripts directory has useful scripts that assist in contributing
back to the Yocto Project, such as create-pull-request and
send-pull-request.
5.1.10. oe-init-build-env¶
This script sets up the OpenEmbedded build environment.
Running this script with the source command in
a shell makes changes to PATH and sets other
core BitBake variables based on the current working directory.
You need to run an environment setup script before running BitBake
commands.
The script uses other scripts within the
scripts directory to do the bulk of the work.
When you run this script, your Yocto Project environment is set up, a Build Directory is created, your working directory becomes the Build Directory, and you are presented with a list of common BitBake targets. Here is an example:
$ source oe-init-build-env
### Shell environment set up for builds. ###
You can now run 'bitbake <target>'
Common targets are:
core-image-minimal
core-image-sato
meta-toolchain
meta-ide-support
You can also run generated qemu images with a command like 'runqemu qemux86'
The script gets its default list of common targets from the
conf-notes.txt file, which is found in the
meta-poky directory within the
Source Directory.
Should you have custom distributions, it is very easy to modify
this configuration file to include your targets for your
distribution.
See the
"Creating a Custom Template Configuration Directory"
section in the Yocto Project Development Tasks Manual for more
information.
By default, running this script without a Build Directory
argument creates the build directory
in your current working directory.
If you provide a Build Directory argument when you
source the script, you direct the OpenEmbedded
build system to create a Build Directory of your choice.
For example, the following command creates a Build Directory named
mybuilds that is outside of the
Source Directory:
$ source oe-init-build-env ~/mybuilds
The OpenEmbedded build system uses the template configuration
files, which are found by default in the
meta-poky/conf directory in the
Source Directory.
See the
"Creating a Custom Template Configuration Directory"
section in the Yocto Project Development Tasks Manual for more
information.
Note
The OpenEmbedded build system does not support file or directory names that contain spaces. If you attempt to run theoe-init-build-env script
from a Source Directory that contains spaces in either the filenames
or directory names, the script returns an error indicating no such
file or directory.
Be sure to use a Source Directory free of names containing spaces.
5.1.11. LICENSE, README, and README.hardware¶
These files are standard top-level files.
5.2. The Build Directory - build/¶
The OpenEmbedded build system creates the
Build Directory
when you run the build environment setup scripts (i.e.
oe-init-build-env).
If you do not give the Build Directory a specific name when you run
a setup script, the name defaults to build.
The
TOPDIR variable
points to the Build Directory.
5.2.1. build/buildhistory¶
The OpenEmbedded build system creates this directory when you enable the build history feature. The directory tracks build information into image, packages, and SDK subdirectories. For information on the build history feature, see the "Maintaining Build Output Quality" section in the Yocto Project Development Tasks Manual.
5.2.2. build/conf/local.conf¶
This configuration file contains all the local user configurations
for your build environment.
The local.conf file contains documentation on
the various configuration options.
Any variable set here overrides any variable set elsewhere within
the environment unless that variable is hard-coded within a file
(e.g. by using '=' instead of '?=').
Some variables are hard-coded for various reasons but these
variables are relatively rare.
Edit this file to set the
MACHINE
for which you want to build, which package types you wish to use
(PACKAGE_CLASSES),
and the location from which you want to access downloaded files
(DL_DIR).
If local.conf is not present when you
start the build, the OpenEmbedded build system creates it from
local.conf.sample when
you source the top-level build environment
setup script (i.e.
oe-init-build-env).
The source local.conf.sample file used
depends on the $TEMPLATECONF script variable,
which defaults to meta-poky/conf
when you are building from the Yocto Project development
environment and defaults to meta/conf when
you are building from the OpenEmbedded-Core environment.
Because the script variable points to the source of the
local.conf.sample file, this implies that
you can configure your build environment from any layer by setting
the variable in the top-level build environment setup script as
follows:
TEMPLATECONF=your_layer/conf
Once the build process gets the sample file, it uses
sed to substitute final
${OEROOT}
values for all ##OEROOT## values.
Note
You can see how theTEMPLATECONF variable
is used by looking at the
scripts/oe-setup-builddir script in the
Source Directory.
You can find the Yocto Project version of the
local.conf.sample file in the
meta-poky/conf directory.
5.2.3. build/conf/bblayers.conf¶
This configuration file defines
layers,
which are directory trees, traversed (or walked) by BitBake.
The bblayers.conf file uses the
BBLAYERS
variable to list the layers BitBake tries to find.
If bblayers.conf is not present when you
start the build, the OpenEmbedded build system creates it from
bblayers.conf.sample when
you source the top-level build environment
setup script (i.e.
oe-init-build-env).
The source bblayers.conf.sample file used
depends on the $TEMPLATECONF script variable,
which defaults to meta-poky/conf
when you are building from the Yocto Project development
environment and defaults to meta/conf when
you are building from the OpenEmbedded-Core environment.
Because the script variable points to the source of the
bblayers.conf.sample file, this implies that
you can base your build from any layer by setting the variable in
the top-level build environment setup script as follows:
TEMPLATECONF=your_layer/conf
Once the build process gets the sample file, it uses
sed to substitute final
${OEROOT}
values for all ##OEROOT## values.
Note
You can see how theTEMPLATECONF variable
scripts/oe-setup-builddir script in the
Source Directory.
You can find the Yocto Project version of the
bblayers.conf.sample file in the
meta-poky/conf directory.
5.2.4. build/conf/sanity_info¶
This file indicates the state of the sanity checks and is created during the build.
5.2.5. build/downloads/¶
This directory contains downloaded upstream source tarballs.
You can reuse the directory for multiple builds or move
the directory to another location.
You can control the location of this directory through the
DL_DIR variable.
5.2.6. build/sstate-cache/¶
This directory contains the shared state cache.
You can reuse the directory for multiple builds or move
the directory to another location.
You can control the location of this directory through the
SSTATE_DIR variable.
5.2.7. build/tmp/¶
The OpenEmbedded build system creates and uses this directory
for all the build system's output.
The
TMPDIR
variable points to this directory.
BitBake creates this directory if it does not exist.
As a last resort, to clean up a build and start it from scratch
(other than the downloads), you can remove everything in the
tmp directory or get rid of the
directory completely.
If you do, you should also completely remove the
build/sstate-cache directory.
5.2.8. build/tmp/buildstats/¶
This directory stores the build statistics.
5.2.9. build/tmp/cache/¶
When BitBake parses the metadata (recipes and configuration files),
it caches the results in build/tmp/cache/
to speed up future builds.
The results are stored on a per-machine basis.
During subsequent builds, BitBake checks each recipe (together with, for example, any files included or appended to it) to see if they have been modified. Changes can be detected, for example, through file modification time (mtime) changes and hashing of file contents. If no changes to the file are detected, then the parsed result stored in the cache is reused. If the file has changed, it is reparsed.
5.2.10. build/tmp/deploy/¶
This directory contains any "end result" output from the
OpenEmbedded build process.
The DEPLOY_DIR
variable points to this directory.
For more detail on the contents of the deploy
directory, see the
"Images"
and
"Application Development SDK"
sections in the Yocto Project Overview and Concepts Manual.
5.2.11. build/tmp/deploy/deb/¶
This directory receives any .deb packages produced by
the build process.
The packages are sorted into feeds for different architecture types.
5.2.12. build/tmp/deploy/rpm/¶
This directory receives any .rpm packages produced by
the build process.
The packages are sorted into feeds for different architecture types.
5.2.13. build/tmp/deploy/ipk/¶
This directory receives .ipk packages produced by
the build process.
5.2.14. build/tmp/deploy/licenses/¶
This directory receives package licensing information.
For example, the directory contains sub-directories for bash,
busybox, and glibc (among others) that in turn
contain appropriate COPYING license files with other licensing information.
For information on licensing, see the
"Maintaining Open Source License Compliance During Your Product's Lifecycle"
section in the Yocto Project Development Tasks Manual.
5.2.15. build/tmp/deploy/images/¶
This directory receives complete filesystem images. If you want to flash the resulting image from a build onto a device, look here for the image.
Be careful when deleting files in this directory.
You can safely delete old images from this directory (e.g.
core-image-*).
However, the kernel (*zImage*, *uImage*, etc.),
bootloader and other supplementary files might be deployed here prior to building an
image.
Because these files are not directly produced from the image, if you
delete them they will not be automatically re-created when you build the image again.
If you do accidentally delete files here, you will need to force them to be re-created. In order to do that, you will need to know the target that produced them. For example, these commands rebuild and re-create the kernel files:
$ bitbake -c clean virtual/kernel
$ bitbake virtual/kernel
5.2.16. build/tmp/deploy/sdk/¶
The OpenEmbedded build system creates this directory to hold toolchain installer scripts, which when executed, install the sysroot that matches your target hardware. You can find out more about these installers in the "Building an SDK Installer" section in the Yocto Project Application Development and the Extensible Software Development Kit (eSDK) manual.
5.2.17. build/tmp/sstate-control/¶
The OpenEmbedded build system uses this directory for the shared state manifest files. The shared state code uses these files to record the files installed by each sstate task so that the files can be removed when cleaning the recipe or when a newer version is about to be installed. The build system also uses the manifests to detect and produce a warning when files from one task are overwriting those from another.
5.2.18. build/tmp/sysroots-components/¶
This directory is the location of the sysroot contents that the
task
do_prepare_recipe_sysroot
links or copies into the recipe-specific sysroot for each
recipe listed in
DEPENDS.
Population of this directory is handled through shared state, while
the path is specified by the
COMPONENTS_DIR
variable. Apart from a few unusual circumstances, handling of the
sysroots-components directory should be
automatic, and recipes should not directly reference
build/tmp/sysroots-components.
5.2.19. build/tmp/sysroots/¶
Previous versions of the OpenEmbedded build system used to
create a global shared sysroot per machine along with a native
sysroot.
Beginning with the 2.6.1 version of the Yocto Project,
sysroots exist in recipe-specific
WORKDIR
directories.
Thus, the build/tmp/sysroots/ directory
is unused.
Note
Thebuild/tmp/sysroots/ directory
can still be populated using the
bitbake build-sysroots command and can
be used for compatibility in some cases.
However, in general it is not recommended to populate
this directory.
Individual recipe-specific sysroots should be used.
5.2.20. build/tmp/stamps/¶
This directory holds information that BitBake uses for accounting purposes to track what tasks have run and when they have run. The directory is sub-divided by architecture, package name, and version. Following is an example:
stamps/all-poky-linux/distcc-config/1.0-r0.do_build-2fdd....2do
Although the files in the directory are empty of data, BitBake uses the filenames and timestamps for tracking purposes.
For information on how BitBake uses stamp files to determine if a task should be rerun, see the "Stamp Files and the Rerunning of Tasks" section in the Yocto Project Overview and Concepts Manual.
5.2.21. build/tmp/log/¶
This directory contains general logs that are not otherwise placed using the
package's WORKDIR.
Examples of logs are the output from the
do_check_pkg or
do_distro_check tasks.
Running a build does not necessarily mean this directory is created.
5.2.22. build/tmp/work/¶
This directory contains architecture-specific work sub-directories
for packages built by BitBake.
All tasks execute from the appropriate work directory.
For example, the source for a particular package is unpacked,
patched, configured and compiled all within its own work directory.
Within the work directory, organization is based on the package group
and version for which the source is being compiled
as defined by the
WORKDIR.
It is worth considering the structure of a typical work directory.
As an example, consider linux-yocto-kernel-3.0
on the machine qemux86
built within the Yocto Project.
For this package, a work directory of
tmp/work/qemux86-poky-linux/linux-yocto/3.0+git1+<.....>,
referred to as the WORKDIR, is created.
Within this directory, the source is unpacked to
linux-qemux86-standard-build and then patched by Quilt.
(See the
"Using Quilt in Your Workflow"
section in the Yocto Project Development Tasks Manual for more
information.)
Within the linux-qemux86-standard-build directory,
standard Quilt directories linux-3.0/patches
and linux-3.0/.pc are created,
and standard Quilt commands can be used.
There are other directories generated within WORKDIR.
The most important directory is WORKDIR/temp/,
which has log files for each task (log.do_*.pid)
and contains the scripts BitBake runs for each task
(run.do_*.pid).
The WORKDIR/image/ directory is where "make
install" places its output that is then split into sub-packages
within WORKDIR/packages-split/.
5.2.23. build/tmp/work/tunearch/recipename/version/¶
tunearch/recipename/version/
The recipe work directory - ${WORKDIR}.
As described earlier in the
"build/tmp/sysroots/"
section, beginning with the 2.6.1 release of the Yocto
Project, the OpenEmbedded build system builds each recipe in its
own work directory (i.e.
WORKDIR).
The path to the work directory is constructed using the
architecture of the given build (e.g.
TUNE_PKGARCH,
MACHINE_ARCH,
or "allarch"), the recipe name, and the version of the recipe (i.e.
PE:PV-PR).
A number of key subdirectories exist within each recipe work directory:
${WORKDIR}/temp: Contains the log files of each task executed for this recipe, the "run" files for each executed task, which contain the code run, and alog.task_orderfile, which lists the order in which tasks were executed.${WORKDIR}/image: Contains the output of thedo_installtask, which corresponds to the${D}variable in that task.${WORKDIR}/pseudo: Contains the pseudo database and log for any tasks executed under pseudo for the recipe.${WORKDIR}/sysroot-destdir: Contains the output of thedo_populate_sysroottask.${WORKDIR}/package: Contains the output of thedo_packagetask before the output is split into individual packages.${WORKDIR}/packages-split: Contains the output of thedo_packagetask after the output has been split into individual packages. Subdirectories exist for each individual package created by the recipe.${WORKDIR}/recipe-sysroot: A directory populated with the target dependencies of the recipe. This directory looks like the target filesystem and contains libraries that the recipe might need to link against (e.g. the C library).${WORKDIR}/recipe-sysroot-native: A directory populated with the native dependencies of the recipe. This directory contains the tools the recipe needs to build (e.g. the compiler, Autoconf, libtool, and so forth).${WORKDIR}/build: This subdirectory applies only to recipes that support builds where the source is separate from the build artifacts. The OpenEmbedded build system uses this directory as a separate build directory (i.e.${B}).
5.2.24. build/tmp/work-shared/¶
For efficiency, the OpenEmbedded build system creates and uses
this directory to hold recipes that share a work directory with
other recipes.
In practice, this is only used for gcc
and its variants (e.g. gcc-cross,
libgcc, gcc-runtime,
and so forth).
5.3. The Metadata - meta/¶
As mentioned previously, Metadata is the core of the Yocto Project. Metadata has several important subdivisions:
5.3.1. meta/classes/¶
This directory contains the *.bbclass files.
Class files are used to abstract common code so it can be reused by multiple
packages.
Every package inherits the base.bbclass file.
Examples of other important classes are autotools.bbclass, which
in theory allows any Autotool-enabled package to work with the Yocto Project with minimal effort.
Another example is kernel.bbclass that contains common code and functions
for working with the Linux kernel.
Functions like image generation or packaging also have their specific class files
such as image.bbclass, rootfs_*.bbclass and
package*.bbclass.
For reference information on classes, see the "Classes" chapter.
5.3.2. meta/conf/¶
This directory contains the core set of configuration files that start from
bitbake.conf and from which all other configuration
files are included.
See the include statements at the end of the
bitbake.conf file and you will note that even
local.conf is loaded from there.
While bitbake.conf sets up the defaults, you can often override
these by using the (local.conf) file, machine file or
the distribution configuration file.
5.3.3. meta/conf/machine/¶
This directory contains all the machine configuration files.
If you set MACHINE = "qemux86",
the OpenEmbedded build system looks for a qemux86.conf file in this
directory.
The include directory contains various data common to multiple machines.
If you want to add support for a new machine to the Yocto Project, look in this directory.
5.3.4. meta/conf/distro/¶
The contents of this directory controls any distribution-specific
configurations.
For the Yocto Project, the defaultsetup.conf is the main file here.
This directory includes the versions and the
SRCDATE definitions for applications that are configured here.
An example of an alternative configuration might be poky-bleeding.conf.
Although this file mainly inherits its configuration from Poky.
5.3.5. meta/conf/machine-sdk/¶
The OpenEmbedded build system searches this directory for
configuration files that correspond to the value of
SDKMACHINE.
By default, 32-bit and 64-bit x86 files ship with the Yocto
Project that support some SDK hosts.
However, it is possible to extend that support to other SDK hosts
by adding additional configuration files in this subdirectory
within another layer.
5.3.6. meta/files/¶
This directory contains common license files and several text files used by the build system. The text files contain minimal device information and lists of files and directories with known permissions.
5.3.7. meta/lib/¶
This directory contains OpenEmbedded Python library code used during the build process.
5.3.8. meta/recipes-bsp/¶
This directory contains anything linking to specific hardware or hardware configuration information such as "u-boot" and "grub".
5.3.9. meta/recipes-connectivity/¶
This directory contains libraries and applications related to communication with other devices.
5.3.10. meta/recipes-core/¶
This directory contains what is needed to build a basic working Linux image including commonly used dependencies.
5.3.11. meta/recipes-devtools/¶
This directory contains tools that are primarily used by the build system. The tools, however, can also be used on targets.
5.3.12. meta/recipes-extended/¶
This directory contains non-essential applications that add features compared to the alternatives in core. You might need this directory for full tool functionality or for Linux Standard Base (LSB) compliance.
5.3.13. meta/recipes-gnome/¶
This directory contains all things related to the GTK+ application framework.
5.3.14. meta/recipes-graphics/¶
This directory contains X and other graphically related system libraries
5.3.15. meta/recipes-kernel/¶
This directory contains the kernel and generic applications and libraries that have strong kernel dependencies.
5.3.16. meta/recipes-lsb4/¶
This directory contains recipes specifically added to support the Linux Standard Base (LSB) version 4.x.
5.3.17. meta/recipes-multimedia/¶
This directory contains codecs and support utilities for audio, images and video.
5.3.18. meta/recipes-rt/¶
This directory contains package and image recipes for using and testing
the PREEMPT_RT kernel.
5.3.19. meta/recipes-sato/¶
This directory contains the Sato demo/reference UI/UX and its associated applications and configuration data.
5.3.20. meta/recipes-support/¶
This directory contains recipes used by other recipes, but that are not directly included in images (i.e. dependencies of other recipes).
5.3.21. meta/site/¶
This directory contains a list of cached results for various architectures. Because certain "autoconf" test results cannot be determined when cross-compiling due to the tests not able to run on a live system, the information in this directory is passed to "autoconf" for the various architectures.
5.3.22. meta/recipes.txt¶
This file is a description of the contents of recipes-*.
Chapter 6. Classes¶
Table of Contents
- 6.1.
allarch.bbclass - 6.2.
archiver.bbclass - 6.3.
autotools*.bbclass - 6.4.
base.bbclass - 6.5.
bash-completion.bbclass - 6.6.
bin_package.bbclass - 6.7.
binconfig.bbclass - 6.8.
binconfig-disabled.bbclass - 6.9.
blacklist.bbclass - 6.10.
bluetooth.bbclass - 6.11.
bugzilla.bbclass - 6.12.
buildhistory.bbclass - 6.13.
buildstats.bbclass - 6.14.
buildstats-summary.bbclass - 6.15.
ccache.bbclass - 6.16.
chrpath.bbclass - 6.17.
clutter.bbclass - 6.18.
cmake.bbclass - 6.19.
cml1.bbclass - 6.20.
compress_doc.bbclass - 6.21.
copyleft_compliance.bbclass - 6.22.
copyleft_filter.bbclass - 6.23.
core-image.bbclass - 6.24.
cpan*.bbclass - 6.25.
cross.bbclass - 6.26.
cross-canadian.bbclass - 6.27.
crosssdk.bbclass - 6.28.
debian.bbclass - 6.29.
deploy.bbclass - 6.30.
devshell.bbclass - 6.31.
devupstream.bbclass - 6.32.
distro_features_check.bbclass - 6.33.
distrodata.bbclass - 6.34.
distutils*.bbclass - 6.35.
distutils3*.bbclass - 6.36.
externalsrc.bbclass - 6.37.
extrausers.bbclass - 6.38.
fontcache.bbclass - 6.39.
fs-uuid.bbclass - 6.40.
gconf.bbclass - 6.41.
gettext.bbclass - 6.42.
gnome.bbclass - 6.43.
gnomebase.bbclass - 6.44.
gobject-introspection.bbclass - 6.45.
grub-efi.bbclass - 6.46.
gsettings.bbclass - 6.47.
gtk-doc.bbclass - 6.48.
gtk-icon-cache.bbclass - 6.49.
gtk-immodules-cache.bbclass - 6.50.
gzipnative.bbclass - 6.51.
icecc.bbclass - 6.52.
image.bbclass - 6.53.
image-buildinfo.bbclass - 6.54.
image_types.bbclass - 6.55.
image-live.bbclass - 6.56.
image-mklibs.bbclass - 6.57.
image-prelink.bbclass - 6.58.
insane.bbclass - 6.59.
insserv.bbclass - 6.60.
kernel.bbclass - 6.61.
kernel-arch.bbclass - 6.62.
kernel-devicetree.bbclass - 6.63.
kernel-fitimage.bbclass - 6.64.
kernel-grub.bbclass - 6.65.
kernel-module-split.bbclass - 6.66.
kernel-uboot.bbclass - 6.67.
kernel-uimage.bbclass - 6.68.
kernel-yocto.bbclass - 6.69.
kernelsrc.bbclass - 6.70.
lib_package.bbclass - 6.71.
libc*.bbclass - 6.72.
license.bbclass - 6.73.
linux-kernel-base.bbclass - 6.74.
linuxloader.bbclass - 6.75.
logging.bbclass - 6.76.
meta.bbclass - 6.77.
metadata_scm.bbclass - 6.78.
migrate_localcount.bbclass - 6.79.
mime.bbclass - 6.80.
mirrors.bbclass - 6.81.
module.bbclass - 6.82.
module-base.bbclass - 6.83.
multilib*.bbclass - 6.84.
native.bbclass - 6.85.
nativesdk.bbclass - 6.86.
nopackages.bbclass - 6.87.
npm.bbclass - 6.88.
oelint.bbclass - 6.89.
own-mirrors.bbclass - 6.90.
package.bbclass - 6.91.
package_deb.bbclass - 6.92.
package_ipk.bbclass - 6.93.
package_rpm.bbclass - 6.94.
package_tar.bbclass - 6.95.
packagedata.bbclass - 6.96.
packagegroup.bbclass - 6.97.
patch.bbclass - 6.98.
perlnative.bbclass - 6.99.
pixbufcache.bbclass - 6.100.
pkgconfig.bbclass - 6.101.
populate_sdk.bbclass - 6.102.
populate_sdk_*.bbclass - 6.103.
prexport.bbclass - 6.104.
primport.bbclass - 6.105.
prserv.bbclass - 6.106.
ptest.bbclass - 6.107.
ptest-gnome.bbclass - 6.108.
python-dir.bbclass - 6.109.
python3native.bbclass - 6.110.
pythonnative.bbclass - 6.111.
qemu.bbclass - 6.112.
recipe_sanity.bbclass - 6.113.
relocatable.bbclass - 6.114.
remove-libtool.bbclass - 6.115.
report-error.bbclass - 6.116.
rm_work.bbclass - 6.117.
rootfs*.bbclass - 6.118.
sanity.bbclass - 6.119.
scons.bbclass - 6.120.
sdl.bbclass - 6.121.
setuptools.bbclass - 6.122.
setuptools3.bbclass - 6.123.
sign_rpm.bbclass - 6.124.
sip.bbclass - 6.125.
siteconfig.bbclass - 6.126.
siteinfo.bbclass - 6.127.
spdx.bbclass - 6.128.
sstate.bbclass - 6.129.
staging.bbclass - 6.130.
syslinux.bbclass - 6.131.
systemd.bbclass - 6.132.
systemd-boot.bbclass - 6.133.
terminal.bbclass - 6.134.
testimage*.bbclass - 6.135.
testsdk.bbclass - 6.136.
texinfo.bbclass - 6.137.
tinderclient.bbclass - 6.138.
toaster.bbclass - 6.139.
toolchain-scripts.bbclass - 6.140.
typecheck.bbclass - 6.141.
uboot-config.bbclass - 6.142.
uninative.bbclass - 6.143.
update-alternatives.bbclass - 6.144.
update-rc.d.bbclass - 6.145.
useradd*.bbclass - 6.146.
utility-tasks.bbclass - 6.147.
utils.bbclass - 6.148.
vala.bbclass - 6.149.
waf.bbclass
Class files are used to abstract common functionality and share it amongst
multiple recipe (.bb) files.
To use a class file, you simply make sure the recipe inherits the class.
In most cases, when a recipe inherits a class it is enough to enable its
features.
There are cases, however, where in the recipe you might need to set
variables or override some default behavior.
Any Metadata usually
found in a recipe can also be placed in a class file.
Class files are identified by the extension .bbclass
and are usually placed in a classes/ directory beneath
the meta*/ directory found in the
Source Directory.
Class files can also be pointed to by
BUILDDIR
(e.g. build/) in the same way as
.conf files in the conf directory.
Class files are searched for in
BBPATH
using the same method by which .conf files are
searched.
This chapter discusses only the most useful and important classes.
Other classes do exist within the meta/classes
directory in the Source Directory.
You can reference the .bbclass files directly
for more information.
6.1. allarch.bbclass¶
The allarch class is inherited
by recipes that do not produce architecture-specific output.
The class disables functionality that is normally needed for recipes
that produce executable binaries (such as building the cross-compiler
and a C library as pre-requisites, and splitting out of debug symbols
during packaging).
Note
Unlike some distro recipes (e.g. Debian), OpenEmbedded recipes
that produce packages that depend on tunings through use of the
RDEPENDS
and
TUNE_PKGARCH
variables, should never be configured for all architectures
using allarch.
This is the case even if the recipes do not produce
architecture-specific output.
Configuring such recipes for all architectures causes the
do_package_write_*
tasks to have different signatures for the machines with different
tunings.
Additionally, unnecessary rebuilds occur every time an
image for a different MACHINE is built
even when the recipe never changes.
By default, all recipes inherit the
base and
package
classes, which enable functionality
needed for recipes that produce executable output.
If your recipe, for example, only produces packages that contain
configuration files, media files, or scripts (e.g. Python and Perl),
then it should inherit the allarch class.
6.2. archiver.bbclass¶
The archiver class supports releasing
source code and other materials with the binaries.
For more details on the source archiver, see the
"Maintaining Open Source License Compliance During Your Product's Lifecycle"
section in the Yocto Project Development Tasks Manual.
You can also see the
ARCHIVER_MODE
variable for information about the variable flags (varflags)
that help control archive creation.
6.3. autotools*.bbclass¶
The autotools* classes support Autotooled
packages.
The autoconf, automake,
and libtool packages bring standardization.
This class defines a set of tasks (e.g.
configure, compile and
so forth) that
work for all Autotooled packages.
It should usually be enough to define a few standard variables
and then simply inherit autotools.
These classes can also work with software that emulates Autotools.
For more information, see the
"Autotooled Package"
section in the Yocto Project Development Tasks Manual.
By default, the autotools* classes
use out-of-tree builds (i.e.
autotools.bbclass building with
B != S).
If the software being built by a recipe does not support
using out-of-tree builds, you should have the recipe inherit the
autotools-brokensep class.
The autotools-brokensep class behaves the same
as the autotools class but builds with
B ==
S.
This method is useful when out-of-tree build support is either not
present or is broken.
Note
It is recommended that out-of-tree support be fixed and used if at all possible.
It's useful to have some idea of how the tasks defined by
the autotools* classes work and what they do
behind the scenes.
do_configure- Regenerates the configure script (usingautoreconf) and then launches it with a standard set of arguments used during cross-compilation. You can pass additional parameters toconfigurethrough theEXTRA_OECONForPACKAGECONFIG_CONFARGSvariables.do_compile- Runsmakewith arguments that specify the compiler and linker. You can pass additional arguments through theEXTRA_OEMAKEvariable.do_install- Runsmake installand passes in${D}asDESTDIR.
6.4. base.bbclass¶
The base class is special in that every
.bb file implicitly inherits the class.
This class contains definitions for standard basic
tasks such as fetching, unpacking, configuring (empty by default),
compiling (runs any Makefile present), installing
(empty by default) and packaging (empty by default).
These classes are often overridden or extended by other classes
such as the
autotools
class or the
package
class.
The class also contains some commonly used functions such as
oe_runmake, which runs
make with the arguments specified in
EXTRA_OEMAKE
variable as well as the arguments passed directly to
oe_runmake.
6.5. bash-completion.bbclass¶
Sets up packaging and dependencies appropriate for recipes that build software that includes bash-completion data.
6.6. bin_package.bbclass¶
The bin_package class is a
helper class for recipes that extract the contents of a binary package
(e.g. an RPM) and install those contents rather than building the
binary from source.
The binary package is extracted and new packages in the configured
output package format are created.
Extraction and installation of proprietary binaries is a good example
use for this class.
Note
For RPMs and other packages that do not contain a subdirectory, you should specify an appropriate fetcher parameter to point to the subdirectory. For example, if BitBake is using the Git fetcher (git://), the "subpath" parameter limits
the checkout to a specific subpath of the tree.
Here is an example where ${BP} is used so that
the files are extracted into the subdirectory expected by the
default value of
S:
SRC_URI = "git://example.com/downloads/somepackage.rpm;subpath=${BP}"
See the
"Fetchers"
section in the BitBake User Manual for more information on
supported BitBake Fetchers.
6.7. binconfig.bbclass¶
The binconfig class helps to correct paths in
shell scripts.
Before pkg-config had become widespread, libraries
shipped shell scripts to give information about the libraries and
include paths needed to build software (usually named
LIBNAME-config).
This class assists any recipe using such scripts.
During staging, the OpenEmbedded build system installs such scripts
into the sysroots/ directory.
Inheriting this class results in all paths in these scripts being
changed to point into the sysroots/ directory so
that all builds that use the script use the correct directories
for the cross compiling layout.
See the
BINCONFIG_GLOB
variable for more information.
6.8. binconfig-disabled.bbclass¶
An alternative version of the
binconfig
class, which disables binary configuration scripts by making them
return an error in favor of using pkg-config
to query the information.
The scripts to be disabled should be specified using the
BINCONFIG
variable within the recipe inheriting the class.
6.9. blacklist.bbclass¶
The blacklist class prevents
the OpenEmbedded build system from building specific recipes
(blacklists them).
To use this class, inherit the class globally and set
PNBLACKLIST
for each recipe you wish to blacklist.
Specify the PN
value as a variable flag (varflag) and provide a reason, which is
reported, if the package is requested to be built as the value.
For example, if you want to blacklist a recipe called "exoticware",
you add the following to your local.conf
or distribution configuration:
INHERIT += "blacklist"
PNBLACKLIST[exoticware] = "Not supported by our organization."
6.10. bluetooth.bbclass¶
The bluetooth class defines a variable that
expands to the recipe (package) providing core
bluetooth support on the platform.
For details on how the class works, see the
meta/classes/bluetooth.bbclass file in the Yocto
Project
Source Directory.
6.11. bugzilla.bbclass¶
The bugzilla class supports setting up an
instance of Bugzilla in which you can automatically files bug reports
in response to build failures.
For this class to work, you need to enable the XML-RPC interface in
the instance of Bugzilla.
6.12. buildhistory.bbclass¶
The buildhistory class records a
history of build output metadata, which can be used to detect possible
regressions as well as used for analysis of the build output.
For more information on using Build History, see the
"Maintaining Build Output Quality"
section in the Yocto Project Development Tasks Manual.
6.13. buildstats.bbclass¶
The buildstats class records
performance statistics about each task executed during the build
(e.g. elapsed time, CPU usage, and I/O usage).
When you use this class, the output goes into the
BUILDSTATS_BASE
directory, which defaults to ${TMPDIR}/buildstats/.
You can analyze the elapsed time using
scripts/pybootchartgui/pybootchartgui.py, which
produces a cascading chart of the entire build process and can be
useful for highlighting bottlenecks.
Collecting build statistics is enabled by default through the
USER_CLASSES
variable from your local.conf file.
Consequently, you do not have to do anything to enable the class.
However, if you want to disable the class, simply remove "buildstats"
from the USER_CLASSES list.
6.14. buildstats-summary.bbclass¶
When inherited globally, prints statistics at the end of the build
on sstate re-use.
In order to function, this class requires the
buildstats
class be enabled.
6.15. ccache.bbclass¶
The ccache class enables the C/C++ Compiler Cache
for the build.
This class is used to give a minor performance boost during the build.
However, using the class can lead to unexpected side-effects.
Thus, it is recommended that you do not use this class.
See http://ccache.samba.org/ for information on
the C/C++ Compiler Cache.
6.16. chrpath.bbclass¶
The chrpath class
is a wrapper around the "chrpath" utility, which is used during the
build process for nativesdk,
cross, and
cross-canadian recipes to change
RPATH records within binaries in order to make
them relocatable.
6.17. clutter.bbclass¶
The clutter class consolidates the
major and minor version naming and other common items used by Clutter
and related recipes.
Note
Unlike some other classes related to specific libraries, recipes building other software that uses Clutter do not need to inherit this class unless they use the same recipe versioning scheme that the Clutter and related recipes do.
6.18. cmake.bbclass¶
The cmake class allows for recipes that need to
build software using the
CMake build system.
You can use the
EXTRA_OECMAKE
variable to specify additional configuration options to be passed
using the cmake command line.
6.19. cml1.bbclass¶
The cml1 class provides basic support for the
Linux kernel style build configuration system.
6.20. compress_doc.bbclass¶
Enables compression for man pages and info pages.
This class is intended to be inherited globally.
The default compression mechanism is gz (gzip) but you can
select an alternative mechanism by setting the
DOC_COMPRESS
variable.
6.21. copyleft_compliance.bbclass¶
The copyleft_compliance class
preserves source code for the purposes of license compliance.
This class is an alternative to the archiver
class and is still used by some users even though it has been
deprecated in favor of the
archiver
class.
6.22. copyleft_filter.bbclass¶
A class used by the
archiver
and
copyleft_compliance
classes for filtering licenses.
The copyleft_filter class is an internal class
and is not intended to be used directly.
6.23. core-image.bbclass¶
The core-image class
provides common definitions for the
core-image-* image recipes, such as support for
additional
IMAGE_FEATURES.
6.24. cpan*.bbclass¶
The cpan* classes support Perl modules.
Recipes for Perl modules are simple. These recipes usually only need to point to the source's archive and then inherit the proper class file. Building is split into two methods depending on which method the module authors used.
Modules that use old
Makefile.PL-based build system requirecpan.bbclassin their recipes.Modules that use
Build.PL-based build system require usingcpan_build.bbclassin their recipes.
Both build methods inherit the cpan-base class
for basic Perl support.
6.25. cross.bbclass¶
The cross class provides support for the recipes
that build the cross-compilation tools.
6.26. cross-canadian.bbclass¶
The cross-canadian class
provides support for the recipes that build the Canadian
Cross-compilation tools for SDKs.
See the
"Cross-Development Toolchain Generation"
section in the Yocto Project Overview and Concepts Manual for more
discussion on these cross-compilation tools.
6.27. crosssdk.bbclass¶
The crosssdk class
provides support for the recipes that build the cross-compilation
tools used for building SDKs.
See the
"Cross-Development Toolchain Generation"
section in the Yocto Project Overview and Concepts Manual for more
discussion on these cross-compilation tools.
6.28. debian.bbclass¶
The debian class renames output packages so that
they follow the Debian naming policy (i.e. glibc
becomes libc6 and glibc-devel
becomes libc6-dev.)
Renaming includes the library name and version as part of the package
name.
If a recipe creates packages for multiple libraries
(shared object files of .so type), use the
LEAD_SONAME
variable in the recipe to specify the library on which to apply the
naming scheme.
6.29. deploy.bbclass¶
The deploy class handles deploying files
to the
DEPLOY_DIR_IMAGE
directory.
The main function of this class is to allow the deploy step to be
accelerated by shared state.
Recipes that inherit this class should define their own
do_deploy
function to copy the files to be deployed to
DEPLOYDIR,
and use addtask to add the task at the appropriate
place, which is usually after
do_compile
or
do_install.
The class then takes care of staging the files from
DEPLOYDIR to
DEPLOY_DIR_IMAGE.
6.30. devshell.bbclass¶
The devshell class adds the
do_devshell task.
Distribution policy dictates whether to include this class.
See the
"Using a Development Shell" section
in the Yocto Project Development Tasks Manual for more information about
using devshell.
6.31. devupstream.bbclass¶
The devupstream class uses
BBCLASSEXTEND
to add a variant of the recipe that fetches from an alternative URI
(e.g. Git) instead of a tarball.
Following is an example:
BBCLASSEXTEND = "devupstream:target"
SRC_URI_class-devupstream = "git://git.example.com/example"
SRCREV_class-devupstream = "abcd1234"
Adding the above statements to your recipe creates a variant that has
DEFAULT_PREFERENCE
set to "-1".
Consequently, you need to select the variant of the recipe to use it.
Any development-specific adjustments can be done by using the
class-devupstream override.
Here is an example:
DEPENDS_append_class-devupstream = " gperf-native"
do_configure_prepend_class-devupstream() {
touch ${S}/README
}
The class currently only supports creating a development variant of
the target recipe, not native or
nativesdk variants.
The BBCLASSEXTEND syntax
(i.e. devupstream:target) provides support for
native and nativesdk
variants.
Consequently, this functionality can be added in a future release.
Support for other version control systems such as Subversion is
limited due to BitBake's automatic fetch dependencies (e.g.
subversion-native).
6.32. distro_features_check.bbclass¶
The distro_features_check class
allows individual recipes to check for required and conflicting
DISTRO_FEATURES.
This class provides support for the
REQUIRED_DISTRO_FEATURES
and
CONFLICT_DISTRO_FEATURES
variables.
If any conditions specified in the recipe using the above variables are
not met, the recipe will be skipped.
6.33. distrodata.bbclass¶
The distrodata class
provides for automatic checking for upstream recipe updates.
The class creates a comma-separated value (CSV) spreadsheet that
contains information about the recipes.
The information provides the
do_distrodata
and
do_distro_check tasks, which do upstream checking
and also verify if a package is used in multiple major distributions.
The class is not included by default.
To use it, you must set the
INHERIT
variable:
INHERIT+= "distrodata"
The distrodata class also provides the
do_checkpkg
task, which can be used against a simple recipe or against an
image to get all its recipe information.
6.34. distutils*.bbclass¶
The distutils* classes support recipes for Python
version 2.x extensions, which are simple.
These recipes usually only need to point to the source's archive and
then inherit the proper class.
Building is split into two methods depending on which method the
module authors used.
Extensions that use an Autotools-based build system require Autotools and the classes based on
distutilsin their recipes.Extensions that use build systems based on
distutilsrequire thedistutilsclass in their recipes.Extensions that use build systems based on
setuptoolsrequire thesetuptoolsclass in their recipes.
The distutils-common-base class is required by
some of the distutils* classes to provide common
Python2 support.
The distutils-tools class supports recipes for
additional "distutils" tools.
6.35. distutils3*.bbclass¶
The distutils3* classes support recipes for Python
version 3.x extensions, which are simple.
These recipes usually only need to point to the source's archive and
then inherit the proper class.
Building is split into three methods depending on which method the
module authors used.
Extensions that use an Autotools-based build system require Autotools and
distutils-based classes in their recipes.Extensions that use
distutils-based build systems require thedistutilsclass in their recipes.Extensions that use build systems based on
setuptools3require thesetuptools3class in their recipes.
The distutils3* classes either inherit their
corresponding distutils* class or replicate them
using a Python3 version instead (e.g.
distutils3-base inherits
distutils-common-base, which is the same as
distutils-base but inherits
python3native instead of
pythonnative).
6.36. externalsrc.bbclass¶
The externalsrc class supports building software
from source code that is external to the OpenEmbedded build system.
Building software from an external source tree means that the build
system's normal fetch, unpack, and patch process is not used.
By default, the OpenEmbedded build system uses the
S and
B variables to
locate unpacked recipe source code and to build it, respectively.
When your recipe inherits the externalsrc class,
you use the
EXTERNALSRC
and
EXTERNALSRC_BUILD
variables to ultimately define S and
B.
By default, this class expects the source code to support recipe builds
that use the B
variable to point to the directory in which the OpenEmbedded build
system places the generated objects built from the recipes.
By default, the B directory is set to the
following, which is separate from the source directory
(S):
${WORKDIR}/${BPN}/{PV}/
See these variables for more information:
WORKDIR,
BPN, and
PV,
For more information on the
externalsrc class, see the comments in
meta/classes/externalsrc.bbclass in the
Source Directory.
For information on how to use the externalsrc
class, see the
"Building Software from an External Source"
section in the Yocto Project Development Tasks Manual.
6.37. extrausers.bbclass¶
The extrausers class allows
additional user and group configuration to be applied at the image
level.
Inheriting this class either globally or from an image recipe allows
additional user and group operations to be performed using the
EXTRA_USERS_PARAMS
variable.
Note
The user and group operations added using theextrausers class are not tied to a specific
recipe outside of the recipe for the image.
Thus, the operations can be performed across the image as a whole.
Use the
useradd
class to add user and group configuration to a specific recipe.
Here is an example that uses this class in an image recipe:
inherit extrausers
EXTRA_USERS_PARAMS = "\
useradd -p '' tester; \
groupadd developers; \
userdel nobody; \
groupdel -g video; \
groupmod -g 1020 developers; \
usermod -s /bin/sh tester; \
"
Here is an example that adds two users named "tester-jim" and "tester-sue" and assigns passwords:
inherit extrausers
EXTRA_USERS_PARAMS = "\
useradd -P tester01 tester-jim; \
useradd -P tester01 tester-sue; \
"
Finally, here is an example that sets the root password to "1876*18":
inherit extrausers
EXTRA_USERS_PARAMS = "\
usermod -P 1876*18 root; \
"
6.38. fontcache.bbclass¶
The fontcache class generates the
proper post-install and post-remove (postinst and postrm)
scriptlets for font packages.
These scriptlets call fc-cache (part of
Fontconfig) to add the fonts to the font
information cache.
Since the cache files are architecture-specific,
fc-cache runs using QEMU if the postinst
scriptlets need to be run on the build host during image creation.
If the fonts being installed are in packages other than the main
package, set
FONT_PACKAGES
to specify the packages containing the fonts.
6.39. fs-uuid.bbclass¶
The fs-uuid class extracts UUID from
${ROOTFS},
which must have been built by the time that this function gets called.
The fs-uuid class only works on
ext file systems and depends on
tune2fs.
6.40. gconf.bbclass¶
The gconf class provides common
functionality for recipes that need to install GConf schemas.
The schemas will be put into a separate package
(${PN}-gconf)
that is created automatically when this class is inherited.
This package uses the appropriate post-install and post-remove
(postinst/postrm) scriptlets to register and unregister the schemas
in the target image.
6.41. gettext.bbclass¶
The gettext class provides support for
building software that uses the GNU gettext
internationalization and localization system.
All recipes building software that use
gettext should inherit this class.
6.42. gnome.bbclass¶
The gnome class supports recipes that
build software from the GNOME stack.
This class inherits the
gnomebase,
gtk-icon-cache,
gconf and
mime classes.
The class also disables GObject introspection where applicable.
6.43. gnomebase.bbclass¶
The gnomebase class is the base
class for recipes that build software from the GNOME stack.
This class sets
SRC_URI to
download the source from the GNOME mirrors as well as extending
FILES
with the typical GNOME installation paths.
6.44. gobject-introspection.bbclass¶
Provides support for recipes building software that
supports GObject introspection.
This functionality is only enabled if the
"gobject-introspection-data" feature is in
DISTRO_FEATURES
as well as "qemu-usermode" being in
MACHINE_FEATURES.
Note
This functionality is backfilled by default and, if not applicable, should be disabled throughDISTRO_FEATURES_BACKFILL_CONSIDERED
or
MACHINE_FEATURES_BACKFILL_CONSIDERED,
respectively.
6.45. grub-efi.bbclass¶
The grub-efi
class provides grub-efi-specific functions for
building bootable images.
This class supports several variables:
INITRD: Indicates list of filesystem images to concatenate and use as an initial RAM disk (initrd) (optional).ROOTFS: Indicates a filesystem image to include as the root filesystem (optional).GRUB_GFXSERIAL: Set this to "1" to have graphics and serial in the boot menu.LABELS: A list of targets for the automatic configuration.APPEND: An override list of append strings for eachLABEL.GRUB_OPTS: Additional options to add to the configuration (optional). Options are delimited using semi-colon characters (;).GRUB_TIMEOUT: Timeout before executing the defaultLABEL(optional).
6.46. gsettings.bbclass¶
The gsettings class
provides common functionality for recipes that need to install
GSettings (glib) schemas.
The schemas are assumed to be part of the main package.
Appropriate post-install and post-remove (postinst/postrm)
scriptlets are added to register and unregister the schemas in the
target image.
6.47. gtk-doc.bbclass¶
The gtk-doc class
is a helper class to pull in the appropriate
gtk-doc dependencies and disable
gtk-doc.
6.48. gtk-icon-cache.bbclass¶
The gtk-icon-cache class
generates the proper post-install and post-remove (postinst/postrm)
scriptlets for packages that use GTK+ and install icons.
These scriptlets call gtk-update-icon-cache to add
the fonts to GTK+'s icon cache.
Since the cache files are architecture-specific,
gtk-update-icon-cache is run using QEMU if the
postinst scriptlets need to be run on the build host during image
creation.
6.49. gtk-immodules-cache.bbclass¶
The gtk-immodules-cache class
generates the proper post-install and post-remove (postinst/postrm)
scriptlets for packages that install GTK+ input method modules for
virtual keyboards.
These scriptlets call gtk-update-icon-cache to add
the input method modules to the cache.
Since the cache files are architecture-specific,
gtk-update-icon-cache is run using QEMU if the
postinst scriptlets need to be run on the build host during image
creation.
If the input method modules being installed are in packages other than
the main package, set
GTKIMMODULES_PACKAGES
to specify the packages containing the modules.
6.50. gzipnative.bbclass¶
The gzipnative class enables the use of
different native versions of gzip
and pigz rather than the versions of these tools
from the build host.
6.51. icecc.bbclass¶
The icecc class supports
Icecream, which
facilitates taking compile jobs and distributing them among remote
machines.
The class stages directories with symlinks from gcc
and g++ to icecc, for both
native and cross compilers.
Depending on each configure or compile, the OpenEmbedded build system
adds the directories at the head of the PATH list
and then sets the ICECC_CXX and
ICEC_CC variables, which are the paths to the
g++ and gcc compilers,
respectively.
For the cross compiler, the class creates a tar.gz
file that contains the Yocto Project toolchain and sets
ICECC_VERSION, which is the version of the
cross-compiler used in the cross-development toolchain, accordingly.
The class handles all three different compile stages
(i.e native ,cross-kernel and target) and creates the necessary
environment tar.gz file to be used by the remote
machines.
The class also supports SDK generation.
If ICECC_PATH
is not set in your local.conf file, then the
class tries to locate the icecc binary
using which.
If
ICECC_ENV_EXEC
is set in your local.conf file, the variable should
point to the icecc-create-env script
provided by the user.
If you do not point to a user-provided script, the build system
uses the default script provided by the recipe
icecc-create-env-native.bb.
Note
This script is a modified version and not the one that comes withicecc.
If you do not want the Icecream distributed compile support to apply
to specific recipes or classes, you can effectively "blacklist" them
by listing the recipes and classes using the
ICECC_USER_PACKAGE_BL
and
ICECC_USER_CLASS_BL,
variables, respectively, in your local.conf file.
Doing so causes the OpenEmbedded build system to handle these
compilations locally.
Additionally, you can list recipes using the
ICECC_USER_PACKAGE_WL
variable in your local.conf file to force
icecc to be enabled for recipes using an empty
PARALLEL_MAKE
variable.
Inheriting the icecc class changes all sstate
signatures.
Consequently, if a development team has a dedicated build system
that populates
STATE_MIRRORS
and they want to reuse sstate from
STATE_MIRRORS, then all developers and the
build system need to either inherit the icecc
class or nobody should.
At the distribution level, you can inherit the
icecc class to be sure that all builders start
with the same sstate signatures.
After inheriting the class, you can then disable the feature by setting
the
ICECC_DISABLED
variable to "1" as follows:
INHERIT_DISTRO_append = " icecc"
ICECC_DISABLED ??= "1"
This practice makes sure everyone is using the same signatures but also
requires individuals that do want to use Icecream to enable the feature
individually as follows in your local.conf file:
ICECC_DISABLED = ""
6.52. image.bbclass¶
The image class helps support creating images
in different formats.
First, the root filesystem is created from packages using
one of the rootfs*.bbclass
files (depending on the package format used) and then one or more image
files are created.
The
IMAGE_FSTYPESvariable controls the types of images to generate.The
IMAGE_INSTALLvariable controls the list of packages to install into the image.
For information on customizing images, see the "Customizing Images" section in the Yocto Project Development Tasks Manual. For information on how images are created, see the "Images" section in the Yocto Project Overview and Concpets Manual.
6.53. image-buildinfo.bbclass¶
The image-buildinfo class writes information
to the target filesystem on /etc/build.
6.54. image_types.bbclass¶
The image_types class defines all of the
standard image output types that you can enable through the
IMAGE_FSTYPES
variable.
You can use this class as a reference on how to add support for
custom image output types.
By default, the
image
class automatically enables the image_types class.
The image class uses the
IMGCLASSES variable as follows:
IMGCLASSES = "rootfs_${IMAGE_PKGTYPE} image_types ${IMAGE_CLASSES}"
IMGCLASSES += "${@['populate_sdk_base', 'populate_sdk_ext']['linux' in d.getVar("SDK_OS")]}"
IMGCLASSES += "${@bb.utils.contains_any('IMAGE_FSTYPES', 'live iso hddimg', 'image-live', '', d)}"
IMGCLASSES += "${@bb.utils.contains('IMAGE_FSTYPES', 'container', 'image-container', '', d)}"
IMGCLASSES += "image_types_wic"
IMGCLASSES += "rootfs-postcommands"
IMGCLASSES += "image-postinst-intercepts"
inherit ${IMGCLASSES}
The image_types class also handles conversion and
compression of images.
Note
To build a VMware VMDK image, you need to add "wic.vmdk" toIMAGE_FSTYPES.
This would also be similar for Virtual Box Virtual Disk Image
("vdi") and QEMU Copy On Write Version 2 ("qcow2") images.
6.55. image-live.bbclass¶
This class controls building "live" (i.e. HDDIMG and ISO) images.
Live images contain syslinux for legacy booting, as well as the
bootloader specified by
EFI_PROVIDER
if
MACHINE_FEATURES
contains "efi".
Normally, you do not use this class directly.
Instead, you add "live" to
IMAGE_FSTYPES.
6.56. image-mklibs.bbclass¶
The image-mklibs class
enables the use of the mklibs utility during the
do_rootfs
task, which optimizes the size of
libraries contained in the image.
By default, the class is enabled in the
local.conf.template using the
USER_CLASSES
variable as follows:
USER_CLASSES ?= "buildstats image-mklibs image-prelink"
6.57. image-prelink.bbclass¶
The image-prelink class
enables the use of the prelink utility during
the
do_rootfs
task, which optimizes the dynamic
linking of shared libraries to reduce executable startup time.
By default, the class is enabled in the
local.conf.template using the
USER_CLASSES
variable as follows:
USER_CLASSES ?= "buildstats image-mklibs image-prelink"
6.58. insane.bbclass¶
The insane class adds a step to the package
generation process so that output quality assurance checks are
generated by the OpenEmbedded build system.
A range of checks are performed that check the build's output
for common problems that show up during runtime.
Distribution policy usually dictates whether to include this class.
You can configure the sanity checks so that specific test failures either raise a warning or an error message. Typically, failures for new tests generate a warning. Subsequent failures for the same test would then generate an error message once the metadata is in a known and good condition. See the "QA Error and Warning Messages" Chapter for a list of all the warning and error messages you might encounter using a default configuration.
Use the
WARN_QA and
ERROR_QA
variables to control the behavior of
these checks at the global level (i.e. in your custom distro
configuration).
However, to skip one or more checks in recipes, you should use
INSANE_SKIP.
For example, to skip the check for symbolic link
.so files in the main package of a recipe,
add the following to the recipe.
You need to realize that the package name override, in this example
${PN}, must be used:
INSANE_SKIP_${PN} += "dev-so"
Please keep in mind that the QA checks exist in order to detect real or potential problems in the packaged output. So exercise caution when disabling these checks.
The following list shows the tests you can list with the
WARN_QA and ERROR_QA
variables:
already-stripped:Checks that produced binaries have not already been stripped prior to the build system extracting debug symbols. It is common for upstream software projects to default to stripping debug symbols for output binaries. In order for debugging to work on the target using-dbgpackages, this stripping must be disabled.arch:Checks the Executable and Linkable Format (ELF) type, bit size, and endianness of any binaries to ensure they match the target architecture. This test fails if any binaries do not match the type since there would be an incompatibility. The test could indicate that the wrong compiler or compiler options have been used. Sometimes software, like bootloaders, might need to bypass this check.buildpaths:Checks for paths to locations on the build host inside the output files. Currently, this test triggers too many false positives and thus is not normally enabled.build-deps:Determines if a build-time dependency that is specified throughDEPENDS, explicitRDEPENDS, or task-level dependencies exists to match any runtime dependency. This determination is particularly useful to discover where runtime dependencies are detected and added during packaging. If no explicit dependency has been specified within the metadata, at the packaging stage it is too late to ensure that the dependency is built, and thus you can end up with an error when the package is installed into the image during thedo_rootfstask because the auto-detected dependency was not satisfied. An example of this would be where theupdate-rc.dclass automatically adds a dependency on theinitscripts-functionspackage to packages that install an initscript that refers to/etc/init.d/functions. The recipe should really have an explicitRDEPENDSfor the package in question oninitscripts-functionsso that the OpenEmbedded build system is able to ensure that theinitscriptsrecipe is actually built and thus theinitscripts-functionspackage is made available.compile-host-path:Checks thedo_compilelog for indications that paths to locations on the build host were used. Using such paths might result in host contamination of the build output.debug-deps:Checks that all packages except-dbgpackages do not depend on-dbgpackages, which would cause a packaging bug.debug-files:Checks for.debugdirectories in anything but the-dbgpackage. The debug files should all be in the-dbgpackage. Thus, anything packaged elsewhere is incorrect packaging.dep-cmp:Checks for invalid version comparison statements in runtime dependency relationships between packages (i.e. inRDEPENDS,RRECOMMENDS,RSUGGESTS,RPROVIDES,RREPLACES, andRCONFLICTSvariable values). Any invalid comparisons might trigger failures or undesirable behavior when passed to the package manager.desktop:Runs thedesktop-file-validateprogram against any.desktopfiles to validate their contents against the specification for.desktopfiles.dev-deps:Checks that all packages except-devor-staticdevpackages do not depend on-devpackages, which would be a packaging bug.dev-so:Checks that the.sosymbolic links are in the-devpackage and not in any of the other packages. In general, these symlinks are only useful for development purposes. Thus, the-devpackage is the correct location for them. Some very rare cases do exist for dynamically loaded modules where these symlinks are needed instead in the main package.file-rdeps:Checks that file-level dependencies identified by the OpenEmbedded build system at packaging time are satisfied. For example, a shell script might start with the line#!/bin/bash. This line would translate to a file dependency on/bin/bash. Of the three package managers that the OpenEmbedded build system supports, only RPM directly handles file-level dependencies, resolving them automatically to packages providing the files. However, the lack of that functionality in the other two package managers does not mean the dependencies do not still need resolving. This QA check attempts to ensure that explicitly declaredRDEPENDSexist to handle any file-level dependency detected in packaged files.files-invalid:Checks forFILESvariable values that contain "//", which is invalid.host-user-contaminated:Checks that no package produced by the recipe contains any files outside of/homewith a user or group ID that matches the user running BitBake. A match usually indicates that the files are being installed with an incorrect UID/GID, since target IDs are independent from host IDs. For additional information, see the section describing thedo_installtask.incompatible-license:Report when packages are excluded from being created due to being marked with a license that is inINCOMPATIBLE_LICENSE.install-host-path:Checks thedo_installlog for indications that paths to locations on the build host were used. Using such paths might result in host contamination of the build output.installed-vs-shipped:Reports when files have been installed withindo_installbut have not been included in any package by way of theFILESvariable. Files that do not appear in any package cannot be present in an image later on in the build process. Ideally, all installed files should be packaged or not installed at all. These files can be deleted at the end ofdo_installif the files are not needed in any package.invalid-chars:Checks that the recipe metadata variablesDESCRIPTION,SUMMARY,LICENSE, andSECTIONdo not contain non-UTF-8 characters. Some package managers do not support such characters.invalid-packageconfig:Checks that no undefined features are being added toPACKAGECONFIG. For example, any name "foo" for which the following form does not exist:PACKAGECONFIG[foo] = "..."la:Checks.lafiles for anyTMPDIRpaths. Any.lafile containing these paths is incorrect sincelibtooladds the correct sysroot prefix when using the files automatically itself.ldflags:Ensures that the binaries were linked with theLDFLAGSoptions provided by the build system. If this test fails, check that theLDFLAGSvariable is being passed to the linker command.libdir:Checks for libraries being installed into incorrect (possibly hardcoded) installation paths. For example, this test will catch recipes that install/lib/bar.sowhen${base_libdir}is "lib32". Another example is when recipes install/usr/lib64/foo.sowhen${libdir}is "/usr/lib".libexec:Checks if a package contains files in/usr/libexec. This check is not performed if thelibexecdirvariable has been set explicitly to/usr/libexec.packages-list:Checks for the same package being listed multiple times through thePACKAGESvariable value. Installing the package in this manner can cause errors during packaging.perm-config:Reports lines infs-perms.txtthat have an invalid format.perm-line:Reports lines infs-perms.txtthat have an invalid format.perm-link:Reports lines infs-perms.txtthat specify 'link' where the specified target already exists.perms:Currently, this check is unused but reserved.pkgconfig:Checks.pcfiles for anyTMPDIR/WORKDIRpaths. Any.pcfile containing these paths is incorrect sincepkg-configitself adds the correct sysroot prefix when the files are accessed.pkgname:Checks that all packages inPACKAGEShave names that do not contain invalid characters (i.e. characters other than 0-9, a-z, ., +, and -).pkgv-undefined:Checks to see if thePKGVvariable is undefined duringdo_package.pkgvarcheck:Checks through the variablesRDEPENDS,RRECOMMENDS,RSUGGESTS,RCONFLICTS,RPROVIDES,RREPLACES,FILES,ALLOW_EMPTY,pkg_preinst,pkg_postinst,pkg_prermandpkg_postrm, and reports if there are variable sets that are not package-specific. Using these variables without a package suffix is bad practice, and might unnecessarily complicate dependencies of other packages within the same recipe or have other unintended consequences.pn-overrides:Checks that a recipe does not have a name (PN) value that appears inOVERRIDES. If a recipe is named such that itsPNvalue matches something already inOVERRIDES(e.g.PNhappens to be the same asMACHINEorDISTRO), it can have unexpected consequences. For example, assignments such asFILES_${PN} = "xyz"effectively turn intoFILES = "xyz".rpaths:Checks for rpaths in the binaries that contain build system paths such asTMPDIR. If this test fails, bad-rpathoptions are being passed to the linker commands and your binaries have potential security issues.split-strip:Reports that splitting or stripping debug symbols from binaries has failed.staticdev:Checks for static library files (*.a) in non-staticdevpackages.symlink-to-sysroot:Checks for symlinks in packages that point intoTMPDIRon the host. Such symlinks will work on the host, but are clearly invalid when running on the target.textrel:Checks for ELF binaries that contain relocations in their.textsections, which can result in a performance impact at runtime. See the explanation for theELF binarymessage for more information regarding runtime performance issues.useless-rpaths:Checks for dynamic library load paths (rpaths) in the binaries that by default on a standard system are searched by the linker (e.g./liband/usr/lib). While these paths will not cause any breakage, they do waste space and are unnecessary.var-undefined:Reports when variables fundamental to packaging (i.e.WORKDIR,DEPLOY_DIR,D,PN, andPKGD) are undefined duringdo_package.version-going-backwards:If Build History is enabled, reports when a package being written out has a lower version than the previously written package under the same name. If you are placing output packages into a feed and upgrading packages on a target system using that feed, the version of a package going backwards can result in the target system not correctly upgrading to the "new" version of the package.Note
If you are not using runtime package management on your target system, then you do not need to worry about this situation.xorg-driver-abi:Checks that all packages containing Xorg drivers have ABI dependencies. Thexserver-xorgrecipe provides driver ABI names. All drivers should depend on the ABI versions that they have been built against. Driver recipes that includexorg-driver-input.incorxorg-driver-video.incwill automatically get these versions. Consequently, you should only need to explicitly add dependencies to binary driver recipes.
6.59. insserv.bbclass¶
The insserv class
uses the insserv utility to update the order of
symbolic links in /etc/rc?.d/ within an image
based on dependencies specified by LSB headers in the
init.d scripts themselves.
6.60. kernel.bbclass¶
The kernel class handles building Linux kernels.
The class contains code to build all kernel trees.
All needed headers are staged into the
STAGING_KERNEL_DIR
directory to allow out-of-tree module builds using
the
module
class.
This means that each built kernel module is packaged separately and
inter-module dependencies are created by parsing the
modinfo output.
If all modules are required, then installing the
kernel-modules package installs all packages with
modules and various other kernel packages such as
kernel-vmlinux.
The kernel class contains logic that allows
you to embed an initial RAM filesystem (initramfs) image when
you build the kernel image.
For information on how to build an initramfs, see the
"Building an Initial RAM Filesystem (initramfs) Image"
section in the Yocto Project Development Tasks Manual.
Various other classes are used by the kernel
and module classes internally including the
kernel-arch,
module-base,
and
linux-kernel-base
classes.
6.61. kernel-arch.bbclass¶
The kernel-arch class
sets the ARCH environment variable for Linux
kernel compilation (including modules).
6.62. kernel-devicetree.bbclass¶
The kernel-devicetree class, which is inherited by
the
kernel
class, supports device tree generation.
6.63. kernel-fitimage.bbclass¶
The kernel-fitimage class provides support to
pack zImages.
6.64. kernel-grub.bbclass¶
The kernel-grub class updates the boot area and
the boot menu with the kernel as the priority boot mechanism while
installing a RPM to update the kernel on a deployed target.
6.65. kernel-module-split.bbclass¶
The kernel-module-split class
provides common functionality for splitting Linux kernel modules into
separate packages.
6.66. kernel-uboot.bbclass¶
The kernel-uboot class provides support for
building from vmlinux-style kernel sources.
6.67. kernel-uimage.bbclass¶
The kernel-uimage class provides support to
pack uImage.
6.68. kernel-yocto.bbclass¶
The kernel-yocto class
provides common functionality for building from linux-yocto style
kernel source repositories.
6.69. kernelsrc.bbclass¶
The kernelsrc class sets the Linux kernel
source and version.
6.70. lib_package.bbclass¶
The lib_package class
supports recipes that build libraries and produce executable
binaries, where those binaries should not be installed by default
along with the library.
Instead, the binaries are added to a separate
${PN}-bin
package to make their installation optional.
6.71. libc*.bbclass¶
The libc* classes support recipes that build
packages with libc:
The
libc-commonclass provides common support for building withlibc.The
libc-packageclass supports packaging upglibcandeglibc.
6.72. license.bbclass¶
The license class provides license
manifest creation and license exclusion.
This class is enabled by default using the default value for the
INHERIT_DISTRO
variable.
6.73. linux-kernel-base.bbclass¶
The linux-kernel-base class
provides common functionality for recipes that build out of the Linux
kernel source tree.
These builds goes beyond the kernel itself.
For example, the Perf recipe also inherits this class.
6.74. linuxloader.bbclass¶
Provides the function linuxloader(), which gives
the value of the dynamic loader/linker provided on the platform.
This value is used by a number of other classes.
6.75. logging.bbclass¶
The logging class provides the standard
shell functions used to log messages for various BitBake severity levels
(i.e. bbplain, bbnote,
bbwarn, bberror,
bbfatal, and bbdebug).
This class is enabled by default since it is inherited by
the base class.
6.76. meta.bbclass¶
The meta class is inherited by recipes
that do not build any output packages themselves, but act as a "meta"
target for building other recipes.
6.77. metadata_scm.bbclass¶
The metadata_scm class provides functionality for
querying the branch and revision of a Source Code Manager (SCM)
repository.
The base
class uses this class to print the revisions of each layer before
starting every build.
The metadata_scm class is enabled by default
because it is inherited by the base class.
6.78. migrate_localcount.bbclass¶
The migrate_localcount class verifies a recipe's
localcount data and increments it appropriately.
6.79. mime.bbclass¶
The mime class generates the proper
post-install and post-remove (postinst/postrm) scriptlets for packages
that install MIME type files.
These scriptlets call update-mime-database to add
the MIME types to the shared database.
6.80. mirrors.bbclass¶
The mirrors class sets up some standard
MIRRORS entries
for source code mirrors.
These mirrors provide a fall-back path in case the upstream source
specified in
SRC_URI
within recipes is unavailable.
This class is enabled by default since it is inherited by the
base class.
6.81. module.bbclass¶
The module class provides support for building
out-of-tree Linux kernel modules.
The class inherits the
module-base
and
kernel-module-split
classes, and implements the
do_compile
and
do_install
tasks.
The class provides everything needed to build and package a kernel
module.
For general information on out-of-tree Linux kernel modules, see the "Incorporating Out-of-Tree Modules" section in the Yocto Project Linux Kernel Development Manual.
6.82. module-base.bbclass¶
The module-base class provides the base
functionality for building Linux kernel modules.
Typically, a recipe that builds software that includes one or
more kernel modules and has its own means of building
the module inherits this class as opposed to inheriting the
module
class.
6.83. multilib*.bbclass¶
The multilib* classes provide support
for building libraries with different target optimizations or target
architectures and installing them side-by-side in the same image.
For more information on using the Multilib feature, see the "Combining Multiple Versions of Library Files into One Image" section in the Yocto Project Development Tasks Manual.
6.84. native.bbclass¶
The native class provides common
functionality for recipes that build tools to run on the
build host
(i.e. tools that use the compiler or other tools from the
build host).
You can create a recipe that builds tools that run natively on the host a couple different ways:
Create a
myrecipe-native.bbrecipe that inherits thenativeclass. If you use this method, you must order the inherit statement in the recipe after all other inherit statements so that thenativeclass is inherited last.Warning
When creating a recipe this way, the recipe name must follow this naming convention:myrecipe-native.bbCreate or modify a target recipe that contains the following:
BBCLASSEXTEND= "native"Inside the recipe, use
_class-nativeand_class-targetoverrides to specify any functionality specific to the respective native or target case.
Although applied differently, the native class is
used with both methods.
The advantage of the second method is that you do not need to have two
separate recipes (assuming you need both) for native and target.
All common parts of the recipe are automatically shared.
6.85. nativesdk.bbclass¶
The nativesdk class provides common
functionality for recipes that wish to build tools to run as part of
an SDK (i.e. tools that run on
SDKMACHINE).
You can create a recipe that builds tools that run on the SDK machine a couple different ways:
Create a
nativesdk-myrecipe.bbrecipe that inherits thenativesdkclass. If you use this method, you must order the inherit statement in the recipe after all other inherit statements so that thenativesdkclass is inherited last.Create a
nativesdkvariant of any recipe by adding the following:BBCLASSEXTEND= "nativesdk"Inside the recipe, use
_class-nativesdkand_class-targetoverrides to specify any functionality specific to the respective SDK machine or target case.
Warning
When creating a recipe, you must follow this naming convention:
nativesdk-myrecipe.bb
Not doing so can lead to subtle problems because code exists
that depends on the naming convention.
Although applied differently, the nativesdk class
is used with both methods.
The advantage of the second method is that you do not need to have two
separate recipes (assuming you need both) for the SDK machine and the
target.
All common parts of the recipe are automatically shared.
6.86. nopackages.bbclass¶
Disables packaging tasks for those recipes and classes where packaging is not needed.
6.87. npm.bbclass¶
Provides support for building Node.js software fetched using the npm package manager.
Note
Currently, recipes inheriting this class must use thenpm:// fetcher to have dependencies fetched
and packaged automatically.
6.88. oelint.bbclass¶
The oelint class is an
obsolete lint checking tool that exists in
meta/classes in the
Source Directory.
A number of classes exist that could be generally useful in
OE-Core but are never actually used within OE-Core itself.
The oelint class is one such example.
However, being aware of this class can reduce the proliferation of
different versions of similar classes across multiple layers.
6.89. own-mirrors.bbclass¶
The own-mirrors class makes it
easier to set up your own
PREMIRRORS
from which to first fetch source before attempting to fetch it from the
upstream specified in
SRC_URI
within each recipe.
To use this class, inherit it globally and specify
SOURCE_MIRROR_URL.
Here is an example:
INHERIT += "own-mirrors"
SOURCE_MIRROR_URL = "http://example.com/my-source-mirror"
You can specify only a single URL in
SOURCE_MIRROR_URL.
6.90. package.bbclass¶
The package class supports generating
packages from a build's output.
The core generic functionality is in
package.bbclass.
The code specific to particular package types resides in these
package-specific classes:
package_deb,
package_rpm,
package_ipk,
and
package_tar.
Warning
Thepackage_tar class is broken and not
supported.
It is recommended that you do not use this class.
You can control the list of resulting package formats by using the
PACKAGE_CLASSES
variable defined in your conf/local.conf
configuration file, which is located in the
Build Directory.
When defining the variable, you can specify one or more package types.
Since images are generated from packages, a packaging class is
needed to enable image generation.
The first class listed in this variable is used for image generation.
If you take the optional step to set up a repository (package feed) on the development host that can be used by DNF, you can install packages from the feed while you are running the image on the target (i.e. runtime installation of packages). For more information, see the "Using Runtime Package Management" section in the Yocto Project Development Tasks Manual.
The package-specific class you choose can affect build-time performance
and has space ramifications.
In general, building a package with IPK takes about thirty percent less
time as compared to using RPM to build the same or similar package.
This comparison takes into account a complete build of the package with
all dependencies previously built.
The reason for this discrepancy is because the RPM package manager
creates and processes more
Metadata than the
IPK package manager.
Consequently, you might consider setting
PACKAGE_CLASSES to "package_ipk" if you are
building smaller systems.
Before making your package manager decision, however, you should consider some further things about using RPM:
RPM starts to provide more abilities than IPK due to the fact that it processes more Metadata. For example, this information includes individual file types, file checksum generation and evaluation on install, sparse file support, conflict detection and resolution for Multilib systems, ACID style upgrade, and repackaging abilities for rollbacks.
For smaller systems, the extra space used for the Berkeley Database and the amount of metadata when using RPM can affect your ability to perform on-device upgrades.
You can find additional information on the effects of the package class at these two Yocto Project mailing list links:
6.91. package_deb.bbclass¶
The package_deb class
provides support for creating packages that use the Debian
(i.e. .deb) file format.
The class ensures the packages are written out in a
.deb file format to the
${DEPLOY_DIR_DEB}
directory.
This class inherits the
package
class and is enabled through the
PACKAGE_CLASSES
variable in the local.conf file.
6.92. package_ipk.bbclass¶
The package_ipk class
provides support for creating packages that use the IPK
(i.e. .ipk) file format.
The class ensures the packages are written out in a
.ipk file format to the
${DEPLOY_DIR_IPK}
directory.
This class inherits the
package
class and is enabled through the
PACKAGE_CLASSES
variable in the local.conf file.
6.93. package_rpm.bbclass¶
The package_rpm class
provides support for creating packages that use the RPM
(i.e. .rpm) file format.
The class ensures the packages are written out in a
.rpm file format to the
${DEPLOY_DIR_RPM}
directory.
This class inherits the
package
class and is enabled through the
PACKAGE_CLASSES
variable in the local.conf file.
6.94. package_tar.bbclass¶
The package_tar class
provides support for creating tarballs.
The class ensures the packages are written out in a
tarball format to the
${DEPLOY_DIR_TAR}
directory.
This class inherits the
package
class and is enabled through the
PACKAGE_CLASSES
variable in the local.conf file.
Note
You cannot specify thepackage_tar class
first using the PACKAGE_CLASSES variable.
You must use .deb,
.ipk, or .rpm file
formats for your image or SDK.
6.95. packagedata.bbclass¶
The packagedata class provides
common functionality for reading pkgdata files
found in
PKGDATA_DIR.
These files contain information about each output package produced by
the OpenEmbedded build system.
This class is enabled by default because it is inherited by the
package
class.
6.96. packagegroup.bbclass¶
The packagegroup class sets default values
appropriate for package group recipes (e.g.
PACKAGES,
PACKAGE_ARCH,
ALLOW_EMPTY,
and so forth).
It is highly recommended that all package group recipes inherit this class.
For information on how to use this class, see the "Customizing Images Using Custom Package Groups" section in the Yocto Project Development Tasks Manual.
Previously, this class was called the task class.
6.97. patch.bbclass¶
The patch class provides all functionality for
applying patches during the
do_patch
task.
This class is enabled by default because it is inherited by the
base
class.
6.98. perlnative.bbclass¶
When inherited by a recipe, the perlnative class
supports using the native version of Perl built by the build system
rather than using the version provided by the build host.
6.99. pixbufcache.bbclass¶
The pixbufcache class generates the proper
post-install and post-remove (postinst/postrm) scriptlets for packages
that install pixbuf loaders, which are used with
gdk-pixbuf.
These scriptlets call update_pixbuf_cache
to add the pixbuf loaders to the cache.
Since the cache files are architecture-specific,
update_pixbuf_cache is run using QEMU if the
postinst scriptlets need to be run on the build host during image
creation.
If the pixbuf loaders being installed are in packages other
than the recipe's main package, set
PIXBUF_PACKAGES
to specify the packages containing the loaders.
6.100. pkgconfig.bbclass¶
The pkgconfig class provides a standard way to get
header and library information by using pkg-config.
This class aims to smooth integration of
pkg-config into libraries that use it.
During staging, BitBake installs pkg-config
data into the sysroots/ directory.
By making use of sysroot functionality within
pkg-config, the pkgconfig
class no longer has to manipulate the files.
6.101. populate_sdk.bbclass¶
The populate_sdk class provides support for
SDK-only recipes.
For information on advantages gained when building a cross-development
toolchain using the
do_populate_sdk
task, see the
"Building an SDK Installer"
section in the Yocto Project Application Development and the
Extensible Software Development Kit (eSDK) manual.
6.102. populate_sdk_*.bbclass¶
The populate_sdk_* classes support SDK creation
and consist of the following classes:
populate_sdk_base: The base class supporting SDK creation under all package managers (i.e. DEB, RPM, and opkg).populate_sdk_deb: Supports creation of the SDK given the Debian package manager.populate_sdk_rpm: Supports creation of the SDK given the RPM package manager.populate_sdk_ipk: Supports creation of the SDK given the opkg (IPK format) package manager.populate_sdk_ext: Supports extensible SDK creation under all package managers.
The populate_sdk_base class inherits the
appropriate populate_sdk_* (i.e.
deb, rpm, and
ipk) based on
IMAGE_PKGTYPE.
The base class ensures all source and destination directories are
established and then populates the SDK.
After populating the SDK, the populate_sdk_base
class constructs two sysroots:
${SDK_ARCH}-nativesdk,
which contains the cross-compiler and associated tooling, and the
target, which contains a target root filesystem that is configured for
the SDK usage.
These two images reside in
SDK_OUTPUT,
which consists of the following:
${SDK_OUTPUT}/${SDK_ARCH}-nativesdk-pkgs
${SDK_OUTPUT}/${SDKTARGETSYSROOT}/target-pkgs
Finally, the base populate SDK class creates the toolchain environment setup script, the tarball of the SDK, and the installer.
The respective populate_sdk_deb,
populate_sdk_rpm, and
populate_sdk_ipk classes each support the
specific type of SDK.
These classes are inherited by and used with the
populate_sdk_base class.
For more information on the cross-development toolchain
generation, see the
"Cross-Development Toolchain Generation"
section in the Yocto Project Overview and Concepts Manual.
For information on advantages gained when building a
cross-development toolchain using the
do_populate_sdk
task, see the
"Building an SDK Installer"
section in the Yocto Project Application Development and the
Extensible Software Development Kit (eSDK) manual.
6.103. prexport.bbclass¶
The prexport class provides functionality for
exporting
PR values.
Note
This class is not intended to be used directly. Rather, it is enabled when using "bitbake-prserv-tool export".
6.104. primport.bbclass¶
The primport class provides functionality for
importing
PR values.
Note
This class is not intended to be used directly. Rather, it is enabled when using "bitbake-prserv-tool import".
6.105. prserv.bbclass¶
The prserv class provides functionality for
using a
PR service
in order to automatically manage the incrementing of the
PR variable for
each recipe.
This class is enabled by default because it is inherited by the
package
class.
However, the OpenEmbedded build system will not enable the
functionality of this class unless
PRSERV_HOST
has been set.
6.106. ptest.bbclass¶
The ptest class provides functionality for
packaging and installing runtime tests for recipes that build software
that provides these tests.
This class is intended to be inherited by individual recipes.
However, the class' functionality is largely disabled unless "ptest"
appears in
DISTRO_FEATURES.
See the
"Testing Packages With ptest"
section in the Yocto Project Development Tasks Manual for more
information on ptest.
6.107. ptest-gnome.bbclass¶
Enables package tests (ptests) specifically for GNOME packages,
which have tests intended to be executed with
gnome-desktop-testing.
For information on setting up and running ptests, see the "Testing Packages With ptest" section in the Yocto Project Development Tasks Manual.
6.108. python-dir.bbclass¶
The python-dir class provides the base version,
location, and site package location for Python.
6.109. python3native.bbclass¶
The python3native class supports using the
native version of Python 3 built by the build system rather than
support of the version provided by the build host.
6.110. pythonnative.bbclass¶
When inherited by a recipe, the pythonnative class
supports using the native version of Python built by the build system
rather than using the version provided by the build host.
6.111. qemu.bbclass¶
The qemu class provides functionality for recipes
that either need QEMU or test for the existence of QEMU.
Typically, this class is used to run programs for a target system on
the build host using QEMU's application emulation mode.
6.112. recipe_sanity.bbclass¶
The recipe_sanity class checks for the presence
of any host system recipe prerequisites that might affect the
build (e.g. variables that are set or software that is present).
6.113. relocatable.bbclass¶
The relocatable class enables relocation of
binaries when they are installed into the sysroot.
This class makes use of the
chrpath
class and is used by both the
cross
and
native
classes.
6.114. remove-libtool.bbclass¶
The remove-libtool class adds a post function
to the
do_install
task to remove all .la files installed by
libtool.
Removing these files results in them being absent from both the
sysroot and target packages.
If a recipe needs the .la files to be installed,
then the recipe can override the removal by setting
REMOVE_LIBTOOL_LA to "0" as follows:
REMOVE_LIBTOOL_LA = "0"
Note
Theremove-libtool class is not enabled by
default.
6.115. report-error.bbclass¶
The report-error class supports enabling the
error reporting tool,
which allows you to submit build error information to a central
database.
The class collects debug information for recipe, recipe version, task,
machine, distro, build system, target system, host distro, branch,
commit, and log.
From the information, report files using a JSON format are created and
stored in
${LOG_DIR}/error-report.
6.116. rm_work.bbclass¶
The rm_work class supports deletion of temporary
workspace, which can ease your hard drive demands during builds.
The OpenEmbedded build system can use a substantial amount of disk
space during the build process.
A portion of this space is the work files under the
${TMPDIR}/work directory for each recipe.
Once the build system generates the packages for a recipe, the work
files for that recipe are no longer needed.
However, by default, the build system preserves these files
for inspection and possible debugging purposes.
If you would rather have these files deleted to save disk space
as the build progresses, you can enable rm_work
by adding the following to your local.conf file,
which is found in the
Build Directory.
INHERIT += "rm_work"
If you are modifying and building source code out of the work directory
for a recipe, enabling rm_work will potentially
result in your changes to the source being lost.
To exclude some recipes from having their work directories deleted by
rm_work, you can add the names of the recipe or
recipes you are working on to the RM_WORK_EXCLUDE
variable, which can also be set in your local.conf
file.
Here is an example:
RM_WORK_EXCLUDE += "busybox glibc"
6.117. rootfs*.bbclass¶
The rootfs* classes support creating
the root filesystem for an image and consist of the following classes:
The
rootfs-postcommandsclass, which defines filesystem post-processing functions for image recipes.The
rootfs_debclass, which supports creation of root filesystems for images built using.debpackages.The
rootfs_rpmclass, which supports creation of root filesystems for images built using.rpmpackages.The
rootfs_ipkclass, which supports creation of root filesystems for images built using.ipkpackages.The
rootfsdebugfilesclass, which installs additional files found on the build host directly into the root filesystem.
The root filesystem is created from packages using one of the
rootfs*.bbclass files as determined by the
PACKAGE_CLASSES
variable.
For information on how root filesystem images are created, see the "Image Generation" section in the Yocto Project Overview and Concepts Manual.
6.118. sanity.bbclass¶
The sanity class checks to see if prerequisite
software is present on the host system so that users can be notified
of potential problems that might affect their build.
The class also performs basic user configuration checks from
the local.conf configuration file to
prevent common mistakes that cause build failures.
Distribution policy usually determines whether to include this class.
6.119. scons.bbclass¶
The scons class supports recipes that need to
build software that uses the SCons build system.
You can use the
EXTRA_OESCONS
variable to specify additional configuration options you want to pass
SCons command line.
6.120. sdl.bbclass¶
The sdl class supports recipes that need to build
software that uses the Simple DirectMedia Layer (SDL) library.
6.121. setuptools.bbclass¶
The setuptools class supports Python
version 2.x extensions that use build systems based on
setuptools.
If your recipe uses these build systems, the recipe needs to
inherit the setuptools class.
6.122. setuptools3.bbclass¶
The setuptools3 class supports Python
version 3.x extensions that use build systems based on
setuptools3.
If your recipe uses these build systems, the recipe needs to
inherit the setuptools3 class.
6.123. sign_rpm.bbclass¶
The sign_rpm class supports generating signed
RPM packages.
6.124. sip.bbclass¶
The sip class
supports recipes that build or package SIP-based Python bindings.
6.125. siteconfig.bbclass¶
The siteconfig class
provides functionality for handling site configuration.
The class is used by the
autotools
class to accelerate the
do_configure
task.
6.126. siteinfo.bbclass¶
The siteinfo class provides information about
the targets that might be needed by other classes or recipes.
As an example, consider Autotools, which can require tests that must
execute on the target hardware.
Since this is not possible in general when cross compiling, site
information is used to provide cached test results so these tests can
be skipped over but still make the correct values available.
The
meta/site directory
contains test results sorted into different categories such as
architecture, endianness, and the libc used.
Site information provides a list of files containing data relevant to
the current build in the
CONFIG_SITE variable
that Autotools automatically picks up.
The class also provides variables like
SITEINFO_ENDIANNESS
and SITEINFO_BITS
that can be used elsewhere in the metadata.
6.127. spdx.bbclass¶
The spdx class integrates real-time license
scanning, generation of SPDX standard output, and verification
of license information during the build.
Note
This class is currently at the prototype stage in the 1.6 release.
6.128. sstate.bbclass¶
The sstate class provides support for Shared
State (sstate).
By default, the class is enabled through the
INHERIT_DISTRO
variable's default value.
For more information on sstate, see the "Shared State Cache" section in the Yocto Project Overview and Concepts Manual.
6.129. staging.bbclass¶
The staging class installs files into individual
recipe work directories for sysroots.
The class contains the following key tasks:
The
do_populate_sysroottask, which is responsible for handing the files that end up in the recipe sysroots.The
do_prepare_recipe_sysroottask (a "partner" task to thepopulate_sysroottask), which installs the files into the individual recipe work directories (i.e.WORKDIR).
The code in the staging class is complex and
basically works in two stages:
Stage One: The first stage addresses recipes that have files they want to share with other recipes that have dependencies on the originating recipe. Normally these dependencies are installed through the
do_installtask into${D}. Thedo_populate_sysroottask copies a subset of these files into${SYSROOT_DESTDIR}. This subset of files is controlled by theSYSROOT_DIRS,SYSROOT_DIRS_NATIVE, andSYSROOT_DIRS_BLACKLISTvariables.Note
Additionally, a recipe can customize the files further by declaring a processing function in theSYSROOT_PREPROCESS_FUNCSvariable.A shared state (sstate) object is built from these files and the files are placed into a subdirectory of
tmp/sysroots-components/. The files are scanned for hardcoded paths to the original installation location. If the location is found in text files, the hardcoded locations are replaced by tokens and a list of the files needing such replacements is created. These adjustments are referred to as "FIXMEs". The list of files that are scanned for paths is controlled by theSSTATE_SCAN_FILESvariable.Stage Two: The second stage addresses recipes that want to use something from another recipe and declare a dependency on that recipe through the
DEPENDSvariable. The recipe will have ado_prepare_recipe_sysroottask and when this task executes, it creates therecipe-sysrootandrecipe-sysroot-nativein the recipe work directory (i.e.WORKDIR). The OpenEmbedded build system creates hard links to copies of the relevant files fromsysroots-componentsinto the recipe work directory.Note
If hard links are not possible, the build system uses actual copies.The build system then addresses any "FIXMEs" to paths as defined from the list created in the first stage.
Finally, any files in
${bindir}within the sysroot that have the prefix "postinst-" are executed.Note
Although such sysroot post installation scripts are not recommended for general use, the files do allow some issues such as user creation and module indexes to be addressed.Because recipes can have other dependencies outside of
DEPENDS(e.g.do_unpack[depends] += "tar-native:do_populate_sysroot"), the sysroot creation functionextend_recipe_sysrootis also added as a pre-function for those tasks whose dependencies are not throughDEPENDSbut operate similarly.When installing dependencies into the sysroot, the code traverses the dependency graph and processes dependencies in exactly the same way as the dependencies would or would not be when installed from sstate. This processing means, for example, a native tool would have its native dependencies added but a target library would not have its dependencies traversed or installed. The same sstate dependency code is used so that builds should be identical regardless of whether sstate was used or not. For a closer look, see the
setscene_depvalid()function in thesstateclass.The build system is careful to maintain manifests of the files it installs so that any given dependency can be installed as needed. The sstate hash of the installed item is also stored so that if it changes, the build system can reinstall it.
6.130. syslinux.bbclass¶
The syslinux class provides syslinux-specific
functions for building bootable images.
The class supports the following variables:
INITRD: Indicates list of filesystem images to concatenate and use as an initial RAM disk (initrd). This variable is optional.ROOTFS: Indicates a filesystem image to include as the root filesystem. This variable is optional.AUTO_SYSLINUXMENU: Enables creating an automatic menu when set to "1".LABELS: Lists targets for automatic configuration.APPEND: Lists append string overrides for each label.SYSLINUX_OPTS: Lists additional options to add to the syslinux file. Semicolon characters separate multiple options.SYSLINUX_SPLASH: Lists a background for the VGA boot menu when you are using the boot menu.SYSLINUX_DEFAULT_CONSOLE: Set to "console=ttyX" to change kernel boot default console.SYSLINUX_SERIAL: Sets an alternate serial port. Or, turns off serial when the variable is set with an empty string.SYSLINUX_SERIAL_TTY: Sets an alternate "console=tty..." kernel boot argument.
6.131. systemd.bbclass¶
The systemd class provides support for recipes
that install systemd unit files.
The functionality for this class is disabled unless you have "systemd"
in
DISTRO_FEATURES.
Under this class, the recipe or Makefile (i.e. whatever the recipe is
calling during the
do_install
task) installs unit files into
${D}${systemd_unitdir}/system.
If the unit files being installed go into packages other than the
main package, you need to set
SYSTEMD_PACKAGES
in your recipe to identify the packages in which the files will be
installed.
You should set
SYSTEMD_SERVICE
to the name of the service file.
You should also use a package name override to indicate the package
to which the value applies.
If the value applies to the recipe's main package, use
${PN}.
Here is an example from the connman recipe:
SYSTEMD_SERVICE_${PN} = "connman.service"
Services are set up to start on boot automatically unless
you have set
SYSTEMD_AUTO_ENABLE
to "disable".
For more information on systemd, see the
"Selecting an Initialization Manager"
section in the Yocto Project Development Tasks Manual.
6.132. systemd-boot.bbclass¶
The systemd-boot class provides functions specific
to the systemd-boot bootloader for building bootable images.
This is an internal class and is not intended to be used directly.
Note
Thesystemd-boot class is a result from
merging the gummiboot class used in previous
Yocto Project releases with the systemd
project.
Set the
EFI_PROVIDER
variable to "systemd-boot" to use this class.
Doing so creates a standalone EFI bootloader that is not dependent
on systemd.
For information on more variables used and supported in this class,
see the
SYSTEMD_BOOT_CFG,
SYSTEMD_BOOT_ENTRIES,
and
SYSTEMD_BOOT_TIMEOUT
variables.
You can also see the Systemd-boot documentation for more information.
6.133. terminal.bbclass¶
The terminal class provides support for starting
a terminal session.
The
OE_TERMINAL
variable controls which terminal emulator is used for the session.
Other classes use the terminal class anywhere a
separate terminal session needs to be started.
For example, the
patch
class assuming
PATCHRESOLVE
is set to "user", the
cml1
class, and the
devshell
class all use the terminal class.
6.134. testimage*.bbclass¶
The testimage* classes support running
automated tests against images using QEMU and on actual hardware.
The classes handle loading the tests and starting the image.
To use the classes, you need to perform steps to set up the
environment.
Tip
Best practices include usingIMAGE_CLASSES
rather than
INHERIT to
inherit the testimage class for automated
image testing.
The tests are commands that run on the target system over
ssh.
Each test is written in Python and makes use of the
unittest module.
The testimage.bbclass runs tests on an image
when called using the following:
$ bitbake -c testimage image
The testimage-auto class runs tests on an image
after the image is constructed (i.e.
TESTIMAGE_AUTO
must be set to "1").
For information on how to enable, run, and create new tests, see the "Performing Automated Runtime Testing" section in the Yocto Project Development Tasks Manual.
6.135. testsdk.bbclass¶
This class supports running automated tests against
software development kits (SDKs).
The testsdk class runs tests on an SDK when
called using the following:
$ bitbake -c testsdk image
Tip
Best practices include usingIMAGE_CLASSES
rather than
INHERIT to
inherit the testsdk class for automated
SDK testing.
6.136. texinfo.bbclass¶
This class should be inherited by recipes whose upstream packages
invoke the texinfo utilities at build-time.
Native and cross recipes are made to use the dummy scripts provided
by texinfo-dummy-native, for improved performance.
Target architecture recipes use the genuine
Texinfo utilities.
By default, they use the Texinfo utilities on the host system.
Note
If you want to use the Texinfo recipe shipped with the build system, you can remove "texinfo-native" fromASSUME_PROVIDED
and makeinfo from
SANITY_REQUIRED_UTILITIES.
6.137. tinderclient.bbclass¶
The tinderclient class submits build results to
an external Tinderbox instance.
Note
This class is currently unmaintained.
6.138. toaster.bbclass¶
The toaster class collects information about
packages and images and sends them as events that the BitBake
user interface can receive.
The class is enabled when the Toaster user interface is running.
This class is not intended to be used directly.
6.139. toolchain-scripts.bbclass¶
The toolchain-scripts class provides the scripts
used for setting up the environment for installed SDKs.
6.140. typecheck.bbclass¶
The typecheck class provides support for
validating the values of variables set at the configuration level
against their defined types.
The OpenEmbedded build system allows you to define the type of a
variable using the "type" varflag.
Here is an example:
IMAGE_FEATURES[type] = "list"
6.141. uboot-config.bbclass¶
The uboot-config class provides support for
U-Boot configuration for a machine.
Specify the machine in your recipe as follows:
UBOOT_CONFIG ??= <default>
UBOOT_CONFIG[foo] = "config,images"
You can also specify the machine using this method:
UBOOT_MACHINE = "config"
See the
UBOOT_CONFIG
and
UBOOT_MACHINE
variables for additional information.
6.142. uninative.bbclass¶
Attempts to isolate the build system from the host
distribution's C library in order to make re-use of native shared state
artifacts across different host distributions practical.
With this class enabled, a tarball containing a pre-built C library
is downloaded at the start of the build.
In the Poky reference distribution this is enabled by default
through
meta/conf/distro/include/yocto-uninative.inc.
Other distributions that do not derive from poky can also
"require conf/distro/include/yocto-uninative.inc"
to use this.
Alternatively if you prefer, you can build the uninative-tarball recipe
yourself, publish the resulting tarball (e.g. via HTTP) and set
UNINATIVE_URL and
UNINATIVE_CHECKSUM appropriately.
For an example, see the
meta/conf/distro/include/yocto-uninative.inc.
The uninative class is also used unconditionally
by the extensible SDK.
When building the extensible SDK,
uninative-tarball is built and the resulting
tarball is included within the SDK.
6.143. update-alternatives.bbclass¶
The update-alternatives class helps the
alternatives system when multiple sources provide the same command.
This situation occurs when several programs that have the same or
similar function are installed with the same name.
For example, the ar command is available from the
busybox, binutils and
elfutils packages.
The update-alternatives class handles
renaming the binaries so that multiple packages can be installed
without conflicts.
The ar command still works regardless of which
packages are installed or subsequently removed.
The class renames the conflicting binary in each package and symlinks
the highest priority binary during installation or removal of packages.
To use this class, you need to define a number of variables:
These variables list alternative commands needed by a package,
provide pathnames for links, default links for targets, and
so forth.
For details on how to use this class, see the comments in the
update-alternatives.bbclass
file.
Note
You can use theupdate-alternatives command
directly in your recipes.
However, this class simplifies things in most cases.
6.144. update-rc.d.bbclass¶
The update-rc.d class uses
update-rc.d to safely install an
initialization script on behalf of the package.
The OpenEmbedded build system takes care of details such as making
sure the script is stopped before a package is removed and started when
the package is installed.
Three variables control this class:
INITSCRIPT_PACKAGES,
INITSCRIPT_NAME and
INITSCRIPT_PARAMS.
See the variable links for details.
6.145. useradd*.bbclass¶
The useradd* classes support the addition of users
or groups for usage by the package on the target.
For example, if you have packages that contain system services that
should be run under their own user or group, you can use these classes
to enable creation of the user or group.
The
meta-skeleton/recipes-skeleton/useradd/useradd-example.bb
recipe in the Source Directory
provides a simple example that shows how to add three
users and groups to two packages.
See the useradd-example.bb recipe for more
information on how to use these classes.
The useradd_base class provides basic
functionality for user or groups settings.
The useradd* classes support the
USERADD_PACKAGES,
USERADD_PARAM,
GROUPADD_PARAM,
and
GROUPMEMS_PARAM
variables.
The useradd-staticids class supports the addition
of users or groups that have static user identification
(uid) and group identification
(gid) values.
The default behavior of the OpenEmbedded build system for assigning
uid and gid values when
packages add users and groups during package install time is to
add them dynamically.
This works fine for programs that do not care what the values of the
resulting users and groups become.
In these cases, the order of the installation determines the final
uid and gid values.
However, if non-deterministic
uid and gid values are a
problem, you can override the default, dynamic application of these
values by setting static values.
When you set static values, the OpenEmbedded build system looks in
BBPATH for
files/passwd and files/group
files for the values.
To use static uid and gid
values, you need to set some variables.
See the
USERADDEXTENSION,
USERADD_UID_TABLES,
USERADD_GID_TABLES,
and
USERADD_ERROR_DYNAMIC
variables.
You can also see the
useradd
class for additional information.
Notes
You do not use theuseradd-staticids
class directly.
You either enable or disable the class by setting the
USERADDEXTENSION variable.
If you enable or disable the class in a configured system,
TMPDIR
might contain incorrect uid and
gid values.
Deleting the TMPDIR directory
will correct this condition.
6.146. utility-tasks.bbclass¶
The utility-tasks class provides support for
various "utility" type tasks that are applicable to all recipes,
such as
do_clean and
do_listtasks.
This class is enabled by default because it is inherited by
the
base
class.
6.147. utils.bbclass¶
The utils class provides some useful Python
functions that are typically used in inline Python expressions
(e.g. ${@...}).
One example use is for bb.utils.contains().
This class is enabled by default because it is inherited by the
base
class.
6.148. vala.bbclass¶
The vala class supports recipes that need to
build software written using the Vala programming language.
6.149. waf.bbclass¶
The waf class supports recipes that need to build
software that uses the Waf build system.
You can use the
EXTRA_OECONF
or
PACKAGECONFIG_CONFARGS
variables to specify additional configuration options to be passed on
the Waf command line.
Chapter 7. Tasks¶
Table of Contents
- 7.1. Normal Recipe Build Tasks
- 7.1.1.
do_build - 7.1.2.
do_compile - 7.1.3.
do_compile_ptest_base - 7.1.4.
do_configure - 7.1.5.
do_configure_ptest_base - 7.1.6.
do_deploy - 7.1.7.
do_distrodata - 7.1.8.
do_fetch - 7.1.9.
do_image - 7.1.10.
do_image_complete - 7.1.11.
do_install - 7.1.12.
do_install_ptest_base - 7.1.13.
do_package - 7.1.14.
do_package_qa - 7.1.15.
do_package_write_deb - 7.1.16.
do_package_write_ipk - 7.1.17.
do_package_write_rpm - 7.1.18.
do_package_write_tar - 7.1.19.
do_packagedata - 7.1.20.
do_patch - 7.1.21.
do_populate_lic - 7.1.22.
do_populate_sdk - 7.1.23.
do_populate_sysroot - 7.1.24.
do_prepare_recipe_sysroot - 7.1.25.
do_rm_work - 7.1.26.
do_unpack
- 7.1.1.
- 7.2. Manually Called Tasks
- 7.3. Image-Related Tasks
- 7.4. Kernel-Related Tasks
- 7.4.1.
do_compile_kernelmodules - 7.4.2.
do_diffconfig - 7.4.3.
do_kernel_checkout - 7.4.4.
do_kernel_configcheck - 7.4.5.
do_kernel_configme - 7.4.6.
do_kernel_menuconfig - 7.4.7.
do_kernel_metadata - 7.4.8.
do_menuconfig - 7.4.9.
do_savedefconfig - 7.4.10.
do_shared_workdir - 7.4.11.
do_sizecheck - 7.4.12.
do_strip - 7.4.13.
do_validate_branches
- 7.4.1.
- 7.5. Miscellaneous Tasks
Tasks are units of execution for BitBake.
Recipes (.bb files) use tasks to complete
configuring, compiling, and packaging software.
This chapter provides a reference of the tasks defined in the
OpenEmbedded build system.
7.1. Normal Recipe Build Tasks¶
The following sections describe normal tasks associated with building a recipe. For more information on tasks and dependencies, see the "Tasks" and "Dependencies" sections in the BitBake User Manual.
7.1.1. do_build¶
The default task for all recipes. This task depends on all other normal tasks required to build a recipe.
7.1.2. do_compile¶
Compiles the source code.
This task runs with the current working directory set
to
${B}.
The default behavior of this task is to run the
oe_runmake function if a makefile
(Makefile, makefile,
or GNUmakefile) is found.
If no such file is found, the do_compile
task does nothing.
7.1.3. do_compile_ptest_base¶
Compiles the runtime test suite included in the software being built.
7.1.4. do_configure¶
Configures the source by enabling and disabling any build-time and
configuration options for the software being built.
The task runs with the current working directory set to
${B}.
The default behavior of this task is to run
oe_runmake clean if a makefile
(Makefile, makefile,
or GNUmakefile) is found and
CLEANBROKEN
is not set to "1".
If no such file is found or the CLEANBROKEN
variable is set to "1", the do_configure
task does nothing.
7.1.5. do_configure_ptest_base¶
Configures the runtime test suite included in the software being built.
7.1.6. do_deploy¶
Writes output files that are to be deployed to
${DEPLOY_DIR_IMAGE}.
The task runs with the current working directory set to
${B}.
Recipes implementing this task should inherit the
deploy
class and should write the output to
${DEPLOYDIR},
which is not to be confused with ${DEPLOY_DIR}.
The deploy class sets up
do_deploy as a shared state (sstate) task that
can be accelerated through sstate use.
The sstate mechanism takes care of copying the output from
${DEPLOYDIR} to
${DEPLOY_DIR_IMAGE}.
Caution
Do not write the output directly to${DEPLOY_DIR_IMAGE}, as this causes
the sstate mechanism to malfunction.
The do_deploy task is not added as a task
by default and consequently needs to be added manually.
If you want the task to run after
do_compile,
you can add it by doing the following:
addtask deploy after do_compile
Adding do_deploy after other tasks works the
same way.
Note
You do not need to addbefore do_build
to the addtask command (though it is
harmless), because the
base
class contains the following:
do_build[recrdeptask] += "do_deploy"
See the
"Dependencies"
section in the BitBake User Manual for more information.
If the do_deploy task re-executes, any
previous output is removed (i.e. "cleaned").
7.1.7. do_distrodata¶
Provides information about the recipe.
The distrodata task is included as part of the
distrodata
class.
To build the distrodata task, use the
bitbake command with the "-c" option and
task name:
$ bitbake core-image-minimal -c distrodata
By default, the results are stored in
$LOG_DIR
(e.g. $BUILD_DIR/tmp/log).
7.1.8. do_fetch¶
Fetches the source code.
This task uses the
SRC_URI
variable and the argument's prefix to determine the correct
fetcher module.
7.1.9. do_image¶
Starts the image generation process.
The do_image task runs after the
OpenEmbedded build system has run the
do_rootfs
task during which packages are identified for installation into
the image and the root filesystem is created, complete with
post-processing.
The do_image task performs pre-processing
on the image through the
IMAGE_PREPROCESS_COMMAND
and dynamically generates supporting
do_image_* tasks as needed.
For more information on image creation, see the "Image Generation" section in the Yocto Project Overview and Concepts Manual.
7.1.10. do_image_complete¶
Completes the image generation process.
The do_image_complete task runs after the
OpenEmbedded build system has run the
do_image
task during which image pre-processing occurs and through
dynamically generated do_image_* tasks the
image is constructed.
The do_image_complete task performs
post-processing on the image through the
IMAGE_POSTPROCESS_COMMAND.
For more information on image creation, see the "Image Generation" section in the Yocto Project Overview and Concepts Manual.
7.1.11. do_install¶
Copies files that are to be packaged into the holding area
${D}.
This task runs with the current working directory set to
${B},
which is the compilation directory.
The do_install task, as well as other tasks
that either directly or indirectly depend on the installed files
(e.g.
do_package,
do_package_write_*,
and
do_rootfs),
run under
fakeroot.
Caution
When installing files, be careful not to set the owner and
group IDs of the installed files to unintended values.
Some methods of copying files, notably when using the
recursive cp command, can preserve the
UID and/or GID of the original file, which is usually not
what you want.
The
host-user-contaminated
QA check checks for files that probably have the wrong
ownership.
Safe methods for installing files include the following:
The
installutility. This utility is the preferred method.The
cpcommand with the "--no-preserve=ownership" option.The
tarcommand with the "--no-same-owner" option. See thebin_package.bbclassfile in themeta/classesdirectory of the Source Directory for an example.
7.1.12. do_install_ptest_base¶
Copies the runtime test suite files from the compilation directory to a holding area.
7.1.13. do_package¶
Analyzes the content of the holding area
${D}
and splits the content into subsets based on available packages
and files.
This task makes use of the
PACKAGES
and
FILES
variables.
The do_package task, in conjunction with the
do_packagedata
task, also saves some important package metadata.
For additional information, see the
PKGDESTWORK
variable and the
"Automatically Added Runtime Dependencies"
section in the Yocto Project Overview and Concepts Manual.
7.1.14. do_package_qa¶
Runs QA checks on packaged files.
For more information on these checks, see the
insane
class.
7.1.15. do_package_write_deb¶
Creates Debian packages (i.e. *.deb files) and
places them in the
${DEPLOY_DIR_DEB}
directory in the package feeds area.
For more information, see the
"Package Feeds"
section in the Yocto Project Overview and Concepts Manual.
7.1.16. do_package_write_ipk¶
Creates IPK packages (i.e. *.ipk files) and
places them in the
${DEPLOY_DIR_IPK}
directory in the package feeds area.
For more information, see the
"Package Feeds"
section in the Yocto Project Overview and Concepts Manual.
7.1.17. do_package_write_rpm¶
Creates RPM packages (i.e. *.rpm files) and
places them in the
${DEPLOY_DIR_RPM}
directory in the package feeds area.
For more information, see the
"Package Feeds"
section in the Yocto Project Overview and Concepts Manual.
7.1.18. do_package_write_tar¶
Creates tarballs and places them in the
${DEPLOY_DIR_TAR}
directory in the package feeds area.
For more information, see the
"Package Feeds"
section in the Yocto Project Overview and Concepts Manual.
7.1.19. do_packagedata¶
Saves package metadata generated by the
do_package
task in
PKGDATA_DIR
to make it available globally.
7.1.20. do_patch¶
Locates patch files and applies them to the source code.
After fetching and unpacking source files, the build system
uses the recipe's
SRC_URI
statements to locate and apply patch files to the source code.
Note
The build system uses theFILESPATH
variable to determine the default set of directories when
searching for patches.
Patch files, by default, are *.patch and
*.diff files created and kept in a
subdirectory of the directory holding the recipe file.
For example, consider the
bluez5
recipe from the OE-Core layer (i.e.
poky/meta):
poky/meta/recipes-connectivity/bluez5
This recipe has two patch files located here:
poky/meta/recipes-connectivity/bluez5/bluez5
In the bluez5 recipe, the
SRC_URI statements point to the source and
patch files needed to build the package.
Note
In the case for thebluez5_5.48.bb
recipe, the SRC_URI statements are from an
include file bluez5.inc.
As mentioned earlier, the build system treats files whose file
types are .patch and
.diff as patch files.
However, you can use the "apply=yes" parameter with the
SRC_URI statement to indicate any file as a
patch file:
SRC_URI = " \
git://path_to_repo/some_package \
file://file;apply=yes \
"
Conversely, if you have a directory full of patch files and you
want to exclude some so that the do_patch
task does not apply them during the patch phase, you can use
the "apply=no" parameter with the SRC_URI
statement:
SRC_URI = " \
git://path_to_repo/some_package \
file://path_to_lots_of_patch_files \
file://path_to_lots_of_patch_files/patch_file5;apply=no \
"
In the previous example, assuming all the files in the directory
holding the patch files end with either .patch
or .diff, every file would be applied as a
patch by default except for the
patch_file5 patch.
You can find out more about the patching process in the "Patching" section in the Yocto Project Overview and Concepts Manual and the "Patching Code" section in the Yocto Project Development Tasks Manual.
7.1.21. do_populate_lic¶
Writes license information for the recipe that is collected later when the image is constructed.
7.1.22. do_populate_sdk¶
Creates the file and directory structure for an installable SDK. See the "SDK Generation" section in the Yocto Project Overview and Concepts Manual for more information.
7.1.23. do_populate_sysroot¶
Stages (copies) a subset of the files installed by the
do_install
task into the appropriate sysroot.
For information on how to access these files from other recipes,
see the
STAGING_DIR*
variables.
Directories that would typically not be needed by other recipes at
build time (e.g. /etc) are not copied by
default.
For information on what directories are copied by default, see the
SYSROOT_DIRS*
variables.
You can change these variables inside your recipe if you need
to make additional (or fewer) directories available to other
recipes at build time.
The do_populate_sysroot task is a
shared state (sstate) task, which means that the task can
be accelerated through sstate use.
Realize also that if the task is re-executed, any previous output
is removed (i.e. "cleaned").
7.1.24. do_prepare_recipe_sysroot¶
Installs the files into the individual recipe specific sysroots
(i.e. recipe-sysroot and
recipe-sysroot-native under
${WORKDIR}
based upon the dependencies specified by
DEPENDS).
See the
"staging"
class for more information.
7.1.25. do_rm_work¶
Removes work files after the OpenEmbedded build system has
finished with them.
You can learn more by looking at the
"rm_work.bbclass"
section.
7.1.26. do_unpack¶
Unpacks the source code into a working directory pointed to
by
${WORKDIR}.
The
S variable also
plays a role in where unpacked source files ultimately reside.
For more information on how source files are unpacked, see the
"Source Fetching"
section in the Yocto Project Overview and Concepts Manual and also
see the WORKDIR and
S variable descriptions.
7.2. Manually Called Tasks¶
These tasks are typically manually triggered (e.g. by using the
bitbake -c command-line option):
7.2.1. do_checkpkg¶
Provides information about the recipe including its upstream version and status. The upstream version and status reveals whether or not a version of the recipe exists upstream and a status of not updated, updated, or unknown.
The checkpkg task is included as part of the
distrodata
class.
To build the checkpkg task, use the
bitbake command with the "-c" option and
task name:
$ bitbake core-image-minimal -c checkpkg
By default, the results are stored in
$LOG_DIR
(e.g. $BUILD_DIR/tmp/log).
7.2.3. do_clean¶
Removes all output files for a target from the
do_unpack
task forward (i.e. do_unpack,
do_configure,
do_compile,
do_install,
and
do_package).
You can run this task using BitBake as follows:
$ bitbake -c clean recipe
Running this task does not remove the
sstate
cache files.
Consequently, if no changes have been made and the recipe is
rebuilt after cleaning, output files are simply restored from the
sstate cache.
If you want to remove the sstate cache files for the recipe,
you need to use the
do_cleansstate
task instead (i.e. bitbake -c cleansstate recipe).
7.2.4. do_cleanall¶
Removes all output files, shared state
(sstate)
cache, and downloaded source files for a target (i.e. the contents
of
DL_DIR).
Essentially, the do_cleanall task is
identical to the
do_cleansstate
task with the added removal of downloaded source files.
You can run this task using BitBake as follows:
$ bitbake -c cleanall recipe
Typically, you would not normally use the
cleanall task.
Do so only if you want to start fresh with the
do_fetch
task.
7.2.5. do_cleansstate¶
Removes all output files and shared state
(sstate)
cache for a target.
Essentially, the do_cleansstate task is
identical to the
do_clean
task with the added removal of shared state
(sstate)
cache.
You can run this task using BitBake as follows:
$ bitbake -c cleansstate recipe
When you run the do_cleansstate task,
the OpenEmbedded build system no longer uses any
sstate.
Consequently, building the recipe from scratch is guaranteed.
Note
Thedo_cleansstate task cannot remove
sstate from a remote sstate mirror.
If you need to build a target from scratch using remote
mirrors, use the "-f" option as follows:
$ bitbake -f -c do_cleansstate target
7.2.6. do_devpyshell¶
Starts a shell in which an interactive Python interpreter allows
you to interact with the BitBake build environment.
From within this shell, you can directly examine and set
bits from the data store and execute functions as if within
the BitBake environment.
See the
"Using a Development Python Shell"
section in the Yocto Project Development Tasks Manual for more
information about using devpyshell.
7.2.7. do_devshell¶
Starts a shell whose environment is set up for
development, debugging, or both.
See the
"Using a Development Shell"
section in the Yocto Project Development Tasks Manual for more
information about using devshell.
7.2.8. do_listtasks¶
Lists all defined tasks for a target.
7.2.9. do_package_index¶
Creates or updates the index in the Package Feeds area.
Note
This task is not triggered with thebitbake -c command-line option as
are the other tasks in this section.
Because this task is specifically for the
package-index recipe,
you run it using
bitbake package-index.
7.3. Image-Related Tasks¶
The following tasks are applicable to image recipes.
7.3.1. do_bootimg¶
Creates a bootable live image.
See the
IMAGE_FSTYPES
variable for additional information on live image types.
7.3.2. do_bundle_initramfs¶
Combines an initial RAM disk (initramfs) image and kernel
together to form a single image.
The
CONFIG_INITRAMFS_SOURCE
variable has some more information about these types of images.
7.3.3. do_rootfs¶
Creates the root filesystem (file and directory structure) for an image. See the "Image Generation" section in the Yocto Project Overview and Concepts Manual for more information on how the root filesystem is created.
7.3.4. do_testimage¶
Boots an image and performs runtime tests within the image. For information on automatically testing images, see the "Performing Automated Runtime Testing" section in the Yocto Project Development Tasks Manual.
7.3.5. do_testimage_auto¶
Boots an image and performs runtime tests within the image
immediately after it has been built.
This task is enabled when you set
TESTIMAGE_AUTO
equal to "1".
For information on automatically testing images, see the "Performing Automated Runtime Testing" section in the Yocto Project Development Tasks Manual.
7.4. Kernel-Related Tasks¶
The following tasks are applicable to kernel recipes.
Some of these tasks (e.g. the
do_menuconfig
task) are also applicable to recipes that use
Linux kernel style configuration such as the BusyBox recipe.
7.4.1. do_compile_kernelmodules¶
Runs the step that builds the kernel modules (if needed).
Building a kernel consists of two steps: 1) the kernel
(vmlinux) is built, and 2) the modules
are built (i.e. make modules).
7.4.2. do_diffconfig¶
When invoked by the user, this task creates a file containing the
differences between the original config as produced by
do_kernel_configme
task and the changes made by the user with other methods
(i.e. using
(do_kernel_menuconfig).
Once the file of differences is created, it can be used to create
a config fragment that only contains the differences.
You can invoke this task from the command line as follows:
$ bitbake linux-yocto -c diffconfig
For more information, see the "Creating Configuration Fragments" section in the Yocto Project Linux Kernel Development Manual.
7.4.3. do_kernel_checkout¶
Converts the newly unpacked kernel source into a form with which
the OpenEmbedded build system can work.
Because the kernel source can be fetched in several different ways,
the do_kernel_checkout task makes sure that
subsequent tasks are given a clean working tree copy of the kernel
with the correct branches checked out.
7.4.4. do_kernel_configcheck¶
Validates the configuration produced by the
do_kernel_menuconfig
task.
The do_kernel_configcheck task produces
warnings when a requested configuration does not appear in the
final .config file or when you override a
policy configuration in a hardware configuration fragment.
You can run this task explicitly and view the output by using
the following command:
$ bitbake linux-yocto -c kernel_configcheck -f
For more information, see the "Validating Configuration" section in the Yocto Project Linux Kernel Development Manual.
7.4.5. do_kernel_configme¶
After the kernel is patched by the
do_patch
task, the do_kernel_configme task assembles
and merges all the kernel config fragments into a merged
configuration that can then be passed to the kernel configuration
phase proper.
This is also the time during which user-specified defconfigs
are applied if present, and where configuration modes such as
--allnoconfig are applied.
7.4.6. do_kernel_menuconfig¶
Invoked by the user to manipulate the
.config file used to build a linux-yocto
recipe.
This task starts the Linux kernel configuration tool, which you
then use to modify the kernel configuration.
Note
You can also invoke this tool from the command line as follows:
$ bitbake linux-yocto -c menuconfig
See the
"Using menuconfig"
section in the Yocto Project Linux Kernel Development Manual
for more information on this configuration tool.
7.4.7. do_kernel_metadata¶
Collects all the features required for a given kernel build,
whether the features come from
SRC_URI
or from Git repositories.
After collection, the do_kernel_metadata task
processes the features into a series of config fragments and
patches, which can then be applied by subsequent tasks such as
do_patch
and
do_kernel_configme.
7.4.8. do_menuconfig¶
Runs make menuconfig for the kernel.
For information on menuconfig, see the
"Using menuconfig"
section in the Yocto Project Linux Kernel Development Manual.
7.4.9. do_savedefconfig¶
When invoked by the user, creates a defconfig file that can be
used instead of the default defconfig.
The saved defconfig contains the differences between the default
defconfig and the changes made by the user using other methods
(i.e. the
do_kernel_menuconfig
task.
You can invoke the task using the following command:
$ bitbake linux-yocto -c savedefconfig
7.4.10. do_shared_workdir¶
After the kernel has been compiled but before the kernel modules
have been compiled, this task copies files required for module
builds and which are generated from the kernel build into the
shared work directory.
With these copies successfully copied, the
do_compile_kernelmodules
task can successfully build the kernel modules in the next step
of the build.
7.4.11. do_sizecheck¶
After the kernel has been built, this task checks the size of the
stripped kernel image against
KERNEL_IMAGE_MAXSIZE.
If that variable was set and the size of the stripped kernel
exceeds that size, the kernel build produces a warning to that
effect.
7.4.12. do_strip¶
If
KERNEL_IMAGE_STRIP_EXTRA_SECTIONS is defined,
this task strips the sections named in that variable from
vmlinux.
This stripping is typically used to remove nonessential sections
such as .comment sections from a
size-sensitive configuration.
7.4.13. do_validate_branches¶
After the kernel is unpacked but before it is patched, this task
makes sure that the machine and metadata branches as specified
by the SRCREV
variables actually exist on the specified branches.
If these branches do not exist and
AUTOREV
is not being used, the do_validate_branches
task fails during the build.
Chapter 8. devtool Quick Reference¶
Table of Contents
- 8.1. Getting Help
- 8.2. The Workspace Layer Structure
- 8.3. Adding a New Recipe to the Workspace Layer
- 8.4. Extracting the Source for an Existing Recipe
- 8.5. Synchronizing a Recipe's Extracted Source Tree
- 8.6. Modifying an Existing Recipe
- 8.7. Edit an Existing Recipe
- 8.8. Updating a Recipe
- 8.9. Upgrading a Recipe
- 8.10. Resetting a Recipe
- 8.11. Building Your Recipe
- 8.12. Building Your Image
- 8.13. Deploying Your Software on the Target Machine
- 8.14. Removing Your Software from the Target Machine
- 8.15. Creating the Workspace Layer in an Alternative Location
- 8.16. Get the Status of the Recipes in Your Workspace
- 8.17. Search for Available Target Recipes
The devtool command-line tool provides a number
of features that help you build, test, and package software.
This command is available alongside the bitbake
command.
Additionally, the devtool command is a key
part of the extensible SDK.
This chapter provides a Quick Reference for the
devtool command.
For more information on how to apply the command when using the
extensible SDK, see the
"Using the Extensible SDK"
chapter in the Yocto Project Application Development and the
Extensible Software Development Kit (eSDK) manual.
8.1. Getting Help¶
The devtool command line is organized
similarly to Git in that it has a number of sub-commands for
each function.
You can run devtool --help to see all
the commands:
$ devtool --help
NOTE: Starting bitbake server...
usage: devtool [--basepath BASEPATH] [--bbpath BBPATH] [-d] [-q]
[--color COLOR] [-h]
<subcommand> ...
OpenEmbedded development tool
options:
--basepath BASEPATH Base directory of SDK / build directory
--bbpath BBPATH Explicitly specify the BBPATH, rather than getting it
from the metadata
-d, --debug Enable debug output
-q, --quiet Print only errors
--color COLOR Colorize output (where COLOR is auto, always, never)
-h, --help show this help message and exit
subcommands:
Beginning work on a recipe:
add Add a new recipe
modify Modify the source for an existing recipe
upgrade Upgrade an existing recipe
Getting information:
status Show workspace status
search Search available recipes
latest-version Report the latest version of an existing recipe
Working on a recipe in the workspace:
build Build a recipe
rename Rename a recipe file in the workspace
edit-recipe Edit a recipe file
find-recipe Find a recipe file
configure-help Get help on configure script options
update-recipe Apply changes from external source tree to recipe
reset Remove a recipe from your workspace
finish Finish working on a recipe in your workspace
Testing changes on target:
deploy-target Deploy recipe output files to live target machine
undeploy-target Undeploy recipe output files in live target machine
build-image Build image including workspace recipe packages
Advanced:
create-workspace Set up workspace in an alternative location
export Export workspace into a tar archive
import Import exported tar archive into workspace
extract Extract the source for an existing recipe
sync Synchronize the source tree for an existing recipe
Use devtool <subcommand> --help to get help on a specific command
As directed in the general help output, you can get more
syntax on a specific command by providing the command
name and using --help:
$ devtool add --help
NOTE: Starting bitbake server...
usage: devtool add [-h] [--same-dir | --no-same-dir] [--fetch URI]
[--fetch-dev] [--version VERSION] [--no-git]
[--srcrev SRCREV | --autorev] [--srcbranch SRCBRANCH]
[--binary] [--also-native] [--src-subdir SUBDIR]
[--mirrors] [--provides PROVIDES]
[recipename] [srctree] [fetchuri]
Adds a new recipe to the workspace to build a specified source tree. Can
optionally fetch a remote URI and unpack it to create the source tree.
arguments:
recipename Name for new recipe to add (just name - no version,
path or extension). If not specified, will attempt to
auto-detect it.
srctree Path to external source tree. If not specified, a
subdirectory of
/home/scottrif/poky/build/workspace/sources will be
used.
fetchuri Fetch the specified URI and extract it to create the
source tree
options:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
--same-dir, -s Build in same directory as source
--no-same-dir Force build in a separate build directory
--fetch URI, -f URI Fetch the specified URI and extract it to create the
source tree (deprecated - pass as positional argument
instead)
--fetch-dev For npm, also fetch devDependencies
--version VERSION, -V VERSION
Version to use within recipe (PV)
--no-git, -g If fetching source, do not set up source tree as a git
repository
--srcrev SRCREV, -S SRCREV
Source revision to fetch if fetching from an SCM such
as git (default latest)
--autorev, -a When fetching from a git repository, set SRCREV in the
recipe to a floating revision instead of fixed
--srcbranch SRCBRANCH, -B SRCBRANCH
Branch in source repository if fetching from an SCM
such as git (default master)
--binary, -b Treat the source tree as something that should be
installed verbatim (no compilation, same directory
structure). Useful with binary packages e.g. RPMs.
--also-native Also add native variant (i.e. support building recipe
for the build host as well as the target machine)
--src-subdir SUBDIR Specify subdirectory within source tree to use
--mirrors Enable PREMIRRORS and MIRRORS for source tree fetching
(disable by default).
--provides PROVIDES, -p PROVIDES
Specify an alias for the item provided by the recipe.
E.g. virtual/libgl
8.2. The Workspace Layer Structure¶
devtool uses a "Workspace" layer
in which to accomplish builds.
This layer is not specific to any single
devtool command but is rather a common
working area used across the tool.
The following figure shows the workspace structure:
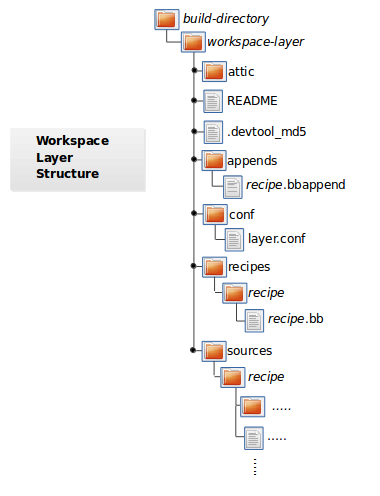 |
attic - A directory created if devtool believes it must preserve
anything when you run "devtool reset". For example, if you
run "devtool add", make changes to the recipe, and then
run "devtool reset", devtool takes notice that the file has
been changed and moves it into the attic should you still
want the recipe.
README - Provides information on what is in workspace layer and how to
manage it.
.devtool_md5 - A checksum file used by devtool.
appends - A directory that contains *.bbappend files, which point to
external source.
conf - A configuration directory that contains the layer.conf file.
recipes - A directory containing recipes. This directory contains a
folder for each directory added whose name matches that of the
added recipe. devtool places the recipe.bb file
within that sub-directory.
sources - A directory containing a working copy of the source files used
when building the recipe. This is the default directory used
as the location of the source tree when you do not provide a
source tree path. This directory contains a folder for each
set of source files matched to a corresponding recipe.
8.3. Adding a New Recipe to the Workspace Layer¶
Use the devtool add command to add a new recipe
to the workspace layer.
The recipe you add should not exist -
devtool creates it for you.
The source files the recipe uses should exist in an external
area.
The following example creates and adds a new recipe named
jackson to a workspace layer the tool creates.
The source code built by the recipes resides in
/home/:
user/sources/jackson
$ devtool add jackson /home/user/sources/jackson
If you add a recipe and the workspace layer does not exist, the command creates the layer and populates it as described in "The Workspace Layer Structure" section.
Running devtool add when the
workspace layer exists causes the tool to add the recipe,
append files, and source files into the existing workspace layer.
The .bbappend file is created to point
to the external source tree.
Note
If your recipe has runtime dependencies defined, you must be sure that these packages exist on the target hardware before attempting to run your application. If dependent packages (e.g. libraries) do not exist on the target, your application, when run, will fail to find those functions. For more information, see the "Deploying Your Software on the Target Machine" section.
By default, devtool add uses the latest
revision (i.e. master) when unpacking files from a remote URI.
In some cases, you might want to specify a source revision by
branch, tag, or commit hash. You can specify these options when
using the devtool add command:
To specify a source branch, use the
--srcbranchoption:$ devtool add --srcbranch thud jackson /home/user/sources/jacksonIn the previous example, you are checking out the thud branch.
To specify a specific tag or commit hash, use the
--srcrevoption:$ devtool add --srcrev yocto-2.6.1 jackson /home/user/sources/jackson $ devtool add --srcrevsome_commit_hash/home/user/sources/jacksonThe previous examples check out the yocto-2.6.1 tag and the commit associated with the
some_commit_hashhash.
Note
If you prefer to use the latest revision every time the recipe is built, use the options--autorev
or -a.
8.4. Extracting the Source for an Existing Recipe¶
Use the devtool extract command to
extract the source for an existing recipe.
When you use this command, you must supply the root name
of the recipe (i.e. no version, paths, or extensions), and
you must supply the directory to which you want the source
extracted.
Additional command options let you control the name of a development branch into which you can checkout the source and whether or not to keep a temporary directory, which is useful for debugging.
8.5. Synchronizing a Recipe's Extracted Source Tree¶
Use the devtool sync command to
synchronize a previously extracted source tree for an
existing recipe.
When you use this command, you must supply the root name
of the recipe (i.e. no version, paths, or extensions), and
you must supply the directory to which you want the source
extracted.
Additional command options let you control the name of a development branch into which you can checkout the source and whether or not to keep a temporary directory, which is useful for debugging.
8.6. Modifying an Existing Recipe¶
Use the devtool modify command to begin
modifying the source of an existing recipe.
This command is very similar to the
add
command except that it does not physically create the
recipe in the workspace layer because the recipe already
exists in an another layer.
The devtool modify command extracts the
source for a recipe, sets it up as a Git repository if the
source had not already been fetched from Git, checks out a
branch for development, and applies any patches from the recipe
as commits on top.
You can use the following command to checkout the source
files:
$ devtool modify recipe
Using the above command form, devtool uses
the existing recipe's
SRC_URI
statement to locate the upstream source, extracts the source
into the default sources location in the workspace.
The default development branch used is "devtool".
8.7. Edit an Existing Recipe¶
Use the devtool edit-recipe command
to run the default editor, which is identified using the
EDITOR variable, on the specified recipe.
When you use the devtool edit-recipe
command, you must supply the root name of the recipe
(i.e. no version, paths, or extensions).
Also, the recipe file itself must reside in the workspace
as a result of the devtool add or
devtool upgrade commands.
However, you can override that requirement by using the
"-a" or "--any-recipe" option.
Using either of these options allows you to edit any recipe
regardless of its location.
8.8. Updating a Recipe¶
Use the devtool update-recipe command to
update your recipe with patches that reflect changes you make
to the source files.
For example, if you know you are going to work on some
code, you could first use the
devtool modify
command to extract the code and set up the workspace.
After which, you could modify, compile, and test the code.
When you are satisfied with the results and you have committed
your changes to the Git repository, you can then
run the devtool update-recipe to create the
patches and update the recipe:
$ devtool update-recipe recipe
If you run the devtool update-recipe
without committing your changes, the command ignores the
changes.
Often, you might want to apply customizations made to your
software in your own layer rather than apply them to the
original recipe.
If so, you can use the
-a or --append
option with the devtool update-recipe
command.
These options allow you to specify the layer into which to
write an append file:
$ devtool update-recipe recipe -a base-layer-directory
The *.bbappend file is created at the
appropriate path within the specified layer directory, which
may or may not be in your bblayers.conf
file.
If an append file already exists, the command updates it
appropriately.
8.9. Upgrading a Recipe¶
As software matures, upstream recipes are upgraded to newer
versions.
As a developer, you need to keep your local recipes up-to-date
with the upstream version releases.
Several methods exist by which you can upgrade recipes.
You can read about them in the
"Upgrading Recipes"
section of the Yocto Project Development Tasks Manual.
This section overviews the devtool upgrade
command.
The devtool upgrade command
upgrades an existing recipe to a more recent version of the
recipe upstream.
The command puts the upgraded recipe file along with any associated
files into a "workspace" and, if necessary, extracts the source
tree to a specified location.
During the upgrade, patches associated with the recipe are
rebased or added as needed.
When you use the devtool upgrade command,
you must supply the root name of the recipe (i.e. no version,
paths, or extensions), and you must supply the directory
to which you want the source extracted.
Additional command options let you control things such as
the version number to which you want to upgrade (i.e. the
PV),
the source revision to which you want to upgrade (i.e. the
SRCREV),
whether or not to apply patches, and so forth.
You can read more on the devtool upgrade
workflow in the
"Use devtool upgrade to Create a Version of the Recipe that Supports a Newer Version of the Software"
section in the Yocto Project Application Development and the
Extensible Software Development Kit (eSDK) manual.
You can also see an example of how to use
devtool upgrade in the
"Using devtool upgrade"
section in the Yocto Project Development Tasks Manual.
8.10. Resetting a Recipe¶
Use the devtool reset command to remove a
recipe and its configuration (e.g. the corresponding
.bbappend file) from the workspace layer.
Realize that this command deletes the recipe and the
append file.
The command does not physically move them for you.
Consequently, you must be sure to physically relocate your
updated recipe and the append file outside of the workspace
layer before running the devtool reset
command.
If the devtool reset command detects that
the recipe or the append files have been modified, the
command preserves the modified files in a separate "attic"
subdirectory under the workspace layer.
Here is an example that resets the workspace directory that
contains the mtr recipe:
$ devtool reset mtr
NOTE: Cleaning sysroot for recipe mtr...
NOTE: Leaving source tree /home/scottrif/poky/build/workspace/sources/mtr as-is; if you no
longer need it then please delete it manually
$
8.11. Building Your Recipe¶
Use the devtool build command to cause the
OpenEmbedded build system to build your recipe.
The devtool build command is equivalent to
bitbake -c populate_sysroot.
When you use the devtool build command,
you must supply the root name of the recipe (i.e. no version,
paths, or extensions).
You can use either the "-s" or the "--disable-parallel-make"
option to disable parallel makes during the build.
Here is an example:
$ devtool build recipe
8.12. Building Your Image¶
Use the devtool build-image command
to build an image, extending it to include packages from
recipes in the workspace.
Using this command is useful when you want an image that
ready for immediate deployment onto a device for testing.
For proper integration into a final image, you need to
edit your custom image recipe appropriately.
When you use the devtool build-image
command, you must supply the name of the image.
This command has no command line options:
$ devtool build-image image
8.13. Deploying Your Software on the Target Machine¶
Use the devtool deploy-target command to
deploy the recipe's build output to the live target machine:
$ devtool deploy-target recipe target
The target is the address of the
target machine, which must be running an SSH server (i.e.
user@hostname[:destdir]).
This command deploys all files installed during the
do_install
task.
Furthermore, you do not need to have package management enabled
within the target machine.
If you do, the package manager is bypassed.
Notes
The deploy-target
functionality is for development only.
You should never use it to update an image that will be
used in production.
Some conditions exist that could prevent a deployed application from behaving as expected. When both of the following conditions exist, your application has the potential to not behave correctly when run on the target:
You are deploying a new application to the target and the recipe you used to build the application had correctly defined runtime dependencies.
The target does not physically have the packages on which the application depends installed.
If both of these conditions exist, your application will not
behave as expected.
The reason for this misbehavior is because the
devtool deploy-target command does not deploy
the packages (e.g. libraries) on which your new application
depends.
The assumption is that the packages are already on the target.
Consequently, when a runtime call is made in the application
for a dependent function (e.g. a library call), the function
cannot be found.
To be sure you have all the dependencies local to the target, you need to be sure that the packages are pre-deployed (installed) on the target before attempting to run your application.
8.14. Removing Your Software from the Target Machine¶
Use the devtool undeploy-target command to
remove deployed build output from the target machine.
For the devtool undeploy-target command to
work, you must have previously used the
devtool deploy-target
command.
$ devtool undeploy-target recipe target
The target is the address of the
target machine, which must be running an SSH server (i.e.
user@hostname).
8.15. Creating the Workspace Layer in an Alternative Location¶
Use the devtool create-workspace command to
create a new workspace layer in your
Build Directory.
When you create a new workspace layer, it is populated with the
README file and the
conf directory only.
The following example creates a new workspace layer in your current working and by default names the workspace layer "workspace":
$ devtool create-workspace
You can create a workspace layer anywhere by supplying a pathname with the command. The following command creates a new workspace layer named "new-workspace":
$ devtool create-workspace /home/scottrif/new-workspace
8.16. Get the Status of the Recipes in Your Workspace¶
Use the devtool status command to
list the recipes currently in your workspace.
Information includes the paths to their respective
external source trees.
The devtool status command has no
command-line options:
$ devtool status
Following is sample output after using
devtool add
to create and add the mtr_0.86.bb recipe
to the workspace directory:
$ devtool status
mtr: /home/scottrif/poky/build/workspace/sources/mtr (/home/scottrif/poky/build/workspace/recipes/mtr/mtr_0.86.bb)
$
8.17. Search for Available Target Recipes¶
Use the devtool search command to
search for available target recipes.
The command matches the recipe name, package name,
description, and installed files.
The command displays the recipe name as a result of a
match.
When you use the devtool search command,
you must supply a keyword.
The command uses the keyword when
searching for a match.
Chapter 9. OpenEmbedded Kickstart (.wks) Reference¶
9.1. Introduction¶
The current Wic implementation supports only the basic kickstart
partitioning commands:
partition (or part
for short) and bootloader.
Note
Future updates will implement more commands and options. If you use anything that is not specifically supported, results can be unpredictable.
This chapter provides a reference on the available kickstart commands. The information lists the commands, their syntax, and meanings. Kickstart commands are based on the Fedora kickstart versions but with modifications to reflect Wic capabilities. You can see the original documentation for those commands at the following link:
http://pykickstart.readthedocs.io/en/latest/kickstart-docs.html
9.2. Command: part or partition¶
Either of these commands creates a partition on the system and uses the following syntax:
part [mntpoint]
partition [mntpoint]
If you do not provide mntpoint, Wic
creates a partition but does not mount it.
The mntpoint
/: For example, "/", "/usr", or "/home"pathswap: The created partition is used as swap space
Specifying a mntpoint causes the
partition to automatically be mounted.
Wic achieves this by adding entries to the filesystem table (fstab)
during image generation.
In order for Wic to generate a valid fstab, you must also provide
one of the --ondrive,
--ondisk, or
--use-uuid partition options as part of the
command.
Note
The mount program must understand the PARTUUID syntax you use with--use-uuid and non-root
mountpoint, including swap.
The busybox versions of these application are currently
excluded.
Here is an example that uses "/" as the
mountpoint.
The command uses --ondisk to force the
partition onto the
sdb disk:
part / --source rootfs --ondisk sdb --fstype=ext3 --label platform --align 1024
Here is a list that describes other supported options you can use
with the part and
partition commands:
--size: The minimum partition size in MBytes. Specify an integer value such as 500. Do not append the number with "MB". You do not need this option if you use--source.--fixed-size: The exact partition size in MBytes. You cannot specify with--size. An error occurs when assembling the disk image if the partition data is larger than--fixed-size.--source: This option is a Wic-specific option that names the source of the data that populates the partition. The most common value for this option is "rootfs", but you can use any value that maps to a valid source plug-in. For information on the source plug-ins, see the "Using the Wic Plug-Ins Interface" section in the Yocto Project Development Tasks Manual.If you use
--source rootfs, Wic creates a partition as large as needed and fills it with the contents of the root filesystem pointed to by the-rcommand-line option or the equivalent rootfs derived from the-ecommand-line option. The filesystem type used to create the partition is driven by the value of the--fstypeoption specified for the partition. See the entry on--fstypethat follows for more information.If you use
--source, Wic creates a partition as large as needed and fills it with the contents of the partition that is generated by the specified plug-in name using the data pointed to by theplugin-name-rcommand-line option or the equivalent rootfs derived from the-ecommand-line option. Exactly what those contents are and filesystem type used are dependent on the given plug-in implementation.If you do not use the
--sourceoption, thewiccommand creates an empty partition. Consequently, you must use the--sizeoption to specify the size of the empty partition.--ondiskor--ondrive: Forces the partition to be created on a particular disk.--fstype: Sets the file system type for the partition. Valid values are:ext4ext3ext2btrfssquashfsswap
--fsoptions: Specifies a free-form string of options to be used when mounting the filesystem. This string is copied into the/etc/fstabfile of the installed system and should be enclosed in quotes. If not specified, the default string is "defaults".--label label: Specifies the label to give to the filesystem to be made on the partition. If the given label is already in use by another filesystem, a new label is created for the partition.--active: Marks the partition as active.--align (in KBytes): This option is a Wic-specific option that says to start partitions on boundaries givenxKBytes.--no-table: This option is a Wic-specific option. Using the option reserves space for the partition and causes it to become populated. However, the partition is not added to the partition table.--exclude-path: This option is a Wic-specific option that excludes the given relative path from the resulting image. This option is only effective with the rootfs source plug-in.--extra-space: This option is a Wic-specific option that adds extra space after the space filled by the content of the partition. The final size can exceed the size specified by the--sizeoption. The default value is 10 Mbytes.--overhead-factor: This option is a Wic-specific option that multiplies the size of the partition by the option's value. You must supply a value greater than or equal to "1". The default value is "1.3".--part-name: This option is a Wic-specific option that specifies a name for GPT partitions.--part-type: This option is a Wic-specific option that specifies the partition type globally unique identifier (GUID) for GPT partitions. You can find the list of partition type GUIDs at http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/GUID_Partition_Table#Partition_type_GUIDs.--use-uuid: This option is a Wic-specific option that causes Wic to generate a random GUID for the partition. The generated identifier is used in the bootloader configuration to specify the root partition.--uuid: This option is a Wic-specific option that specifies the partition UUID.--fsuuid: This option is a Wic-specific option that specifies the filesystem UUID. You can generate or modifyWKS_FILEwith this option if a preconfigured filesystem UUID is added to the kernel command line in the bootloader configuration before you run Wic.--system-id: This option is a Wic-specific option that specifies the partition system ID, which is a one byte long, hexadecimal parameter with or without the 0x prefix.--mkfs-extraopts: This option specifies additional options to pass to themkfsutility. Some default options for certain filesystems do not take effect. See Wic's help on kickstart (i.e.wic help kickstart).
9.3. Command: bootloader¶
This command specifies how the bootloader should be configured and supports the following options:
Note
Bootloader functionality and boot partitions are implemented by the various--source plug-ins that
implement bootloader functionality.
The bootloader command essentially provides a means of
modifying bootloader configuration.
--timeout: Specifies the number of seconds before the bootloader times out and boots the default option.--append: Specifies kernel parameters. These parameters will be added to the syslinuxAPPENDorgrubkernel command line.--configfile: Specifies a user-defined configuration file for the bootloader. You can provide a full pathname for the file or a file that exists in thecanned-wksfolder. This option overrides all other bootloader options.
Chapter 10. QA Error and Warning Messages¶
Table of Contents
10.1. Introduction¶
When building a recipe, the OpenEmbedded build system performs various QA checks on the output to ensure that common issues are detected and reported. Sometimes when you create a new recipe to build new software, it will build with no problems. When this is not the case, or when you have QA issues building any software, it could take a little time to resolve them.
While it is tempting to ignore a QA message or even to disable QA checks, it is best to try and resolve any reported QA issues. This chapter provides a list of the QA messages and brief explanations of the issues you could encounter so that you can properly resolve problems.
The next section provides a list of all QA error and warning messages based on a default configuration. Each entry provides the message or error form along with an explanation.
Notes
At the end of each message, the name of the associated QA test (as listed in the "
insane.bbclass" section) appears within square brackets.As mentioned, this list of error and warning messages is for QA checks only. The list does not cover all possible build errors or warnings you could encounter.
Because some QA checks are disabled by default, this list does not include all possible QA check errors and warnings.
10.2. Errors and Warnings¶
<packagename>: <path> is using libexec please relocate to <libexecdir> [libexec]¶The specified package contains files in
/usr/libexecwhen the distro configuration uses a different path for<libexecdir>By default,<libexecdir>is$prefix/libexec. However, this default can be changed (e.g.${libdir}).
package <packagename> contains bad RPATH <rpath> in file <file> [rpaths]¶The specified binary produced by the recipe contains dynamic library load paths (rpaths) that contain build system paths such as
TMPDIR, which are incorrect for the target and could potentially be a security issue. Check for bad-rpathoptions being passed to the linker in yourdo_compilelog. Depending on the build system used by the software being built, there might be a configure option to disable rpath usage completely within the build of the software.
<packagename>: <file> contains probably-redundant RPATH <rpath> [useless-rpaths]¶The specified binary produced by the recipe contains dynamic library load paths (rpaths) that on a standard system are searched by default by the linker (e.g.
/liband/usr/lib). While these paths will not cause any breakage, they do waste space and are unnecessary. Depending on the build system used by the software being built, there might be a configure option to disable rpath usage completely within the build of the software.
<packagename> requires <files>, but no providers in its RDEPENDS [file-rdeps]¶A file-level dependency has been identified from the specified package on the specified files, but there is no explicit corresponding entry in
RDEPENDS. If particular files are required at runtime thenRDEPENDSshould be declared in the recipe to ensure the packages providing them are built.
<packagename1> rdepends on <packagename2>, but it isn't a build dependency? [build-deps]¶A runtime dependency exists between the two specified packages, but there is nothing explicit within the recipe to enable the OpenEmbedded build system to ensure that dependency is satisfied. This condition is usually triggered by an
RDEPENDSvalue being added at the packaging stage rather than up front, which is usually automatic based on the contents of the package. In most cases, you should change the recipe to add an explicitRDEPENDSfor the dependency.
non -dev/-dbg/nativesdk- package contains symlink .so: <packagename> path '<path>' [dev-so]¶Symlink
.sofiles are for development only, and should therefore go into the-devpackage. This situation might occur if you add*.so*rather than*.so.*to a non-dev package. ChangeFILES(and possiblyPACKAGES) such that the specified.sofile goes into an appropriate-devpackage.
<packagename>: found library in wrong location [libdir]¶The specified file may have been installed into an incorrect (possibly hardcoded) installation path. For example, this test will catch recipes that install
/lib/bar.sowhen${base_libdir}is "lib32". Another example is when recipes install/usr/lib64/foo.sowhen${libdir}is "/usr/lib". False positives occasionally exist. For these cases add "libdir" toINSANE_SKIPfor the package.
non debug package contains .debug directory: <packagename> path <path> [debug-files]¶The specified package contains a
.debugdirectory, which should not appear in anything but the-dbgpackage. This situation might occur if you add a path which contains a.debugdirectory and do not explicitly add the.debugdirectory to the-dbgpackage. If this is the case, add the.debugdirectory explicitly toFILES_${PN}-dbg. SeeFILESfor additional information onFILES.
Architecture did not match (<machine_arch> to <file_arch>) on <file> [arch]¶By default, the OpenEmbedded build system checks the Executable and Linkable Format (ELF) type, bit size, and endianness of any binaries to ensure they match the target architecture. This test fails if any binaries do not match the type since there would be an incompatibility. The test could indicate that the wrong compiler or compiler options have been used. Sometimes software, like bootloaders, might need to bypass this check. If the file you receive the error for is firmware that is not intended to be executed within the target operating system or is intended to run on a separate processor within the device, you can add "arch" to
INSANE_SKIPfor the package. Another option is to check thedo_compilelog and verify that the compiler options being used are correct.
Bit size did not match (<machine_bits> to <file_bits>) <recipe> on <file> [arch]¶By default, the OpenEmbedded build system checks the Executable and Linkable Format (ELF) type, bit size, and endianness of any binaries to ensure they match the target architecture. This test fails if any binaries do not match the type since there would be an incompatibility. The test could indicate that the wrong compiler or compiler options have been used. Sometimes software, like bootloaders, might need to bypass this check. If the file you receive the error for is firmware that is not intended to be executed within the target operating system or is intended to run on a separate processor within the device, you can add "arch" to
INSANE_SKIPfor the package. Another option is to check thedo_compilelog and verify that the compiler options being used are correct.
Endianness did not match (<machine_endianness> to <file_endianness>) on <file> [arch]¶By default, the OpenEmbedded build system checks the Executable and Linkable Format (ELF) type, bit size, and endianness of any binaries to ensure they match the target architecture. This test fails if any binaries do not match the type since there would be an incompatibility. The test could indicate that the wrong compiler or compiler options have been used. Sometimes software, like bootloaders, might need to bypass this check. If the file you receive the error for is firmware that is not intended to be executed within the target operating system or is intended to run on a separate processor within the device, you can add "arch" to
INSANE_SKIPfor the package. Another option is to check thedo_compilelog and verify that the compiler options being used are correct.
ELF binary '<file>' has relocations in .text [textrel]¶The specified ELF binary contains relocations in its
.textsections. This situation can result in a performance impact at runtime.Typically, the way to solve this performance issue is to add "-fPIC" or "-fpic" to the compiler command-line options. For example, given software that reads
CFLAGSwhen you build it, you could add the following to your recipe:CFLAGS_append = " -fPIC "For more information on text relocations at runtime, see http://www.akkadia.org/drepper/textrelocs.html.
No GNU_HASH in the elf binary: '<file>' [ldflags]¶This indicates that binaries produced when building the recipe have not been linked with the
LDFLAGSoptions provided by the build system. Check to be sure that theLDFLAGSvariable is being passed to the linker command. A common workaround for this situation is to pass inLDFLAGSusingTARGET_CC_ARCHwithin the recipe as follows:TARGET_CC_ARCH += "${LDFLAGS}"
Package <packagename> contains Xorg driver (<driver>) but no xorg-abi- dependencies [xorg-driver-abi]¶The specified package contains an Xorg driver, but does not have a corresponding ABI package dependency. The xserver-xorg recipe provides driver ABI names. All drivers should depend on the ABI versions that they have been built against. Driver recipes that include
xorg-driver-input.incorxorg-driver-video.incwill automatically get these versions. Consequently, you should only need to explicitly add dependencies to binary driver recipes.
The /usr/share/info/dir file is not meant to be shipped in a particular package. [infodir]¶The
/usr/share/info/dirshould not be packaged. Add the following line to yourdo_installtask or to yourdo_install_appendwithin the recipe as follows:rm ${D}${infodir}/dir
Symlink <path> in <packagename> points to TMPDIR [symlink-to-sysroot]¶The specified symlink points into
TMPDIRon the host. Such symlinks will work on the host. However, they are clearly invalid when running on the target. You should either correct the symlink to use a relative path or remove the symlink.
<packagename> rdepends on <debug_packagename> [debug-deps]¶A dependency exists between the specified non-dbg package (i.e. a package whose name does not end in
-dbg) and a package that is adbgpackage. Thedbgpackages contain debug symbols and are brought in using several different methods:Using the
dbg-pkgsIMAGE_FEATURESvalue.Using
IMAGE_INSTALL.As a dependency of another
dbgpackage that was brought in using one of the above methods.
The dependency might have been automatically added because the
dbgpackage erroneously contains files that it should not contain (e.g. a non-symlink.sofile) or it might have been added manually (e.g. by adding toRDEPENDS).
<packagename> rdepends on <dev_packagename> [dev-deps]¶A dependency exists between the specified non-dev package (a package whose name does not end in
-dev) and a package that is adevpackage. Thedevpackages contain development headers and are usually brought in using several different methods:Using the
dev-pkgsIMAGE_FEATURESvalue.Using
IMAGE_INSTALL.As a dependency of another
devpackage that was brought in using one of the above methods.
The dependency might have been automatically added (because the
devpackage erroneously contains files that it should not have (e.g. a non-symlink.sofile) or it might have been added manually (e.g. by adding toRDEPENDS).
<var>_<packagename> is invalid: <comparison> (<value>) only comparisons <, =, >, <=, and >= are allowed [dep-cmp]¶If you are adding a versioned dependency relationship to one of the dependency variables (
RDEPENDS,RRECOMMENDS,RSUGGESTS,RPROVIDES,RREPLACES, orRCONFLICTS), you must only use the named comparison operators. Change the versioned dependency values you are adding to match those listed in the message.
<recipename>: The compile log indicates that host include and/or library paths were used. Please check the log '<logfile>' for more information. [compile-host-path]¶The log for the
do_compiletask indicates that paths on the host were searched for files, which is not appropriate when cross-compiling. Look for "is unsafe for cross-compilation" or "CROSS COMPILE Badness" in the specified log file.
<recipename>: The install log indicates that host include and/or library paths were used. Please check the log '<logfile>' for more information. [install-host-path]¶The log for the
do_installtask indicates that paths on the host were searched for files, which is not appropriate when cross-compiling. Look for "is unsafe for cross-compilation" or "CROSS COMPILE Badness" in the specified log file.
This autoconf log indicates errors, it looked at host include and/or library paths while determining system capabilities. Rerun configure task after fixing this. The path was '<path>'¶The log for the
do_configuretask indicates that paths on the host were searched for files, which is not appropriate when cross-compiling. Look for "is unsafe for cross-compilation" or "CROSS COMPILE Badness" in the specified log file.
<packagename> doesn't match the [a-z0-9.+-]+ regex [pkgname]¶The convention within the OpenEmbedded build system (sometimes enforced by the package manager itself) is to require that package names are all lower case and to allow a restricted set of characters. If your recipe name does not match this, or you add packages to
PACKAGESthat do not conform to the convention, then you will receive this error. Rename your recipe. Or, if you have added a non-conforming package name toPACKAGES, change the package name appropriately.
<recipe>: configure was passed unrecognized options: <options> [unknown-configure-option]¶The configure script is reporting that the specified options are unrecognized. This situation could be because the options were previously valid but have been removed from the configure script. Or, there was a mistake when the options were added and there is another option that should be used instead. If you are unsure, consult the upstream build documentation, the
./configure --helpoutput, and the upstream change log or release notes. Once you have worked out what the appropriate change is, you can updateEXTRA_OECONF,PACKAGECONFIG_CONFARGS, or the individualPACKAGECONFIGoption values accordingly.
Recipe <recipefile> has PN of "<recipename>" which is in OVERRIDES, this can result in unexpected behavior. [pn-overrides]¶The specified recipe has a name (
PN) value that appears inOVERRIDES. If a recipe is named such that itsPNvalue matches something already inOVERRIDES(e.g.PNhappens to be the same asMACHINEorDISTRO), it can have unexpected consequences. For example, assignments such asFILES_${PN} = "xyz"effectively turn intoFILES = "xyz". Rename your recipe (or ifPNis being set explicitly, change thePNvalue) so that the conflict does not occur. SeeFILESfor additional information.
<recipefile>: Variable <variable> is set as not being package specific, please fix this. [pkgvarcheck]¶Certain variables (
RDEPENDS,RRECOMMENDS,RSUGGESTS,RCONFLICTS,RPROVIDES,RREPLACES,FILES,pkg_preinst,pkg_postinst,pkg_prerm,pkg_postrm, andALLOW_EMPTY) should always be set specific to a package (i.e. they should be set with a package name override such asRDEPENDS_${PN} = "value"rather thanRDEPENDS = "value"). If you receive this error, correct any assignments to these variables within your recipe.
File '<file>' from <recipename> was already stripped, this will prevent future debugging! [already-stripped]¶Produced binaries have already been stripped prior to the build system extracting debug symbols. It is common for upstream software projects to default to stripping debug symbols for output binaries. In order for debugging to work on the target using
-dbgpackages, this stripping must be disabled.Depending on the build system used by the software being built, disabling this stripping could be as easy as specifying an additional configure option. If not, disabling stripping might involve patching the build scripts. In the latter case, look for references to "strip" or "STRIP", or the "-s" or "-S" command-line options being specified on the linker command line (possibly through the compiler command line if preceded with "-Wl,").
Note
Disabling stripping here does not mean that the final packaged binaries will be unstripped. Once the OpenEmbedded build system splits out debug symbols to the-dbgpackage, it will then strip the symbols from the binaries.
<recipename>: Files/directories were installed but not shipped in any package [installed-vs-shipped]¶Files have been installed within the
do_installtask but have not been included in any package by way of theFILESvariable. Files that do not appear in any package cannot be present in an image later on in the build process. You need to do one of the following:Add the files to
FILESfor the package you want them to appear in (e.g.FILES_${PN}for the main package).Delete the files at the end of the
do_installtask if the files are not needed in any package.
<oldpackage>-<oldpkgversion> was registered as shlib provider for <library>, changing it to <newpackage>-<newpkgversion> because it was built later¶This message means that both
<oldpackage>and<newpackage>provide the specified shared library. You can expect this message when a recipe has been renamed. However, if that is not the case, the message might indicate that a private version of a library is being erroneously picked up as the provider for a common library. If that is the case, you should add the library's.sofile name toPRIVATE_LIBSin the recipe that provides the private version of the library.
10.3. Configuring and Disabling QA Checks¶
You can configure the QA checks globally so that specific check
failures either raise a warning or an error message, using the
WARN_QA and
ERROR_QA
variables, respectively.
You can also disable checks within a particular recipe using
INSANE_SKIP.
For information on how to work with the QA checks, see the
"insane.bbclass"
section.
Tip
Please keep in mind that the QA checks exist in order to detect real or potential problems in the packaged output. So exercise caution when disabling these checks.
Chapter 11. Images¶
The OpenEmbedded build system provides several example
images to satisfy different needs.
When you issue the bitbake command you provide a “top-level” recipe
that essentially begins the build for the type of image you want.
Note
Building an image without GNU General Public License Version 3 (GPLv3), GNU Lesser General Public License Version 3 (LGPLv3), and the GNU Affero General Public License Version 3 (AGPL-3.0) components is only supported for minimal and base images. Furthermore, if you are going to build an image using non-GPLv3 and similarly licensed components, you must make the following changes in thelocal.conf file before using the BitBake
command to build the minimal or base image:
1. Comment out the EXTRA_IMAGE_FEATURES line
2. Set INCOMPATIBLE_LICENSE = "GPL-3.0 LGPL-3.0 AGPL-3.0"
From within the poky Git repository, you can use
the following command to display the list of directories within the
Source Directory
that contain image recipe files:
$ ls meta*/recipes*/images/*.bb
Following is a list of supported recipes:
build-appliance-image: An example virtual machine that contains all the pieces required to run builds using the build system as well as the build system itself. You can boot and run the image using either the VMware Player or VMware Workstation. For more information on this image, see the Build Appliance page on the Yocto Project website.core-image-base: A console-only image that fully supports the target device hardware.core-image-clutter: An image with support for the Open GL-based toolkit Clutter, which enables development of rich and animated graphical user interfaces.core-image-full-cmdline: A console-only image with more full-featured Linux system functionality installed.core-image-lsb: An image that conforms to the Linux Standard Base (LSB) specification. This image requires a distribution configuration that enables LSB compliance (e.g.poky-lsb). If you buildcore-image-lsbwithout that configuration, the image will not be LSB-compliant.core-image-lsb-dev: Acore-image-lsbimage that is suitable for development work using the host. The image includes headers and libraries you can use in a host development environment. This image requires a distribution configuration that enables LSB compliance (e.g.poky-lsb). If you buildcore-image-lsb-devwithout that configuration, the image will not be LSB-compliant.core-image-lsb-sdk: Acore-image-lsbthat includes everything in the cross-toolchain but also includes development headers and libraries to form a complete standalone SDK. This image requires a distribution configuration that enables LSB compliance (e.g.poky-lsb). If you buildcore-image-lsb-sdkwithout that configuration, the image will not be LSB-compliant. This image is suitable for development using the target.core-image-minimal: A small image just capable of allowing a device to boot.core-image-minimal-dev: Acore-image-minimalimage suitable for development work using the host. The image includes headers and libraries you can use in a host development environment.core-image-minimal-initramfs: Acore-image-minimalimage that has the Minimal RAM-based Initial Root Filesystem (initramfs) as part of the kernel, which allows the system to find the first “init” program more efficiently. See thePACKAGE_INSTALLvariable for additional information helpful when working with initramfs images.core-image-minimal-mtdutils: Acore-image-minimalimage that has support for the Minimal MTD Utilities, which let the user interact with the MTD subsystem in the kernel to perform operations on flash devices.core-image-rt: Acore-image-minimalimage plus a real-time test suite and tools appropriate for real-time use.core-image-rt-sdk: Acore-image-rtimage that includes everything in the cross-toolchain. The image also includes development headers and libraries to form a complete stand-alone SDK and is suitable for development using the target.core-image-sato: An image with Sato support, a mobile environment and visual style that works well with mobile devices. The image supports X11 with a Sato theme and applications such as a terminal, editor, file manager, media player, and so forth.core-image-sato-dev: Acore-image-satoimage suitable for development using the host. The image includes libraries needed to build applications on the device itself, testing and profiling tools, and debug symbols. This image was formerlycore-image-sdk.core-image-sato-sdk: Acore-image-satoimage that includes everything in the cross-toolchain. The image also includes development headers and libraries to form a complete standalone SDK and is suitable for development using the target.core-image-testmaster: A "master" image designed to be used for automated runtime testing. Provides a "known good" image that is deployed to a separate partition so that you can boot into it and use it to deploy a second image to be tested. You can find more information about runtime testing in the "Performing Automated Runtime Testing" section in the Yocto Project Development Tasks Manual.core-image-testmaster-initramfs: A RAM-based Initial Root Filesystem (initramfs) image tailored for use with thecore-image-testmasterimage.core-image-weston: A very basic Wayland image with a terminal. This image provides the Wayland protocol libraries and the reference Weston compositor. For more information, see the "Using Wayland and Weston" section in the Yocto Project Development Tasks Manual.core-image-x11: A very basic X11 image with a terminal.
Chapter 12. Features¶
Table of Contents
This chapter provides a reference of shipped machine and distro features you can include as part of your image, a reference on image features you can select, and a reference on feature backfilling.
Features provide a mechanism for working out which packages
should be included in the generated images.
Distributions can select which features they want to support through the
DISTRO_FEATURES
variable, which is set or appended to in a distribution's configuration file such as
poky.conf,
poky-tiny.conf,
poky-lsb.conf and so forth.
Machine features are set in the
MACHINE_FEATURES
variable, which is set in the machine configuration file and
specifies the hardware features for a given machine.
These two variables combine to work out which kernel modules, utilities, and other packages to include. A given distribution can support a selected subset of features so some machine features might not be included if the distribution itself does not support them.
One method you can use to determine which recipes are checking to see if a
particular feature is contained or not is to grep through
the Metadata
for the feature.
Here is an example that discovers the recipes whose build is potentially
changed based on a given feature:
$ cd poky
$ git grep 'contains.*MACHINE_FEATURES.*feature'
12.1. Machine Features¶
The items below are features you can use with
MACHINE_FEATURES.
Features do not have a one-to-one correspondence to packages, and they can
go beyond simply controlling the installation of a package or packages.
Sometimes a feature can influence how certain recipes are built.
For example, a feature might determine whether a particular configure option
is specified within the
do_configure
task for a particular recipe.
This feature list only represents features as shipped with the Yocto Project metadata:
acpi: Hardware has ACPI (x86/x86_64 only)
alsa: Hardware has ALSA audio drivers
apm: Hardware uses APM (or APM emulation)
bluetooth: Hardware has integrated BT
efi: Support for booting through EFI
ext2: Hardware HDD or Microdrive
irda: Hardware has IrDA support
keyboard: Hardware has a keyboard
pcbios: Support for booting through BIOS
pci: Hardware has a PCI bus
pcmcia: Hardware has PCMCIA or CompactFlash sockets
phone: Mobile phone (voice) support
qvga: Machine has a QVGA (320x240) display
rtc: Machine has a Real-Time Clock
screen: Hardware has a screen
serial: Hardware has serial support (usually RS232)
touchscreen: Hardware has a touchscreen
usbgadget: Hardware is USB gadget device capable
usbhost: Hardware is USB Host capable
vfat: FAT file system support
wifi: Hardware has integrated WiFi
12.2. Distro Features¶
The items below are features you can use with
DISTRO_FEATURES
to enable features across your distribution.
Features do not have a one-to-one correspondence to packages,
and they can go beyond simply controlling the installation of a
package or packages.
In most cases, the presence or absence of a feature translates to
the appropriate option supplied to the configure script during the
do_configure
task for the recipes that optionally
support the feature.
Some distro features are also machine features.
These select features make sense to be controlled both at
the machine and distribution configuration level.
See the
COMBINED_FEATURES
variable for more information.
This list only represents features as shipped with the Yocto Project metadata:
alsa: Include ALSA support (OSS compatibility kernel modules installed if available).
api-documentation: Enables generation of API documentation during recipe builds. The resulting documentation is added to SDK tarballs when the
bitbake -c populate_sdkcommand is used. See the "Adding API Documentation to the Standard SDK" section in the Yocto Project Application Development and the Extensible Software Development Kit (eSDK) manual.bluetooth: Include bluetooth support (integrated BT only).
bluez5: Include BlueZ Version 5, which provides core Bluetooth layers and protocols support.
Note
The default value for theDISTRO FEATURESvariable includes "bluetooth", which causes bluez5 to be backfilled in for bluetooth support. If you do not want bluez5 backfilled and would rather use bluez4, you need to use theDISTRO_FEATURES_BACKFILL_CONSIDEREDvariable as follows:DISTRO_FEATURES_BACKFILL_CONSIDERED = "bluez5"Setting this variable tells the OpenEmbedded build system that you have considered but ruled out using the bluez5 feature and that bluez4 will be used.cramfs: Include CramFS support.
directfb: Include DirectFB support.
ext2: Include tools for supporting for devices with internal HDD/Microdrive for storing files (instead of Flash only devices).
ipsec: Include IPSec support.
ipv6: Include IPv6 support.
irda: Include IrDA support.
keyboard: Include keyboard support (e.g. keymaps will be loaded during boot).
ldconfig: Include support for ldconfig and
ld.so.confon the target.nfs: Include NFS client support (for mounting NFS exports on device).
opengl: Include the Open Graphics Library, which is a cross-language, multi-platform application programming interface used for rendering two and three-dimensional graphics.
pci: Include PCI bus support.
pcmcia: Include PCMCIA/CompactFlash support.
ppp: Include PPP dialup support.
ptest: Enables building the package tests where supported by individual recipes. For more information on package tests, see the "Testing Packages With ptest" section in the Yocto Project Development Tasks Manual.
smbfs: Include SMB networks client support (for mounting Samba/Microsoft Windows shares on device).
systemd: Include support for this
initmanager, which is a full replacement of forinitwith parallel starting of services, reduced shell overhead, and other features. Thisinitmanager is used by many distributions.usbgadget: Include USB Gadget Device support (for USB networking/serial/storage).
usbhost: Include USB Host support (allows to connect external keyboard, mouse, storage, network etc).
wayland: Include the Wayland display server protocol and the library that supports it.
wifi: Include WiFi support (integrated only).
x11: Include the X server and libraries.
12.3. Image Features¶
The contents of images generated by the OpenEmbedded build system
can be controlled by the
IMAGE_FEATURES
and
EXTRA_IMAGE_FEATURES
variables that you typically configure in your image recipes.
Through these variables, you can add several different
predefined packages such as development utilities or packages with
debug information needed to investigate application problems or
profile applications.
The following image features are available for all images:
allow-empty-password: Allows Dropbear and OpenSSH to accept root logins and logins from accounts having an empty password string.
dbg-pkgs: Installs debug symbol packages for all packages installed in a given image.
debug-tweaks: Makes an image suitable for development (e.g. allows root logins without passwords and enables post-installation logging). See the 'allow-empty-password', 'empty-root-password', and 'post-install-logging' features in this list for additional information.
dev-pkgs: Installs development packages (headers and extra library links) for all packages installed in a given image.
doc-pkgs: Installs documentation packages for all packages installed in a given image.
empty-root-password: Sets the root password to an empty string, which allows logins with a blank password.
package-management: Installs package management tools and preserves the package manager database.
post-install-logging: Enables logging postinstall script runs to the
/var/log/postinstall.logfile on first boot of the image on the target system.Note
To make the/var/logdirectory on the target persistent, use theVOLATILE_LOG_DIRvariable by setting it to "no".ptest-pkgs: Installs ptest packages for all ptest-enabled recipes.
read-only-rootfs: Creates an image whose root filesystem is read-only. See the "Creating a Read-Only Root Filesystem" section in the Yocto Project Development Tasks Manual for more information.
splash: Enables showing a splash screen during boot. By default, this screen is provided by
psplash, which does allow customization. If you prefer to use an alternative splash screen package, you can do so by setting theSPLASHvariable to a different package name (or names) within the image recipe or at the distro configuration level.staticdev-pkgs: Installs static development packages, which are static libraries (i.e.
*.afiles), for all packages installed in a given image.
Some image features are available only when you inherit the
core-image
class.
The current list of these valid features is as follows:
eclipse-debug: Provides Eclipse remote debugging support.
hwcodecs: Installs hardware acceleration codecs.
nfs-server: Installs an NFS server.
perf: Installs profiling tools such as
perf,systemtap, andLTTng. For general information on user-space tools, see the Yocto Project Application Development and the Extensible Software Development Kit (eSDK) manual.ssh-server-dropbear: Installs the Dropbear minimal SSH server.
ssh-server-openssh: Installs the OpenSSH SSH server, which is more full-featured than Dropbear. Note that if both the OpenSSH SSH server and the Dropbear minimal SSH server are present in
IMAGE_FEATURES, then OpenSSH will take precedence and Dropbear will not be installed.tools-debug: Installs debugging tools such as
straceandgdb. For information on GDB, see the "Debugging With the GNU Project Debugger (GDB) Remotely" section in the Yocto Project Development Tasks Manual. For information on tracing and profiling, see the Yocto Project Profiling and Tracing Manual.tools-sdk: Installs a full SDK that runs on the device.
tools-testapps: Installs device testing tools (e.g. touchscreen debugging).
x11: Installs the X server.
x11-base: Installs the X server with a minimal environment.
x11-sato: Installs the OpenedHand Sato environment.
12.4. Feature Backfilling¶
Sometimes it is necessary in the OpenEmbedded build system to extend
MACHINE_FEATURES
or DISTRO_FEATURES
to control functionality that was previously enabled and not able
to be disabled.
For these cases, we need to add an
additional feature item to appear in one of these variables,
but we do not want to force developers who have existing values
of the variables in their configuration to add the new feature
in order to retain the same overall level of functionality.
Thus, the OpenEmbedded build system has a mechanism to
automatically "backfill" these added features into existing
distro or machine configurations.
You can see the list of features for which this is done by
finding the
DISTRO_FEATURES_BACKFILL
and MACHINE_FEATURES_BACKFILL
variables in the meta/conf/bitbake.conf file.
Because such features are backfilled by default into all
configurations as described in the previous paragraph, developers
who wish to disable the new features need to be able to selectively
prevent the backfilling from occurring.
They can do this by adding the undesired feature or features to the
DISTRO_FEATURES_BACKFILL_CONSIDERED
or MACHINE_FEATURES_BACKFILL_CONSIDERED
variables for distro features and machine features respectively.
Here are two examples to help illustrate feature backfilling:
The "pulseaudio" distro feature option: Previously, PulseAudio support was enabled within the Qt and GStreamer frameworks. Because of this, the feature is backfilled and thus enabled for all distros through the
DISTRO_FEATURES_BACKFILLvariable in themeta/conf/bitbake.conffile. However, your distro needs to disable the feature. You can disable the feature without affecting other existing distro configurations that need PulseAudio support by adding "pulseaudio" toDISTRO_FEATURES_BACKFILL_CONSIDEREDin your distro's.conffile. Adding the feature to this variable when it also exists in theDISTRO_FEATURES_BACKFILLvariable prevents the build system from adding the feature to your configuration'sDISTRO_FEATURES, effectively disabling the feature for that particular distro.The "rtc" machine feature option: Previously, real time clock (RTC) support was enabled for all target devices. Because of this, the feature is backfilled and thus enabled for all machines through the
MACHINE_FEATURES_BACKFILLvariable in themeta/conf/bitbake.conffile. However, your target device does not have this capability. You can disable RTC support for your device without affecting other machines that need RTC support by adding the feature to your machine'sMACHINE_FEATURES_BACKFILL_CONSIDEREDlist in the machine's.conffile. Adding the feature to this variable when it also exists in theMACHINE_FEATURES_BACKFILLvariable prevents the build system from adding the feature to your configuration'sMACHINE_FEATURES, effectively disabling RTC support for that particular machine.
Chapter 13. Variables Glossary¶
Table of Contents
This chapter lists common variables used in the OpenEmbedded build system and gives an overview of their function and contents.
Glossary¶
A B C D E F G H I K L M N O P R S T U V W X
A
- ABIEXTENSION¶
Extension to the Application Binary Interface (ABI) field of the GNU canonical architecture name (e.g. "eabi").
ABI extensions are set in the machine include files. For example, the
meta/conf/machine/include/arm/arch-arm.incfile sets the following extension:ABIEXTENSION = "eabi"- ALLOW_EMPTY¶
Specifies whether to produce an output package even if it is empty. By default, BitBake does not produce empty packages. This default behavior can cause issues when there is an
RDEPENDSor some other hard runtime requirement on the existence of the package.Like all package-controlling variables, you must always use them in conjunction with a package name override, as in:
ALLOW_EMPTY_${PN} = "1" ALLOW_EMPTY_${PN}-dev = "1" ALLOW_EMPTY_${PN}-staticdev = "1"- ALTERNATIVE¶
Lists commands in a package that need an alternative binary naming scheme. Sometimes the same command is provided in multiple packages. When this occurs, the OpenEmbedded build system needs to use the alternatives system to create a different binary naming scheme so the commands can co-exist.
To use the variable, list out the package's commands that also exist as part of another package. For example, if the
busyboxpackage has four commands that also exist as part of another package, you identify them as follows:ALTERNATIVE_busybox = "sh sed test bracket"For more information on the alternatives system, see the "
update-alternatives.bbclass" section.- ALTERNATIVE_LINK_NAME¶
Used by the alternatives system to map duplicated commands to actual locations. For example, if the
bracketcommand provided by thebusyboxpackage is duplicated through another package, you must use theALTERNATIVE_LINK_NAMEvariable to specify the actual location:ALTERNATIVE_LINK_NAME[bracket] = "/usr/bin/["In this example, the binary for the
bracketcommand (i.e.[) from thebusyboxpackage resides in/usr/bin/.Note
IfALTERNATIVE_LINK_NAMEis not defined, it defaults to${bindir}/.nameFor more information on the alternatives system, see the "
update-alternatives.bbclass" section.- ALTERNATIVE_PRIORITY¶
Used by the alternatives system to create default priorities for duplicated commands. You can use the variable to create a single default regardless of the command name or package, a default for specific duplicated commands regardless of the package, or a default for specific commands tied to particular packages. Here are the available syntax forms:
ALTERNATIVE_PRIORITY = "priority" ALTERNATIVE_PRIORITY[name] = "priority" ALTERNATIVE_PRIORITY_pkg[name] = "priority"For more information on the alternatives system, see the "
update-alternatives.bbclass" section.- ALTERNATIVE_TARGET¶
Used by the alternatives system to create default link locations for duplicated commands. You can use the variable to create a single default location for all duplicated commands regardless of the command name or package, a default for specific duplicated commands regardless of the package, or a default for specific commands tied to particular packages. Here are the available syntax forms:
ALTERNATIVE_TARGET = "target" ALTERNATIVE_TARGET[name] = "target" ALTERNATIVE_TARGET_pkg[name] = "target"Note
If
ALTERNATIVE_TARGETis not defined, it inherits the value from theALTERNATIVE_LINK_NAMEvariable.If
ALTERNATIVE_LINK_NAMEandALTERNATIVE_TARGETare the same, the target forALTERNATIVE_TARGEThas ".{BPN}" appended to it.Finally, if the file referenced has not been renamed, the alternatives system will rename it to avoid the need to rename alternative files in the
do_installtask while retaining support for the command if necessary.For more information on the alternatives system, see the "
update-alternatives.bbclass" section.- APPEND¶
An override list of append strings for each target specified with
LABELS.See the
grub-eficlass for more information on how this variable is used.- AR¶
The minimal command and arguments used to run
ar.- ARCHIVER_MODE¶
When used with the
archiverclass, determines the type of information used to create a released archive. You can use this variable to create archives of patched source, original source, configured source, and so forth by employing the following variable flags (varflags):ARCHIVER_MODE[src] = "original" # Uses original (unpacked) source # files. ARCHIVER_MODE[src] = "patched" # Uses patched source files. This is # the default. ARCHIVER_MODE[src] = "configured" # Uses configured source files. ARCHIVER_MODE[diff] = "1" # Uses patches between do_unpack and # do_patch. ARCHIVER_MODE[diff-exclude] ?= "filefile..." # Lists files and directories to # exclude from diff. ARCHIVER_MODE[dumpdata] = "1" # Uses environment data. ARCHIVER_MODE[recipe] = "1" # Uses recipe and include files. ARCHIVER_MODE[srpm] = "1" # Uses RPM package files.For information on how the variable works, see the
meta/classes/archiver.bbclassfile in the Source Directory.- AS¶
The minimal command and arguments used to run the assembler.
- ASSUME_PROVIDED¶
Lists recipe names (
PNvalues) BitBake does not attempt to build. Instead, BitBake assumes these recipes have already been built.In OpenEmbedded-Core,
ASSUME_PROVIDEDmostly specifies native tools that should not be built. An example isgit-native, which when specified, allows for the Git binary from the host to be used rather than buildinggit-native.- ASSUME_SHLIBS¶
Provides additional
shlibsprovider mapping information, which adds to or overwrites the information provided automatically by the system. Separate multiple entries using spaces.As an example, use the following form to add an
shlibprovider ofshlibnameinpackagenamewith the optionalversion:shlibname:packagename[_version]Here is an example that adds a shared library named
libEGL.so.1as being provided by thelibegl-implementationpackage:ASSUME_SHLIBS = "libEGL.so.1:libegl-implementation"- AUTHOR¶
The email address used to contact the original author or authors in order to send patches and forward bugs.
- AUTO_LIBNAME_PKGS¶
When the
debianclass is inherited, which is the default behavior,AUTO_LIBNAME_PKGSspecifies which packages should be checked for libraries and renamed according to Debian library package naming.The default value is "${PACKAGES}", which causes the debian class to act on all packages that are explicitly generated by the recipe.
- AUTO_SYSLINUXMENU¶
Enables creating an automatic menu for the syslinux bootloader. You must set this variable in your recipe. The
syslinuxclass checks this variable.- AUTOREV¶
When
SRCREVis set to the value of this variable, it specifies to use the latest source revision in the repository. Here is an example:SRCREV = "${AUTOREV}"If you use the previous statement to retrieve the latest version of software, you need to be sure
PVcontains${SRCPV}. For example, suppose you have a kernel recipe that inherits the kernel class and you use the previous statement. In this example,${SRCPV}does not automatically get intoPV. Consequently, you need to changePVin your recipe so that it does contain${SRCPV}.For more information see the "Automatically Incrementing a Binary Package Revision Number" section in the Yocto Project Development Tasks Manual.
- AVAILTUNES¶
The list of defined CPU and Application Binary Interface (ABI) tunings (i.e. "tunes") available for use by the OpenEmbedded build system.
The list simply presents the tunes that are available. Not all tunes may be compatible with a particular machine configuration, or with each other in a Multilib configuration.
To add a tune to the list, be sure to append it with spaces using the "+=" BitBake operator. Do not simply replace the list by using the "=" operator. See the "Basic Syntax" section in the BitBake User Manual for more information.
B
- B¶
The directory within the Build Directory in which the OpenEmbedded build system places generated objects during a recipe's build process. By default, this directory is the same as the
Sdirectory, which is defined as:S = "${WORKDIR}/${BP}"You can separate the (
S) directory and the directory pointed to by theBvariable. Most Autotools-based recipes support separating these directories. The build system defaults to using separate directories forgccand some kernel recipes.- BAD_RECOMMENDATIONS¶
Lists "recommended-only" packages to not install. Recommended-only packages are packages installed only through the
RRECOMMENDSvariable. You can prevent any of these "recommended" packages from being installed by listing them with theBAD_RECOMMENDATIONSvariable:BAD_RECOMMENDATIONS = "package_namepackage_namepackage_name..."You can set this variable globally in your
local.conffile or you can attach it to a specific image recipe by using the recipe name override:BAD_RECOMMENDATIONS_pn-target_image= "package_name"It is important to realize that if you choose to not install packages using this variable and some other packages are dependent on them (i.e. listed in a recipe's
RDEPENDSvariable), the OpenEmbedded build system ignores your request and will install the packages to avoid dependency errors.Support for this variable exists only when using the IPK and RPM packaging backend. Support does not exist for DEB.
See the
NO_RECOMMENDATIONSand thePACKAGE_EXCLUDEvariables for related information.- BASE_LIB¶
The library directory name for the CPU or Application Binary Interface (ABI) tune. The
BASE_LIBapplies only in the Multilib context. See the "Combining Multiple Versions of Library Files into One Image" section in the Yocto Project Development Tasks Manual for information on Multilib.The
BASE_LIBvariable is defined in the machine include files in the Source Directory. If Multilib is not being used, the value defaults to "lib".- BASE_WORKDIR¶
Points to the base of the work directory for all recipes. The default value is "${TMPDIR}/work".
- BB_ALLOWED_NETWORKS¶
Specifies a space-delimited list of hosts that the fetcher is allowed to use to obtain the required source code. Following are considerations surrounding this variable:
This host list is only used if
BB_NO_NETWORKis either not set or set to "0".Limited support for wildcard matching against the beginning of host names exists. For example, the following setting matches
git.gnu.org,ftp.gnu.org, andfoo.git.gnu.org.BB_ALLOWED_NETWORKS = "*.gnu.org"Important
The use of the "
*" character only works at the beginning of a host name and it must be isolated from the remainder of the host name. You cannot use the wildcard character in any other location of the name or combined with the front part of the name.For example,
*.foo.baris supported, while*aa.foo.baris not.Mirrors not in the host list are skipped and logged in debug.
Attempts to access networks not in the host list cause a failure.
Using
BB_ALLOWED_NETWORKSin conjunction withPREMIRRORSis very useful. Adding the host you want to use toPREMIRRORSresults in the source code being fetched from an allowed location and avoids raising an error when a host that is not allowed is in aSRC_URIstatement. This is because the fetcher does not attempt to use the host listed inSRC_URIafter a successful fetch from thePREMIRRORSoccurs.- BB_DANGLINGAPPENDS_WARNONLY¶
Defines how BitBake handles situations where an append file (
.bbappend) has no corresponding recipe file (.bb). This condition often occurs when layers get out of sync (e.g.oe-corebumps a recipe version and the old recipe no longer exists and the other layer has not been updated to the new version of the recipe yet).The default fatal behavior is safest because it is the sane reaction given something is out of sync. It is important to realize when your changes are no longer being applied.
You can change the default behavior by setting this variable to "1", "yes", or "true" in your
local.conffile, which is located in the Build Directory: Here is an example:BB_DANGLINGAPPENDS_WARNONLY = "1"- BB_DISKMON_DIRS¶
Monitors disk space and available inodes during the build and allows you to control the build based on these parameters.
Disk space monitoring is disabled by default. To enable monitoring, add the
BB_DISKMON_DIRSvariable to yourconf/local.conffile found in the Build Directory. Use the following form:BB_DISKMON_DIRS = "action,dir,threshold[...]" where:actionis: ABORT: Immediately abort the build when a threshold is broken. STOPTASKS: Stop the build after the currently executing tasks have finished when a threshold is broken. WARN: Issue a warning but continue the build when a threshold is broken. Subsequent warnings are issued as defined by the BB_DISKMON_WARNINTERVAL variable, which must be defined in the conf/local.conf file.diris: Any directory you choose. You can specify one or more directories to monitor by separating the groupings with a space. If two directories are on the same device, only the first directory is monitored.thresholdis: Either the minimum available disk space, the minimum number of free inodes, or both. You must specify at least one. To omit one or the other, simply omit the value. Specify the threshold using G, M, K for Gbytes, Mbytes, and Kbytes, respectively. If you do not specify G, M, or K, Kbytes is assumed by default. Do not use GB, MB, or KB.Here are some examples:
BB_DISKMON_DIRS = "ABORT,${TMPDIR},1G,100K WARN,${SSTATE_DIR},1G,100K" BB_DISKMON_DIRS = "STOPTASKS,${TMPDIR},1G" BB_DISKMON_DIRS = "ABORT,${TMPDIR},,100K"The first example works only if you also provide the
BB_DISKMON_WARNINTERVALvariable in theconf/local.conf. This example causes the build system to immediately abort when either the disk space in${TMPDIR}drops below 1 Gbyte or the available free inodes drops below 100 Kbytes. Because two directories are provided with the variable, the build system also issue a warning when the disk space in the${SSTATE_DIR}directory drops below 1 Gbyte or the number of free inodes drops below 100 Kbytes. Subsequent warnings are issued during intervals as defined by theBB_DISKMON_WARNINTERVALvariable.The second example stops the build after all currently executing tasks complete when the minimum disk space in the
${TMPDIR}directory drops below 1 Gbyte. No disk monitoring occurs for the free inodes in this case.The final example immediately aborts the build when the number of free inodes in the
${TMPDIR}directory drops below 100 Kbytes. No disk space monitoring for the directory itself occurs in this case.- BB_DISKMON_WARNINTERVAL¶
Defines the disk space and free inode warning intervals. To set these intervals, define the variable in your
conf/local.conffile in the Build Directory.If you are going to use the
BB_DISKMON_WARNINTERVALvariable, you must also use theBB_DISKMON_DIRSvariable and define its action as "WARN". During the build, subsequent warnings are issued each time disk space or number of free inodes further reduces by the respective interval.If you do not provide a
BB_DISKMON_WARNINTERVALvariable and you do useBB_DISKMON_DIRSwith the "WARN" action, the disk monitoring interval defaults to the following:BB_DISKMON_WARNINTERVAL = "50M,5K"When specifying the variable in your configuration file, use the following form:
BB_DISKMON_WARNINTERVAL = "disk_space_interval,disk_inode_interval" where:disk_space_intervalis: An interval of memory expressed in either G, M, or K for Gbytes, Mbytes, or Kbytes, respectively. You cannot use GB, MB, or KB.disk_inode_intervalis: An interval of free inodes expressed in either G, M, or K for Gbytes, Mbytes, or Kbytes, respectively. You cannot use GB, MB, or KB.Here is an example:
BB_DISKMON_DIRS = "WARN,${SSTATE_DIR},1G,100K" BB_DISKMON_WARNINTERVAL = "50M,5K"These variables cause the OpenEmbedded build system to issue subsequent warnings each time the available disk space further reduces by 50 Mbytes or the number of free inodes further reduces by 5 Kbytes in the
${SSTATE_DIR}directory. Subsequent warnings based on the interval occur each time a respective interval is reached beyond the initial warning (i.e. 1 Gbytes and 100 Kbytes).- BB_GENERATE_MIRROR_TARBALLS¶
Causes tarballs of the Git repositories, including the Git metadata, to be placed in the
DL_DIRdirectory.For performance reasons, creating and placing tarballs of the Git repositories is not the default action by the OpenEmbedded build system.
BB_GENERATE_MIRROR_TARBALLS = "1"Set this variable in your
local.conffile in the Build Directory.- BB_NUMBER_THREADS¶
The maximum number of tasks BitBake should run in parallel at any one time. The OpenEmbedded build system automatically configures this variable to be equal to the number of cores on the build system. For example, a system with a dual core processor that also uses hyper-threading causes the
BB_NUMBER_THREADSvariable to default to "4".For single socket systems (i.e. one CPU), you should not have to override this variable to gain optimal parallelism during builds. However, if you have very large systems that employ multiple physical CPUs, you might want to make sure the
BB_NUMBER_THREADSvariable is not set higher than "20".For more information on speeding up builds, see the "Speeding Up a Build" section in the Yocto Project Development Tasks Manual.
- BB_SERVER_TIMEOUT¶
Specifies the time (in seconds) after which to unload the BitBake server due to inactivity. Set
BB_SERVER_TIMEOUTto determine how long the BitBake server stays resident between invocations.For example, the following statement in your
local.conffile instructs the server to be unloaded after 20 seconds of inactivity:BB_SERVER_TIMEOUT = "20"If you want the server to never be unloaded, set
BB_SERVER_TIMEOUTto "-1".- BBCLASSEXTEND¶
Allows you to extend a recipe so that it builds variants of the software. Common variants for recipes exist such as "natives" like
quilt-native, which is a copy of Quilt built to run on the build system; "crosses" such asgcc-cross, which is a compiler built to run on the build machine but produces binaries that run on the targetMACHINE; "nativesdk", which targets the SDK machine instead ofMACHINE; and "mulitlibs" in the form "multilib:multilib_name".To build a different variant of the recipe with a minimal amount of code, it usually is as simple as adding the following to your recipe:
BBCLASSEXTEND =+ "native nativesdk" BBCLASSEXTEND =+ "multilib:multilib_name"Note
Internally, the
BBCLASSEXTENDmechanism generates recipe variants by rewriting variable values and applying overrides such as_class-native. For example, to generate a native version of a recipe, aDEPENDSon "foo" is rewritten to aDEPENDSon "foo-native".Even when using
BBCLASSEXTEND, the recipe is only parsed once. Parsing once adds some limitations. For example, it is not possible to include a different file depending on the variant, sinceincludestatements are processed when the recipe is parsed.- BBFILE_COLLECTIONS¶
Lists the names of configured layers. These names are used to find the other
BBFILE_*variables. Typically, each layer will append its name to this variable in itsconf/layer.conffile.- BBFILE_PATTERN¶
Variable that expands to match files from
BBFILESin a particular layer. This variable is used in theconf/layer.conffile and must be suffixed with the name of the specific layer (e.g.BBFILE_PATTERN_emenlow).- BBFILE_PRIORITY¶
Assigns the priority for recipe files in each layer.
This variable is useful in situations where the same recipe appears in more than one layer. Setting this variable allows you to prioritize a layer against other layers that contain the same recipe - effectively letting you control the precedence for the multiple layers. The precedence established through this variable stands regardless of a recipe's version (
PVvariable). For example, a layer that has a recipe with a higherPVvalue but for which theBBFILE_PRIORITYis set to have a lower precedence still has a lower precedence.A larger value for the
BBFILE_PRIORITYvariable results in a higher precedence. For example, the value 6 has a higher precedence than the value 5. If not specified, theBBFILE_PRIORITYvariable is set based on layer dependencies (see theLAYERDEPENDSvariable for more information. The default priority, if unspecified for a layer with no dependencies, is the lowest defined priority + 1 (or 1 if no priorities are defined).Tip
You can use the commandbitbake-layers show-layersto list all configured layers along with their priorities.- BBFILES¶
A space-separated list of recipe files BitBake uses to build software.
When specifying recipe files, you can pattern match using Python's
globsyntax. For details on the syntax, see the documentation by following the previous link.- BBFILES_DYNAMIC¶
Activates content when identified layers are present. You identify the layers by the collections that the layers define.
Use the
BBFILES_DYNAMICvariable to avoid.bbappendfiles whose corresponding.bbfile is in a layer that attempts to modify other layers through.bbappendbut does not want to introduce a hard dependency on those other layers.Use the following form for
BBFILES_DYNAMIC:collection_name:filename_patternThe following example identifies two collection names and two filename patterns:
BBFILES_DYNAMIC += " \ clang-layer:${LAYERDIR}/bbappends/meta-clang/*/*/*.bbappend \ core:${LAYERDIR}/bbappends/openembedded-core/meta/*/*/*.bbappend \ "This next example shows an error message that occurs because invalid entries are found, which cause parsing to abort:
ERROR: BBFILES_DYNAMIC entries must be of the form <collection name>:<filename pattern>, not: /work/my-layer/bbappends/meta-security-isafw/*/*/*.bbappend /work/my-layer/bbappends/openembedded-core/meta/*/*/*.bbappend- BBINCLUDELOGS¶
Variable that controls how BitBake displays logs on build failure.
- BBINCLUDELOGS_LINES¶
If
BBINCLUDELOGSis set, specifies the maximum number of lines from the task log file to print when reporting a failed task. If you do not setBBINCLUDELOGS_LINES, the entire log is printed.- BBLAYERS¶
Lists the layers to enable during the build. This variable is defined in the
bblayers.confconfiguration file in the Build Directory. Here is an example:BBLAYERS = " \ /home/scottrif/poky/meta \ /home/scottrif/poky/meta-poky \ /home/scottrif/poky/meta-yocto-bsp \ /home/scottrif/poky/meta-mykernel \ "This example enables four layers, one of which is a custom, user-defined layer named
meta-mykernel.- BBMASK¶
Prevents BitBake from processing recipes and recipe append files.
You can use the
BBMASKvariable to "hide" these.bband.bbappendfiles. BitBake ignores any recipe or recipe append files that match any of the expressions. It is as if BitBake does not see them at all. Consequently, matching files are not parsed or otherwise used by BitBake.The values you provide are passed to Python's regular expression compiler. Consequently, the syntax follows Python's Regular Expression (re) syntax. The expressions are compared against the full paths to the files. For complete syntax information, see Python's documentation at http://docs.python.org/3/library/re.html#re.
The following example uses a complete regular expression to tell BitBake to ignore all recipe and recipe append files in the
meta-ti/recipes-misc/directory:BBMASK = "meta-ti/recipes-misc/"If you want to mask out multiple directories or recipes, you can specify multiple regular expression fragments. This next example masks out multiple directories and individual recipes:
BBMASK += "/meta-ti/recipes-misc/ meta-ti/recipes-ti/packagegroup/" BBMASK += "/meta-oe/recipes-support/" BBMASK += "/meta-foo/.*/openldap" BBMASK += "opencv.*\.bbappend" BBMASK += "lzma"Note
When specifying a directory name, use the trailing slash character to ensure you match just that directory name.- BBMULTICONFIG¶
Specifies each separate configuration when you are building targets with multiple configurations. Use this variable in your
conf/local.confconfiguration file. Specify amulticonfignamefor each configuration file you are using. For example, the following line specifies three configuration files:BBMULTIFONFIG = "configA configB configC"Each configuration file you use must reside in the Build Directory
conf/multiconfigdirectory (e.g.build_directory/conf/multiconfig/configA.conf).For information on how to use
BBMULTICONFIGin an environment that supports building targets with multiple configurations, see the "Building Images for Multiple Targets Using Multiple Configurations" section in the Yocto Project Development Tasks Manual.- BBPATH¶
Used by BitBake to locate
.bbclassand configuration files. This variable is analogous to thePATHvariable.Note
If you run BitBake from a directory outside of the Build Directory, you must be sure to setBBPATHto point to the Build Directory. Set the variable as you would any environment variable and then run BitBake:$ BBPATH = "build_directory" $ export BBPATH $ bitbaketarget- BBSERVER¶
If defined in the BitBake environment,
BBSERVERpoints to the BitBake remote server.Use the following format to export the variable to the BitBake environment:
export BBSERVER=localhost:$port"By default,
BBSERVERalso appears inBB_HASHBASE_WHITELIST. Consequently,BBSERVERis excluded from checksum and dependency data.- BINCONFIG¶
When inheriting the
binconfig-disabledclass, this variable specifies binary configuration scripts to disable in favor of usingpkg-configto query the information. Thebinconfig-disabledclass will modify the specified scripts to return an error so that calls to them can be easily found and replaced.To add multiple scripts, separate them by spaces. Here is an example from the
libpngrecipe:BINCONFIG = "${bindir}/libpng-config ${bindir}/libpng16-config"- BINCONFIG_GLOB¶
When inheriting the
binconfigclass, this variable specifies a wildcard for configuration scripts that need editing. The scripts are edited to correct any paths that have been set up during compilation so that they are correct for use when installed into the sysroot and called by the build processes of other recipes.Note
TheBINCONFIG_GLOBvariable uses shell globbing, which is recognition and expansion of wildcards during pattern matching. Shell globbing is very similar tofnmatchandglob.For more information on how this variable works, see
meta/classes/binconfig.bbclassin the Source Directory. You can also find general information on the class in the "binconfig.bbclass" section.- BP¶
The base recipe name and version but without any special recipe name suffix (i.e.
-native,lib64-, and so forth).BPis comprised of the following:${BPN}-${PV}- BPN¶
This variable is a version of the
PNvariable with common prefixes and suffixes removed, such asnativesdk-,-cross,-native, and multilib'slib64-andlib32-. The exact lists of prefixes and suffixes removed are specified by theMLPREFIXandSPECIAL_PKGSUFFIXvariables, respectively.- BUGTRACKER¶
Specifies a URL for an upstream bug tracking website for a recipe. The OpenEmbedded build system does not use this variable. Rather, the variable is a useful pointer in case a bug in the software being built needs to be manually reported.
- BUILD_ARCH¶
Specifies the architecture of the build host (e.g.
i686). The OpenEmbedded build system sets the value ofBUILD_ARCHfrom the machine name reported by theunamecommand.- BUILD_AS_ARCH¶
Specifies the architecture-specific assembler flags for the build host. By default, the value of
BUILD_AS_ARCHis empty.- BUILD_CC_ARCH¶
Specifies the architecture-specific C compiler flags for the build host. By default, the value of
BUILD_CC_ARCHis empty.- BUILD_CCLD¶
Specifies the linker command to be used for the build host when the C compiler is being used as the linker. By default,
BUILD_CCLDpoints to GCC and passes as arguments the value ofBUILD_CC_ARCH, assumingBUILD_CC_ARCHis set.- BUILD_CFLAGS¶
Specifies the flags to pass to the C compiler when building for the build host. When building in the
-nativecontext,CFLAGSis set to the value of this variable by default.- BUILD_CPPFLAGS¶
Specifies the flags to pass to the C preprocessor (i.e. to both the C and the C++ compilers) when building for the build host. When building in the
-nativecontext,CPPFLAGSis set to the value of this variable by default.- BUILD_CXXFLAGS¶
Specifies the flags to pass to the C++ compiler when building for the build host. When building in the
-nativecontext,CXXFLAGSis set to the value of this variable by default.- BUILD_FC¶
Specifies the Fortran compiler command for the build host. By default,
BUILD_FCpoints to Gfortran and passes as arguments the value ofBUILD_CC_ARCH, assumingBUILD_CC_ARCHis set.- BUILD_LD¶
Specifies the linker command for the build host. By default,
BUILD_LDpoints to the GNU linker (ld) and passes as arguments the value ofBUILD_LD_ARCH, assumingBUILD_LD_ARCHis set.- BUILD_LD_ARCH¶
Specifies architecture-specific linker flags for the build host. By default, the value of
BUILD_LD_ARCHis empty.- BUILD_LDFLAGS¶
Specifies the flags to pass to the linker when building for the build host. When building in the
-nativecontext,LDFLAGSis set to the value of this variable by default.- BUILD_OPTIMIZATION¶
Specifies the optimization flags passed to the C compiler when building for the build host or the SDK. The flags are passed through the
BUILD_CFLAGSandBUILDSDK_CFLAGSdefault values.The default value of the
BUILD_OPTIMIZATIONvariable is "-O2 -pipe".- BUILD_OS¶
Specifies the operating system in use on the build host (e.g. "linux"). The OpenEmbedded build system sets the value of
BUILD_OSfrom the OS reported by theunamecommand - the first word, converted to lower-case characters.- BUILD_PREFIX¶
The toolchain binary prefix used for native recipes. The OpenEmbedded build system uses the
BUILD_PREFIXvalue to set theTARGET_PREFIXwhen building fornativerecipes.- BUILD_STRIP¶
Specifies the command to be used to strip debugging symbols from binaries produced for the build host. By default,
BUILD_STRIPpoints to${BUILD_PREFIX}strip.- BUILD_SYS¶
Specifies the system, including the architecture and the operating system, to use when building for the build host (i.e. when building
nativerecipes).The OpenEmbedded build system automatically sets this variable based on
BUILD_ARCH,BUILD_VENDOR, andBUILD_OS. You do not need to set theBUILD_SYSvariable yourself.- BUILD_VENDOR¶
Specifies the vendor name to use when building for the build host. The default value is an empty string ("").
- BUILDDIR¶
Points to the location of the Build Directory. You can define this directory indirectly through the
oe-init-build-envscript by passing in a Build Directory path when you run the script. If you run the script and do not provide a Build Directory path, theBUILDDIRdefaults tobuildin the current directory.- BUILDHISTORY_COMMIT¶
When inheriting the
buildhistoryclass, this variable specifies whether or not to commit the build history output in a local Git repository. If set to "1", this local repository will be maintained automatically by thebuildhistoryclass and a commit will be created on every build for changes to each top-level subdirectory of the build history output (images, packages, and sdk). If you want to track changes to build history over time, you should set this value to "1".By default, the
buildhistoryclass does not commit the build history output in a local Git repository:BUILDHISTORY_COMMIT ?= "0"- BUILDHISTORY_COMMIT_AUTHOR¶
When inheriting the
buildhistoryclass, this variable specifies the author to use for each Git commit. In order for theBUILDHISTORY_COMMIT_AUTHORvariable to work, theBUILDHISTORY_COMMITvariable must be set to "1".Git requires that the value you provide for the
BUILDHISTORY_COMMIT_AUTHORvariable takes the form of "nameemail@host". Providing an email address or host that is not valid does not produce an error.By default, the
buildhistoryclass sets the variable as follows:BUILDHISTORY_COMMIT_AUTHOR ?= "buildhistory <buildhistory@${DISTRO}>"- BUILDHISTORY_DIR¶
When inheriting the
buildhistoryclass, this variable specifies the directory in which build history information is kept. For more information on how the variable works, see thebuildhistory.class.By default, the
buildhistoryclass sets the directory as follows:BUILDHISTORY_DIR ?= "${TOPDIR}/buildhistory"- BUILDHISTORY_FEATURES¶
When inheriting the
buildhistoryclass, this variable specifies the build history features to be enabled. For more information on how build history works, see the "Maintaining Build Output Quality" section in the Yocto Project Development Tasks Manual.You can specify these features in the form of a space-separated list:
image: Analysis of the contents of images, which includes the list of installed packages among other things.
package: Analysis of the contents of individual packages.
sdk: Analysis of the contents of the software development kit (SDK).
task: Save output file signatures for shared state (sstate) tasks. This saves one file per task and lists the SHA-256 checksums for each file staged (i.e. the output of the task).
By default, the
buildhistoryclass enables the following features:BUILDHISTORY_FEATURES ?= "image package sdk"- BUILDHISTORY_IMAGE_FILES¶
When inheriting the
buildhistoryclass, this variable specifies a list of paths to files copied from the image contents into the build history directory under an "image-files" directory in the directory for the image, so that you can track the contents of each file. The default is to copy/etc/passwdand/etc/group, which allows you to monitor for changes in user and group entries. You can modify the list to include any file. Specifying an invalid path does not produce an error. Consequently, you can include files that might not always be present.By default, the
buildhistoryclass provides paths to the following files:BUILDHISTORY_IMAGE_FILES ?= "/etc/passwd /etc/group"- BUILDHISTORY_PUSH_REPO¶
When inheriting the
buildhistoryclass, this variable optionally specifies a remote repository to which build history pushes Git changes. In order forBUILDHISTORY_PUSH_REPOto work,BUILDHISTORY_COMMITmust be set to "1".The repository should correspond to a remote address that specifies a repository as understood by Git, or alternatively to a remote name that you have set up manually using
git remotewithin the local repository.By default, the
buildhistoryclass sets the variable as follows:BUILDHISTORY_PUSH_REPO ?= ""- BUILDSDK_CFLAGS¶
Specifies the flags to pass to the C compiler when building for the SDK. When building in the
nativesdk-context,CFLAGSis set to the value of this variable by default.- BUILDSDK_CPPFLAGS¶
Specifies the flags to pass to the C pre-processor (i.e. to both the C and the C++ compilers) when building for the SDK. When building in the
nativesdk-context,CPPFLAGSis set to the value of this variable by default.- BUILDSDK_CXXFLAGS¶
Specifies the flags to pass to the C++ compiler when building for the SDK. When building in the
nativesdk-context,CXXFLAGSis set to the value of this variable by default.- BUILDSDK_LDFLAGS¶
Specifies the flags to pass to the linker when building for the SDK. When building in the
nativesdk-context,LDFLAGSis set to the value of this variable by default.- BUILDSTATS_BASE¶
Points to the location of the directory that holds build statistics when you use and enable the
buildstatsclass. TheBUILDSTATS_BASEdirectory defaults to${TMPDIR}/buildstats/.- BUSYBOX_SPLIT_SUID¶
For the BusyBox recipe, specifies whether to split the output executable file into two parts: one for features that require
setuid root, and one for the remaining features (i.e. those that do not requiresetuid root).The
BUSYBOX_SPLIT_SUIDvariable defaults to "1", which results in a single output executable file. Set the variable to "0" to split the output file.
C
- CACHE¶
Specifies the directory BitBake uses to store a cache of the Metadata so it does not need to be parsed every time BitBake is started.
- CC¶
The minimal command and arguments used to run the C compiler.
- CFLAGS¶
Specifies the flags to pass to the C compiler. This variable is exported to an environment variable and thus made visible to the software being built during the compilation step.
Default initialization for
CFLAGSvaries depending on what is being built:TARGET_CFLAGSwhen building for the targetBUILD_CFLAGSwhen building for the build host (i.e.-native)BUILDSDK_CFLAGSwhen building for an SDK (i.e.nativesdk-)
- CLASSOVERRIDE¶
An internal variable specifying the special class override that should currently apply (e.g. "class-target", "class-native", and so forth). The classes that use this variable (e.g.
native,nativesdk, and so forth) set the variable to appropriate values.Note
CLASSOVERRIDEgets its default "class-target" value from thebitbake.conffile.As an example, the following override allows you to install extra files, but only when building for the target:
do_install_append_class-target() { install my-extra-file ${D}${sysconfdir} }Here is an example where
FOOis set to "native" when building for the build host, and to "other" when not building for the build host:FOO_class-native = "native" FOO = "other"The underlying mechanism behind
CLASSOVERRIDEis simply that it is included in the default value ofOVERRIDES.- CLEANBROKEN¶
If set to "1" within a recipe,
CLEANBROKENspecifies that themake cleancommand does not work for the software being built. Consequently, the OpenEmbedded build system will not try to runmake cleanduring thedo_configuretask, which is the default behavior.- COMBINED_FEATURES¶
Provides a list of hardware features that are enabled in both
MACHINE_FEATURESandDISTRO_FEATURES. This select list of features contains features that make sense to be controlled both at the machine and distribution configuration level. For example, the "bluetooth" feature requires hardware support but should also be optional at the distribution level, in case the hardware supports Bluetooth but you do not ever intend to use it.- COMMON_LICENSE_DIR¶
Points to
meta/files/common-licensesin the Source Directory, which is where generic license files reside.- COMPATIBLE_HOST¶
A regular expression that resolves to one or more hosts (when the recipe is native) or one or more targets (when the recipe is non-native) with which a recipe is compatible. The regular expression is matched against
HOST_SYS. You can use the variable to stop recipes from being built for classes of systems with which the recipes are not compatible. Stopping these builds is particularly useful with kernels. The variable also helps to increase parsing speed since the build system skips parsing recipes not compatible with the current system.- COMPATIBLE_MACHINE¶
A regular expression that resolves to one or more target machines with which a recipe is compatible. The regular expression is matched against
MACHINEOVERRIDES. You can use the variable to stop recipes from being built for machines with which the recipes are not compatible. Stopping these builds is particularly useful with kernels. The variable also helps to increase parsing speed since the build system skips parsing recipes not compatible with the current machine.- COMPLEMENTARY_GLOB¶
Defines wildcards to match when installing a list of complementary packages for all the packages explicitly (or implicitly) installed in an image.
Note
TheCOMPLEMENTARY_GLOBvariable uses Unix filename pattern matching (fnmatch), which is similar to the Unix style pathname pattern expansion (glob).The resulting list of complementary packages is associated with an item that can be added to
IMAGE_FEATURES. An example usage of this is the "dev-pkgs" item that when added toIMAGE_FEATURESwill install -dev packages (containing headers and other development files) for every package in the image.To add a new feature item pointing to a wildcard, use a variable flag to specify the feature item name and use the value to specify the wildcard. Here is an example:
COMPLEMENTARY_GLOB[dev-pkgs] = '*-dev'- COMPONENTS_DIR¶
Stores sysroot components for each recipe. The OpenEmbedded build system uses
COMPONENTS_DIRwhen constructing recipe-specific sysroots for other recipes.The default is "
${STAGING_DIR}-components." (i.e. "${TMPDIR}/sysroots-components").- CONF_VERSION¶
Tracks the version of the local configuration file (i.e.
local.conf). The value forCONF_VERSIONincrements each timebuild/conf/compatibility changes.- CONFFILES¶
Identifies editable or configurable files that are part of a package. If the Package Management System (PMS) is being used to update packages on the target system, it is possible that configuration files you have changed after the original installation and that you now want to remain unchanged are overwritten. In other words, editable files might exist in the package that you do not want reset as part of the package update process. You can use the
CONFFILESvariable to list the files in the package that you wish to prevent the PMS from overwriting during this update process.To use the
CONFFILESvariable, provide a package name override that identifies the resulting package. Then, provide a space-separated list of files. Here is an example:CONFFILES_${PN} += "${sysconfdir}/file1 \ ${sysconfdir}/file2 ${sysconfdir}/file3"A relationship exists between the
CONFFILESandFILESvariables. The files listed withinCONFFILESmust be a subset of the files listed withinFILES. Because the configuration files you provide withCONFFILESare simply being identified so that the PMS will not overwrite them, it makes sense that the files must already be included as part of the package through theFILESvariable.Note
When specifying paths as part of theCONFFILESvariable, it is good practice to use appropriate path variables. For example,${sysconfdir}rather than/etcor${bindir}rather than/usr/bin. You can find a list of these variables at the top of themeta/conf/bitbake.conffile in the Source Directory.- CONFIG_INITRAMFS_SOURCE¶
Identifies the initial RAM filesystem (initramfs) source files. The OpenEmbedded build system receives and uses this kernel Kconfig variable as an environment variable. By default, the variable is set to null ("").
The
CONFIG_INITRAMFS_SOURCEcan be either a single cpio archive with a.cpiosuffix or a space-separated list of directories and files for building the initramfs image. A cpio archive should contain a filesystem archive to be used as an initramfs image. Directories should contain a filesystem layout to be included in the initramfs image. Files should contain entries according to the format described by theusr/gen_init_cpioprogram in the kernel tree.If you specify multiple directories and files, the initramfs image will be the aggregate of all of them.
For information on creating an initramfs, see the "Building an Initial RAM Filesystem (initramfs) Image" section in the Yocto Project Development Tasks Manual.
- CONFIG_SITE¶
A list of files that contains
autoconftest results relevant to the current build. This variable is used by the Autotools utilities when runningconfigure.- CONFIGURE_FLAGS¶
The minimal arguments for GNU configure.
- CONFLICT_DISTRO_FEATURES¶
When inheriting the
distro_features_checkclass, this variable identifies distribution features that would be in conflict should the recipe be built. In other words, if theCONFLICT_DISTRO_FEATURESvariable lists a feature that also appears inDISTRO_FEATURESwithin the current configuration, an error occurs and the build stops.- COPYLEFT_LICENSE_EXCLUDE¶
A space-separated list of licenses to exclude from the source archived by the
archiverclass. In other words, if a license in a recipe'sLICENSEvalue is in the value ofCOPYLEFT_LICENSE_EXCLUDE, then its source is not archived by the class.Note
TheCOPYLEFT_LICENSE_EXCLUDEvariable takes precedence over theCOPYLEFT_LICENSE_INCLUDEvariable.The default value, which is "CLOSED Proprietary", for
COPYLEFT_LICENSE_EXCLUDEis set by thecopyleft_filterclass, which is inherited by thearchiverclass.- COPYLEFT_LICENSE_INCLUDE¶
A space-separated list of licenses to include in the source archived by the
archiverclass. In other words, if a license in a recipe'sLICENSEvalue is in the value ofCOPYLEFT_LICENSE_INCLUDE, then its source is archived by the class.The default value is set by the
copyleft_filterclass, which is inherited by thearchiverclass. The default value includes "GPL*", "LGPL*", and "AGPL*".- COPYLEFT_PN_EXCLUDE¶
A list of recipes to exclude in the source archived by the
archiverclass. TheCOPYLEFT_PN_EXCLUDEvariable overrides the license inclusion and exclusion caused through theCOPYLEFT_LICENSE_INCLUDEandCOPYLEFT_LICENSE_EXCLUDEvariables, respectively.The default value, which is "" indicating to not explicitly exclude any recipes by name, for
COPYLEFT_PN_EXCLUDEis set by thecopyleft_filterclass, which is inherited by thearchiverclass.- COPYLEFT_PN_INCLUDE¶
A list of recipes to include in the source archived by the
archiverclass. TheCOPYLEFT_PN_INCLUDEvariable overrides the license inclusion and exclusion caused through theCOPYLEFT_LICENSE_INCLUDEandCOPYLEFT_LICENSE_EXCLUDEvariables, respectively.The default value, which is "" indicating to not explicitly include any recipes by name, for
COPYLEFT_PN_INCLUDEis set by thecopyleft_filterclass, which is inherited by thearchiverclass.- COPYLEFT_RECIPE_TYPES¶
A space-separated list of recipe types to include in the source archived by the
archiverclass. Recipe types aretarget,native,nativesdk,cross,crosssdk, andcross-canadian.The default value, which is "target*", for
COPYLEFT_RECIPE_TYPESis set by thecopyleft_filterclass, which is inherited by thearchiverclass.- COPY_LIC_DIRS¶
If set to "1" along with the
COPY_LIC_MANIFESTvariable, the OpenEmbedded build system copies into the image the license files, which are located in/usr/share/common-licenses, for each package. The license files are placed in directories within the image itself during build time.Note
TheCOPY_LIC_DIRSdoes not offer a path for adding licenses for newly installed packages to an image, which might be most suitable for read-only filesystems that cannot be upgraded. See theLICENSE_CREATE_PACKAGEvariable for additional information. You can also reference the "Providing License Text" section in the Yocto Project Development Tasks Manual for information on providing license text.- COPY_LIC_MANIFEST¶
If set to "1", the OpenEmbedded build system copies the license manifest for the image to
/usr/share/common-licenses/license.manifestwithin the image itself during build time.Note
TheCOPY_LIC_MANIFESTdoes not offer a path for adding licenses for newly installed packages to an image, which might be most suitable for read-only filesystems that cannot be upgraded. See theLICENSE_CREATE_PACKAGEvariable for additional information. You can also reference the "Providing License Text" section in the Yocto Project Development Tasks Manual for information on providing license text.- CORE_IMAGE_EXTRA_INSTALL¶
Specifies the list of packages to be added to the image. You should only set this variable in the
local.confconfiguration file found in the Build Directory.This variable replaces
POKY_EXTRA_INSTALL, which is no longer supported.- COREBASE¶
Specifies the parent directory of the OpenEmbedded-Core Metadata layer (i.e.
meta).It is an important distinction that
COREBASEpoints to the parent of this layer and not the layer itself. Consider an example where you have cloned the Poky Git repository and retained thepokyname for your local copy of the repository. In this case,COREBASEpoints to thepokyfolder because it is the parent directory of thepoky/metalayer.- COREBASE_FILES¶
Lists files from the
COREBASEdirectory that should be copied other than the layers listed in thebblayers.conffile. TheCOREBASE_FILESvariable exists for the purpose of copying metadata from the OpenEmbedded build system into the extensible SDK.Explicitly listing files in
COREBASEis needed because it typically contains build directories and other files that should not normally be copied into the extensible SDK. Consequently, the value ofCOREBASE_FILESis used in order to only copy the files that are actually needed.- CPP¶
The minimal command and arguments used to run the C preprocessor.
- CPPFLAGS¶
Specifies the flags to pass to the C pre-processor (i.e. to both the C and the C++ compilers). This variable is exported to an environment variable and thus made visible to the software being built during the compilation step.
Default initialization for
CPPFLAGSvaries depending on what is being built:TARGET_CPPFLAGSwhen building for the targetBUILD_CPPFLAGSwhen building for the build host (i.e.-native)BUILDSDK_CPPFLAGSwhen building for an SDK (i.e.nativesdk-)
- CROSS_COMPILE¶
The toolchain binary prefix for the target tools. The
CROSS_COMPILEvariable is the same as theTARGET_PREFIXvariable.Note
The OpenEmbedded build system sets theCROSS_COMPILEvariable only in certain contexts (e.g. when building for kernel and kernel module recipes).- CVSDIR¶
The directory in which files checked out under the CVS system are stored.
- CXX¶
The minimal command and arguments used to run the C++ compiler.
- CXXFLAGS¶
Specifies the flags to pass to the C++ compiler. This variable is exported to an environment variable and thus made visible to the software being built during the compilation step.
Default initialization for
CXXFLAGSvaries depending on what is being built:TARGET_CXXFLAGSwhen building for the targetBUILD_CXXFLAGSwhen building for the build host (i.e.-native)BUILDSDK_CXXFLAGSwhen building for an SDK (i.e.nativesdk-)
D
- D¶
The destination directory. The location in the Build Directory where components are installed by the
do_installtask. This location defaults to:${WORKDIR}/imageCaution
Tasks that read from or write to this directory should run under fakeroot.- DATE¶
The date the build was started. Dates appear using the year, month, and day (YMD) format (e.g. "20150209" for February 9th, 2015).
- DATETIME¶
The date and time on which the current build started. The format is suitable for timestamps.
- DEBIAN_NOAUTONAME¶
When the
debianclass is inherited, which is the default behavior,DEBIAN_NOAUTONAMEspecifies a particular package should not be renamed according to Debian library package naming. You must use the package name as an override when you set this variable. Here is an example from thefontconfigrecipe:DEBIAN_NOAUTONAME_fontconfig-utils = "1"- DEBIANNAME¶
When the
debianclass is inherited, which is the default behavior,DEBIANNAMEallows you to override the library name for an individual package. Overriding the library name in these cases is rare. You must use the package name as an override when you set this variable. Here is an example from thedbusrecipe:DEBIANNAME_${PN} = "dbus-1"- DEBUG_BUILD¶
Specifies to build packages with debugging information. This influences the value of the
SELECTED_OPTIMIZATIONvariable.- DEBUG_OPTIMIZATION¶
The options to pass in
TARGET_CFLAGSandCFLAGSwhen compiling a system for debugging. This variable defaults to "-O -fno-omit-frame-pointer ${DEBUG_FLAGS} -pipe".- DEFAULT_PREFERENCE¶
Specifies a weak bias for recipe selection priority.
The most common usage of this is variable is to set it to "-1" within a recipe for a development version of a piece of software. Using the variable in this way causes the stable version of the recipe to build by default in the absence of
PREFERRED_VERSIONbeing used to build the development version.Note
The bias provided byDEFAULT_PREFERENCEis weak and is overridden byBBFILE_PRIORITYif that variable is different between two layers that contain different versions of the same recipe.- DEFAULTTUNE¶
The default CPU and Application Binary Interface (ABI) tunings (i.e. the "tune") used by the OpenEmbedded build system. The
DEFAULTTUNEhelps defineTUNE_FEATURES.The default tune is either implicitly or explicitly set by the machine (
MACHINE). However, you can override the setting using available tunes as defined withAVAILTUNES.- DEPENDS¶
Lists a recipe's build-time dependencies. These are dependencies on other recipes whose contents (e.g. headers and shared libraries) are needed by the recipe at build time.
As an example, consider a recipe
foothat contains the following assignment:DEPENDS = "bar"The practical effect of the previous assignment is that all files installed by bar will be available in the appropriate staging sysroot, given by the
STAGING_DIR*variables, by the time thedo_configuretask forfooruns. This mechanism is implemented by havingdo_configuredepend on thedo_populate_sysroottask of each recipe listed inDEPENDS, through a[deptask]declaration in thebaseclass.Note
It seldom is necessary to reference, for example,STAGING_DIR_HOSTexplicitly. The standard classes and build-related variables are configured to automatically use the appropriate staging sysroots.As another example,
DEPENDScan also be used to add utilities that run on the build machine during the build. For example, a recipe that makes use of a code generator built by the recipecodegenmight have the following:DEPENDS = "codegen-native"For more information, see the
nativeclass and theEXTRANATIVEPATHvariable.Notes
DEPENDSis a list of recipe names. Or, to be more precise, it is a list ofPROVIDESnames, which usually match recipe names. Putting a package name such as "foo-dev" inDEPENDSdoes not make sense. Use "foo" instead, as this will put files from all the packages that make upfoo, which includes those fromfoo-dev, into the sysroot.One recipe having another recipe in
DEPENDSdoes not by itself add any runtime dependencies between the packages produced by the two recipes. However, as explained in the "Automatically Added Runtime Dependencies" section in the Yocto Project Overview and Concepts Manual, runtime dependencies will often be added automatically, meaningDEPENDSalone is sufficient for most recipes.Counterintuitively,
DEPENDSis often necessary even for recipes that install precompiled components. For example, iflibfoois a precompiled library that links againstlibbar, then linking againstlibfoorequires bothlibfooandlibbarto be available in the sysroot. Without aDEPENDSfrom the recipe that installslibfooto the recipe that installslibbar, other recipes might fail to link againstlibfoo.
For information on runtime dependencies, see the
RDEPENDSvariable. You can also see the "Tasks" and "Dependencies" sections in the BitBake User Manual for additional information on tasks and dependencies.- DEPLOY_DIR¶
Points to the general area that the OpenEmbedded build system uses to place images, packages, SDKs, and other output files that are ready to be used outside of the build system. By default, this directory resides within the Build Directory as
${TMPDIR}/deploy.For more information on the structure of the Build Directory, see "The Build Directory -
build/" section. For more detail on the contents of thedeploydirectory, see the "Images", "Package Feeds", and "Application Development SDK" sections all in the Yocto Project Overview and Concepts Manual.- DEPLOY_DIR_DEB¶
Points to the area that the OpenEmbedded build system uses to place Debian packages that are ready to be used outside of the build system. This variable applies only when
PACKAGE_CLASSEScontains "package_deb".The BitBake configuration file initially defines the
DEPLOY_DIR_DEBvariable as a sub-folder ofDEPLOY_DIR:DEPLOY_DIR_DEB = "${DEPLOY_DIR}/deb"The
package_debclass uses theDEPLOY_DIR_DEBvariable to make sure thedo_package_write_debtask writes Debian packages into the appropriate folder. For more information on how packaging works, see the "Package Feeds" section in the Yocto Project Overview and Concepts Manual.- DEPLOY_DIR_IMAGE¶
Points to the area that the OpenEmbedded build system uses to place images and other associated output files that are ready to be deployed onto the target machine. The directory is machine-specific as it contains the
${MACHINE}name. By default, this directory resides within the Build Directory as${DEPLOY_DIR}/images/${MACHINE}/.For more information on the structure of the Build Directory, see "The Build Directory -
build/" section. For more detail on the contents of thedeploydirectory, see the "Images" and "Application Development SDK" sections both in the Yocto Project Overview and Concepts Manual.- DEPLOY_DIR_IPK¶
Points to the area that the OpenEmbedded build system uses to place IPK packages that are ready to be used outside of the build system. This variable applies only when
PACKAGE_CLASSEScontains "package_ipk".The BitBake configuration file initially defines this variable as a sub-folder of
DEPLOY_DIR:DEPLOY_DIR_IPK = "${DEPLOY_DIR}/ipk"The
package_ipkclass uses theDEPLOY_DIR_IPKvariable to make sure thedo_package_write_ipktask writes IPK packages into the appropriate folder. For more information on how packaging works, see the "Package Feeds" section in the Yocto Project Overview and Concepts Manual.- DEPLOY_DIR_RPM¶
Points to the area that the OpenEmbedded build system uses to place RPM packages that are ready to be used outside of the build system. This variable applies only when
PACKAGE_CLASSEScontains "package_rpm".The BitBake configuration file initially defines this variable as a sub-folder of
DEPLOY_DIR:DEPLOY_DIR_RPM = "${DEPLOY_DIR}/rpm"The
package_rpmclass uses theDEPLOY_DIR_RPMvariable to make sure thedo_package_write_rpmtask writes RPM packages into the appropriate folder. For more information on how packaging works, see the "Package Feeds" section in the Yocto Project Overview and Concepts Manual.- DEPLOY_DIR_TAR¶
Points to the area that the OpenEmbedded build system uses to place tarballs that are ready to be used outside of the build system. This variable applies only when
PACKAGE_CLASSEScontains "package_tar".The BitBake configuration file initially defines this variable as a sub-folder of
DEPLOY_DIR:DEPLOY_DIR_TAR = "${DEPLOY_DIR}/tar"The
package_tarclass uses theDEPLOY_DIR_TARvariable to make sure thedo_package_write_tartask writes TAR packages into the appropriate folder. For more information on how packaging works, see the "Package Feeds" section in the Yocto Project Overview and Concepts Manual.- DEPLOYDIR¶
When inheriting the
deployclass, theDEPLOYDIRpoints to a temporary work area for deployed files that is set in thedeployclass as follows:DEPLOYDIR = "${WORKDIR}/deploy-${PN}"Recipes inheriting the
deployclass should copy files to be deployed intoDEPLOYDIR, and the class will take care of copying them intoDEPLOY_DIR_IMAGEafterwards.- DESCRIPTION¶
The package description used by package managers. If not set,
DESCRIPTIONtakes the value of theSUMMARYvariable.- DISK_SIGNATURE¶
A 32-bit MBR disk signature used by
directdiskimages.By default, the signature is set to an automatically generated random value that allows the OpenEmbedded build system to create a boot loader. You can override the signature in the image recipe by setting
DISK_SIGNATUREto an 8-digit hex string. You might want to overrideDISK_SIGNATUREif you want the disk signature to remain constant between image builds.When using Linux 3.8 or later, you can use
DISK_SIGNATUREto specify the root by UUID to allow the kernel to locate the root device even if the device name changes due to differences in hardware configuration. By default,ROOT_VMis set as follows:ROOT_VM ?= "root=/dev/sda2"However, you can change this to locate the root device using the disk signature instead:
ROOT_VM = "root=PARTUUID=${DISK_SIGNATURE}-02"As previously mentioned, it is possible to set the
DISK_SIGNATUREvariable in yourlocal.conffile to a fixed value if you do not wantsyslinux.cfgchanging for each build. You might find this useful when you want to upgrade the root filesystem on a device without having to recreate or modify the master boot record.- DISTRO¶
The short name of the distribution. For information on the long name of the distribution, see the
DISTRO_NAMEvariable.The
DISTROvariable corresponds to a distribution configuration file whose root name is the same as the variable's argument and whose filename extension is.conf. For example, the distribution configuration file for the Poky distribution is namedpoky.confand resides in themeta-poky/conf/distrodirectory of the Source Directory.Within that
poky.conffile, theDISTROvariable is set as follows:DISTRO = "poky"Distribution configuration files are located in a
conf/distrodirectory within the Metadata that contains the distribution configuration. The value forDISTROmust not contain spaces, and is typically all lower-case.Note
If theDISTROvariable is blank, a set of default configurations are used, which are specified withinmeta/conf/distro/defaultsetup.confalso in the Source Directory.- DISTRO_CODENAME¶
Specifies a codename for the distribution being built.
- DISTRO_EXTRA_RDEPENDS¶
Specifies a list of distro-specific packages to add to all images. This variable takes affect through
packagegroup-baseso the variable only really applies to the more full-featured images that includepackagegroup-base. You can use this variable to keep distro policy out of generic images. As with all other distro variables, you set this variable in the distro.conffile.- DISTRO_EXTRA_RRECOMMENDS¶
Specifies a list of distro-specific packages to add to all images if the packages exist. The packages might not exist or be empty (e.g. kernel modules). The list of packages are automatically installed but you can remove them.
- DISTRO_FEATURES¶
The software support you want in your distribution for various features. You define your distribution features in the distribution configuration file.
In most cases, the presence or absence of a feature in
DISTRO_FEATURESis translated to the appropriate option supplied to the configure script during thedo_configuretask for recipes that optionally support the feature. For example, specifying "x11" inDISTRO_FEATURES, causes every piece of software built for the target that can optionally support X11 to have its X11 support enabled.Two more examples are Bluetooth and NFS support. For a more complete list of features that ships with the Yocto Project and that you can provide with this variable, see the "Distro Features" section.
- DISTRO_FEATURES_BACKFILL¶
Features to be added to
DISTRO_FEATURESif not also present inDISTRO_FEATURES_BACKFILL_CONSIDERED.This variable is set in the
meta/conf/bitbake.conffile. It is not intended to be user-configurable. It is best to just reference the variable to see which distro features are being backfilled for all distro configurations. See the Feature Backfilling section for more information.- DISTRO_FEATURES_BACKFILL_CONSIDERED¶
Features from
DISTRO_FEATURES_BACKFILLthat should not be backfilled (i.e. added toDISTRO_FEATURES) during the build. See the "Feature Backfilling" section for more information.- DISTRO_FEATURES_DEFAULT¶
A convenience variable that gives you the default list of distro features with the exception of any features specific to the C library (
libc).When creating a custom distribution, you might find it useful to be able to reuse the default
DISTRO_FEATURESoptions without the need to write out the full set. Here is an example that usesDISTRO_FEATURES_DEFAULTfrom a custom distro configuration file:DISTRO_FEATURES ?= "${DISTRO_FEATURES_DEFAULT} ${DISTRO_FEATURES_LIBC} myfeature"- DISTRO_FEATURES_FILTER_NATIVE¶
Specifies a list of features that if present in the target
DISTRO_FEATURESvalue should be included inDISTRO_FEATURESwhen building native recipes. This variable is used in addition to the features filtered using theDISTRO_FEATURES_NATIVEvariable.- DISTRO_FEATURES_FILTER_NATIVESDK¶
Specifies a list of features that if present in the target
DISTRO_FEATURESvalue should be included inDISTRO_FEATURESwhen building nativesdk recipes. This variable is used in addition to the features filtered using theDISTRO_FEATURES_NATIVESDKvariable.- DISTRO_FEATURES_LIBC¶
A convenience variable that specifies the list of distro features that are specific to the C library (
libc). Typically, these features are prefixed with "libc-" and control which features are enabled at during the build within the C library itself.- DISTRO_FEATURES_NATIVE¶
Specifies a list of features that should be included in
DISTRO_FEATURESwhen building native recipes. This variable is used in addition to the features filtered using theDISTRO_FEATURES_FILTER_NATIVEvariable.- DISTRO_FEATURES_NATIVESDK¶
Specifies a list of features that should be included in
DISTRO_FEATURESwhen building nativesdk recipes. This variable is used in addition to the features filtered using theDISTRO_FEATURES_FILTER_NATIVESDKvariable.- DISTRO_NAME¶
The long name of the distribution. For information on the short name of the distribution, see the
DISTROvariable.The
DISTRO_NAMEvariable corresponds to a distribution configuration file whose root name is the same as the variable's argument and whose filename extension is.conf. For example, the distribution configuration file for the Poky distribution is namedpoky.confand resides in themeta-poky/conf/distrodirectory of the Source Directory.Within that
poky.conffile, theDISTRO_NAMEvariable is set as follows:DISTRO_NAME = "Poky (Yocto Project Reference Distro)"Distribution configuration files are located in a
conf/distrodirectory within the Metadata that contains the distribution configuration.Note
If theDISTRO_NAMEvariable is blank, a set of default configurations are used, which are specified withinmeta/conf/distro/defaultsetup.confalso in the Source Directory.- DISTRO_VERSION¶
The version of the distribution.
- DISTROOVERRIDES¶
A colon-separated list of overrides specific to the current distribution. By default, this list includes the value of
DISTRO.You can extend
DISTROOVERRIDESto add extra overrides that should apply to the distribution.The underlying mechanism behind
DISTROOVERRIDESis simply that it is included in the default value ofOVERRIDES.- DL_DIR¶
The central download directory used by the build process to store downloads. By default,
DL_DIRgets files suitable for mirroring for everything except Git repositories. If you want tarballs of Git repositories, use theBB_GENERATE_MIRROR_TARBALLSvariable.You can set this directory by defining the
DL_DIRvariable in theconf/local.conffile. This directory is self-maintaining and you should not have to touch it. By default, the directory isdownloadsin the Build Directory.#DL_DIR ?= "${TOPDIR}/downloads"To specify a different download directory, simply remove the comment from the line and provide your directory.
During a first build, the system downloads many different source code tarballs from various upstream projects. Downloading can take a while, particularly if your network connection is slow. Tarballs are all stored in the directory defined by
DL_DIRand the build system looks there first to find source tarballs.Note
When wiping and rebuilding, you can preserve this directory to speed up this part of subsequent builds.You can safely share this directory between multiple builds on the same development machine. For additional information on how the build process gets source files when working behind a firewall or proxy server, see this specific question in the "FAQ" chapter. You can also refer to the "Working Behind a Network Proxy" Wiki page.
- DOC_COMPRESS¶
When inheriting the
compress_docclass, this variable sets the compression policy used when the OpenEmbedded build system compresses man pages and info pages. By default, the compression method used is gz (gzip). Other policies available are xz and bz2.For information on policies and on how to use this variable, see the comments in the
meta/classes/compress_doc.bbclassfile.
E
- EFI_PROVIDER¶
When building bootable images (i.e. where
hddimg,iso, orwic.vmdkis inIMAGE_FSTYPES), theEFI_PROVIDERvariable specifies the EFI bootloader to use. The default is "grub-efi", but "systemd-boot" can be used instead.See the
systemd-bootandimage-liveclasses for more information.- ENABLE_BINARY_LOCALE_GENERATION¶
Variable that controls which locales for
glibcare generated during the build (useful if the target device has 64Mbytes of RAM or less).- ERR_REPORT_DIR¶
When used with the
report-errorclass, specifies the path used for storing the debug files created by the error reporting tool, which allows you to submit build errors you encounter to a central database. By default, the value of this variable is${LOG_DIR}/error-report.You can set
ERR_REPORT_DIRto the path you want the error reporting tool to store the debug files as follows in yourlocal.conffile:ERR_REPORT_DIR = "path"- ERROR_QA¶
Specifies the quality assurance checks whose failures are reported as errors by the OpenEmbedded build system. You set this variable in your distribution configuration file. For a list of the checks you can control with this variable, see the "
insane.bbclass" section.- EXCLUDE_FROM_SHLIBS¶
Triggers the OpenEmbedded build system's shared libraries resolver to exclude an entire package when scanning for shared libraries.
Note
The shared libraries resolver's functionality results in part from the internal functionpackage_do_shlibs, which is part of thedo_packagetask. You should be aware that the shared libraries resolver might implicitly define some dependencies between packages.The
EXCLUDE_FROM_SHLIBSvariable is similar to thePRIVATE_LIBSvariable, which excludes a package's particular libraries only and not the whole package.Use the
EXCLUDE_FROM_SHLIBSvariable by setting it to "1" for a particular package:EXCLUDE_FROM_SHLIBS = "1"- EXCLUDE_FROM_WORLD¶
Directs BitBake to exclude a recipe from world builds (i.e.
bitbake world). During world builds, BitBake locates, parses and builds all recipes found in every layer exposed in thebblayers.confconfiguration file.To exclude a recipe from a world build using this variable, set the variable to "1" in the recipe.
Note
Recipes added toEXCLUDE_FROM_WORLDmay still be built during a world build in order to satisfy dependencies of other recipes. Adding a recipe toEXCLUDE_FROM_WORLDonly ensures that the recipe is not explicitly added to the list of build targets in a world build.- EXTENDPE¶
Used with file and pathnames to create a prefix for a recipe's version based on the recipe's
PEvalue. IfPEis set and greater than zero for a recipe,EXTENDPEbecomes that value (e.g ifPEis equal to "1" thenEXTENDPEbecomes "1_"). If a recipe'sPEis not set (the default) or is equal to zero,EXTENDPEbecomes "".See the
STAMPvariable for an example.- EXTENDPKGV¶
The full package version specification as it appears on the final packages produced by a recipe. The variable's value is normally used to fix a runtime dependency to the exact same version of another package in the same recipe:
RDEPENDS_${PN}-additional-module = "${PN} (= ${EXTENDPKGV})"The dependency relationships are intended to force the package manager to upgrade these types of packages in lock-step.
- EXTERNAL_KERNEL_TOOLS¶
When set, the
EXTERNAL_KERNEL_TOOLSvariable indicates that these tools are not in the source tree.When kernel tools are available in the tree, they are preferred over any externally installed tools. Setting the
EXTERNAL_KERNEL_TOOLSvariable tells the OpenEmbedded build system to prefer the installed external tools. See thekernel-yoctoclass inmeta/classesto see how the variable is used.- EXTERNALSRC¶
When inheriting the
externalsrcclass, this variable points to the source tree, which is outside of the OpenEmbedded build system. When set, this variable sets theSvariable, which is what the OpenEmbedded build system uses to locate unpacked recipe source code.For more information on
externalsrc.bbclass, see the "externalsrc.bbclass" section. You can also find information on how to use this variable in the "Building Software from an External Source" section in the Yocto Project Development Tasks Manual.- EXTERNALSRC_BUILD¶
When inheriting the
externalsrcclass, this variable points to the directory in which the recipe's source code is built, which is outside of the OpenEmbedded build system. When set, this variable sets theBvariable, which is what the OpenEmbedded build system uses to locate the Build Directory.For more information on
externalsrc.bbclass, see the "externalsrc.bbclass" section. You can also find information on how to use this variable in the "Building Software from an External Source" section in the Yocto Project Development Tasks Manual.- EXTRA_AUTORECONF¶
For recipes inheriting the
autotoolsclass, you can useEXTRA_AUTORECONFto specify extra options to pass to theautoreconfcommand that is executed during thedo_configuretask.The default value is "--exclude=autopoint".
- EXTRA_IMAGE_FEATURES¶
A list of additional features to include in an image. When listing more than one feature, separate them with a space.
Typically, you configure this variable in your
local.conffile, which is found in the Build Directory. Although you can use this variable from within a recipe, best practices dictate that you do not.Note
To enable primary features from within the image recipe, use theIMAGE_FEATURESvariable.Here are some examples of features you can add:
"dbg-pkgs" - Adds -dbg packages for all installed packages including symbol information for debugging and profiling. "debug-tweaks" - Makes an image suitable for debugging. For example, allows root logins without passwords and enables post-installation logging. See the 'allow-empty-password' and 'post-install-logging' features in the "Image Features" section for more information. "dev-pkgs" - Adds -dev packages for all installed packages. This is useful if you want to develop against the libraries in the image. "read-only-rootfs" - Creates an image whose root filesystem is read-only. See the "Creating a Read-Only Root Filesystem" section in the Yocto Project Development Tasks Manual for more information "tools-debug" - Adds debugging tools such as gdb and strace. "tools-sdk" - Adds development tools such as gcc, make, pkgconfig and so forth. "tools-testapps" - Adds useful testing tools such as ts_print, aplay, arecord and so forth.For a complete list of image features that ships with the Yocto Project, see the "Image Features" section.
For an example that shows how to customize your image by using this variable, see the "Customizing Images Using Custom
IMAGE_FEATURESandEXTRA_IMAGE_FEATURES" section in the Yocto Project Development Tasks Manual.- EXTRA_IMAGECMD¶
Specifies additional options for the image creation command that has been specified in
IMAGE_CMD. When setting this variable, use an override for the associated image type. Here is an example:EXTRA_IMAGECMD_ext3 ?= "-i 4096"- EXTRA_IMAGEDEPENDS¶
A list of recipes to build that do not provide packages for installing into the root filesystem.
Sometimes a recipe is required to build the final image but is not needed in the root filesystem. You can use the
EXTRA_IMAGEDEPENDSvariable to list these recipes and thus specify the dependencies. A typical example is a required bootloader in a machine configuration.- EXTRANATIVEPATH¶
A list of subdirectories of
${STAGING_BINDIR_NATIVE}added to the beginning of the environment variablePATH. As an example, the following prepends "${STAGING_BINDIR_NATIVE}/foo:${STAGING_BINDIR_NATIVE}/bar:" toPATH:EXTRANATIVEPATH = "foo bar"- EXTRA_OECMAKE¶
Additional CMake options. See the
cmakeclass for additional information.- EXTRA_OECONF¶
Additional
configurescript options. SeePACKAGECONFIG_CONFARGSfor additional information on passing configure script options.- EXTRA_OEMAKE¶
Additional GNU
makeoptions.Because the
EXTRA_OEMAKEdefaults to "", you need to set the variable to specify any required GNU options.PARALLEL_MAKEandPARALLEL_MAKEINSTalso make use ofEXTRA_OEMAKEto pass the required flags.- EXTRA_OESCONS¶
When inheriting the
sconsclass, this variable specifies additional configuration options you want to pass to thesconscommand line.- EXTRA_USERS_PARAMS¶
When inheriting the
extrausersclass, this variable provides image level user and group operations. This is a more global method of providing user and group configuration as compared to using theuseraddclass, which ties user and group configurations to a specific recipe.The set list of commands you can configure using the
EXTRA_USERS_PARAMSis shown in theextrausersclass. These commands map to the normal Unix commands of the same names:# EXTRA_USERS_PARAMS = "\ # useradd -p '' tester; \ # groupadd developers; \ # userdel nobody; \ # groupdel -g video; \ # groupmod -g 1020 developers; \ # usermod -s /bin/sh tester; \ # "
F
- FEATURE_PACKAGES¶
Defines one or more packages to include in an image when a specific item is included in
IMAGE_FEATURES. When setting the value,FEATURE_PACKAGESshould have the name of the feature item as an override. Here is an example:FEATURE_PACKAGES_widget = "package1package2"In this example, if "widget" were added to
IMAGE_FEATURES,package1andpackage2would be included in the image.Note
Packages installed by features defined throughFEATURE_PACKAGESare often package groups. While similarly named, you should not confuse theFEATURE_PACKAGESvariable with package groups, which are discussed elsewhere in the documentation.- FEED_DEPLOYDIR_BASE_URI¶
Points to the base URL of the server and location within the document-root that provides the metadata and packages required by OPKG to support runtime package management of IPK packages. You set this variable in your
local.conffile.Consider the following example:
FEED_DEPLOYDIR_BASE_URI = "http://192.168.7.1/BOARD-dir"This example assumes you are serving your packages over HTTP and your databases are located in a directory named
BOARD-dir, which is underneath your HTTP server's document-root. In this case, the OpenEmbedded build system generates a set of configuration files for you in your target that work with the feed.- FILES¶
The list of files and directories that are placed in a package. The
PACKAGESvariable lists the packages generated by a recipe.To use the
FILESvariable, provide a package name override that identifies the resulting package. Then, provide a space-separated list of files or paths that identify the files you want included as part of the resulting package. Here is an example:FILES_${PN} += "${bindir}/mydir1 ${bindir}/mydir2/myfile"Notes
When specifying files or paths, you can pattern match using Python's
globsyntax. For details on the syntax, see the documentation by following the previous link.When specifying paths as part of the
FILESvariable, it is good practice to use appropriate path variables. For example, use${sysconfdir}rather than/etc, or${bindir}rather than/usr/bin. You can find a list of these variables at the top of themeta/conf/bitbake.conffile in the Source Directory. You will also find the default values of the variousFILES_*variables in this file.
If some of the files you provide with the
FILESvariable are editable and you know they should not be overwritten during the package update process by the Package Management System (PMS), you can identify these files so that the PMS will not overwrite them. See theCONFFILESvariable for information on how to identify these files to the PMS.- FILES_SOLIBSDEV¶
Defines the file specification to match
SOLIBSDEV. In other words,FILES_SOLIBSDEVdefines the full path name of the development symbolic link (symlink) for shared libraries on the target platform.The following statement from the
bitbake.confshows how it is set:FILES_SOLIBSDEV ?= "${base_libdir}/lib*${SOLIBSDEV} ${libdir}/lib*${SOLIBSDEV}"- FILESEXTRAPATHS¶
Extends the search path the OpenEmbedded build system uses when looking for files and patches as it processes recipes and append files. The default directories BitBake uses when it processes recipes are initially defined by the
FILESPATHvariable. You can extendFILESPATHvariable by usingFILESEXTRAPATHS.Best practices dictate that you accomplish this by using
FILESEXTRAPATHSfrom within a.bbappendfile and that you prepend paths as follows:FILESEXTRAPATHS_prepend := "${THISDIR}/${PN}:"In the above example, the build system first looks for files in a directory that has the same name as the corresponding append file.
Note
When extending
FILESEXTRAPATHS, be sure to use the immediate expansion (:=) operator. Immediate expansion makes sure that BitBake evaluatesTHISDIRat the time the directive is encountered rather than at some later time when expansion might result in a directory that does not contain the files you need.Also, include the trailing separating colon character if you are prepending. The trailing colon character is necessary because you are directing BitBake to extend the path by prepending directories to the search path.
Here is another common use:
FILESEXTRAPATHS_prepend := "${THISDIR}/files:"In this example, the build system extends the
FILESPATHvariable to include a directory namedfilesthat is in the same directory as the corresponding append file.This next example specifically adds three paths:
FILESEXTRAPATHS_prepend := "path_1:path_2:path_3:"A final example shows how you can extend the search path and include a
MACHINE-specific override, which is useful in a BSP layer:FILESEXTRAPATHS_prepend_intel-x86-common := "${THISDIR}/${PN}:"The previous statement appears in the
linux-yocto-dev.bbappendfile, which is found in the Yocto Project Source Repositories inmeta-intel/common/recipes-kernel/linux. Here, the machine override is a specialPACKAGE_ARCHdefinition for multiplemeta-intelmachines.Note
For a layer that supports a single BSP, the override could just be the value ofMACHINE.By prepending paths in
.bbappendfiles, you allow multiple append files that reside in different layers but are used for the same recipe to correctly extend the path.- FILESOVERRIDES¶
A subset of
OVERRIDESused by the OpenEmbedded build system for creatingFILESPATH. You can find more information on how overrides are handled in the BitBake User Manual.By default, the
FILESOVERRIDESvariable is defined as:FILESOVERRIDES = "${TRANSLATED_TARGET_ARCH}:${MACHINEOVERRIDES}:${DISTROOVERRIDES}"Note
Do not hand-edit theFILESOVERRIDESvariable. The values match up with expected overrides and are used in an expected manner by the build system.- FILESPATH¶
The default set of directories the OpenEmbedded build system uses when searching for patches and files. During the build process, BitBake searches each directory in
FILESPATHin the specified order when looking for files and patches specified by eachfile://URI in a recipe'sSRC_URIstatements.The default value for the
FILESPATHvariable is defined in thebase.bbclassclass found inmeta/classesin the Source Directory:FILESPATH = "${@base_set_filespath(["${FILE_DIRNAME}/${BP}", \ "${FILE_DIRNAME}/${BPN}", "${FILE_DIRNAME}/files"], d)}"Note
Do not hand-edit theFILESPATHvariable. If you want the build system to look in directories other than the defaults, extend theFILESPATHvariable by using theFILESEXTRAPATHSvariable.Be aware that the default
FILESPATHdirectories do not map to directories in custom layers where append files (.bbappend) are used. If you want the build system to find patches or files that reside with your append files, you need to extend theFILESPATHvariable by using theFILESEXTRAPATHSvariable.You can find out more about the patching process in the "Patching" section in the Yocto Project Overview and Concepts Manual and the "Patching Code" section in the Yocto Project Development Tasks Manual. See the
do_patchtask as well.- FILESYSTEM_PERMS_TABLES¶
Allows you to define your own file permissions settings table as part of your configuration for the packaging process. For example, suppose you need a consistent set of custom permissions for a set of groups and users across an entire work project. It is best to do this in the packages themselves but this is not always possible.
By default, the OpenEmbedded build system uses the
fs-perms.txt, which is located in themeta/filesfolder in the Source Directory. If you create your own file permissions setting table, you should place it in your layer or the distro's layer.You define the
FILESYSTEM_PERMS_TABLESvariable in theconf/local.conffile, which is found in the Build Directory, to point to your customfs-perms.txt. You can specify more than a single file permissions setting table. The paths you specify to these files must be defined within theBBPATHvariable.For guidance on how to create your own file permissions settings table file, examine the existing
fs-perms.txt.- FONT_EXTRA_RDEPENDS¶
When inheriting the
fontcacheclass, this variable specifies the runtime dependencies for font packages. By default, theFONT_EXTRA_RDEPENDSis set to "fontconfig-utils".- FONT_PACKAGES¶
When inheriting the
fontcacheclass, this variable identifies packages containing font files that need to be cached by Fontconfig. By default, thefontcacheclass assumes that fonts are in the recipe's main package (i.e.${PN}). Use this variable if fonts you need are in a package other than that main package.- FORCE_RO_REMOVE¶
Forces the removal of the packages listed in
ROOTFS_RO_UNNEEDEDduring the generation of the root filesystem.Set the variable to "1" to force the removal of these packages.
- FULL_OPTIMIZATION¶
The options to pass in
TARGET_CFLAGSandCFLAGSwhen compiling an optimized system. This variable defaults to "-O2 -pipe ${DEBUG_FLAGS}".
G
- GCCPIE¶
Enables Position Independent Executables (PIE) within the GNU C Compiler (GCC). Enabling PIE in the GCC makes Return Oriented Programming (ROP) attacks much more difficult to execute.
By default the
security_flags.incfile enables PIE by setting the variable as follows:GCCPIE ?= "--enable-default-pie"- GCCVERSION¶
Specifies the default version of the GNU C Compiler (GCC) used for compilation. By default,
GCCVERSIONis set to "8.x" in themeta/conf/distro/include/tcmode-default.incinclude file:GCCVERSION ?= "8.%"You can override this value by setting it in a configuration file such as the
local.conf.- GDB¶
The minimal command and arguments to run the GNU Debugger.
- GITDIR¶
The directory in which a local copy of a Git repository is stored when it is cloned.
- GLIBC_GENERATE_LOCALES¶
Specifies the list of GLIBC locales to generate should you not wish to generate all LIBC locals, which can be time consuming.
You can set
GLIBC_GENERATE_LOCALESin yourlocal.conffile. By default, all locales are generated.GLIBC_GENERATE_LOCALES = "en_GB.UTF-8 en_US.UTF-8"- GROUPADD_PARAM¶
When inheriting the
useraddclass, this variable specifies for a package what parameters should be passed to thegroupaddcommand if you wish to add a group to the system when the package is installed.Here is an example from the
dbusrecipe:GROUPADD_PARAM_${PN} = "-r netdev"For information on the standard Linux shell command
groupadd, see http://linux.die.net/man/8/groupadd.- GROUPMEMS_PARAM¶
When inheriting the
useraddclass, this variable specifies for a package what parameters should be passed to thegroupmemscommand if you wish to modify the members of a group when the package is installed.For information on the standard Linux shell command
groupmems, see http://linux.die.net/man/8/groupmems.- GRUB_GFXSERIAL¶
Configures the GNU GRand Unified Bootloader (GRUB) to have graphics and serial in the boot menu. Set this variable to "1" in your
local.confor distribution configuration file to enable graphics and serial in the menu.See the
grub-eficlass for more information on how this variable is used.- GRUB_OPTS¶
Additional options to add to the GNU GRand Unified Bootloader (GRUB) configuration. Use a semi-colon character (
;) to separate multiple options.The
GRUB_OPTSvariable is optional. See thegrub-eficlass for more information on how this variable is used.- GRUB_TIMEOUT¶
Specifies the timeout before executing the default
LABELin the GNU GRand Unified Bootloader (GRUB).The
GRUB_TIMEOUTvariable is optional. See thegrub-eficlass for more information on how this variable is used.- GTKIMMODULES_PACKAGES¶
When inheriting the
gtk-immodules-cacheclass, this variable specifies the packages that contain the GTK+ input method modules being installed when the modules are in packages other than the main package.
H
- HOMEPAGE¶
Website where more information about the software the recipe is building can be found.
- HOST_ARCH¶
The name of the target architecture, which is normally the same as
TARGET_ARCH. The OpenEmbedded build system supports many architectures. Here is an example list of architectures supported. This list is by no means complete as the architecture is configurable:arm i586 x86_64 powerpc powerpc64 mips mipsel- HOST_CC_ARCH¶
Specifies architecture-specific compiler flags that are passed to the C compiler.
Default initialization for
HOST_CC_ARCHvaries depending on what is being built:TARGET_CC_ARCHwhen building for the targetBUILD_CC_ARCHwhen building for the build host (i.e.-native)BUILDSDK_CC_ARCHwhen building for an SDK (i.e.nativesdk-)
- HOST_OS¶
Specifies the name of the target operating system, which is normally the same as the
TARGET_OS. The variable can be set to "linux" forglibc-based systems and to "linux-musl" formusl. For ARM/EABI targets, there are also "linux-gnueabi" and "linux-musleabi" values possible.- HOST_PREFIX¶
Specifies the prefix for the cross-compile toolchain.
HOST_PREFIXis normally the same asTARGET_PREFIX.- HOST_SYS¶
Specifies the system, including the architecture and the operating system, for which the build is occurring in the context of the current recipe.
The OpenEmbedded build system automatically sets this variable based on
HOST_ARCH,HOST_VENDOR, andHOST_OSvariables.Note
You do not need to set the variable yourself.Consider these two examples:
Given a native recipe on a 32-bit x86 machine running Linux, the value is "i686-linux".
Given a recipe being built for a little-endian MIPS target running Linux, the value might be "mipsel-linux".
- HOSTTOOLS¶
A space-separated list (filter) of tools on the build host that should be allowed to be called from within build tasks. Using this filter helps reduce the possibility of host contamination. If a tool specified in the value of
HOSTTOOLSis not found on the build host, the OpenEmbedded build system produces an error and the build is not started.For additional information, see
HOSTTOOLS_NONFATAL.- HOSTTOOLS_NONFATAL¶
A space-separated list (filter) of tools on the build host that should be allowed to be called from within build tasks. Using this filter helps reduce the possibility of host contamination. Unlike
HOSTTOOLS, the OpenEmbedded build system does not produce an error if a tool specified in the value ofHOSTTOOLS_NONFATALis not found on the build host. Thus, you can useHOSTTOOLS_NONFATALto filter optional host tools.- HOST_VENDOR¶
Specifies the name of the vendor.
HOST_VENDORis normally the same asTARGET_VENDOR.
I
- ICECC_DISABLED¶
Disables or enables the
icecc(Icecream) function. For more information on this function and best practices for using this variable, see the "icecc.bbclass" section.Setting this variable to "1" in your
local.confdisables the function:ICECC_DISABLED ??= "1"To enable the function, set the variable as follows:
ICECC_DISABLED = ""- ICECC_ENV_EXEC¶
Points to the
icecc-create-envscript that you provide. This variable is used by theiceccclass. You set this variable in yourlocal.conffile.If you do not point to a script that you provide, the OpenEmbedded build system uses the default script provided by the
icecc-create-env.bbrecipe, which is a modified version and not the one that comes withicecc.- ICECC_PARALLEL_MAKE¶
Extra options passed to the
makecommand during thedo_compiletask that specify parallel compilation. This variable usually takes the form of "-jx", wherexrepresents the maximum number of parallel threadsmakecan run.Note
The options passed affect builds on all enabled machines on the network, which are machines running theiceccddaemon.If your enabled machines support multiple cores, coming up with the maximum number of parallel threads that gives you the best performance could take some experimentation since machine speed, network lag, available memory, and existing machine loads can all affect build time. Consequently, unlike the
PARALLEL_MAKEvariable, there is no rule-of-thumb for settingICECC_PARALLEL_MAKEto achieve optimal performance.If you do not set
ICECC_PARALLEL_MAKE, the build system does not use it (i.e. the system does not detect and assign the number of cores as is done withPARALLEL_MAKE).- ICECC_PATH¶
The location of the
iceccbinary. You can set this variable in yourlocal.conffile. If yourlocal.conffile does not define this variable, theiceccclass attempts to define it by locatingiceccusingwhich.- ICECC_USER_CLASS_BL¶
Identifies user classes that you do not want the Icecream distributed compile support to consider. This variable is used by the
iceccclass. You set this variable in yourlocal.conffile.When you list classes using this variable, you are "blacklisting" them from distributed compilation across remote hosts. Any classes you list will be distributed and compiled locally.
- ICECC_USER_PACKAGE_BL¶
Identifies user recipes that you do not want the Icecream distributed compile support to consider. This variable is used by the
iceccclass. You set this variable in yourlocal.conffile.When you list packages using this variable, you are "blacklisting" them from distributed compilation across remote hosts. Any packages you list will be distributed and compiled locally.
- ICECC_USER_PACKAGE_WL¶
Identifies user recipes that use an empty
PARALLEL_MAKEvariable that you want to force remote distributed compilation on using the Icecream distributed compile support. This variable is used by theiceccclass. You set this variable in yourlocal.conffile.- IMAGE_BASENAME¶
The base name of image output files. This variable defaults to the recipe name (
${PN}).- IMAGE_BOOT_FILES¶
A space-separated list of files installed into the boot partition when preparing an image using the Wic tool with the
bootimg-partitionsource plugin. By default, the files are installed under the same name as the source files. To change the installed name, separate it from the original name with a semi-colon (;). Source files need to be located inDEPLOY_DIR_IMAGE. Here are two examples:IMAGE_BOOT_FILES = "u-boot.img uImage;kernel" IMAGE_BOOT_FILES = "u-boot.${UBOOT_SUFFIX} ${KERNEL_IMAGETYPE}"Alternatively, source files can be picked up using a glob pattern. In this case, the destination file must have the same name as the base name of the source file path. To install files into a directory within the target location, pass its name after a semi-colon (;). Here are two examples:
IMAGE_BOOT_FILES = "bcm2835-bootfiles/*" IMAGE_BOOT_FILES = "bcm2835-bootfiles/*;boot/"The first example installs all files from
${DEPLOY_DIR_IMAGE}/bcm2835-bootfilesinto the root of the target partition. The second example installs the same files into abootdirectory within the target partition.You can find information on how to use the Wic tool in the "Creating Partitioned Images Using Wic" section of the Yocto Project Development Tasks Manual. Reference material for Wic is located in the "OpenEmbedded Kickstart (.wks) Reference" chapter.
- IMAGE_CLASSES¶
A list of classes that all images should inherit. You typically use this variable to specify the list of classes that register the different types of images the OpenEmbedded build system creates.
The default value for
IMAGE_CLASSESisimage_types. You can set this variable in yourlocal.confor in a distribution configuration file.For more information, see
meta/classes/image_types.bbclassin the Source Directory.- IMAGE_CMD¶
Specifies the command to create the image file for a specific image type, which corresponds to the value set set in
IMAGE_FSTYPES, (e.g.ext3,btrfs, and so forth). When setting this variable, you should use an override for the associated type. Here is an example:IMAGE_CMD_jffs2 = "mkfs.jffs2 --root=${IMAGE_ROOTFS} \ --faketime --output=${DEPLOY_DIR_IMAGE}/${IMAGE_NAME}.rootfs.jffs2 \ ${EXTRA_IMAGECMD}"You typically do not need to set this variable unless you are adding support for a new image type. For more examples on how to set this variable, see the
image_typesclass file, which ismeta/classes/image_types.bbclass.- IMAGE_DEVICE_TABLES¶
Specifies one or more files that contain custom device tables that are passed to the
makedevscommand as part of creating an image. These files list basic device nodes that should be created under/devwithin the image. IfIMAGE_DEVICE_TABLESis not set,files/device_table-minimal.txtis used, which is located byBBPATH. For details on how you should write device table files, seemeta/files/device_table-minimal.txtas an example.- IMAGE_FEATURES¶
The primary list of features to include in an image. Typically, you configure this variable in an image recipe. Although you can use this variable from your
local.conffile, which is found in the Build Directory, best practices dictate that you do not.Note
To enable extra features from outside the image recipe, use theEXTRA_IMAGE_FEATURESvariable.For a list of image features that ships with the Yocto Project, see the "Image Features" section.
For an example that shows how to customize your image by using this variable, see the "Customizing Images Using Custom
IMAGE_FEATURESandEXTRA_IMAGE_FEATURES" section in the Yocto Project Development Tasks Manual.- IMAGE_FSTYPES¶
Specifies the formats the OpenEmbedded build system uses during the build when creating the root filesystem. For example, setting
IMAGE_FSTYPESas follows causes the build system to create root filesystems using two formats:.ext3and.tar.bz2:IMAGE_FSTYPES = "ext3 tar.bz2"For the complete list of supported image formats from which you can choose, see
IMAGE_TYPES.Notes
If you add "live" to
IMAGE_FSTYPESinside an image recipe, be sure that you do so prior to the "inherit image" line of the recipe or the live image will not build.Due to the way the OpenEmbedded build system processes this variable, you cannot update its contents by using
_appendor_prepend. You must use the+=operator to add one or more options to theIMAGE_FSTYPESvariable.
- IMAGE_INSTALL¶
Used by recipes to specify the packages to install into an image through the
imageclass. Use theIMAGE_INSTALLvariable with care to avoid ordering issues.Image recipes set
IMAGE_INSTALLto specify the packages to install into an image throughimage.bbclass. Additionally, "helper" classes such as thecore-imageclass exist that can take lists used withIMAGE_FEATURESand turn them into auto-generated entries inIMAGE_INSTALLin addition to its default contents.When you use this variable, it is best to use it as follows:
IMAGE_INSTALL_append = "package-name"Be sure to include the space between the quotation character and the start of the package name or names.
Caution
When working with a
core-image-minimal-initramfsimage, do not use theIMAGE_INSTALLvariable to specify packages for installation. Instead, use thePACKAGE_INSTALLvariable, which allows the initial RAM filesystem (initramfs) recipe to use a fixed set of packages and not be affected byIMAGE_INSTALL. For information on creating an initramfs, see the "Building an Initial RAM Filesystem (initramfs) Image" section in the Yocto Project Development Tasks Manual.Using
IMAGE_INSTALLwith the+=BitBake operator within the/conf/local.conffile or from within an image recipe is not recommended. Use of this operator in these ways can cause ordering issues. Sincecore-image.bbclasssetsIMAGE_INSTALLto a default value using the?=operator, using a+=operation againstIMAGE_INSTALLresults in unexpected behavior when used withinconf/local.conf. Furthermore, the same operation from within an image recipe may or may not succeed depending on the specific situation. In both these cases, the behavior is contrary to how most users expect the+=operator to work.
- IMAGE_LINGUAS¶
Specifies the list of locales to install into the image during the root filesystem construction process. The OpenEmbedded build system automatically splits locale files, which are used for localization, into separate packages. Setting the
IMAGE_LINGUASvariable ensures that any locale packages that correspond to packages already selected for installation into the image are also installed. Here is an example:IMAGE_LINGUAS = "pt-br de-de"In this example, the build system ensures any Brazilian Portuguese and German locale files that correspond to packages in the image are installed (i.e.
*-locale-pt-brand*-locale-de-deas well as*-locale-ptand*-locale-de, since some software packages only provide locale files by language and not by country-specific language).See the
GLIBC_GENERATE_LOCALESvariable for information on generating GLIBC locales.- IMAGE_MANIFEST¶
The manifest file for the image. This file lists all the installed packages that make up the image. The file contains package information on a line-per-package basis as follows:
packagenamepackagearchversionThe
imageclass defines the manifest file as follows:IMAGE_MANIFEST = "${DEPLOY_DIR_IMAGE}/${IMAGE_NAME}.rootfs.manifest"The location is derived using the
DEPLOY_DIR_IMAGEandIMAGE_NAMEvariables. You can find information on how the image is created in the "Image Generation" section in the Yocto Project Overview and Concepts Manual.- IMAGE_NAME¶
The name of the output image files minus the extension. This variable is derived using the
IMAGE_BASENAME,MACHINE, andDATETIMEvariables:IMAGE_NAME = "${IMAGE_BASENAME}-${MACHINE}-${DATETIME}"- IMAGE_OVERHEAD_FACTOR¶
Defines a multiplier that the build system applies to the initial image size for cases when the multiplier times the returned disk usage value for the image is greater than the sum of
IMAGE_ROOTFS_SIZEandIMAGE_ROOTFS_EXTRA_SPACE. The result of the multiplier applied to the initial image size creates free disk space in the image as overhead. By default, the build process uses a multiplier of 1.3 for this variable. This default value results in 30% free disk space added to the image when this method is used to determine the final generated image size. You should be aware that post install scripts and the package management system uses disk space inside this overhead area. Consequently, the multiplier does not produce an image with all the theoretical free disk space. SeeIMAGE_ROOTFS_SIZEfor information on how the build system determines the overall image size.The default 30% free disk space typically gives the image enough room to boot and allows for basic post installs while still leaving a small amount of free disk space. If 30% free space is inadequate, you can increase the default value. For example, the following setting gives you 50% free space added to the image:
IMAGE_OVERHEAD_FACTOR = "1.5"Alternatively, you can ensure a specific amount of free disk space is added to the image by using the
IMAGE_ROOTFS_EXTRA_SPACEvariable.- IMAGE_PKGTYPE¶
Defines the package type (i.e. DEB, RPM, IPK, or TAR) used by the OpenEmbedded build system. The variable is defined appropriately by the
package_deb,package_rpm,package_ipk, orpackage_tarclass.Warning
Thepackage_tarclass is broken and is not supported. It is recommended that you do not use it.The
populate_sdk_*andimageclasses use theIMAGE_PKGTYPEfor packaging up images and SDKs.You should not set the
IMAGE_PKGTYPEmanually. Rather, the variable is set indirectly through the appropriatepackage_*class using thePACKAGE_CLASSESvariable. The OpenEmbedded build system uses the first package type (e.g. DEB, RPM, or IPK) that appears with the variableNote
Files using the.tarformat are never used as a substitute packaging format for DEB, RPM, and IPK formatted files for your image or SDK.- IMAGE_POSTPROCESS_COMMAND¶
Specifies a list of functions to call once the OpenEmbedded build system creates the final image output files. You can specify functions separated by semicolons:
IMAGE_POSTPROCESS_COMMAND += "function; ... "If you need to pass the root filesystem path to a command within the function, you can use
${IMAGE_ROOTFS}, which points to the directory that becomes the root filesystem image. See theIMAGE_ROOTFSvariable for more information.- IMAGE_PREPROCESS_COMMAND¶
Specifies a list of functions to call before the OpenEmbedded build system creates the final image output files. You can specify functions separated by semicolons:
IMAGE_PREPROCESS_COMMAND += "function; ... "If you need to pass the root filesystem path to a command within the function, you can use
${IMAGE_ROOTFS}, which points to the directory that becomes the root filesystem image. See theIMAGE_ROOTFSvariable for more information.- IMAGE_ROOTFS¶
The location of the root filesystem while it is under construction (i.e. during the
do_rootfstask). This variable is not configurable. Do not change it.- IMAGE_ROOTFS_ALIGNMENT¶
Specifies the alignment for the output image file in Kbytes. If the size of the image is not a multiple of this value, then the size is rounded up to the nearest multiple of the value. The default value is "1". See
IMAGE_ROOTFS_SIZEfor additional information.- IMAGE_ROOTFS_EXTRA_SPACE¶
Defines additional free disk space created in the image in Kbytes. By default, this variable is set to "0". This free disk space is added to the image after the build system determines the image size as described in
IMAGE_ROOTFS_SIZE.This variable is particularly useful when you want to ensure that a specific amount of free disk space is available on a device after an image is installed and running. For example, to be sure 5 Gbytes of free disk space is available, set the variable as follows:
IMAGE_ROOTFS_EXTRA_SPACE = "5242880"For example, the Yocto Project Build Appliance specifically requests 40 Gbytes of extra space with the line:
IMAGE_ROOTFS_EXTRA_SPACE = "41943040"- IMAGE_ROOTFS_SIZE¶
Defines the size in Kbytes for the generated image. The OpenEmbedded build system determines the final size for the generated image using an algorithm that takes into account the initial disk space used for the generated image, a requested size for the image, and requested additional free disk space to be added to the image. Programatically, the build system determines the final size of the generated image as follows:
if (image-du * overhead) < rootfs-size: internal-rootfs-size = rootfs-size + xspace else: internal-rootfs-size = (image-du * overhead) + xspace where: image-du = Returned value of the du command on the image. overhead = IMAGE_OVERHEAD_FACTOR rootfs-size = IMAGE_ROOTFS_SIZE internal-rootfs-size = Initial root filesystem size before any modifications. xspace = IMAGE_ROOTFS_EXTRA_SPACESee the
IMAGE_OVERHEAD_FACTORandIMAGE_ROOTFS_EXTRA_SPACEvariables for related information.- IMAGE_TYPEDEP¶
Specifies a dependency from one image type on another. Here is an example from the
image-liveclass:IMAGE_TYPEDEP_live = "ext3"In the previous example, the variable ensures that when "live" is listed with the
IMAGE_FSTYPESvariable, the OpenEmbedded build system produces anext3image first since one of the components of the live image is anext3formatted partition containing the root filesystem.- IMAGE_TYPES¶
Specifies the complete list of supported image types by default:
btrfs cpio cpio.gz cpio.lz4 cpio.lzma cpio.xz cramfs elf ext2 ext2.bz2 ext2.gz ext2.lzma ext3 ext3.gz ext4 ext4.gz hdddirect hddimg iso jffs2 jffs2.sum multiubi squashfs squashfs-lzo squashfs-xz tar tar.bz2 tar.gz tar.lz4 tar.xz ubi ubifs wic wic.bz2 wic.gz wic.lzmaFor more information about these types of images, see
meta/classes/image_types*.bbclassin the Source Directory.- INC_PR¶
Helps define the recipe revision for recipes that share a common
includefile. You can think of this variable as part of the recipe revision as set from within an include file.Suppose, for example, you have a set of recipes that are used across several projects. And, within each of those recipes the revision (its
PRvalue) is set accordingly. In this case, when the revision of those recipes changes, the burden is on you to find all those recipes and be sure that they get changed to reflect the updated version of the recipe. In this scenario, it can get complicated when recipes that are used in many places and provide common functionality are upgraded to a new revision.A more efficient way of dealing with this situation is to set the
INC_PRvariable inside theincludefiles that the recipes share and then expand theINC_PRvariable within the recipes to help define the recipe revision.The following provides an example that shows how to use the
INC_PRvariable given a commonincludefile that defines the variable. Once the variable is defined in theincludefile, you can use the variable to set thePRvalues in each recipe. You will notice that when you set a recipe'sPRyou can provide more granular revisioning by appending values to theINC_PRvariable:recipes-graphics/xorg-font/xorg-font-common.inc:INC_PR = "r2" recipes-graphics/xorg-font/encodings_1.0.4.bb:PR = "${INC_PR}.1" recipes-graphics/xorg-font/font-util_1.3.0.bb:PR = "${INC_PR}.0" recipes-graphics/xorg-font/font-alias_1.0.3.bb:PR = "${INC_PR}.3"The first line of the example establishes the baseline revision to be used for all recipes that use the
includefile. The remaining lines in the example are from individual recipes and show how thePRvalue is set.- INCOMPATIBLE_LICENSE¶
Specifies a space-separated list of license names (as they would appear in
LICENSE) that should be excluded from the build. Recipes that provide no alternatives to listed incompatible licenses are not built. Packages that are individually licensed with the specified incompatible licenses will be deleted.Note
This functionality is only regularly tested using the following setting:INCOMPATIBLE_LICENSE = "GPL-3.0 LGPL-3.0 AGPL-3.0"Although you can use other settings, you might be required to remove dependencies on or provide alternatives to components that are required to produce a functional system image.- INHERIT¶
Causes the named class or classes to be inherited globally. Anonymous functions in the class or classes are not executed for the base configuration and in each individual recipe. The OpenEmbedded build system ignores changes to
INHERITin individual recipes.For more information on
INHERIT, see the "INHERITConfiguration Directive" section in the Bitbake User Manual.- INHERIT_DISTRO¶
Lists classes that will be inherited at the distribution level. It is unlikely that you want to edit this variable.
The default value of the variable is set as follows in the
meta/conf/distro/defaultsetup.conffile:INHERIT_DISTRO ?= "debian devshell sstate license"- INHIBIT_DEFAULT_DEPS¶
Prevents the default dependencies, namely the C compiler and standard C library (libc), from being added to
DEPENDS. This variable is usually used within recipes that do not require any compilation using the C compiler.Set the variable to "1" to prevent the default dependencies from being added.
- INHIBIT_PACKAGE_DEBUG_SPLIT¶
Prevents the OpenEmbedded build system from splitting out debug information during packaging. By default, the build system splits out debugging information during the
do_packagetask. For more information on how debug information is split out, see thePACKAGE_DEBUG_SPLIT_STYLEvariable.To prevent the build system from splitting out debug information during packaging, set the
INHIBIT_PACKAGE_DEBUG_SPLITvariable as follows:INHIBIT_PACKAGE_DEBUG_SPLIT = "1"- INHIBIT_PACKAGE_STRIP¶
If set to "1", causes the build to not strip binaries in resulting packages and prevents the
-dbgpackage from containing the source files.By default, the OpenEmbedded build system strips binaries and puts the debugging symbols into
${PN}-dbg. Consequently, you should not setINHIBIT_PACKAGE_STRIPwhen you plan to debug in general.- INITRAMFS_FSTYPES¶
Defines the format for the output image of an initial RAM filesystem (initramfs), which is used during boot. Supported formats are the same as those supported by the
IMAGE_FSTYPESvariable.The default value of this variable, which is set in the
meta/conf/bitbake.confconfiguration file in the Source Directory, is "cpio.gz". The Linux kernel's initramfs mechanism, as opposed to the initial RAM filesystem initrd mechanism, expects an optionally compressed cpio archive.- INITRAMFS_IMAGE¶
Specifies the
PROVIDESname of an image recipe that is used to build an initial RAM filesystem (initramfs) image. In other words, theINITRAMFS_IMAGEvariable causes an additional recipe to be built as a dependency to whatever root filesystem recipe you might be using (e.g.core-image-sato). The initramfs image recipe you provide should setIMAGE_FSTYPEStoINITRAMFS_FSTYPES.An initramfs image provides a temporary root filesystem used for early system initialization (e.g. loading of modules needed to locate and mount the "real" root filesystem).
Note
See themeta/recipes-core/images/core-image-minimal-initramfs.bbrecipe in the Source Directory for an example initramfs recipe. To select this sample recipe as the one built to provide the initramfs image, setINITRAMFS_IMAGEto "core-image-minimal-initramfs".You can also find more information by referencing the
meta-poky/conf/local.conf.sample.extendedconfiguration file in the Source Directory, theimageclass, and thekernelclass to see how to use theINITRAMFS_IMAGEvariable.If
INITRAMFS_IMAGEis empty, which is the default, then no initramfs image is built.For more information, you can also see the
INITRAMFS_IMAGE_BUNDLEvariable, which allows the generated image to be bundled inside the kernel image. Additionally, for information on creating an initramfs image, see the "Building an Initial RAM Filesystem (initramfs) Image" section in the Yocto Project Development Tasks Manual.- INITRAMFS_IMAGE_BUNDLE¶
Controls whether or not the image recipe specified by
INITRAMFS_IMAGEis run through an extra pass (do_bundle_initramfs) during kernel compilation in order to build a single binary that contains both the kernel image and the initial RAM filesystem (initramfs) image. This makes use of theCONFIG_INITRAMFS_SOURCEkernel feature.Note
Using an extra compilation pass to bundle the initramfs avoids a circular dependency between the kernel recipe and the initramfs recipe should the initramfs include kernel modules. Should that be the case, the initramfs recipe depends on the kernel for the kernel modules, and the kernel depends on the initramfs recipe since the initramfs is bundled inside the kernel image.The combined binary is deposited into the
tmp/deploydirectory, which is part of the Build Directory.Setting the variable to "1" in a configuration file causes the OpenEmbedded build system to generate a kernel image with the initramfs specified in
INITRAMFS_IMAGEbundled within:INITRAMFS_IMAGE_BUNDLE = "1"By default, the
kernelclass sets this variable to a null string as follows:INITRAMFS_IMAGE_BUNDLE ?= ""Note
You must set theINITRAMFS_IMAGE_BUNDLEvariable in a configuration file. You cannot set the variable in a recipe file.See the
local.conf.sample.extendedfile for additional information. Also, for information on creating an initramfs, see the "Building an Initial RAM Filesystem (initramfs) Image" section in the Yocto Project Development Tasks Manual.- INITRAMFS_LINK_NAME¶
The link name of the initial RAM filesystem image. This variable is set in the
meta/classes/kernel-artifact-names.bbclassfile as follows:INITRAMFS_LINK_NAME ?= "initramfs-${KERNEL_ARTIFACT_LINK_NAME}"The value of the
KERNEL_ARTIFACT_LINK_NAMEvariable, which is set in the same file, has the following value:KERNEL_ARTIFACT_LINK_NAME ?= "${MACHINE}"See the
MACHINEvariable for additional information.- INITRAMFS_NAME¶
The base name of the initial RAM filesystem image. This variable is set in the
meta/classes/kernel-artifact-names.bbclassfile as follows:INITRAMFS_NAME ?= "initramfs-${KERNEL_ARTIFACT_NAME}"The value of the
KERNEL_ARTIFACT_NAMEvariable, which is set in the same file, has the following value:KERNEL_ARTIFACT_NAME ?= "${PKGE}-${PKGV}-${PKGR}-${MACHINE}${IMAGE_VERSION_SUFFIX}"- INITRD¶
Indicates list of filesystem images to concatenate and use as an initial RAM disk (
initrd).The
INITRDvariable is an optional variable used with theimage-liveclass.- INITRD_IMAGE¶
When building a "live" bootable image (i.e. when
IMAGE_FSTYPEScontains "live"),INITRD_IMAGEspecifies the image recipe that should be built to provide the initial RAM disk image. The default value is "core-image-minimal-initramfs".See the
image-liveclass for more information.- INITSCRIPT_NAME¶
The filename of the initialization script as installed to
${sysconfdir}/init.d.This variable is used in recipes when using
update-rc.d.bbclass. The variable is mandatory.- INITSCRIPT_PACKAGES¶
A list of the packages that contain initscripts. If multiple packages are specified, you need to append the package name to the other
INITSCRIPT_*as an override.This variable is used in recipes when using
update-rc.d.bbclass. The variable is optional and defaults to thePNvariable.- INITSCRIPT_PARAMS¶
Specifies the options to pass to
update-rc.d. Here is an example:INITSCRIPT_PARAMS = "start 99 5 2 . stop 20 0 1 6 ."In this example, the script has a runlevel of 99, starts the script in initlevels 2 and 5, and stops the script in levels 0, 1 and 6.
The variable's default value is "defaults", which is set in the
update-rc.dclass.The value in
INITSCRIPT_PARAMSis passed through to theupdate-rc.dcommand. For more information on valid parameters, please see theupdate-rc.dmanual page at http://www.tin.org/bin/man.cgi?section=8&topic=update-rc.d.- INSANE_SKIP¶
Specifies the QA checks to skip for a specific package within a recipe. For example, to skip the check for symbolic link
.sofiles in the main package of a recipe, add the following to the recipe. The package name override must be used, which in this example is${PN}:INSANE_SKIP_${PN} += "dev-so"See the "
insane.bbclass" section for a list of the valid QA checks you can specify using this variable.- INSTALL_TIMEZONE_FILE¶
By default, the
tzdatarecipe packages an/etc/timezonefile. Set theINSTALL_TIMEZONE_FILEvariable to "0" at the configuration level to disable this behavior.- IPK_FEED_URIS¶
When the IPK backend is in use and package management is enabled on the target, you can use this variable to set up
opkgin the target image to point to package feeds on a nominated server. Once the feed is established, you can perform installations or upgrades using the package manager at runtime.
K
- KARCH¶
Defines the kernel architecture used when assembling the configuration. Architectures supported for this release are:
powerpc i386 x86_64 arm qemu mipsYou define the
KARCHvariable in the BSP Descriptions.- KBRANCH¶
A regular expression used by the build process to explicitly identify the kernel branch that is validated, patched, and configured during a build. You must set this variable to ensure the exact kernel branch you want is being used by the build process.
Values for this variable are set in the kernel's recipe file and the kernel's append file. For example, if you are using the
linux-yocto_4.12kernel, the kernel recipe file is themeta/recipes-kernel/linux/linux-yocto_4.12.bbfile.KBRANCHis set as follows in that kernel recipe file:KBRANCH ?= "standard/base"This variable is also used from the kernel's append file to identify the kernel branch specific to a particular machine or target hardware. Continuing with the previous kernel example, the kernel's append file (i.e.
linux-yocto_4.12.bbappend) is located in the BSP layer for a given machine. For example, the append file for the Beaglebone, EdgeRouter, and generic versions of both 32 and 64-bit IA machines (meta-yocto-bsp) is namedmeta-yocto-bsp/recipes-kernel/linux/linux-yocto_4.12.bbappend. Here are the related statements from that append file:KBRANCH_genericx86 = "standard/base" KBRANCH_genericx86-64 = "standard/base" KBRANCH_edgerouter = "standard/edgerouter" KBRANCH_beaglebone = "standard/beaglebone" KBRANCH_mpc8315e-rdb = "standard/fsl-mpc8315e-rdb"The
KBRANCHstatements identify the kernel branch to use when building for each supported BSP.- KBUILD_DEFCONFIG¶
When used with the
kernel-yoctoclass, specifies an "in-tree" kernel configuration file for use during a kernel build.Typically, when using a
defconfigto configure a kernel during a build, you place the file in your layer in the same manner as you would place patch files and configuration fragment files (i.e. "out-of-tree"). However, if you want to use adefconfigfile that is part of the kernel tree (i.e. "in-tree"), you can use theKBUILD_DEFCONFIGvariable and append theKMACHINEvariable to point to thedefconfigfile.To use the variable, set it in the append file for your kernel recipe using the following form:
KBUILD_DEFCONFIG_KMACHINE?=defconfig_fileHere is an example from a "raspberrypi2"
KMACHINEbuild that uses adefconfigfile named "bcm2709_defconfig":KBUILD_DEFCONFIG_raspberrypi2 = "bcm2709_defconfig"As an alternative, you can use the following within your append file:
KBUILD_DEFCONFIG_pn-linux-yocto ?=defconfig_fileFor more information on how to use the
KBUILD_DEFCONFIGvariable, see the "Using an "In-Tree"defconfigFile" section in the Yocto Project Linux Kernel Development Manual.- KERNEL_ALT_IMAGETYPE¶
Specifies an alternate kernel image type for creation in addition to the kernel image type specified using the
KERNEL_IMAGETYPEvariable.- KERNEL_ARTIFACT_NAME¶
Specifies the name of all of the build artifacts. You can change the name of the artifacts by changing the
KERNEL_ARTIFACT_NAMEvariable.The value of
KERNEL_ARTIFACT_NAME, which is set in themeta/classes/kernel-artifact-names.bbclassfile, has the following default value:KERNEL_ARTIFACT_NAME ?= "${PKGE}-${PKGV}-${PKGR}-${MACHINE}${IMAGE_VERSION_SUFFIX}"See the
PKGE,PKGV,PKGR, andMACHINEvariables for additional information.- KERNEL_CLASSES¶
A list of classes defining kernel image types that the
kernelclass should inherit. You typically append this variable to enable extended image types. An example is the "kernel-fitimage", which enables fitImage support and resides inmeta/classes/kernel-fitimage.bbclass. You can register custom kernel image types with thekernelclass using this variable.- KERNEL_DEVICETREE¶
Specifies the name of the generated Linux kernel device tree (i.e. the
.dtb) file.Note
Legacy support exists for specifying the full path to the device tree. However, providing just the.dtbfile is preferred.In order to use this variable, you must have the include files in your kernel recipe:
require recipes-kernel/linux/linux-dtb.incor
require recipes-kernel/linux/linux-yocto.inc- KERNEL_DTB_LINK_NAME¶
The link name of the kernel device tree binary (DTB). This variable is set in the
meta/classes/kernel-artifact-names.bbclassfile as follows:KERNEL_DTB_LINK_NAME ?= "${KERNEL_ARTIFACT_LINK_NAME}"The value of the
KERNEL_ARTIFACT_LINK_NAMEvariable, which is set in the same file, has the following value:KERNEL_ARTIFACT_LINK_NAME ?= "${MACHINE}"See the
MACHINEvariable for additional information.- KERNEL_DTB_NAME¶
The base name of the kernel device tree binary (DTB). This variable is set in the
meta/classes/kernel-artifact-names.bbclassfile as follows:KERNEL_DTB_NAME ?= "${KERNEL_ARTIFACT_NAME}"The value of the
KERNEL_ARTIFACT_NAMEvariable, which is set in the same file, has the following value:KERNEL_ARTIFACT_NAME ?= "${PKGE}-${PKGV}-${PKGR}-${MACHINE}${IMAGE_VERSION_SUFFIX}"- KERNEL_EXTRA_ARGS¶
Specifies additional
makecommand-line arguments the OpenEmbedded build system passes on when compiling the kernel.- KERNEL_FEATURES¶
Includes additional kernel metadata. In the OpenEmbedded build system, the default Board Support Packages (BSPs) Metadata is provided through the
KMACHINEandKBRANCHvariables. You can use theKERNEL_FEATURESvariable from within the kernel recipe or kernel append file to further add metadata for all BSPs or specific BSPs.The metadata you add through this variable includes config fragments and features descriptions, which usually includes patches as well as config fragments. You typically override the
KERNEL_FEATURESvariable for a specific machine. In this way, you can provide validated, but optional, sets of kernel configurations and features.For example, the following example from the
linux-yocto-rt_4.12kernel recipe adds "netfilter" and "taskstats" features to all BSPs as well as "virtio" configurations to all QEMU machines. The last two statements add specific configurations to targeted machine types:KERNEL_EXTRA_FEATURES ?= "features/netfilter/netfilter.scc features/taskstats/taskstats.scc" KERNEL_FEATURES_append = " ${KERNEL_EXTRA_FEATURES}" KERNEL_FEATURES_append_qemuall = " cfg/virtio.scc" KERNEL_FEATURES_append_qemux86 = " cfg/sound.scc cfg/paravirt_kvm.scc" KERNEL_FEATURES_append_qemux86-64 = " cfg/sound.scc"- KERNEL_FIT_LINK_NAME¶
The link name of the kernel flattened image tree (FIT) image. This variable is set in the
meta/classes/kernel-artifact-names.bbclassfile as follows:KERNEL_FIT_LINK_NAME ?= "${KERNEL_ARTIFACT_LINK_NAME}"The value of the
KERNEL_ARTIFACT_LINK_NAMEvariable, which is set in the same file, has the following value:KERNEL_ARTIFACT_LINK_NAME ?= "${MACHINE}"See the
MACHINEvariable for additional information.- KERNEL_FIT_NAME¶
The base name of the kernel flattened image tree (FIT) image. This variable is set in the
meta/classes/kernel-artifact-names.bbclassfile as follows:KERNEL_FIT_NAME ?= "${KERNEL_ARTIFACT_NAME}"The value of the
KERNEL_ARTIFACT_NAMEvariable, which is set in the same file, has the following value:KERNEL_ARTIFACT_NAME ?= "${PKGE}-${PKGV}-${PKGR}-${MACHINE}${IMAGE_VERSION_SUFFIX}"- KERNEL_IMAGE_LINK_NAME¶
The link name for the kernel image. This variable is set in the
meta/classes/kernel-artifact-names.bbclassfile as follows:KERNEL_IMAGE_LINK_NAME ?= "${KERNEL_ARTIFACT_LINK_NAME}"The value of the
KERNEL_ARTIFACT_LINK_NAMEvariable, which is set in the same file, has the following value:KERNEL_ARTIFACT_LINK_NAME ?= "${MACHINE}"See the
MACHINEvariable for additional information.- KERNEL_IMAGE_MAXSIZE¶
Specifies the maximum size of the kernel image file in kilobytes. If
KERNEL_IMAGE_MAXSIZEis set, the size of the kernel image file is checked against the set value during thedo_sizechecktask. The task fails if the kernel image file is larger than the setting.KERNEL_IMAGE_MAXSIZEis useful for target devices that have a limited amount of space in which the kernel image must be stored.By default, this variable is not set, which means the size of the kernel image is not checked.
- KERNEL_IMAGE_NAME¶
The base name of the kernel image. This variable is set in the
meta/classes/kernel-artifact-names.bbclassfile as follows:KERNEL_IMAGE_NAME ?= "${KERNEL_ARTIFACT_NAME}"The value of the
KERNEL_ARTIFACT_NAMEvariable, which is set in the same file, has the following value:KERNEL_ARTIFACT_NAME ?= "${PKGE}-${PKGV}-${PKGR}-${MACHINE}${IMAGE_VERSION_SUFFIX}"- KERNEL_IMAGETYPE¶
The type of kernel to build for a device, usually set by the machine configuration files and defaults to "zImage". This variable is used when building the kernel and is passed to
makeas the target to build.If you want to build an alternate kernel image type, use the
KERNEL_ALT_IMAGETYPEvariable.- KERNEL_MODULE_AUTOLOAD¶
Lists kernel modules that need to be auto-loaded during boot.
Note
This variable replaces the deprecatedmodule_autoloadvariable.You can use the
KERNEL_MODULE_AUTOLOADvariable anywhere that it can be recognized by the kernel recipe or by an out-of-tree kernel module recipe (e.g. a machine configuration file, a distribution configuration file, an append file for the recipe, or the recipe itself).Specify it as follows:
KERNEL_MODULE_AUTOLOAD += "module_name1module_name2module_name3"Including
KERNEL_MODULE_AUTOLOADcauses the OpenEmbedded build system to populate the/etc/modules-load.d/modname.conffile with the list of modules to be auto-loaded on boot. The modules appear one-per-line in the file. Here is an example of the most common use case:KERNEL_MODULE_AUTOLOAD += "module_name"For information on how to populate the
modname.conffile withmodprobe.dsyntax lines, see theKERNEL_MODULE_PROBECONFvariable.- KERNEL_MODULE_PROBECONF¶
Provides a list of modules for which the OpenEmbedded build system expects to find
module_conf_modnamevalues that specify configuration for each of the modules. For information on how to provide those module configurations, see themodule_conf_*variable.- KERNEL_PATH¶
The location of the kernel sources. This variable is set to the value of the
STAGING_KERNEL_DIRwithin themoduleclass. For information on how this variable is used, see the "Incorporating Out-of-Tree Modules" section in the Yocto Project Linux Kernel Development Manual.To help maximize compatibility with out-of-tree drivers used to build modules, the OpenEmbedded build system also recognizes and uses the
KERNEL_SRCvariable, which is identical to theKERNEL_PATHvariable. Both variables are common variables used by external Makefiles to point to the kernel source directory.- KERNEL_SRC¶
The location of the kernel sources. This variable is set to the value of the
STAGING_KERNEL_DIRwithin themoduleclass. For information on how this variable is used, see the "Incorporating Out-of-Tree Modules" section in the Yocto Project Linux Kernel Development Manual.To help maximize compatibility with out-of-tree drivers used to build modules, the OpenEmbedded build system also recognizes and uses the
KERNEL_PATHvariable, which is identical to theKERNEL_SRCvariable. Both variables are common variables used by external Makefiles to point to the kernel source directory.- KERNEL_VERSION¶
Specifies the version of the kernel as extracted from
version.horutsrelease.hwithin the kernel sources. Effects of setting this variable do not take affect until the kernel has been configured. Consequently, attempting to refer to this variable in contexts prior to configuration will not work.- KERNELDEPMODDEPEND¶
Specifies whether the data referenced through
PKGDATA_DIRis needed or not. TheKERNELDEPMODDEPENDdoes not control whether or not that data exists, but simply whether or not it is used. If you do not need to use the data, set theKERNELDEPMODDEPENDvariable in yourinitramfsrecipe. Setting the variable there when the data is not needed avoids a potential dependency loop.- KFEATURE_DESCRIPTION¶
Provides a short description of a configuration fragment. You use this variable in the
.sccfile that describes a configuration fragment file. Here is the variable used in a file namedsmp.sccto describe SMP being enabled:define KFEATURE_DESCRIPTION "Enable SMP"- KMACHINE¶
The machine as known by the kernel. Sometimes the machine name used by the kernel does not match the machine name used by the OpenEmbedded build system. For example, the machine name that the OpenEmbedded build system understands as
core2-32-intel-commongoes by a different name in the Linux Yocto kernel. The kernel understands that machine asintel-core2-32. For cases like these, theKMACHINEvariable maps the kernel machine name to the OpenEmbedded build system machine name.These mappings between different names occur in the Yocto Linux Kernel's
metabranch. As an example take a look in thecommon/recipes-kernel/linux/linux-yocto_3.19.bbappendfile:LINUX_VERSION_core2-32-intel-common = "3.19.0" COMPATIBLE_MACHINE_core2-32-intel-common = "${MACHINE}" SRCREV_meta_core2-32-intel-common = "8897ef68b30e7426bc1d39895e71fb155d694974" SRCREV_machine_core2-32-intel-common = "43b9eced9ba8a57add36af07736344dcc383f711" KMACHINE_core2-32-intel-common = "intel-core2-32" KBRANCH_core2-32-intel-common = "standard/base" KERNEL_FEATURES_append_core2-32-intel-common = "${KERNEL_FEATURES_INTEL_COMMON}"The
KMACHINEstatement says that the kernel understands the machine name as "intel-core2-32". However, the OpenEmbedded build system understands the machine as "core2-32-intel-common".- KTYPE¶
Defines the kernel type to be used in assembling the configuration. The linux-yocto recipes define "standard", "tiny", and "preempt-rt" kernel types. See the "Kernel Types" section in the Yocto Project Linux Kernel Development Manual for more information on kernel types.
You define the
KTYPEvariable in the BSP Descriptions. The value you use must match the value used for theLINUX_KERNEL_TYPEvalue used by the kernel recipe.
L
- LABELS¶
Provides a list of targets for automatic configuration.
See the
grub-eficlass for more information on how this variable is used.- LAYERDEPENDS¶
Lists the layers, separated by spaces, on which this recipe depends. Optionally, you can specify a specific layer version for a dependency by adding it to the end of the layer name. Here is an example:
LAYERDEPENDS_mylayer = "anotherlayer (=3)"In this previous example, version 3 of "anotherlayer" is compared against
LAYERVERSION_anotherlayer.An error is produced if any dependency is missing or the version numbers (if specified) do not match exactly. This variable is used in the
conf/layer.conffile and must be suffixed with the name of the specific layer (e.g.LAYERDEPENDS_mylayer).- LAYERDIR¶
When used inside the
layer.confconfiguration file, this variable provides the path of the current layer. This variable is not available outside oflayer.confand references are expanded immediately when parsing of the file completes.- LAYERRECOMMENDS¶
Lists the layers, separated by spaces, recommended for use with this layer.
Optionally, you can specify a specific layer version for a recommendation by adding the version to the end of the layer name. Here is an example:
LAYERRECOMMENDS_mylayer = "anotherlayer (=3)"In this previous example, version 3 of "anotherlayer" is compared against
LAYERVERSION_anotherlayer.This variable is used in the
conf/layer.conffile and must be suffixed with the name of the specific layer (e.g.LAYERRECOMMENDS_mylayer).- LAYERSERIES_COMPAT¶
Lists the versions of the OpenEmbedded-Core for which a layer is compatible. Using the
LAYERSERIES_COMPATvariable allows the layer maintainer to indicate which combinations of the layer and OE-Core can be expected to work. The variable gives the system a way to detect when a layer has not been tested with new releases of OE-Core (e.g. the layer is not maintained).To specify the OE-Core versions for which a layer is compatible, use this variable in your layer's
conf/layer.confconfiguration file. For the list, use the Yocto Project Release Name (e.g. thud). To specify multiple OE-Core versions for the layer, use a space-separated list:LAYERSERIES_COMPAT_layer_root_name= "thud sumo"Note
SettingLAYERSERIES_COMPATis required by the Yocto Project Compatible version 2 standard. The OpenEmbedded build system produces a warning if the variable is not set for any given layer.See the "Creating Your Own Layer" section in the Yocto Project Development Tasks Manual.
- LAYERVERSION¶
Optionally specifies the version of a layer as a single number. You can use this within
LAYERDEPENDSfor another layer in order to depend on a specific version of the layer. This variable is used in theconf/layer.conffile and must be suffixed with the name of the specific layer (e.g.LAYERVERSION_mylayer).- LD¶
The minimal command and arguments used to run the linker.
- LDFLAGS¶
Specifies the flags to pass to the linker. This variable is exported to an environment variable and thus made visible to the software being built during the compilation step.
Default initialization for
LDFLAGSvaries depending on what is being built:TARGET_LDFLAGSwhen building for the targetBUILD_LDFLAGSwhen building for the build host (i.e.-native)BUILDSDK_LDFLAGSwhen building for an SDK (i.e.nativesdk-)
- LEAD_SONAME¶
Specifies the lead (or primary) compiled library file (i.e.
.so) that thedebianclass applies its naming policy to given a recipe that packages multiple libraries.This variable works in conjunction with the
debianclass.- LIC_FILES_CHKSUM¶
Checksums of the license text in the recipe source code.
This variable tracks changes in license text of the source code files. If the license text is changed, it will trigger a build failure, which gives the developer an opportunity to review any license change.
This variable must be defined for all recipes (unless
LICENSEis set to "CLOSED").For more information, see the "Tracking License Changes" section in the Yocto Project Development Tasks Manual.
- LICENSE¶
The list of source licenses for the recipe. Follow these rules:
Do not use spaces within individual license names.
Separate license names using | (pipe) when there is a choice between licenses.
Separate license names using & (ampersand) when multiple licenses exist that cover different parts of the source.
You can use spaces between license names.
For standard licenses, use the names of the files in
meta/files/common-licenses/or theSPDXLICENSEMAPflag names defined inmeta/conf/licenses.conf.
Here are some examples:
LICENSE = "LGPLv2.1 | GPLv3" LICENSE = "MPL-1 & LGPLv2.1" LICENSE = "GPLv2+"The first example is from the recipes for Qt, which the user may choose to distribute under either the LGPL version 2.1 or GPL version 3. The second example is from Cairo where two licenses cover different parts of the source code. The final example is from
sysstat, which presents a single license.You can also specify licenses on a per-package basis to handle situations where components of the output have different licenses. For example, a piece of software whose code is licensed under GPLv2 but has accompanying documentation licensed under the GNU Free Documentation License 1.2 could be specified as follows:
LICENSE = "GFDL-1.2 & GPLv2" LICENSE_${PN} = "GPLv2" LICENSE_${PN}-doc = "GFDL-1.2"- LICENSE_CREATE_PACKAGE¶
Setting
LICENSE_CREATE_PACKAGEto "1" causes the OpenEmbedded build system to create an extra package (i.e.${PN}-lic) for each recipe and to add those packages to theRRECOMMENDS_${PN}.The
${PN}-licpackage installs a directory in/usr/share/licensesnamed${PN}, which is the recipe's base name, and installs files in that directory that contain license and copyright information (i.e. copies of the appropriate license files frommeta/common-licensesthat match the licenses specified in theLICENSEvariable of the recipe metadata and copies of files marked inLIC_FILES_CHKSUMas containing license text).For related information on providing license text, see the
COPY_LIC_DIRSvariable, theCOPY_LIC_MANIFESTvariable, and the "Providing License Text" section in the Yocto Project Development Tasks Manual.- LICENSE_FLAGS¶
Specifies additional flags for a recipe you must whitelist through
LICENSE_FLAGS_WHITELISTin order to allow the recipe to be built. When providing multiple flags, separate them with spaces.This value is independent of
LICENSEand is typically used to mark recipes that might require additional licenses in order to be used in a commercial product. For more information, see the "Enabling Commercially Licensed Recipes" section in the Yocto Project Development Tasks Manual.- LICENSE_FLAGS_WHITELIST¶
Lists license flags that when specified in
LICENSE_FLAGSwithin a recipe should not prevent that recipe from being built. This practice is otherwise known as "whitelisting" license flags. For more information, see the "Enabling Commercially Licensed Recipes" section in the Yocto Project Development Tasks Manual.- LICENSE_PATH¶
Path to additional licenses used during the build. By default, the OpenEmbedded build system uses
COMMON_LICENSE_DIRto define the directory that holds common license text used during the build. TheLICENSE_PATHvariable allows you to extend that location to other areas that have additional licenses:LICENSE_PATH += "path-to-additional-common-licenses"- LINUX_KERNEL_TYPE¶
Defines the kernel type to be used in assembling the configuration. The linux-yocto recipes define "standard", "tiny", and "preempt-rt" kernel types. See the "Kernel Types" section in the Yocto Project Linux Kernel Development Manual for more information on kernel types.
If you do not specify a
LINUX_KERNEL_TYPE, it defaults to "standard". Together withKMACHINE, theLINUX_KERNEL_TYPEvariable defines the search arguments used by the kernel tools to find the appropriate description within the kernel Metadata with which to build out the sources and configuration.- LINUX_VERSION¶
The Linux version from
kernel.orgon which the Linux kernel image being built using the OpenEmbedded build system is based. You define this variable in the kernel recipe. For example, thelinux-yocto-3.4.bbkernel recipe found inmeta/recipes-kernel/linuxdefines the variables as follows:LINUX_VERSION ?= "3.4.24"The
LINUX_VERSIONvariable is used to definePVfor the recipe:PV = "${LINUX_VERSION}+git${SRCPV}"- LINUX_VERSION_EXTENSION¶
A string extension compiled into the version string of the Linux kernel built with the OpenEmbedded build system. You define this variable in the kernel recipe. For example, the linux-yocto kernel recipes all define the variable as follows:
LINUX_VERSION_EXTENSION ?= "-yocto-${LINUX_KERNEL_TYPE}"Defining this variable essentially sets the Linux kernel configuration item
CONFIG_LOCALVERSION, which is visible through theunamecommand. Here is an example that shows the extension assuming it was set as previously shown:$ uname -r 3.7.0-rc8-custom- LOG_DIR¶
Specifies the directory to which the OpenEmbedded build system writes overall log files. The default directory is
${TMPDIR}/log.For the directory containing logs specific to each task, see the
Tvariable.
M
- MACHINE¶
Specifies the target device for which the image is built. You define
MACHINEin thelocal.conffile found in the Build Directory. By default,MACHINEis set to "qemux86", which is an x86-based architecture machine to be emulated using QEMU:MACHINE ?= "qemux86"The variable corresponds to a machine configuration file of the same name, through which machine-specific configurations are set. Thus, when
MACHINEis set to "qemux86" there exists the correspondingqemux86.confmachine configuration file, which can be found in the Source Directory inmeta/conf/machine.The list of machines supported by the Yocto Project as shipped include the following:
MACHINE ?= "qemuarm" MACHINE ?= "qemuarm64" MACHINE ?= "qemumips" MACHINE ?= "qemumips64" MACHINE ?= "qemuppc" MACHINE ?= "qemux86" MACHINE ?= "qemux86-64" MACHINE ?= "genericx86" MACHINE ?= "genericx86-64" MACHINE ?= "beaglebone" MACHINE ?= "mpc8315e-rdb" MACHINE ?= "edgerouter"The last five are Yocto Project reference hardware boards, which are provided in the
meta-yocto-bsplayer.Note
Adding additional Board Support Package (BSP) layers to your configuration adds new possible settings forMACHINE.- MACHINE_ARCH¶
Specifies the name of the machine-specific architecture. This variable is set automatically from
MACHINEorTUNE_PKGARCH. You should not hand-edit theMACHINE_ARCHvariable.- MACHINE_ESSENTIAL_EXTRA_RDEPENDS¶
A list of required machine-specific packages to install as part of the image being built. The build process depends on these packages being present. Furthermore, because this is a "machine-essential" variable, the list of packages are essential for the machine to boot. The impact of this variable affects images based on
packagegroup-core-boot, including thecore-image-minimalimage.This variable is similar to the
MACHINE_ESSENTIAL_EXTRA_RRECOMMENDSvariable with the exception that the image being built has a build dependency on the variable's list of packages. In other words, the image will not build if a file in this list is not found.As an example, suppose the machine for which you are building requires
example-initto be run during boot to initialize the hardware. In this case, you would use the following in the machine's.confconfiguration file:MACHINE_ESSENTIAL_EXTRA_RDEPENDS += "example-init"- MACHINE_ESSENTIAL_EXTRA_RRECOMMENDS¶
A list of recommended machine-specific packages to install as part of the image being built. The build process does not depend on these packages being present. However, because this is a "machine-essential" variable, the list of packages are essential for the machine to boot. The impact of this variable affects images based on
packagegroup-core-boot, including thecore-image-minimalimage.This variable is similar to the
MACHINE_ESSENTIAL_EXTRA_RDEPENDSvariable with the exception that the image being built does not have a build dependency on the variable's list of packages. In other words, the image will still build if a package in this list is not found. Typically, this variable is used to handle essential kernel modules, whose functionality may be selected to be built into the kernel rather than as a module, in which case a package will not be produced.Consider an example where you have a custom kernel where a specific touchscreen driver is required for the machine to be usable. However, the driver can be built as a module or into the kernel depending on the kernel configuration. If the driver is built as a module, you want it to be installed. But, when the driver is built into the kernel, you still want the build to succeed. This variable sets up a "recommends" relationship so that in the latter case, the build will not fail due to the missing package. To accomplish this, assuming the package for the module was called
kernel-module-ab123, you would use the following in the machine's.confconfiguration file:MACHINE_ESSENTIAL_EXTRA_RRECOMMENDS += "kernel-module-ab123"Note
In this example, thekernel-module-ab123recipe needs to explicitly set itsPACKAGESvariable to ensure that BitBake does not use the kernel recipe'sPACKAGES_DYNAMICvariable to satisfy the dependency.Some examples of these machine essentials are flash, screen, keyboard, mouse, or touchscreen drivers (depending on the machine).
- MACHINE_EXTRA_RDEPENDS¶
A list of machine-specific packages to install as part of the image being built that are not essential for the machine to boot. However, the build process for more fully-featured images depends on the packages being present.
This variable affects all images based on
packagegroup-base, which does not include thecore-image-minimalorcore-image-full-cmdlineimages.The variable is similar to the
MACHINE_EXTRA_RRECOMMENDSvariable with the exception that the image being built has a build dependency on the variable's list of packages. In other words, the image will not build if a file in this list is not found.An example is a machine that has WiFi capability but is not essential for the machine to boot the image. However, if you are building a more fully-featured image, you want to enable the WiFi. The package containing the firmware for the WiFi hardware is always expected to exist, so it is acceptable for the build process to depend upon finding the package. In this case, assuming the package for the firmware was called
wifidriver-firmware, you would use the following in the.conffile for the machine:MACHINE_EXTRA_RDEPENDS += "wifidriver-firmware"- MACHINE_EXTRA_RRECOMMENDS¶
A list of machine-specific packages to install as part of the image being built that are not essential for booting the machine. The image being built has no build dependency on this list of packages.
This variable affects only images based on
packagegroup-base, which does not include thecore-image-minimalorcore-image-full-cmdlineimages.This variable is similar to the
MACHINE_EXTRA_RDEPENDSvariable with the exception that the image being built does not have a build dependency on the variable's list of packages. In other words, the image will build if a file in this list is not found.An example is a machine that has WiFi capability but is not essential For the machine to boot the image. However, if you are building a more fully-featured image, you want to enable WiFi. In this case, the package containing the WiFi kernel module will not be produced if the WiFi driver is built into the kernel, in which case you still want the build to succeed instead of failing as a result of the package not being found. To accomplish this, assuming the package for the module was called
kernel-module-examplewifi, you would use the following in the.conffile for the machine:MACHINE_EXTRA_RRECOMMENDS += "kernel-module-examplewifi"- MACHINE_FEATURES¶
Specifies the list of hardware features the
MACHINEis capable of supporting. For related information on enabling features, see theDISTRO_FEATURES,COMBINED_FEATURES, andIMAGE_FEATURESvariables.For a list of hardware features supported by the Yocto Project as shipped, see the "Machine Features" section.
- MACHINE_FEATURES_BACKFILL¶
Features to be added to
MACHINE_FEATURESif not also present inMACHINE_FEATURES_BACKFILL_CONSIDERED.This variable is set in the
meta/conf/bitbake.conffile. It is not intended to be user-configurable. It is best to just reference the variable to see which machine features are being backfilled for all machine configurations. See the "Feature Backfilling" section for more information.- MACHINE_FEATURES_BACKFILL_CONSIDERED¶
Features from
MACHINE_FEATURES_BACKFILLthat should not be backfilled (i.e. added toMACHINE_FEATURES) during the build. See the "Feature Backfilling" section for more information.- MACHINEOVERRIDES¶
A colon-separated list of overrides that apply to the current machine. By default, this list includes the value of
MACHINE.You can extend
MACHINEOVERRIDESto add extra overrides that should apply to a machine. For example, all machines emulated in QEMU (e.g.qemuarm,qemux86, and so forth) include a file namedmeta/conf/machine/include/qemu.incthat prepends the following override toMACHINEOVERRIDES:MACHINEOVERRIDES =. "qemuall:"This override allows variables to be overriden for all machines emulated in QEMU, like in the following example from the
connman-confrecipe:SRC_URI_append_qemuall = "file://wired.config \ file://wired-setup \ "The underlying mechanism behind
MACHINEOVERRIDESis simply that it is included in the default value ofOVERRIDES.- MAINTAINER¶
The email address of the distribution maintainer.
- MIRRORS¶
Specifies additional paths from which the OpenEmbedded build system gets source code. When the build system searches for source code, it first tries the local download directory. If that location fails, the build system tries locations defined by
PREMIRRORS, the upstream source, and then locations specified byMIRRORSin that order.Assuming your distribution (
DISTRO) is "poky", the default value forMIRRORSis defined in theconf/distro/poky.conffile in themeta-pokyGit repository.- MLPREFIX¶
Specifies a prefix has been added to
PNto create a special version of a recipe or package (i.e. a Multilib version). The variable is used in places where the prefix needs to be added to or removed from a the name (e.g. theBPNvariable).MLPREFIXgets set when a prefix has been added toPN.Note
The "ML" inMLPREFIXstands for "MultiLib". This representation is historical and comes from a time whennativesdkwas a suffix rather than a prefix on the recipe name. Whennativesdkwas turned into a prefix, it made sense to setMLPREFIXfor it as well.To help understand when
MLPREFIXmight be needed, consider whenBBCLASSEXTENDis used to provide anativesdkversion of a recipe in addition to the target version. If that recipe declares build-time dependencies on tasks in other recipes by usingDEPENDS, then a dependency on "foo" will automatically get rewritten to a dependency on "nativesdk-foo". However, dependencies like the following will not get rewritten automatically:do_foo[depends] += "recipe:do_foo"If you want such a dependency to also get transformed, you can do the following:
do_foo[depends] += "${MLPREFIX}recipe:do_foo"- module_autoload¶
This variable has been replaced by the
KERNEL_MODULE_AUTOLOADvariable. You should replace all occurrences ofmodule_autoloadwith additions toKERNEL_MODULE_AUTOLOAD, for example:module_autoload_rfcomm = "rfcomm"should now be replaced with:
KERNEL_MODULE_AUTOLOAD += "rfcomm"See the
KERNEL_MODULE_AUTOLOADvariable for more information.- module_conf¶
Specifies
modprobe.dsyntax lines for inclusion in the/etc/modprobe.d/modname.conffile.You can use this variable anywhere that it can be recognized by the kernel recipe or out-of-tree kernel module recipe (e.g. a machine configuration file, a distribution configuration file, an append file for the recipe, or the recipe itself). If you use this variable, you must also be sure to list the module name in the
KERNEL_MODULE_AUTOLOADvariable.Here is the general syntax:
module_conf_module_name= "modprobe.d-syntax"You must use the kernel module name override.
Run
man modprobe.din the shell to find out more information on the exact syntax you want to provide withmodule_conf.Including
module_confcauses the OpenEmbedded build system to populate the/etc/modprobe.d/modname.conffile withmodprobe.dsyntax lines. Here is an example that adds the optionsarg1andarg2to a module namedmymodule:module_conf_mymodule = "options mymodule arg1=val1 arg2=val2"For information on how to specify kernel modules to auto-load on boot, see the
KERNEL_MODULE_AUTOLOADvariable.- MODULE_TARBALL_DEPLOY¶
Controls creation of the
modules-*.tgzfile. Set this variable to "0" to disable creation of this file, which contains all of the kernel modules resulting from a kernel build.- MODULE_TARBALL_LINK_NAME¶
The link name of the kernel module tarball. This variable is set in the
meta/classes/kernel-artifact-names.bbclassfile as follows:MODULE_TARBALL_LINK_NAME ?= "${KERNEL_ARTIFACT_LINK_NAME}"The value of the
KERNEL_ARTIFACT_LINK_NAMEvariable, which is set in the same file, has the following value:KERNEL_ARTIFACT_LINK_NAME ?= "${MACHINE}"See the
MACHINEvariable for additional information.- MODULE_TARBALL_NAME¶
The base name of the kernel module tarball. This variable is set in the
meta/classes/kernel-artifact-names.bbclassfile as follows:MODULE_TARBALL_NAME ?= "${KERNEL_ARTIFACT_NAME}"The value of the
KERNEL_ARTIFACT_NAMEvariable, which is set in the same file, has the following value:KERNEL_ARTIFACT_NAME ?= "${PKGE}-${PKGV}-${PKGR}-${MACHINE}${IMAGE_VERSION_SUFFIX}"- MULTIMACH_TARGET_SYS¶
Uniquely identifies the type of the target system for which packages are being built. This variable allows output for different types of target systems to be put into different subdirectories of the same output directory.
The default value of this variable is:
${PACKAGE_ARCH}${TARGET_VENDOR}-${TARGET_OS}Some classes (e.g.
cross-canadian) modify theMULTIMACH_TARGET_SYSvalue.See the
STAMPvariable for an example. See theSTAGING_DIR_TARGETvariable for more information.
N
- NATIVELSBSTRING¶
A string identifying the host distribution. Strings consist of the host distributor ID followed by the release, as reported by the
lsb_releasetool or as read from/etc/lsb-release. For example, when running a build on Ubuntu 12.10, the value is "Ubuntu-12.10". If this information is unable to be determined, the value resolves to "Unknown".This variable is used by default to isolate native shared state packages for different distributions (e.g. to avoid problems with
glibcversion incompatibilities). Additionally, the variable is checked againstSANITY_TESTED_DISTROSif that variable is set.- NM¶
The minimal command and arguments to run
nm.- NO_GENERIC_LICENSE¶
Avoids QA errors when you use a non-common, non-CLOSED license in a recipe. Packages exist, such as the linux-firmware package, with many licenses that are not in any way common. Also, new licenses are added occasionally to avoid introducing a lot of common license files, which are only applicable to a specific package.
NO_GENERIC_LICENSEis used to allow copying a license that does not exist in common licenses.The following example shows how to add
NO_GENERIC_LICENSEto a recipe:NO_GENERIC_LICENSE[license_name] = "license_file_in_fetched_source"The following is an example that uses the
LICENSE.Abilis.txtfile as the license from the fetched source:NO_GENERIC_LICENSE[Firmware-Abilis] = "LICENSE.Abilis.txt"- NO_RECOMMENDATIONS¶
Prevents installation of all "recommended-only" packages. Recommended-only packages are packages installed only through the
RRECOMMENDSvariable). Setting theNO_RECOMMENDATIONSvariable to "1" turns this feature on:NO_RECOMMENDATIONS = "1"You can set this variable globally in your
local.conffile or you can attach it to a specific image recipe by using the recipe name override:NO_RECOMMENDATIONS_pn-target_image= "1"It is important to realize that if you choose to not install packages using this variable and some other packages are dependent on them (i.e. listed in a recipe's
RDEPENDSvariable), the OpenEmbedded build system ignores your request and will install the packages to avoid dependency errors.Note
Some recommended packages might be required for certain system functionality, such as kernel modules. It is up to you to add packages with theIMAGE_INSTALLvariable.Support for this variable exists only when using the IPK and RPM packaging backend. Support does not exist for DEB.
See the
BAD_RECOMMENDATIONSand thePACKAGE_EXCLUDEvariables for related information.- NOAUTOPACKAGEDEBUG¶
Disables auto package from splitting
.debugfiles. If a recipe requiresFILES_${PN}-dbgto be set manually, theNOAUTOPACKAGEDEBUGcan be defined allowing you to define the content of the debug package. For example:NOAUTOPACKAGEDEBUG = "1" FILES_${PN}-dev = "${includedir}/${QT_DIR_NAME}/Qt/*" FILES_${PN}-dbg = "/usr/src/debug/" FILES_${QT_BASE_NAME}-demos-doc = "${docdir}/${QT_DIR_NAME}/qch/qt.qch"
O
- OBJCOPY¶
The minimal command and arguments to run
objcopy.- OBJDUMP¶
The minimal command and arguments to run
objdump.- OE_BINCONFIG_EXTRA_MANGLE¶
When inheriting the
binconfigclass, this variable specifies additional arguments passed to the "sed" command. The sed command alters any paths in configuration scripts that have been set up during compilation. Inheriting this class results in all paths in these scripts being changed to point into thesysroots/directory so that all builds that use the script will use the correct directories for the cross compiling layout.See the
meta/classes/binconfig.bbclassin the Source Directory for details on how this class applies these additional sed command arguments. For general information on thebinconfigclass, see the "binconfig.bbclass" section.- OE_IMPORTS¶
An internal variable used to tell the OpenEmbedded build system what Python modules to import for every Python function run by the system.
Note
Do not set this variable. It is for internal use only.- OE_INIT_ENV_SCRIPT¶
The name of the build environment setup script for the purposes of setting up the environment within the extensible SDK. The default value is "oe-init-build-env".
If you use a custom script to set up your build environment, set the
OE_INIT_ENV_SCRIPTvariable to its name.- OE_TERMINAL¶
Controls how the OpenEmbedded build system spawns interactive terminals on the host development system (e.g. using the BitBake command with the
-c devshellcommand-line option). For more information, see the "Using a Development Shell" section in the Yocto Project Development Tasks Manual.You can use the following values for the
OE_TERMINALvariable:auto gnome xfce rxvt screen konsole none- OEROOT¶
The directory from which the top-level build environment setup script is sourced. The Yocto Project provides a top-level build environment setup script:
oe-init-build-env. When you run this script, theOEROOTvariable resolves to the directory that contains the script.For additional information on how this variable is used, see the initialization script.
- OLDEST_KERNEL¶
Declares the oldest version of the Linux kernel that the produced binaries must support. This variable is passed into the build of the Embedded GNU C Library (
glibc).The default for this variable comes from the
meta/conf/bitbake.confconfiguration file. You can override this default by setting the variable in a custom distribution configuration file.- OVERRIDES¶
A colon-separated list of overrides that currently apply. Overrides are a BitBake mechanism that allows variables to be selectively overridden at the end of parsing. The set of overrides in
OVERRIDESrepresents the "state" during building, which includes the current recipe being built, the machine for which it is being built, and so forth.As an example, if the string "an-override" appears as an element in the colon-separated list in
OVERRIDES, then the following assignment will overrideFOOwith the value "overridden" at the end of parsing:FOO_an-override = "overridden"See the "Conditional Syntax (Overrides)" section in the BitBake User Manual for more information on the overrides mechanism.
The default value of
OVERRIDESincludes the values of theCLASSOVERRIDE,MACHINEOVERRIDES, andDISTROOVERRIDESvariables. Another important override included by default ispn-${PN}. This override allows variables to be set for a single recipe within configuration (.conf) files. Here is an example:FOO_pn-myrecipe = "myrecipe-specific value"Tip
An easy way to see what overrides apply is to search forOVERRIDESin the output of thebitbake -ecommand. See the "Viewing Variable Values" section in the Yocto Project Development Tasks Manual for more information.
P
- P¶
The recipe name and version.
Pis comprised of the following:${PN}-${PV}- PACKAGE_ARCH¶
The architecture of the resulting package or packages.
By default, the value of this variable is set to
TUNE_PKGARCHwhen building for the target,BUILD_ARCHwhen building for the build host, and "${SDK_ARCH}-${SDKPKGSUFFIX}" when building for the SDK.Note
SeeSDK_ARCHfor more information.However, if your recipe's output packages are built specific to the target machine rather than generally for the architecture of the machine, you should set
PACKAGE_ARCHto the value ofMACHINE_ARCHin the recipe as follows:PACKAGE_ARCH = "${MACHINE_ARCH}"- PACKAGE_ARCHS¶
Specifies a list of architectures compatible with the target machine. This variable is set automatically and should not normally be hand-edited. Entries are separated using spaces and listed in order of priority. The default value for
PACKAGE_ARCHSis "all any noarch ${PACKAGE_EXTRA_ARCHS} ${MACHINE_ARCH}".- PACKAGE_BEFORE_PN¶
Enables easily adding packages to
PACKAGESbefore${PN}so that those added packages can pick up files that would normally be included in the default package.- PACKAGE_CLASSES¶
This variable, which is set in the
local.confconfiguration file found in theconffolder of the Build Directory, specifies the package manager the OpenEmbedded build system uses when packaging data.You can provide one or more of the following arguments for the variable:
PACKAGE_CLASSES ?= "package_rpm package_deb package_ipk package_tar"Warning
While it is a legal option, thepackage_tarclass has limited functionality due to no support for package dependencies by that backend. Therefore, it is recommended that you do not use it.The build system uses only the first argument in the list as the package manager when creating your image or SDK. However, packages will be created using any additional packaging classes you specify. For example, if you use the following in your
local.conffile:PACKAGE_CLASSES ?= "package_ipk"The OpenEmbedded build system uses the IPK package manager to create your image or SDK.
For information on packaging and build performance effects as a result of the package manager in use, see the "
package.bbclass" section.- PACKAGE_DEBUG_SPLIT_STYLE¶
Determines how to split up the binary and debug information when creating
*-dbgpackages to be used with the GNU Project Debugger (GDB).With the
PACKAGE_DEBUG_SPLIT_STYLEvariable, you can control where debug information, which can include or exclude source files, is stored:".debug": Debug symbol files are placed next to the binary in a
.debugdirectory on the target. For example, if a binary is installed into/bin, the corresponding debug symbol files are installed in/bin/.debug. Source files are placed in/usr/src/debug. This is the default behavior."debug-file-directory": Debug symbol files are placed under
/usr/lib/debugon the target, and separated by the path from where the binary is installed. For example, if a binary is installed in/bin, the corresponding debug symbols are installed in/usr/lib/debug/bin. Source files are placed in/usr/src/debug."debug-without-src": The same behavior as ".debug" previously described with the exception that no source files are installed.
"debug-with-srcpkg": The same behavior as ".debug" previously described with the exception that all source files are placed in a separate
*-srcpkg.
You can find out more about debugging using GDB by reading the "Debugging With the GNU Project Debugger (GDB) Remotely" section in the Yocto Project Development Tasks Manual.
- PACKAGE_EXCLUDE_COMPLEMENTARY¶
Prevents specific packages from being installed when you are installing complementary packages.
You might find that you want to prevent installing certain packages when you are installing complementary packages. For example, if you are using
IMAGE_FEATURESto installdev-pkgs, you might not want to install all packages from a particular multilib. If you find yourself in this situation, you can use thePACKAGE_EXCLUDE_COMPLEMENTARYvariable to specify regular expressions to match the packages you want to exclude.- PACKAGE_EXCLUDE¶
Lists packages that should not be installed into an image. For example:
PACKAGE_EXCLUDE = "package_namepackage_namepackage_name..."You can set this variable globally in your
local.conffile or you can attach it to a specific image recipe by using the recipe name override:PACKAGE_EXCLUDE_pn-target_image= "package_name"If you choose to not install a package using this variable and some other package is dependent on it (i.e. listed in a recipe's
RDEPENDSvariable), the OpenEmbedded build system generates a fatal installation error. Because the build system halts the process with a fatal error, you can use the variable with an iterative development process to remove specific components from a system.Support for this variable exists only when using the IPK and RPM packaging backend. Support does not exist for DEB.
See the
NO_RECOMMENDATIONSand theBAD_RECOMMENDATIONSvariables for related information.- PACKAGE_EXTRA_ARCHS¶
Specifies the list of architectures compatible with the device CPU. This variable is useful when you build for several different devices that use miscellaneous processors such as XScale and ARM926-EJS.
- PACKAGE_FEED_ARCHS¶
Optionally specifies the package architectures used as part of the package feed URIs during the build. When used, the
PACKAGE_FEED_ARCHSvariable is appended to the final package feed URI, which is constructed using thePACKAGE_FEED_URISandPACKAGE_FEED_BASE_PATHSvariables.Tip
You can use thePACKAGE_FEEDS_ARCHSvariable to whitelist specific package architectures. If you do not need to whitelist specific architectures, which is a common case, you can omit this variable. Omitting the variable results in all available architectures for the current machine being included into remote package feeds.Consider the following example where the
PACKAGE_FEED_URIS,PACKAGE_FEED_BASE_PATHS, andPACKAGE_FEED_ARCHSvariables are defined in yourlocal.conffile:PACKAGE_FEED_URIS = "https://example.com/packagerepos/release \ https://example.com/packagerepos/updates" PACKAGE_FEED_BASE_PATHS = "rpm rpm-dev" PACKAGE_FEED_ARCHS = "all core2-64"Given these settings, the resulting package feeds are as follows:
https://example.com/packagerepos/release/rpm/all https://example.com/packagerepos/release/rpm/core2-64 https://example.com/packagerepos/release/rpm-dev/all https://example.com/packagerepos/release/rpm-dev/core2-64 https://example.com/packagerepos/updates/rpm/all https://example.com/packagerepos/updates/rpm/core2-64 https://example.com/packagerepos/updates/rpm-dev/all https://example.com/packagerepos/updates/rpm-dev/core2-64- PACKAGE_FEED_BASE_PATHS¶
Specifies the base path used when constructing package feed URIs. The
PACKAGE_FEED_BASE_PATHSvariable makes up the middle portion of a package feed URI used by the OpenEmbedded build system. The base path lies between thePACKAGE_FEED_URISandPACKAGE_FEED_ARCHSvariables.Consider the following example where the
PACKAGE_FEED_URIS,PACKAGE_FEED_BASE_PATHS, andPACKAGE_FEED_ARCHSvariables are defined in yourlocal.conffile:PACKAGE_FEED_URIS = "https://example.com/packagerepos/release \ https://example.com/packagerepos/updates" PACKAGE_FEED_BASE_PATHS = "rpm rpm-dev" PACKAGE_FEED_ARCHS = "all core2-64"Given these settings, the resulting package feeds are as follows:
https://example.com/packagerepos/release/rpm/all https://example.com/packagerepos/release/rpm/core2-64 https://example.com/packagerepos/release/rpm-dev/all https://example.com/packagerepos/release/rpm-dev/core2-64 https://example.com/packagerepos/updates/rpm/all https://example.com/packagerepos/updates/rpm/core2-64 https://example.com/packagerepos/updates/rpm-dev/all https://example.com/packagerepos/updates/rpm-dev/core2-64- PACKAGE_FEED_URIS¶
Specifies the front portion of the package feed URI used by the OpenEmbedded build system. Each final package feed URI is comprised of
PACKAGE_FEED_URIS,PACKAGE_FEED_BASE_PATHS, andPACKAGE_FEED_ARCHSvariables.Consider the following example where the
PACKAGE_FEED_URIS,PACKAGE_FEED_BASE_PATHS, andPACKAGE_FEED_ARCHSvariables are defined in yourlocal.conffile:PACKAGE_FEED_URIS = "https://example.com/packagerepos/release \ https://example.com/packagerepos/updates" PACKAGE_FEED_BASE_PATHS = "rpm rpm-dev" PACKAGE_FEED_ARCHS = "all core2-64"Given these settings, the resulting package feeds are as follows:
https://example.com/packagerepos/release/rpm/all https://example.com/packagerepos/release/rpm/core2-64 https://example.com/packagerepos/release/rpm-dev/all https://example.com/packagerepos/release/rpm-dev/core2-64 https://example.com/packagerepos/updates/rpm/all https://example.com/packagerepos/updates/rpm/core2-64 https://example.com/packagerepos/updates/rpm-dev/all https://example.com/packagerepos/updates/rpm-dev/core2-64- PACKAGE_GROUP¶
The
PACKAGE_GROUPvariable has been renamed toFEATURE_PACKAGES. See the variable description forFEATURE_PACKAGESfor information.If if you use the
PACKAGE_GROUPvariable, the OpenEmbedded build system issues a warning message.- PACKAGE_INSTALL¶
The final list of packages passed to the package manager for installation into the image.
Because the package manager controls actual installation of all packages, the list of packages passed using
PACKAGE_INSTALLis not the final list of packages that are actually installed. This variable is internal to the image construction code. Consequently, in general, you should use theIMAGE_INSTALLvariable to specify packages for installation. The exception to this is when working with thecore-image-minimal-initramfsimage. When working with an initial RAM filesystem (initramfs) image, use thePACKAGE_INSTALLvariable. For information on creating an initramfs, see the "Building an Initial RAM Filesystem (initramfs) Image" section in the Yocto Project Development Tasks Manual.- PACKAGE_INSTALL_ATTEMPTONLY¶
Specifies a list of packages the OpenEmbedded build system attempts to install when creating an image. If a listed package fails to install, the build system does not generate an error. This variable is generally not user-defined.
- PACKAGE_PREPROCESS_FUNCS¶
Specifies a list of functions run to pre-process the
PKGDdirectory prior to splitting the files out to individual packages.- PACKAGE_WRITE_DEPS¶
Specifies a list of dependencies for post-installation and pre-installation scripts on native/cross tools. If your post-installation or pre-installation script can execute at rootfs creation time rather than on the target but depends on a native tool in order to execute, you need to list the tools in
PACKAGE_WRITE_DEPS.For information on running post-installation scripts, see the "Post-Installation Scripts" section in the Yocto Project Development Tasks Manual.
- PACKAGECONFIG¶
This variable provides a means of enabling or disabling features of a recipe on a per-recipe basis.
PACKAGECONFIGblocks are defined in recipes when you specify features and then arguments that define feature behaviors. Here is the basic block structure:PACKAGECONFIG ??= "f1 f2 f3 ..." PACKAGECONFIG[f1] = "--with-f1,--without-f1,build-deps-f1,rt-deps-f1,rt-recs-f1" PACKAGECONFIG[f2] = "--with-f2,--without-f2,build-deps-f2,rt-deps-f2,rt-recs-f2" PACKAGECONFIG[f3] = "--with-f3,--without-f3,build-deps-f3,rt-deps-f3,rt-recs-f3"The
PACKAGECONFIGvariable itself specifies a space-separated list of the features to enable. Following the features, you can determine the behavior of each feature by providing up to five order-dependent arguments, which are separated by commas. You can omit any argument you like but must retain the separating commas. The order is important and specifies the following:Extra arguments that should be added to the configure script argument list (
EXTRA_OECONForPACKAGECONFIG_CONFARGS) if the feature is enabled.Extra arguments that should be added to
EXTRA_OECONForPACKAGECONFIG_CONFARGSif the feature is disabled.Additional build dependencies (
DEPENDS) that should be added if the feature is enabled.Additional runtime dependencies (
RDEPENDS) that should be added if the feature is enabled.Additional runtime recommendations (
RRECOMMENDS) that should be added if the feature is enabled.
Consider the following
PACKAGECONFIGblock taken from thelibrsvgrecipe. In this example the feature iscroco, which has three arguments that determine the feature's behavior.PACKAGECONFIG ??= "croco" PACKAGECONFIG[croco] = "--with-croco,--without-croco,libcroco"The
--with-crocoandlibcrocoarguments apply only if the feature is enabled. In this case,--with-crocois added to the configure script argument list andlibcrocois added toDEPENDS. On the other hand, if the feature is disabled say through a.bbappendfile in another layer, then the second argument--without-crocois added to the configure script rather than--with-croco.The basic
PACKAGECONFIGstructure previously described holds true regardless of whether you are creating a block or changing a block. When creating a block, use the structure inside your recipe.If you want to change an existing
PACKAGECONFIGblock, you can do so one of two ways:Append file: Create an append file named
recipename.bbappendin your layer and override the value ofPACKAGECONFIG. You can either completely override the variable:PACKAGECONFIG = "f4 f5"Or, you can just append the variable:
PACKAGECONFIG_append = " f4"Configuration file: This method is identical to changing the block through an append file except you edit your
local.conformydistro.confPACKAGECONFIG_pn-recipename= "f4 f5"Or, you can just amend the variable:
PACKAGECONFIG_append_pn-recipename= " f4"
- PACKAGECONFIG_CONFARGS¶
A space-separated list of configuration options generated from the
PACKAGECONFIGsetting.Classes such as
autotoolsandcmakeusePACKAGECONFIG_CONFARGSto passPACKAGECONFIGoptions toconfigureandcmake, respectively. If you are usingPACKAGECONFIGbut not a class that handles thedo_configuretask, then you need to usePACKAGECONFIG_CONFARGSappropriately.- PACKAGEGROUP_DISABLE_COMPLEMENTARY¶
For recipes inheriting the
packagegroupclass, settingPACKAGEGROUP_DISABLE_COMPLEMENTARYto "1" specifies that the normal complementary packages (i.e.-dev,-dbg, and so forth) should not be automatically created by thepackagegrouprecipe, which is the default behavior.- PACKAGES¶
The list of packages the recipe creates. The default value is the following:
${PN}-dbg ${PN}-staticdev ${PN}-dev ${PN}-doc ${PN}-locale ${PACKAGE_BEFORE_PN} ${PN}During packaging, the
do_packagetask goes throughPACKAGESand uses theFILESvariable corresponding to each package to assign files to the package. If a file matches theFILESvariable for more than one package inPACKAGES, it will be assigned to the earliest (leftmost) package.Packages in the variable's list that are empty (i.e. where none of the patterns in
FILES_pkgmatch any files installed by thedo_installtask) are not generated, unless generation is forced through theALLOW_EMPTYvariable.- PACKAGES_DYNAMIC¶
A promise that your recipe satisfies runtime dependencies for optional modules that are found in other recipes.
PACKAGES_DYNAMICdoes not actually satisfy the dependencies, it only states that they should be satisfied. For example, if a hard, runtime dependency (RDEPENDS) of another package is satisfied at build time through thePACKAGES_DYNAMICvariable, but a package with the module name is never actually produced, then the other package will be broken. Thus, if you attempt to include that package in an image, you will get a dependency failure from the packaging system during thedo_rootfstask.Typically, if there is a chance that such a situation can occur and the package that is not created is valid without the dependency being satisfied, then you should use
RRECOMMENDS(a soft runtime dependency) instead ofRDEPENDS.For an example of how to use the
PACKAGES_DYNAMICvariable when you are splitting packages, see the "Handling Optional Module Packaging" section in the Yocto Project Development Tasks Manual.- PACKAGESPLITFUNCS¶
Specifies a list of functions run to perform additional splitting of files into individual packages. Recipes can either prepend to this variable or prepend to the
populate_packagesfunction in order to perform additional package splitting. In either case, the function should setPACKAGES,FILES,RDEPENDSand other packaging variables appropriately in order to perform the desired splitting.- PARALLEL_MAKE¶
Extra options passed to the
makecommand during thedo_compiletask in order to specify parallel compilation on the local build host. This variable is usually in the form "-jx", wherexrepresents the maximum number of parallel threadsmakecan run.Caution
In order forPARALLEL_MAKEto be effective,makemust be called with${EXTRA_OEMAKE}. An easy way to ensure this is to use theoe_runmakefunction.By default, the OpenEmbedded build system automatically sets this variable to be equal to the number of cores the build system uses.
Note
If the software being built experiences dependency issues during thedo_compiletask that result in race conditions, you can clear thePARALLEL_MAKEvariable within the recipe as a workaround. For information on addressing race conditions, see the "Debugging Parallel Make Races" section in the Yocto Project Development Tasks Manual.For single socket systems (i.e. one CPU), you should not have to override this variable to gain optimal parallelism during builds. However, if you have very large systems that employ multiple physical CPUs, you might want to make sure the
PARALLEL_MAKEvariable is not set higher than "-j 20".For more information on speeding up builds, see the "Speeding Up a Build" section in the Yocto Project Development Tasks Manual.
- PARALLEL_MAKEINST¶
Extra options passed to the
make installcommand during thedo_installtask in order to specify parallel installation. This variable defaults to the value ofPARALLEL_MAKE.Notes and Cautions
In order for
PARALLEL_MAKEINSTto be effective,makemust be called with${EXTRA_OEMAKE}. An easy way to ensure this is to use theoe_runmakefunction.If the software being built experiences dependency issues during the
do_installtask that result in race conditions, you can clear thePARALLEL_MAKEINSTvariable within the recipe as a workaround. For information on addressing race conditions, see the "Debugging Parallel Make Races" section in the Yocto Project Development Tasks Manual.- PATCHRESOLVE¶
Determines the action to take when a patch fails. You can set this variable to one of two values: "noop" and "user".
The default value of "noop" causes the build to simply fail when the OpenEmbedded build system cannot successfully apply a patch. Setting the value to "user" causes the build system to launch a shell and places you in the right location so that you can manually resolve the conflicts.
Set this variable in your
local.conffile.- PATCHTOOL¶
Specifies the utility used to apply patches for a recipe during the
do_patchtask. You can specify one of three utilities: "patch", "quilt", or "git". The default utility used is "quilt" except for the quilt-native recipe itself. Because the quilt tool is not available at the time quilt-native is being patched, it uses "patch".If you wish to use an alternative patching tool, set the variable in the recipe using one of the following:
PATCHTOOL = "patch" PATCHTOOL = "quilt" PATCHTOOL = "git"- PE¶
The epoch of the recipe. By default, this variable is unset. The variable is used to make upgrades possible when the versioning scheme changes in some backwards incompatible way.
PEis the default value of thePKGEvariable.- PF¶
Specifies the recipe or package name and includes all version and revision numbers (i.e.
glibc-2.13-r20+svnr15508/andbash-4.2-r1/). This variable is comprised of the following:${PN}-${EXTENDPE}${PV}-${PR}- PIXBUF_PACKAGES¶
When inheriting the
pixbufcacheclass, this variable identifies packages that contain the pixbuf loaders used withgdk-pixbuf. By default, thepixbufcacheclass assumes that the loaders are in the recipe's main package (i.e.${PN}). Use this variable if the loaders you need are in a package other than that main package.- PKG¶
The name of the resulting package created by the OpenEmbedded build system.
Note
When using thePKGvariable, you must use a package name override.For example, when the
debianclass renames the output package, it does so by settingPKG_.packagename- PKG_CONFIG_PATH¶
The path to
pkg-configfiles for the current build context.pkg-configreads this variable from the environment.- PKGD¶
Points to the destination directory for files to be packaged before they are split into individual packages. This directory defaults to the following:
${WORKDIR}/packageDo not change this default.
- PKGDATA_DIR¶
Points to a shared, global-state directory that holds data generated during the packaging process. During the packaging process, the
do_packagedatatask packages data for each recipe and installs it into this temporary, shared area. This directory defaults to the following, which you should not change:${STAGING_DIR_HOST}/pkgdataFor examples of how this data is used, see the "Automatically Added Runtime Dependencies" section in the Yocto Project Overview and Concepts Manual and the "Viewing Package Information with
oe-pkgdata-util" section in the Yocto Project Development Tasks Manual. For more information on the shared, global-state directory, seeSTAGING_DIR_HOST.- PKGDEST¶
Points to the parent directory for files to be packaged after they have been split into individual packages. This directory defaults to the following:
${WORKDIR}/packages-splitUnder this directory, the build system creates directories for each package specified in
PACKAGES. Do not change this default.- PKGDESTWORK¶
Points to a temporary work area where the
do_packagetask saves package metadata. ThePKGDESTWORKlocation defaults to the following:${WORKDIR}/pkgdataDo not change this default.
The
do_packagedatatask copies the package metadata fromPKGDESTWORKtoPKGDATA_DIRto make it available globally.- PKGE¶
The epoch of the package(s) built by the recipe. By default,
PKGEis set toPE.- PKGR¶
The revision of the package(s) built by the recipe. By default,
PKGRis set toPR.- PKGV¶
The version of the package(s) built by the recipe. By default,
PKGVis set toPV.- PN¶
This variable can have two separate functions depending on the context: a recipe name or a resulting package name.
PNrefers to a recipe name in the context of a file used by the OpenEmbedded build system as input to create a package. The name is normally extracted from the recipe file name. For example, if the recipe is namedexpat_2.0.1.bb, then the default value ofPNwill be "expat".The variable refers to a package name in the context of a file created or produced by the OpenEmbedded build system.
If applicable, the
PNvariable also contains any special suffix or prefix. For example, usingbashto build packages for the native machine,PNisbash-native. Usingbashto build packages for the target and for Multilib,PNwould bebashandlib64-bash, respectively.- PNBLACKLIST¶
Lists recipes you do not want the OpenEmbedded build system to build. This variable works in conjunction with the
blacklistclass, which is inherited globally.To prevent a recipe from being built, use the
PNBLACKLISTvariable in yourlocal.conffile. Here is an example that preventsmyrecipefrom being built:PNBLACKLIST[myrecipe] = "Not supported by our organization."- POPULATE_SDK_POST_HOST_COMMAND¶
Specifies a list of functions to call once the OpenEmbedded build system has created the host part of the SDK. You can specify functions separated by semicolons:
POPULATE_SDK_POST_HOST_COMMAND += "function; ... "If you need to pass the SDK path to a command within a function, you can use
${SDK_DIR}, which points to the parent directory used by the OpenEmbedded build system when creating SDK output. See theSDK_DIRvariable for more information.- POPULATE_SDK_POST_TARGET_COMMAND¶
Specifies a list of functions to call once the OpenEmbedded build system has created the target part of the SDK. You can specify functions separated by semicolons:
POPULATE_SDK_POST_TARGET_COMMAND += "function; ... "If you need to pass the SDK path to a command within a function, you can use
${SDK_DIR}, which points to the parent directory used by the OpenEmbedded build system when creating SDK output. See theSDK_DIRvariable for more information.- PR¶
The revision of the recipe. The default value for this variable is "r0". Subsequent revisions of the recipe conventionally have the values "r1", "r2", and so forth. When
PVincreases,PRis conventionally reset to "r0".Note
The OpenEmbedded build system does not need the aid ofPRto know when to rebuild a recipe. The build system uses the task input checksums along with the stamp and shared state cache mechanisms.The
PRvariable primarily becomes significant when a package manager dynamically installs packages on an already built image. In this case,PR, which is the default value ofPKGR, helps the package manager distinguish which package is the most recent one in cases where many packages have the samePV(i.e.PKGV). A component having many packages with the samePVusually means that the packages all install the same upstream version, but with later (PR) version packages including packaging fixes.Note
PRdoes not need to be increased for changes that do not change the package contents or metadata.Because manually managing
PRcan be cumbersome and error-prone, an automated solution exists. See the "Working With a PR Service" section in the Yocto Project Development Tasks Manual for more information.- PREFERRED_PROVIDER¶
If multiple recipes provide the same item, this variable determines which recipe is preferred and thus provides the item (i.e. the preferred provider). You should always suffix this variable with the name of the provided item. And, you should define the variable using the preferred recipe's name (
PN). Here is a common example:PREFERRED_PROVIDER_virtual/kernel ?= "linux-yocto"In the previous example, multiple recipes are providing "virtual/kernel". The
PREFERRED_PROVIDERvariable is set with the name (PN) of the recipe you prefer to provide "virtual/kernel".Following are more examples:
PREFERRED_PROVIDER_virtual/xserver = "xserver-xf86" PREFERRED_PROVIDER_virtual/libgl ?= "mesa"For more information, see the "Using Virtual Providers" section in the Yocto Project Development Tasks Manual.
Note
If you use avirtual/*item withPREFERRED_PROVIDER, then any recipe thatPROVIDESthat item but is not selected (defined) byPREFERRED_PROVIDERis prevented from building, which is usually desirable since this mechanism is designed to select between mutually exclusive alternative providers.- PREFERRED_VERSION¶
If multiple versions of recipes exist, this variable determines which version is given preference. You must always suffix the variable with the
PNyou want to select, and you should set thePVaccordingly for precedence.The
PREFERRED_VERSIONvariable supports limited wildcard use through the "%" character. You can use the character to match any number of characters, which can be useful when specifying versions that contain long revision numbers that potentially change. Here are two examples:PREFERRED_VERSION_python = "3.4.0" PREFERRED_VERSION_linux-yocto = "4.12%"Important
The use of the "%" character is limited in that it only works at the end of the string. You cannot use the wildcard character in any other location of the string.The specified version is matched against
PV, which does not necessarily match the version part of the recipe's filename. For example, consider two recipesfoo_1.2.bbandfoo_git.bbwherefoo_git.bbcontains the following assignment:PV = "1.1+git${SRCPV}"In this case, the correct way to select
foo_git.bbis by using an assignment such as the following:PREFERRED_VERSION_foo = "1.1+git%"Compare that previous example against the following incorrect example, which does not work:
PREFERRED_VERSION_foo = "git"Sometimes the
PREFERRED_VERSIONvariable can be set by configuration files in a way that is hard to change. You can useOVERRIDESto set a machine-specific override. Here is an example:PREFERRED_VERSION_linux-yocto_qemux86 = "4.12%"Although not recommended, worst case, you can also use the "forcevariable" override, which is the strongest override possible. Here is an example:
PREFERRED_VERSION_linux-yocto_forcevariable = "4.12%"Note
The_forcevariableoverride is not handled specially. This override only works because the default value ofOVERRIDESincludes "forcevariable".- PREMIRRORS¶
Specifies additional paths from which the OpenEmbedded build system gets source code. When the build system searches for source code, it first tries the local download directory. If that location fails, the build system tries locations defined by
PREMIRRORS, the upstream source, and then locations specified byMIRRORSin that order.Assuming your distribution (
DISTRO) is "poky", the default value forPREMIRRORSis defined in theconf/distro/poky.conffile in themeta-pokyGit repository.Typically, you could add a specific server for the build system to attempt before any others by adding something like the following to the
local.confconfiguration file in the Build Directory:PREMIRRORS_prepend = "\ git://.*/.* http://www.yoctoproject.org/sources/ \n \ ftp://.*/.* http://www.yoctoproject.org/sources/ \n \ http://.*/.* http://www.yoctoproject.org/sources/ \n \ https://.*/.* http://www.yoctoproject.org/sources/ \n"These changes cause the build system to intercept Git, FTP, HTTP, and HTTPS requests and direct them to the
http://sources mirror. You can usefile://URLs to point to local directories or network shares as well.- PRIORITY¶
Indicates the importance of a package.
PRIORITYis considered to be part of the distribution policy because the importance of any given recipe depends on the purpose for which the distribution is being produced. Thus,PRIORITYis not normally set within recipes.You can set
PRIORITYto "required", "standard", "extra", and "optional", which is the default.- PRIVATE_LIBS¶
Specifies libraries installed within a recipe that should be ignored by the OpenEmbedded build system's shared library resolver. This variable is typically used when software being built by a recipe has its own private versions of a library normally provided by another recipe. In this case, you would not want the package containing the private libraries to be set as a dependency on other unrelated packages that should instead depend on the package providing the standard version of the library.
Libraries specified in this variable should be specified by their file name. For example, from the Firefox recipe in meta-browser:
PRIVATE_LIBS = "libmozjs.so \ libxpcom.so \ libnspr4.so \ libxul.so \ libmozalloc.so \ libplc4.so \ libplds4.so"For more information, see the "Automatically Added Runtime Dependencies" section in the Yocto Project Overview and Concepts Manual.
- PROVIDES¶
A list of aliases by which a particular recipe can be known. By default, a recipe's own
PNis implicitly already in itsPROVIDESlist. If a recipe usesPROVIDES, the additional aliases are synonyms for the recipe and can be useful satisfying dependencies of other recipes during the build as specified byDEPENDS.Consider the following example
PROVIDESstatement from a recipe filelibav_0.8.11.bb:PROVIDES += "libpostproc"The
PROVIDESstatement results in the "libav" recipe also being known as "libpostproc".In addition to providing recipes under alternate names, the
PROVIDESmechanism is also used to implement virtual targets. A virtual target is a name that corresponds to some particular functionality (e.g. a Linux kernel). Recipes that provide the functionality in question list the virtual target inPROVIDES. Recipes that depend on the functionality in question can include the virtual target inDEPENDSto leave the choice of provider open.Conventionally, virtual targets have names on the form "virtual/function" (e.g. "virtual/kernel"). The slash is simply part of the name and has no syntactical significance.
The
PREFERRED_PROVIDERvariable is used to select which particular recipe provides a virtual target.Note
A corresponding mechanism for virtual runtime dependencies (packages) exists. However, the mechanism does not depend on any special functionality beyond ordinary variable assignments. For example,
VIRTUAL-RUNTIME_dev_managerrefers to the package of the component that manages the/devdirectory.Setting the "preferred provider" for runtime dependencies is as simple as using the following assignment in a configuration file:
VIRTUAL-RUNTIME_dev_manager = "udev"- PRSERV_HOST¶
The network based
PRservice host and port.The
conf/local.conf.sample.extendedconfiguration file in the Source Directory shows how thePRSERV_HOSTvariable is set:PRSERV_HOST = "localhost:0"You must set the variable if you want to automatically start a local PR service. You can set
PRSERV_HOSTto other values to use a remote PR service.- PTEST_ENABLED¶
Specifies whether or not Package Test (ptest) functionality is enabled when building a recipe. You should not set this variable directly. Enabling and disabling building Package Tests at build time should be done by adding "ptest" to (or removing it from)
DISTRO_FEATURES.- PV¶
The version of the recipe. The version is normally extracted from the recipe filename. For example, if the recipe is named
expat_2.0.1.bb, then the default value ofPVwill be "2.0.1".PVis generally not overridden within a recipe unless it is building an unstable (i.e. development) version from a source code repository (e.g. Git or Subversion).PVis the default value of thePKGVvariable.- PYTHON_ABI¶
When used by recipes that inherit the
distutils3,setuptools3,distutils, orsetuptoolsclasses, denotes the Application Binary Interface (ABI) currently in use for Python. By default, the ABI is "m". You do not have to set this variable as the OpenEmbedded build system sets it for you.The OpenEmbedded build system uses the ABI to construct directory names used when installing the Python headers and libraries in sysroot (e.g.
.../python3.3m/...).Recipes that inherit the
distutilsclass during cross-builds also use this variable to locate the headers and libraries of the appropriate Python that the extension is targeting.- PYTHON_PN¶
When used by recipes that inherit the
distutils3,setuptools3,distutils, orsetuptoolsclasses, specifies the major Python version being built. For Python 2.x,PYTHON_PNwould be "python2". For Python 3.x, the variable would be "python3". You do not have to set this variable as the OpenEmbedded build system automatically sets it for you.The variable allows recipes to use common infrastructure such as the following:
DEPENDS += "${PYTHON_PN}-native"In the previous example, the version of the dependency is
PYTHON_PN.
R
- RANLIB¶
The minimal command and arguments to run
ranlib.- RCONFLICTS¶
The list of packages that conflict with packages. Note that packages will not be installed if conflicting packages are not first removed.
Like all package-controlling variables, you must always use them in conjunction with a package name override. Here is an example:
RCONFLICTS_${PN} = "another_conflicting_package_name"BitBake, which the OpenEmbedded build system uses, supports specifying versioned dependencies. Although the syntax varies depending on the packaging format, BitBake hides these differences from you. Here is the general syntax to specify versions with the
RCONFLICTSvariable:RCONFLICTS_${PN} = "package(operatorversion)"For
operator, you can specify the following:= < > <= >=For example, the following sets up a dependency on version 1.2 or greater of the package
foo:RCONFLICTS_${PN} = "foo (>= 1.2)"- RDEPENDS¶
Lists runtime dependencies of a package. These dependencies are other packages that must be installed in order for the package to function correctly. As an example, the following assignment declares that the package
fooneeds the packagesbarandbazto be installed:RDEPENDS_foo = "bar baz"The most common types of package runtime dependencies are automatically detected and added. Therefore, most recipes do not need to set
RDEPENDS. For more information, see the "Automatically Added Runtime Dependencies" section in the Yocto Project Overview and Concepts Manual.The practical effect of the above
RDEPENDSassignment is thatbarandbazwill be declared as dependencies inside the packagefoowhen it is written out by one of thedo_package_write_*tasks. Exactly how this is done depends on which package format is used, which is determined byPACKAGE_CLASSES. When the corresponding package manager installs the package, it will know to also install the packages on which it depends.To ensure that the packages
barandbazget built, the previousRDEPENDSassignment also causes a task dependency to be added. This dependency is from the recipe'sdo_build(not to be confused withdo_compile) task to thedo_package_write_*task of the recipes that buildbarandbaz.The names of the packages you list within
RDEPENDSmust be the names of other packages - they cannot be recipe names. Although package names and recipe names usually match, the important point here is that you are providing package names within theRDEPENDSvariable. For an example of the default list of packages created from a recipe, see thePACKAGESvariable.Because the
RDEPENDSvariable applies to packages being built, you should always use the variable in a form with an attached package name (remember that a single recipe can build multiple packages). For example, suppose you are building a development package that depends on theperlpackage. In this case, you would use the followingRDEPENDSstatement:RDEPENDS_${PN}-dev += "perl"In the example, the development package depends on the
perlpackage. Thus, theRDEPENDSvariable has the${PN}-devpackage name as part of the variable.Caution
RDEPENDS_${PN}-devincludes${PN}by default. This default is set in the BitBake configuration file (meta/conf/bitbake.conf). Be careful not to accidentally remove${PN}when modifyingRDEPENDS_${PN}-dev. Use the "+=" operator rather than the "=" operator.The package names you use with
RDEPENDSmust appear as they would in thePACKAGESvariable. ThePKGvariable allows a different name to be used for the final package (e.g. thedebianclass uses this to rename packages), but this final package name cannot be used withRDEPENDS, which makes sense asRDEPENDSis meant to be independent of the package format used.BitBake, which the OpenEmbedded build system uses, supports specifying versioned dependencies. Although the syntax varies depending on the packaging format, BitBake hides these differences from you. Here is the general syntax to specify versions with the
RDEPENDSvariable:RDEPENDS_${PN} = "package(operatorversion)"For
operator, you can specify the following:= < > <= >=For
version, provide the version number.Tip
You can useEXTENDPKGVto provide a full package version specification.For example, the following sets up a dependency on version 1.2 or greater of the package
foo:RDEPENDS_${PN} = "foo (>= 1.2)"For information on build-time dependencies, see the
DEPENDSvariable. You can also see the "Tasks" and "Dependencies" sections in the BitBake User Manual for additional information on tasks and dependencies.- REQUIRED_DISTRO_FEATURES¶
When inheriting the
distro_features_checkclass, this variable identifies distribution features that must exist in the current configuration in order for the OpenEmbedded build system to build the recipe. In other words, if theREQUIRED_DISTRO_FEATURESvariable lists a feature that does not appear inDISTRO_FEATURESwithin the current configuration, an error occurs and the build stops.- RM_WORK_EXCLUDE¶
With
rm_workenabled, this variable specifies a list of recipes whose work directories should not be removed. See the "rm_work.bbclass" section for more details.- ROOT_HOME¶
Defines the root home directory. By default, this directory is set as follows in the BitBake configuration file:
ROOT_HOME ??= "/home/root"Note
This default value is likely used because some embedded solutions prefer to have a read-only root filesystem and prefer to keep writeable data in one place.You can override the default by setting the variable in any layer or in the
local.conffile. Because the default is set using a "weak" assignment (i.e. "??="), you can use either of the following forms to define your override:ROOT_HOME = "/root" ROOT_HOME ?= "/root"These override examples use
/root, which is probably the most commonly used override.- ROOTFS¶
Indicates a filesystem image to include as the root filesystem.
The
ROOTFSvariable is an optional variable used with theimage-liveclass.- ROOTFS_POSTINSTALL_COMMAND¶
Specifies a list of functions to call after the OpenEmbedded build system has installed packages. You can specify functions separated by semicolons:
ROOTFS_POSTINSTALL_COMMAND += "function; ... "If you need to pass the root filesystem path to a command within a function, you can use
${IMAGE_ROOTFS}, which points to the directory that becomes the root filesystem image. See theIMAGE_ROOTFSvariable for more information.- ROOTFS_POSTPROCESS_COMMAND¶
Specifies a list of functions to call once the OpenEmbedded build system has created the root filesystem. You can specify functions separated by semicolons:
ROOTFS_POSTPROCESS_COMMAND += "function; ... "If you need to pass the root filesystem path to a command within a function, you can use
${IMAGE_ROOTFS}, which points to the directory that becomes the root filesystem image. See theIMAGE_ROOTFSvariable for more information.- ROOTFS_POSTUNINSTALL_COMMAND¶
Specifies a list of functions to call after the OpenEmbedded build system has removed unnecessary packages. When runtime package management is disabled in the image, several packages are removed including
base-passwd,shadow, andupdate-alternatives. You can specify functions separated by semicolons:ROOTFS_POSTUNINSTALL_COMMAND += "function; ... "If you need to pass the root filesystem path to a command within a function, you can use
${IMAGE_ROOTFS}, which points to the directory that becomes the root filesystem image. See theIMAGE_ROOTFSvariable for more information.- ROOTFS_PREPROCESS_COMMAND¶
Specifies a list of functions to call before the OpenEmbedded build system has created the root filesystem. You can specify functions separated by semicolons:
ROOTFS_PREPROCESS_COMMAND += "function; ... "If you need to pass the root filesystem path to a command within a function, you can use
${IMAGE_ROOTFS}, which points to the directory that becomes the root filesystem image. See theIMAGE_ROOTFSvariable for more information.- RPROVIDES¶
A list of package name aliases that a package also provides. These aliases are useful for satisfying runtime dependencies of other packages both during the build and on the target (as specified by
RDEPENDS).Note
A package's own name is implicitly already in itsRPROVIDESlist.As with all package-controlling variables, you must always use the variable in conjunction with a package name override. Here is an example:
RPROVIDES_${PN} = "widget-abi-2"- RRECOMMENDS¶
A list of packages that extends the usability of a package being built. The package being built does not depend on this list of packages in order to successfully build, but rather uses them for extended usability. To specify runtime dependencies for packages, see the
RDEPENDSvariable.The package manager will automatically install the
RRECOMMENDSlist of packages when installing the built package. However, you can prevent listed packages from being installed by using theBAD_RECOMMENDATIONS,NO_RECOMMENDATIONS, andPACKAGE_EXCLUDEvariables.Packages specified in
RRECOMMENDSneed not actually be produced. However, a recipe must exist that provides each package, either through thePACKAGESorPACKAGES_DYNAMICvariables or theRPROVIDESvariable, or an error will occur during the build. If such a recipe does exist and the package is not produced, the build continues without error.Because the
RRECOMMENDSvariable applies to packages being built, you should always attach an override to the variable to specify the particular package whose usability is being extended. For example, suppose you are building a development package that is extended to support wireless functionality. In this case, you would use the following:RRECOMMENDS_${PN}-dev += "wireless_package_name"In the example, the package name (
${PN}-dev) must appear as it would in thePACKAGESnamespace before any renaming of the output package by classes such asdebian.bbclass.BitBake, which the OpenEmbedded build system uses, supports specifying versioned recommends. Although the syntax varies depending on the packaging format, BitBake hides these differences from you. Here is the general syntax to specify versions with the
RRECOMMENDSvariable:RRECOMMENDS_${PN} = "package(operatorversion)"For
operator, you can specify the following:= < > <= >=For example, the following sets up a recommend on version 1.2 or greater of the package
foo:RRECOMMENDS_${PN} = "foo (>= 1.2)"- RREPLACES¶
A list of packages replaced by a package. The package manager uses this variable to determine which package should be installed to replace other package(s) during an upgrade. In order to also have the other package(s) removed at the same time, you must add the name of the other package to the
RCONFLICTSvariable.As with all package-controlling variables, you must use this variable in conjunction with a package name override. Here is an example:
RREPLACES_${PN} = "other_package_being_replaced"BitBake, which the OpenEmbedded build system uses, supports specifying versioned replacements. Although the syntax varies depending on the packaging format, BitBake hides these differences from you. Here is the general syntax to specify versions with the
RREPLACESvariable:RREPLACES_${PN} = "package(operatorversion)"For
operator, you can specify the following:= < > <= >=For example, the following sets up a replacement using version 1.2 or greater of the package
foo:RREPLACES_${PN} = "foo (>= 1.2)"- RSUGGESTS¶
A list of additional packages that you can suggest for installation by the package manager at the time a package is installed. Not all package managers support this functionality.
As with all package-controlling variables, you must always use this variable in conjunction with a package name override. Here is an example:
RSUGGESTS_${PN} = "useful_packageanother_package"
S
- S¶
The location in the Build Directory where unpacked recipe source code resides. By default, this directory is
${WORKDIR}/${BPN}-${PV}, where${BPN}is the base recipe name and${PV}is the recipe version. If the source tarball extracts the code to a directory named anything other than${BPN}-${PV}, or if the source code is fetched from an SCM such as Git or Subversion, then you must setSin the recipe so that the OpenEmbedded build system knows where to find the unpacked source.As an example, assume a Source Directory top-level folder named
pokyand a default Build Directory atpoky/build. In this case, the work directory the build system uses to keep the unpacked recipe fordbis the following:poky/build/tmp/work/qemux86-poky-linux/db/5.1.19-r3/db-5.1.19The unpacked source code resides in the
db-5.1.19folder.This next example assumes a Git repository. By default, Git repositories are cloned to
${WORKDIR}/gitduringdo_fetch. Since this path is different from the default value ofS, you must set it specifically so the source can be located:SRC_URI = "git://path/to/repo.git" S = "${WORKDIR}/git"- SANITY_REQUIRED_UTILITIES¶
Specifies a list of command-line utilities that should be checked for during the initial sanity checking process when running BitBake. If any of the utilities are not installed on the build host, then BitBake immediately exits with an error.
- SANITY_TESTED_DISTROS¶
A list of the host distribution identifiers that the build system has been tested against. Identifiers consist of the host distributor ID followed by the release, as reported by the
lsb_releasetool or as read from/etc/lsb-release. Separate the list items with explicit newline characters (\n). IfSANITY_TESTED_DISTROSis not empty and the current value ofNATIVELSBSTRINGdoes not appear in the list, then the build system reports a warning that indicates the current host distribution has not been tested as a build host.- SDK_ARCH¶
The target architecture for the SDK. Typically, you do not directly set this variable. Instead, use
SDKMACHINE.- SDK_DEPLOY¶
The directory set up and used by the
populate_sdk_baseclass to which the SDK is deployed. Thepopulate_sdk_baseclass definesSDK_DEPLOYas follows:SDK_DEPLOY = "${TMPDIR}/deploy/sdk"- SDK_DIR¶
The parent directory used by the OpenEmbedded build system when creating SDK output. The
populate_sdk_baseclass defines the variable as follows:SDK_DIR = "${WORKDIR}/sdk"Note
TheSDK_DIRdirectory is a temporary directory as it is part ofWORKDIR. The final output directory isSDK_DEPLOY.- SDK_EXT_TYPE¶
Controls whether or not shared state artifacts are copied into the extensible SDK. The default value of "full" copies all of the required shared state artifacts into the extensible SDK. The value "minimal" leaves these artifacts out of the SDK.
Note
If you set the variable to "minimal", you need to ensureSSTATE_MIRRORSis set in the SDK's configuration to enable the artifacts to be fetched as needed.- SDK_HOST_MANIFEST¶
The manifest file for the host part of the SDK. This file lists all the installed packages that make up the host part of the SDK. The file contains package information on a line-per-package basis as follows:
packagenamepackagearchversionThe
populate_sdk_baseclass defines the manifest file as follows:SDK_HOST_MANIFEST = "${SDK_DEPLOY}/${TOOLCHAIN_OUTPUTNAME}.host.manifest"The location is derived using the
SDK_DEPLOYandTOOLCHAIN_OUTPUTNAMEvariables.- SDK_INCLUDE_PKGDATA¶
When set to "1", specifies to include the packagedata for all recipes in the "world" target in the extensible SDK. Including this data allows the
devtool searchcommand to find these recipes in search results, as well as allows thedevtool addcommand to map dependencies more effectively.Note
Enabling theSDK_INCLUDE_PKGDATAvariable significantly increases build time because all of world needs to be built. Enabling the variable also slightly increases the size of the extensible SDK.- SDK_INCLUDE_TOOLCHAIN¶
When set to "1", specifies to include the toolchain in the extensible SDK. Including the toolchain is useful particularly when
SDK_EXT_TYPEis set to "minimal" to keep the SDK reasonably small but you still want to provide a usable toolchain. For example, suppose you want to use the toolchain from an IDE (e.g. Eclipse) or from other tools and you do not want to perform additional steps to install the toolchain.The
SDK_INCLUDE_TOOLCHAINvariable defaults to "0" ifSDK_EXT_TYPEis set to "minimal", and defaults to "1" ifSDK_EXT_TYPEis set to "full".- SDK_INHERIT_BLACKLIST¶
A list of classes to remove from the
INHERITvalue globally within the extensible SDK configuration. Thepopulate-sdk-extclass sets the default value:SDK_INHERIT_BLACKLIST ?= "buildhistory icecc"Some classes are not generally applicable within the extensible SDK context. You can use this variable to disable those classes.
For additional information on how to customize the extensible SDK's configuration, see the "Configuring the Extensible SDK" section in the Yocto Project Application Development and the Extensible Software Development Kit (eSDK) manual.
- SDK_LOCAL_CONF_BLACKLIST¶
A list of variables not allowed through from the OpenEmbedded build system configuration into the extensible SDK configuration. Usually, these are variables that are specific to the machine on which the build system is running and thus would be potentially problematic within the extensible SDK.
By default,
SDK_LOCAL_CONF_BLACKLISTis set in thepopulate-sdk-extclass and excludes the following variables:CONF_VERSION BB_NUMBER_THREADS BB_NUMBER_PARSE_THREADS PARALLEL_MAKE PRSERV_HOST SSTATE_MIRRORS DL_DIR SSTATE_DIR TMPDIR BB_SERVER_TIMEOUTFor additional information on how to customize the extensible SDK's configuration, see the "Configuring the Extensible SDK" section in the Yocto Project Application Development and the Extensible Software Development Kit (eSDK) manual.
- SDK_LOCAL_CONF_WHITELIST¶
A list of variables allowed through from the OpenEmbedded build system configuration into the extensible SDK configuration. By default, the list of variables is empty and is set in the
populate-sdk-extclass.This list overrides the variables specified using the
SDK_LOCAL_CONF_BLACKLISTvariable as well as any variables identified by automatic blacklisting due to the "/" character being found at the start of the value, which is usually indicative of being a path and thus might not be valid on the system where the SDK is installed.For additional information on how to customize the extensible SDK's configuration, see the "Configuring the Extensible SDK" section in the Yocto Project Application Development and the Extensible Software Development Kit (eSDK) manual.
- SDK_NAME¶
The base name for SDK output files. The name is derived from the
DISTRO,TCLIBC,SDK_ARCH,IMAGE_BASENAME, andTUNE_PKGARCHvariables:SDK_NAME = "${DISTRO}-${TCLIBC}-${SDK_ARCH}-${IMAGE_BASENAME}-${TUNE_PKGARCH}"- SDK_OS¶
Specifies the operating system for which the SDK will be built. The default value is the value of
BUILD_OS.- SDK_OUTPUT¶
The location used by the OpenEmbedded build system when creating SDK output. The
populate_sdk_baseclass defines the variable as follows:SDK_DIR = "${WORKDIR}/sdk" SDK_OUTPUT = "${SDK_DIR}/image" SDK_DEPLOY = "${DEPLOY_DIR}/sdk"Note
TheSDK_OUTPUTdirectory is a temporary directory as it is part ofWORKDIRby way ofSDK_DIR. The final output directory isSDK_DEPLOY.- SDK_PACKAGE_ARCHS¶
Specifies a list of architectures compatible with the SDK machine. This variable is set automatically and should not normally be hand-edited. Entries are separated using spaces and listed in order of priority. The default value for
SDK_PACKAGE_ARCHSis "all any noarch ${SDK_ARCH}-${SDKPKGSUFFIX}".- SDK_POSTPROCESS_COMMAND¶
Specifies a list of functions to call once the OpenEmbedded build system creates the SDK. You can specify functions separated by semicolons:
SDK_POSTPROCESS_COMMAND += "function; ... "If you need to pass an SDK path to a command within a function, you can use
${SDK_DIR}, which points to the parent directory used by the OpenEmbedded build system when creating SDK output. See theSDK_DIRvariable for more information.- SDK_PREFIX¶
The toolchain binary prefix used for
nativesdkrecipes. The OpenEmbedded build system uses theSDK_PREFIXvalue to set theTARGET_PREFIXwhen buildingnativesdkrecipes. The default value is "${SDK_SYS}-".- SDK_RECRDEP_TASKS¶
A list of shared state tasks added to the extensible SDK. By default, the following tasks are added:
do_populate_lic do_package_qa do_populate_sysroot do_deployDespite the default value of "" for the
SDK_RECRDEP_TASKSvariable, the above four tasks are always added to the SDK. To specify tasks beyond these four, you need to use theSDK_RECRDEP_TASKSvariable (e.g. you are defining additional tasks that are needed in order to buildSDK_TARGETS).- SDK_SYS¶
Specifies the system, including the architecture and the operating system, for which the SDK will be built.
The OpenEmbedded build system automatically sets this variable based on
SDK_ARCH,SDK_VENDOR, andSDK_OS. You do not need to set theSDK_SYSvariable yourself.- SDK_TARGET_MANIFEST¶
The manifest file for the target part of the SDK. This file lists all the installed packages that make up the target part of the SDK. The file contains package information on a line-per-package basis as follows:
packagenamepackagearchversionThe
populate_sdk_baseclass defines the manifest file as follows:SDK_TARGET_MANIFEST = "${SDK_DEPLOY}/${TOOLCHAIN_OUTPUTNAME}.target.manifest"The location is derived using the
SDK_DEPLOYandTOOLCHAIN_OUTPUTNAMEvariables.- SDK_TARGETS¶
A list of targets to install from shared state as part of the standard or extensible SDK installation. The default value is "${PN}" (i.e. the image from which the SDK is built).
The
SDK_TARGETSvariable is an internal variable and typically would not be changed.- SDK_TITLE¶
The title to be printed when running the SDK installer. By default, this title is based on the
DISTRO_NAMEorDISTROvariable and is set in thepopulate_sdk_baseclass as follows:SDK_TITLE ??= "${@d.getVar('DISTRO_NAME') or d.getVar('DISTRO')} SDK"For the default distribution "poky",
SDK_TITLEis set to "Poky (Yocto Project Reference Distro)".For information on how to change this default title, see the "Changing the Extensible SDK Installer Title" section in the Yocto Project Application Development and the Extensible Software Development Kit (eSDK) manual.
- SDK_UPDATE_URL¶
An optional URL for an update server for the extensible SDK. If set, the value is used as the default update server when running
devtool sdk-updatewithin the extensible SDK.- SDK_VENDOR¶
Specifies the name of the SDK vendor.
- SDK_VERSION¶
Specifies the version of the SDK. The distribution configuration file (e.g.
/meta-poky/conf/distro/poky.conf) defines theSDK_VERSIONas follows:SDK_VERSION := "${@'${DISTRO_VERSION}'.replace('snapshot-${DATE}','snapshot')}"For additional information, see the
DISTRO_VERSIONandDATEvariables.- SDKEXTPATH¶
The default installation directory for the Extensible SDK. By default, this directory is based on the
DISTROvariable and is set in thepopulate_sdk_baseclass as follows:SDKEXTPATH ??= "~/${@d.getVar('DISTRO')}_sdk"For the default distribution "poky", the
SDKEXTPATHis set to "poky_sdk".For information on how to change this default directory, see the "Changing the Default SDK Installation Directory" section in the Yocto Project Application Development and the Extensible Software Development Kit (eSDK) manual.
- SDKIMAGE_FEATURES¶
Equivalent to
IMAGE_FEATURES. However, this variable applies to the SDK generated from an image using the following command:$ bitbake -c populate_sdkimagename- SDKMACHINE¶
The machine for which the SDK is built. In other words, the SDK is built such that it runs on the target you specify with the
SDKMACHINEvalue. The value points to a corresponding.conffile underconf/machine-sdk/.You can use "i686" and "x86_64" as possible values for this variable. The variable defaults to "i686" and is set in the local.conf file in the Build Directory.
SDKMACHINE ?= "i686"Note
You cannot set theSDKMACHINEvariable in your distribution configuration file. If you do, the configuration will not take affect.- SDKPATH¶
Defines the path offered to the user for installation of the SDK that is generated by the OpenEmbedded build system. The path appears as the default location for installing the SDK when you run the SDK's installation script. You can override the offered path when you run the script.
- SDKTARGETSYSROOT¶
The full path to the sysroot used for cross-compilation within an SDK as it will be when installed into the default
SDKPATH.- SECTION¶
The section in which packages should be categorized. Package management utilities can make use of this variable.
- SELECTED_OPTIMIZATION¶
Specifies the optimization flags passed to the C compiler when building for the target. The flags are passed through the default value of the
TARGET_CFLAGSvariable.The
SELECTED_OPTIMIZATIONvariable takes the value ofFULL_OPTIMIZATIONunlessDEBUG_BUILD= "1". If that is the case, the value ofDEBUG_OPTIMIZATIONis used.- SERIAL_CONSOLE¶
Defines a serial console (TTY) to enable using getty. Provide a value that specifies the baud rate followed by the TTY device name separated by a space. You cannot specify more than one TTY device:
SERIAL_CONSOLE = "115200 ttyS0"- SERIAL_CONSOLES¶
Defines a serial console (TTY) to enable using getty. Provide a value that specifies the baud rate followed by the TTY device name separated by a semicolon. Use spaces to separate multiple devices:
SERIAL_CONSOLES = "115200;ttyS0 115200;ttyS1"- SERIAL_CONSOLES_CHECK¶
Specifies serial consoles, which must be listed in
SERIAL_CONSOLES, to check against/proc/consolebefore enabling them using getty. This variable allows aliasing in the format: <device>:<alias>. If a device was listed as "sclp_line0" in/dev/and "ttyS0" was listed in/proc/console, you would do the following:SERIAL_CONSOLES_CHECK = "slcp_line0:ttyS0"This variable is currently only supported with SysVinit (i.e. not with systemd).
- SIGGEN_EXCLUDE_SAFE_RECIPE_DEPS¶
A list of recipe dependencies that should not be used to determine signatures of tasks from one recipe when they depend on tasks from another recipe. For example:
SIGGEN_EXCLUDE_SAFE_RECIPE_DEPS += "intone->mplayer2"In the previous example,
intonedepends onmplayer2.You can use the special token
"*"on the left-hand side of the dependency to match all recipes except the one on the right-hand side. Here is an example:SIGGEN_EXCLUDE_SAFE_RECIPE_DEPS += "*->quilt-native"In the previous example, all recipes except
quilt-nativeignore task signatures from thequilt-nativerecipe when determining their task signatures.Use of this variable is one mechanism to remove dependencies that affect task signatures and thus force rebuilds when a recipe changes.
Caution
If you add an inappropriate dependency for a recipe relationship, the software might break during runtime if the interface of the second recipe was changed after the first recipe had been built.- SIGGEN_EXCLUDERECIPES_ABISAFE¶
A list of recipes that are completely stable and will never change. The ABI for the recipes in the list are presented by output from the tasks run to build the recipe. Use of this variable is one way to remove dependencies from one recipe on another that affect task signatures and thus force rebuilds when the recipe changes.
Caution
If you add an inappropriate variable to this list, the software might break at runtime if the interface of the recipe was changed after the other had been built.- SITEINFO_BITS¶
Specifies the number of bits for the target system CPU. The value should be either "32" or "64".
- SITEINFO_ENDIANNESS¶
Specifies the endian byte order of the target system. The value should be either "le" for little-endian or "be" for big-endian.
- SKIP_FILEDEPS¶
Enables removal of all files from the "Provides" section of an RPM package. Removal of these files is required for packages containing prebuilt binaries and libraries such as
libstdc++andglibc.To enable file removal, set the variable to "1" in your
conf/local.confconfiguration file in your: Build Directory.SKIP_FILEDEPS = "1"- SOC_FAMILY¶
Groups together machines based upon the same family of SOC (System On Chip). You typically set this variable in a common
.incfile that you include in the configuration files of all the machines.Note
You must includeconf/machine/include/soc-family.incfor this variable to appear inMACHINEOVERRIDES.- SOLIBS¶
Defines the suffix for shared libraries used on the target platform. By default, this suffix is ".so.*" for all Linux-based systems and is defined in the
meta/conf/bitbake.confconfiguration file.You will see this variable referenced in the default values of
FILES_${PN}.- SOLIBSDEV¶
Defines the suffix for the development symbolic link (symlink) for shared libraries on the target platform. By default, this suffix is ".so" for Linux-based systems and is defined in the
meta/conf/bitbake.confconfiguration file.You will see this variable referenced in the default values of
FILES_${PN}-dev.- SOURCE_MIRROR_FETCH¶
When you are fetching files to create a mirror of sources (i.e. creating a source mirror), setting
SOURCE_MIRROR_FETCHto "1" in yourlocal.confconfiguration file ensures the source for all recipes are fetched regardless of whether or not a recipe is compatible with the configuration. A recipe is considered incompatible with the currently configured machine when either or both theCOMPATIBLE_MACHINEvariable andCOMPATIBLE_HOSTvariables specify compatibility with a machine other than that of the current machine or host.Warning
Do not set theSOURCE_MIRROR_FETCHvariable unless you are creating a source mirror. In other words, do not set the variable during a normal build.- SOURCE_MIRROR_URL¶
Defines your own
PREMIRRORSfrom which to first fetch source before attempting to fetch from the upstream specified inSRC_URI.To use this variable, you must globally inherit the
own-mirrorsclass and then provide the URL to your mirrors. Here is the general syntax:INHERIT += "own-mirrors" SOURCE_MIRROR_URL = "http://example.com/my_source_mirror"Note
You can specify only a single URL inSOURCE_MIRROR_URL.- SPDXLICENSEMAP¶
Maps commonly used license names to their SPDX counterparts found in
meta/files/common-licenses/. For the defaultSPDXLICENSEMAPmappings, see themeta/conf/licenses.conffile.For additional information, see the
LICENSEvariable.- SPECIAL_PKGSUFFIX¶
A list of prefixes for
PNused by the OpenEmbedded build system to create variants of recipes or packages. The list specifies the prefixes to strip off during certain circumstances such as the generation of theBPNvariable.- SPL_BINARY¶
The file type for the Secondary Program Loader (SPL). Some devices use an SPL from which to boot (e.g. the BeagleBone development board). For such cases, you can declare the file type of the SPL binary in the
u-boot.incinclude file, which is used in the U-Boot recipe.The SPL file type is set to "null" by default in the
u-boot.incfile as follows:# Some versions of u-boot build an SPL (Second Program Loader) image that # should be packaged along with the u-boot binary as well as placed in the # deploy directory. For those versions they can set the following variables # to allow packaging the SPL. SPL_BINARY ?= "" SPL_BINARYNAME ?= "${@os.path.basename(d.getVar("SPL_BINARY"))}" SPL_IMAGE ?= "${SPL_BINARYNAME}-${MACHINE}-${PV}-${PR}" SPL_SYMLINK ?= "${SPL_BINARYNAME}-${MACHINE}"The
SPL_BINARYvariable helps form variousSPL_*variables used by the OpenEmbedded build system.See the BeagleBone machine configuration example in the "Creating a new BSP Layer Using the
bitbake-layersScript" section in the Yocto Project Board Support Package Developer's Guide for additional information.- SRC_URI¶
The list of source files - local or remote. This variable tells the OpenEmbedded build system which bits to pull in for the build and how to pull them in. For example, if the recipe or append file only needs to fetch a tarball from the Internet, the recipe or append file uses a single
SRC_URIentry. On the other hand, if the recipe or append file needs to fetch a tarball, apply two patches, and include a custom file, the recipe or append file would include four instances of the variable.The following list explains the available URI protocols. URI protocols are highly dependent on particular BitBake Fetcher submodules. Depending on the fetcher BitBake uses, various URL parameters are employed. For specifics on the supported Fetchers, see the "Fetchers" section in the BitBake User Manual.
file://- Fetches files, which are usually files shipped with the Metadata, from the local machine (e.g. patch files). The path is relative to theFILESPATHvariable. Thus, the build system searches, in order, from the following directories, which are assumed to be a subdirectories of the directory in which the recipe file (.bb) or append file (.bbappend) resides:${BPN}- The base recipe name without any special suffix or version numbers.${BP}-${BPN}-${PV}. The base recipe name and version but without any special package name suffix.files - Files within a directory, which is named
filesand is also alongside the recipe or append file.
Note
If you want the build system to pick up files specified through aSRC_URIstatement from your append file, you need to be sure to extend theFILESPATHvariable by also using theFILESEXTRAPATHSvariable from within your append file.bzr://- Fetches files from a Bazaar revision control repository.git://- Fetches files from a Git revision control repository.osc://- Fetches files from an OSC (OpenSUSE Build service) revision control repository.repo://- Fetches files from a repo (Git) repository.ccrc://- Fetches files from a ClearCase repository.http://- Fetches files from the Internet usinghttp.https://- Fetches files from the Internet usinghttps.ftp://- Fetches files from the Internet usingftp.cvs://- Fetches files from a CVS revision control repository.hg://- Fetches files from a Mercurial (hg) revision control repository.p4://- Fetches files from a Perforce (p4) revision control repository.ssh://- Fetches files from a secure shell.svn://- Fetches files from a Subversion (svn) revision control repository.
Standard and recipe-specific options for
SRC_URIexist. Here are standard options:apply- Whether to apply the patch or not. The default action is to apply the patch.striplevel- Which striplevel to use when applying the patch. The default level is 1.patchdir- Specifies the directory in which the patch should be applied. The default is${S}.
Here are options specific to recipes building code from a revision control system:
mindate- Apply the patch only ifSRCDATEis equal to or greater thanmindate.maxdate- Apply the patch only ifSRCDATEis not later thanmaxdate.minrev- Apply the patch only ifSRCREVis equal to or greater thanminrev.maxrev- Apply the patch only ifSRCREVis not later thanmaxrev.rev- Apply the patch only ifSRCREVis equal torev.notrev- Apply the patch only ifSRCREVis not equal torev.
Here are some additional options worth mentioning:
unpack- Controls whether or not to unpack the file if it is an archive. The default action is to unpack the file.destsuffix- Places the file (or extracts its contents) into the specified subdirectory ofWORKDIRwhen the Git fetcher is used.subdir- Places the file (or extracts its contents) into the specified subdirectory ofWORKDIRwhen the local (file://) fetcher is used.localdir- Places the file (or extracts its contents) into the specified subdirectory ofWORKDIRwhen the CVS fetcher is used.subpath- Limits the checkout to a specific subpath of the tree when using the Git fetcher is used.name- Specifies a name to be used for association withSRC_URIchecksums when you have more than one file specified inSRC_URI.downloadfilename- Specifies the filename used when storing the downloaded file.
- SRC_URI_OVERRIDES_PACKAGE_ARCH¶
By default, the OpenEmbedded build system automatically detects whether
SRC_URIcontains files that are machine-specific. If so, the build system automatically changesPACKAGE_ARCH. Setting this variable to "0" disables this behavior.- SRCDATE¶
The date of the source code used to build the package. This variable applies only if the source was fetched from a Source Code Manager (SCM).
- SRCPV¶
Returns the version string of the current package. This string is used to help define the value of
PV.The
SRCPVvariable is defined in themeta/conf/bitbake.confconfiguration file in the Source Directory as follows:SRCPV = "${@bb.fetch2.get_srcrev(d)}"Recipes that need to define
PVdo so with the help of theSRCPV. For example, theofonorecipe (ofono_git.bb) located inmeta/recipes-connectivityin the Source Directory definesPVas follows:PV = "0.12-git${SRCPV}"- SRCREV¶
The revision of the source code used to build the package. This variable applies to Subversion, Git, Mercurial, and Bazaar only. Note that if you want to build a fixed revision and you want to avoid performing a query on the remote repository every time BitBake parses your recipe, you should specify a
SRCREVthat is a full revision identifier and not just a tag.Note
For information on limitations when inheriting the latest revision of software usingSRCREV, see theAUTOREVvariable description and the "Automatically Incrementing a Binary Package Revision Number" section, which is in the Yocto Project Development Tasks Manual.- SSTATE_DIR¶
The directory for the shared state cache.
- SSTATE_MIRROR_ALLOW_NETWORK¶
If set to "1", allows fetches from mirrors that are specified in
SSTATE_MIRRORSto work even when fetching from the network is disabled by settingBB_NO_NETWORKto "1". Using theSSTATE_MIRROR_ALLOW_NETWORKvariable is useful if you have setSSTATE_MIRRORSto point to an internal server for your shared state cache, but you want to disable any other fetching from the network.- SSTATE_MIRRORS¶
Configures the OpenEmbedded build system to search other mirror locations for prebuilt cache data objects before building out the data. This variable works like fetcher
MIRRORSandPREMIRRORSand points to the cache locations to check for the shared state (sstate) objects.You can specify a filesystem directory or a remote URL such as HTTP or FTP. The locations you specify need to contain the shared state cache (sstate-cache) results from previous builds. The sstate-cache you point to can also be from builds on other machines.
When pointing to sstate build artifacts on another machine that uses a different GCC version for native builds, you must configure
SSTATE_MIRRORwith a regular expression that maps local search paths to server paths. The paths need to take into accountNATIVELSBSTRINGset by theuninativeclass. For example, the following maps the local search pathuniversal-4.9to the server-provided pathserver_url_sstate_path:SSTATE_MIRRORS ?= file://universal-4.9/(.*) http://server_url_sstate_path/universal-4.8/\1 \nIf a mirror uses the same structure as
SSTATE_DIR, you need to add "PATH" at the end as shown in the examples below. The build system substitutes the correct path within the directory structure.SSTATE_MIRRORS ?= "\ file://.* http://someserver.tld/share/sstate/PATH;downloadfilename=PATH \n \ file://.* file:///some-local-dir/sstate/PATH"- SSTATE_SCAN_FILES¶
Controls the list of files the OpenEmbedded build system scans for hardcoded installation paths. The variable uses a space-separated list of filenames (not paths) with standard wildcard characters allowed.
During a build, the OpenEmbedded build system creates a shared state (sstate) object during the first stage of preparing the sysroots. That object is scanned for hardcoded paths for original installation locations. The list of files that are scanned for paths is controlled by the
SSTATE_SCAN_FILESvariable. Typically, recipes add files they want to be scanned to the value ofSSTATE_SCAN_FILESrather than the variable being comprehensively set. Thesstateclass specifies the default list of files.For details on the process, see the
stagingclass.- STAGING_BASE_LIBDIR_NATIVE¶
Specifies the path to the
/libsubdirectory of the sysroot directory for the build host.- STAGING_BASELIBDIR¶
Specifies the path to the
/libsubdirectory of the sysroot directory for the target for which the current recipe is being built (STAGING_DIR_HOST).- STAGING_BINDIR¶
Specifies the path to the
/usr/binsubdirectory of the sysroot directory for the target for which the current recipe is being built (STAGING_DIR_HOST).- STAGING_BINDIR_CROSS¶
Specifies the path to the directory containing binary configuration scripts. These scripts provide configuration information for other software that wants to make use of libraries or include files provided by the software associated with the script.
Note
This style of build configuration has been largely replaced bypkg-config. Consequently, ifpkg-configis supported by the library to which you are linking, it is recommended you usepkg-configinstead of a provided configuration script.- STAGING_BINDIR_NATIVE¶
Specifies the path to the
/usr/binsubdirectory of the sysroot directory for the build host.- STAGING_DATADIR¶
Specifies the path to the
/usr/sharesubdirectory of the sysroot directory for the target for which the current recipe is being built (STAGING_DIR_HOST).- STAGING_DATADIR_NATIVE¶
Specifies the path to the
/usr/sharesubdirectory of the sysroot directory for the build host.- STAGING_DIR¶
Helps construct the
recipe-sysrootsdirectory, which is used during packaging.For information on how staging for recipe-specific sysroots occurs, see the
do_populate_sysroottask, the "Sharing Files Between Recipes" section in the Yocto Project Development Tasks Manual, the "Configuration, Compilation, and Staging" section in the Yocto Project Overview and Concepts Manual, and theSYSROOT_DIRSvariable.Note
Recipes should never write files directly under theSTAGING_DIRdirectory because the OpenEmbedded build system manages the directory automatically. Instead, files should be installed to${D}within your recipe'sdo_installtask and then the OpenEmbedded build system will stage a subset of those files into the sysroot.- STAGING_DIR_HOST¶
Specifies the path to the sysroot directory for the system on which the component is built to run (the system that hosts the component). For most recipes, this sysroot is the one in which that recipe's
do_populate_sysroottask copies files. Exceptions include-nativerecipes, where thedo_populate_sysroottask instead usesSTAGING_DIR_NATIVE. Depending on the type of recipe and the build target,STAGING_DIR_HOSTcan have the following values:For recipes building for the target machine, the value is "${STAGING_DIR}/${MACHINE}".
For native recipes building for the build host, the value is empty given the assumption that when building for the build host, the build host's own directories should be used.
Note
-nativerecipes are not installed into host paths like such as/usr. Rather, these recipes are installed intoSTAGING_DIR_NATIVE. When compiling-nativerecipes, standard build environment variables such asCPPFLAGSandCFLAGSare set up so that both host paths andSTAGING_DIR_NATIVEare searched for libraries and headers using, for example, GCC's-isystemoption.Thus, the emphasis is that the
STAGING_DIR*variables should be viewed as input variables by tasks such asdo_configure,do_compile, anddo_install. Having the real system root correspond toSTAGING_DIR_HOSTmakes conceptual sense for-nativerecipes, as they make use of host headers and libraries.
- STAGING_DIR_NATIVE¶
Specifies the path to the sysroot directory used when building components that run on the build host itself.
- STAGING_DIR_TARGET¶
Specifies the path to the sysroot used for the system for which the component generates code. For components that do not generate code, which is the majority,
STAGING_DIR_TARGETis set to matchSTAGING_DIR_HOST.Some recipes build binaries that can run on the target system but those binaries in turn generate code for another different system (e.g. cross-canadian recipes). Using terminology from GNU, the primary system is referred to as the "HOST" and the secondary, or different, system is referred to as the "TARGET". Thus, the binaries run on the "HOST" system and generate binaries for the "TARGET" system. The
STAGING_DIR_HOSTvariable points to the sysroot used for the "HOST" system, whileSTAGING_DIR_TARGETpoints to the sysroot used for the "TARGET" system.- STAGING_ETCDIR_NATIVE¶
Specifies the path to the
/etcsubdirectory of the sysroot directory for the build host.- STAGING_EXECPREFIXDIR¶
Specifies the path to the
/usrsubdirectory of the sysroot directory for the target for which the current recipe is being built (STAGING_DIR_HOST).- STAGING_INCDIR¶
Specifies the path to the
/usr/includesubdirectory of the sysroot directory for the target for which the current recipe being built (STAGING_DIR_HOST).- STAGING_INCDIR_NATIVE¶
Specifies the path to the
/usr/includesubdirectory of the sysroot directory for the build host.- STAGING_KERNEL_BUILDDIR¶
Points to the directory containing the kernel build artifacts. Recipes building software that needs to access kernel build artifacts (e.g.
systemtap-uprobes) can look in the directory specified with theSTAGING_KERNEL_BUILDDIRvariable to find these artifacts after the kernel has been built.- STAGING_KERNEL_DIR¶
The directory with kernel headers that are required to build out-of-tree modules.
- STAGING_LIBDIR¶
Specifies the path to the
/usr/libsubdirectory of the sysroot directory for the target for which the current recipe is being built (STAGING_DIR_HOST).- STAGING_LIBDIR_NATIVE¶
Specifies the path to the
/usr/libsubdirectory of the sysroot directory for the build host.- STAMP¶
Specifies the base path used to create recipe stamp files. The path to an actual stamp file is constructed by evaluating this string and then appending additional information. Currently, the default assignment for
STAMPas set in themeta/conf/bitbake.conffile is:STAMP = "${STAMPS_DIR}/${MULTIMACH_TARGET_SYS}/${PN}/${EXTENDPE}${PV}-${PR}"For information on how BitBake uses stamp files to determine if a task should be rerun, see the "Stamp Files and the Rerunning of Tasks" section in the Yocto Project Overview and Concepts Manual.
See
STAMPS_DIR,MULTIMACH_TARGET_SYS,PN,EXTENDPE,PV, andPRfor related variable information.- STAMPS_DIR¶
Specifies the base directory in which the OpenEmbedded build system places stamps. The default directory is
${TMPDIR}/stamps.- STRIP¶
The minimal command and arguments to run
strip, which is used to strip symbols.- SUMMARY¶
The short (72 characters or less) summary of the binary package for packaging systems such as
opkg,rpm, ordpkg. By default,SUMMARYis used to define theDESCRIPTIONvariable ifDESCRIPTIONis not set in the recipe.- SVNDIR¶
The directory in which files checked out of a Subversion system are stored.
- SYSLINUX_DEFAULT_CONSOLE¶
Specifies the kernel boot default console. If you want to use a console other than the default, set this variable in your recipe as follows where "X" is the console number you want to use:
SYSLINUX_DEFAULT_CONSOLE = "console=ttyX"The
syslinuxclass initially sets this variable to null but then checks for a value later.- SYSLINUX_OPTS¶
Lists additional options to add to the syslinux file. You need to set this variable in your recipe. If you want to list multiple options, separate the options with a semicolon character (
;).The
syslinuxclass uses this variable to create a set of options.- SYSLINUX_SERIAL¶
Specifies the alternate serial port or turns it off. To turn off serial, set this variable to an empty string in your recipe. The variable's default value is set in the
syslinuxclass as follows:SYSLINUX_SERIAL ?= "0 115200"The class checks for and uses the variable as needed.
- SYSLINUX_SPLASH¶
An
.LSSfile used as the background for the VGA boot menu when you use the boot menu. You need to set this variable in your recipe.The
syslinuxclass checks for this variable and if found, the OpenEmbedded build system installs the splash screen.- SYSLINUX_SERIAL_TTY¶
Specifies the alternate console=tty... kernel boot argument. The variable's default value is set in the
syslinuxclass as follows:SYSLINUX_SERIAL_TTY ?= "console=ttyS0,115200"The class checks for and uses the variable as needed.
- SYSROOT_DESTDIR¶
Points to the temporary directory under the work directory (default "
${WORKDIR}/sysroot-destdir") where the files populated into the sysroot are assembled during thedo_populate_sysroottask.- SYSROOT_DIRS¶
Directories that are staged into the sysroot by the
do_populate_sysroottask. By default, the following directories are staged:SYSROOT_DIRS = " \ ${includedir} \ ${libdir} \ ${base_libdir} \ ${nonarch_base_libdir} \ ${datadir} \ "- SYSROOT_DIRS_BLACKLIST¶
Directories that are not staged into the sysroot by the
do_populate_sysroottask. You can use this variable to exclude certain subdirectories of directories listed inSYSROOT_DIRSfrom staging. By default, the following directories are not staged:SYSROOT_DIRS_BLACKLIST = " \ ${mandir} \ ${docdir} \ ${infodir} \ ${datadir}/locale \ ${datadir}/applications \ ${datadir}/fonts \ ${datadir}/pixmaps \ "- SYSROOT_DIRS_NATIVE¶
Extra directories staged into the sysroot by the
do_populate_sysroottask for-nativerecipes, in addition to those specified inSYSROOT_DIRS. By default, the following extra directories are staged:SYSROOT_DIRS_NATIVE = " \ ${bindir} \ ${sbindir} \ ${base_bindir} \ ${base_sbindir} \ ${libexecdir} \ ${sysconfdir} \ ${localstatedir} \ "Note
Programs built by-nativerecipes run directly from the sysroot (STAGING_DIR_NATIVE), which is why additional directories containing program executables and supporting files need to be staged.- SYSROOT_PREPROCESS_FUNCS¶
A list of functions to execute after files are staged into the sysroot. These functions are usually used to apply additional processing on the staged files, or to stage additional files.
- SYSTEMD_AUTO_ENABLE¶
When inheriting the
systemdclass, this variable specifies whether the specified service inSYSTEMD_SERVICEshould start automatically or not. By default, the service is enabled to automatically start at boot time. The default setting is in thesystemdclass as follows:SYSTEMD_AUTO_ENABLE ??= "enable"You can disable the service by setting the variable to "disable".
- SYSTEMD_BOOT_CFG¶
When
EFI_PROVIDERis set to "systemd-boot", theSYSTEMD_BOOT_CFGvariable specifies the configuration file that should be used. By default, thesystemd-bootclass sets theSYSTEMD_BOOT_CFGas follows:SYSTEMD_BOOT_CFG ?= "${S}/loader.conf"For information on Systemd-boot, see the Systemd-boot documentation.
- SYSTEMD_BOOT_ENTRIES¶
When
EFI_PROVIDERis set to "systemd-boot", theSYSTEMD_BOOT_ENTRIESvariable specifies a list of entry files (*.conf) to install that contain one boot entry per file. By default, thesystemd-bootclass sets theSYSTEMD_BOOT_ENTRIESas follows:SYSTEMD_BOOT_ENTRIES ?= ""For information on Systemd-boot, see the Systemd-boot documentation.
- SYSTEMD_BOOT_TIMEOUT¶
When
EFI_PROVIDERis set to "systemd-boot", theSYSTEMD_BOOT_TIMEOUTvariable specifies the boot menu timeout in seconds. By default, thesystemd-bootclass sets theSYSTEMD_BOOT_TIMEOUTas follows:SYSTEMD_BOOT_TIMEOUT ?= "10"For information on Systemd-boot, see the Systemd-boot documentation.
- SYSTEMD_PACKAGES¶
When inheriting the
systemdclass, this variable locates the systemd unit files when they are not found in the main recipe's package. By default, theSYSTEMD_PACKAGESvariable is set such that the systemd unit files are assumed to reside in the recipes main package:SYSTEMD_PACKAGES ?= "${PN}"If these unit files are not in this recipe's main package, you need to use
SYSTEMD_PACKAGESto list the package or packages in which the build system can find the systemd unit files.- SYSTEMD_SERVICE¶
When inheriting the
systemdclass, this variable specifies the systemd service name for a package.When you specify this file in your recipe, use a package name override to indicate the package to which the value applies. Here is an example from the connman recipe:
SYSTEMD_SERVICE_${PN} = "connman.service"- SYSVINIT_ENABLED_GETTYS¶
When using SysVinit, specifies a space-separated list of the virtual terminals that should run a getty (allowing login), assuming
USE_VTis not set to "0".The default value for
SYSVINIT_ENABLED_GETTYSis "1" (i.e. only run a getty on the first virtual terminal).
T
- T¶
This variable points to a directory were BitBake places temporary files, which consist mostly of task logs and scripts, when building a particular recipe. The variable is typically set as follows:
T = "${WORKDIR}/temp"The
WORKDIRis the directory into which BitBake unpacks and builds the recipe. The defaultbitbake.conffile sets this variable.The
Tvariable is not to be confused with theTMPDIRvariable, which points to the root of the directory tree where BitBake places the output of an entire build.- TARGET_ARCH¶
The target machine's architecture. The OpenEmbedded build system supports many architectures. Here is an example list of architectures supported. This list is by no means complete as the architecture is configurable:
arm i586 x86_64 powerpc powerpc64 mips mipselFor additional information on machine architectures, see the
TUNE_ARCHvariable.- TARGET_AS_ARCH¶
Specifies architecture-specific assembler flags for the target system.
TARGET_AS_ARCHis initialized fromTUNE_ASARGSby default in the BitBake configuration file (meta/conf/bitbake.conf):TARGET_AS_ARCH = "${TUNE_ASARGS}"- TARGET_CC_ARCH¶
Specifies architecture-specific C compiler flags for the target system.
TARGET_CC_ARCHis initialized fromTUNE_CCARGSby default.Note
It is a common workaround to appendLDFLAGStoTARGET_CC_ARCHin recipes that build software for the target that would not otherwise respect the exportedLDFLAGSvariable.- TARGET_CC_KERNEL_ARCH¶
This is a specific kernel compiler flag for a CPU or Application Binary Interface (ABI) tune. The flag is used rarely and only for cases where a userspace
TUNE_CCARGSis not compatible with the kernel compilation. TheTARGET_CC_KERNEL_ARCHvariable allows the kernel (and associated modules) to use a different configuration. See themeta/conf/machine/include/arm/feature-arm-thumb.incfile in the Source Directory for an example.- TARGET_CFLAGS¶
Specifies the flags to pass to the C compiler when building for the target. When building in the target context,
CFLAGSis set to the value of this variable by default.Additionally, the SDK's environment setup script sets the
CFLAGSvariable in the environment to theTARGET_CFLAGSvalue so that executables built using the SDK also have the flags applied.- TARGET_CPPFLAGS¶
Specifies the flags to pass to the C pre-processor (i.e. to both the C and the C++ compilers) when building for the target. When building in the target context,
CPPFLAGSis set to the value of this variable by default.Additionally, the SDK's environment setup script sets the
CPPFLAGSvariable in the environment to theTARGET_CPPFLAGSvalue so that executables built using the SDK also have the flags applied.- TARGET_CXXFLAGS¶
Specifies the flags to pass to the C++ compiler when building for the target. When building in the target context,
CXXFLAGSis set to the value of this variable by default.Additionally, the SDK's environment setup script sets the
CXXFLAGSvariable in the environment to theTARGET_CXXFLAGSvalue so that executables built using the SDK also have the flags applied.- TARGET_FPU¶
Specifies the method for handling FPU code. For FPU-less targets, which include most ARM CPUs, the variable must be set to "soft". If not, the kernel emulation gets used, which results in a performance penalty.
- TARGET_LD_ARCH¶
Specifies architecture-specific linker flags for the target system.
TARGET_LD_ARCHis initialized fromTUNE_LDARGSby default in the BitBake configuration file (meta/conf/bitbake.conf):TARGET_LD_ARCH = "${TUNE_LDARGS}"- TARGET_LDFLAGS¶
Specifies the flags to pass to the linker when building for the target. When building in the target context,
LDFLAGSis set to the value of this variable by default.Additionally, the SDK's environment setup script sets the
LDFLAGSvariable in the environment to theTARGET_LDFLAGSvalue so that executables built using the SDK also have the flags applied.- TARGET_OS¶
Specifies the target's operating system. The variable can be set to "linux" for glibc-based systems (GNU C Library) and to "linux-musl" for musl libc. For ARM/EABI targets, "linux-gnueabi" and "linux-musleabi" possible values exist.
- TARGET_PREFIX¶
Specifies the prefix used for the toolchain binary target tools.
Depending on the type of recipe and the build target,
TARGET_PREFIXis set as follows:For recipes building for the target machine, the value is "${TARGET_SYS}-".
For native recipes, the build system sets the variable to the value of
BUILD_PREFIX.For native SDK recipes (
nativesdk), the build system sets the variable to the value ofSDK_PREFIX.
- TARGET_SYS¶
Specifies the system, including the architecture and the operating system, for which the build is occurring in the context of the current recipe.
The OpenEmbedded build system automatically sets this variable based on
TARGET_ARCH,TARGET_VENDOR, andTARGET_OSvariables.Note
You do not need to set theTARGET_SYSvariable yourself.Consider these two examples:
Given a native recipe on a 32-bit, x86 machine running Linux, the value is "i686-linux".
Given a recipe being built for a little-endian, MIPS target running Linux, the value might be "mipsel-linux".
- TARGET_VENDOR¶
Specifies the name of the target vendor.
- TCLIBC¶
Specifies the GNU standard C library (
libc) variant to use during the build process. This variable replacesPOKYLIBC, which is no longer supported.You can select "glibc", "musl", "newlib", or "baremetal"
- TCLIBCAPPEND¶
Specifies a suffix to be appended onto the
TMPDIRvalue. The suffix identifies thelibcvariant for building. When you are building for multiple variants with the same Build Directory, this mechanism ensures that output for differentlibcvariants is kept separate to avoid potential conflicts.In the
defaultsetup.conffile, the default value ofTCLIBCAPPENDis "-${TCLIBC}". However, distros such as poky, which normally only support onelibcvariant, setTCLIBCAPPENDto "" in their distro configuration file resulting in no suffix being applied.- TCMODE¶
Specifies the toolchain selector.
TCMODEcontrols the characteristics of the generated packages and images by telling the OpenEmbedded build system which toolchain profile to use. By default, the OpenEmbedded build system builds its own internal toolchain. The variable's default value is "default", which uses that internal toolchain.Note
IfTCMODEis set to a value other than "default", then it is your responsibility to ensure that the toolchain is compatible with the default toolchain. Using older or newer versions of these components might cause build problems. See the Release Notes for the Yocto Project release for the specific components with which the toolchain must be compatible. To access the Release Notes, go to the Downloads page on the Yocto Project website and click on the "RELEASE INFORMATION" link for the appropriate release.The
TCMODEvariable is similar toTCLIBC, which controls the variant of the GNU standard C library (libc) used during the build process:glibcormusl.With additional layers, it is possible to use a pre-compiled external toolchain. One example is the Sourcery G++ Toolchain. The support for this toolchain resides in the separate Mentor Graphics®
meta-sourcerylayer at http://github.com/MentorEmbedded/meta-sourcery/.The layer's
READMEfile contains information on how to use the Sourcery G++ Toolchain as an external toolchain. In summary, you must be sure to add the layer to yourbblayers.conffile in front of themetalayer and then set theEXTERNAL_TOOLCHAINvariable in yourlocal.conffile to the location in which you installed the toolchain.The fundamentals used for this example apply to any external toolchain. You can use
meta-sourceryas a template for adding support for other external toolchains.- TEST_EXPORT_DIR¶
The location the OpenEmbedded build system uses to export tests when the
TEST_EXPORT_ONLYvariable is set to "1".The
TEST_EXPORT_DIRvariable defaults to"${TMPDIR}/testimage/${PN}".- TEST_EXPORT_ONLY¶
Specifies to export the tests only. Set this variable to "1" if you do not want to run the tests but you want them to be exported in a manner that you to run them outside of the build system.
- TEST_LOG_DIR¶
Holds the SSH log and the boot log for QEMU machines. The
TEST_LOG_DIRvariable defaults to"${WORKDIR}/testimage".Note
Actual test results reside in the task log (log.do_testimage), which is in the${WORKDIR}/temp/directory.- TEST_POWERCONTROL_CMD¶
For automated hardware testing, specifies the command to use to control the power of the target machine under test. Typically, this command would point to a script that performs the appropriate action (e.g. interacting with a web-enabled power strip). The specified command should expect to receive as the last argument "off", "on" or "cycle" specifying to power off, on, or cycle (power off and then power on) the device, respectively.
- TEST_POWERCONTROL_EXTRA_ARGS¶
For automated hardware testing, specifies additional arguments to pass through to the command specified in
TEST_POWERCONTROL_CMD. SettingTEST_POWERCONTROL_EXTRA_ARGSis optional. You can use it if you wish, for example, to separate the machine-specific and non-machine-specific parts of the arguments.- TEST_QEMUBOOT_TIMEOUT¶
The time in seconds allowed for an image to boot before automated runtime tests begin to run against an image. The default timeout period to allow the boot process to reach the login prompt is 500 seconds. You can specify a different value in the
local.conffile.For more information on testing images, see the "Performing Automated Runtime Testing" section in the Yocto Project Development Tasks Manual.
- TEST_SERIALCONTROL_CMD¶
For automated hardware testing, specifies the command to use to connect to the serial console of the target machine under test. This command simply needs to connect to the serial console and forward that connection to standard input and output as any normal terminal program does.
For example, to use the Picocom terminal program on serial device
/dev/ttyUSB0at 115200bps, you would set the variable as follows:TEST_SERIALCONTROL_CMD = "picocom /dev/ttyUSB0 -b 115200"- TEST_SERIALCONTROL_EXTRA_ARGS¶
For automated hardware testing, specifies additional arguments to pass through to the command specified in
TEST_SERIALCONTROL_CMD. SettingTEST_SERIALCONTROL_EXTRA_ARGSis optional. You can use it if you wish, for example, to separate the machine-specific and non-machine-specific parts of the command.- TEST_SERVER_IP¶
The IP address of the build machine (host machine). This IP address is usually automatically detected. However, if detection fails, this variable needs to be set to the IP address of the build machine (i.e. where the build is taking place).
Note
TheTEST_SERVER_IPvariable is only used for a small number of tests such as the "dnf" test suite, which needs to download packages fromWORKDIR/oe-rootfs-repo.- TEST_TARGET¶
Specifies the target controller to use when running tests against a test image. The default controller to use is "QemuTarget":
TEST_TARGET = "QemuTarget"A target controller is a class that defines how an image gets deployed on a target and how a target is started. A layer can extend the controllers by adding a module in the layer's
/lib/oeqa/controllersdirectory and by inheriting theBaseTargetclass, which is an abstract class that cannot be used as a value ofTEST_TARGET.You can provide the following arguments with
TEST_TARGET:"QemuTarget": Boots a QEMU image and runs the tests. See the "Enabling Runtime Tests on QEMU" section in the Yocto Project Development Tasks Manual for more information.
"SimpleRemoteTarget": Runs the tests on target hardware that is already up and running. The hardware can be on the network or it can be a device running an image on QEMU. You must also set
TEST_TARGET_IPwhen you use "SimpleRemoteTarget".Note
This argument is defined inmeta/lib/oeqa/controllers/simpleremote.py.
For information on running tests on hardware, see the "Enabling Runtime Tests on Hardware" section in the Yocto Project Development Tasks Manual.
- TEST_TARGET_IP¶
The IP address of your hardware under test. The
TEST_TARGET_IPvariable has no effect whenTEST_TARGETis set to "qemu".When you specify the IP address, you can also include a port. Here is an example:
TEST_TARGET_IP = "192.168.1.4:2201"Specifying a port is useful when SSH is started on a non-standard port or in cases when your hardware under test is behind a firewall or network that is not directly accessible from your host and you need to do port address translation.
- TEST_SUITES¶
An ordered list of tests (modules) to run against an image when performing automated runtime testing.
The OpenEmbedded build system provides a core set of tests that can be used against images.
Note
Currently, there is only support for running these tests under QEMU.Tests include
ping,ssh,dfamong others. You can add your own tests to the list of tests by appendingTEST_SUITESas follows:TEST_SUITES_append = "mytest"Alternatively, you can provide the "auto" option to have all applicable tests run against the image.
TEST_SUITES_append = " auto"Using this option causes the build system to automatically run tests that are applicable to the image. Tests that are not applicable are skipped.
The order in which tests are run is important. Tests that depend on another test must appear later in the list than the test on which they depend. For example, if you append the list of tests with two tests (
test_Aandtest_B) wheretest_Bis dependent ontest_A, then you must order the tests as follows:TEST_SUITES = " test_A test_B"For more information on testing images, see the "Performing Automated Runtime Testing" section in the Yocto Project Development Tasks Manual.
- TESTIMAGE_AUTO¶
Automatically runs the series of automated tests for images when an image is successfully built. Setting
TESTIMAGE_AUTOto "1" causes any image that successfully builds to automatically boot under QEMU. Using the variable also adds in dependencies so that any SDK for which testing is requested is automatically built first.These tests are written in Python making use of the
unittestmodule, and the majority of them run commands on the target system overssh. You can set this variable to "1" in yourlocal.conffile in the Build Directory to have the OpenEmbedded build system automatically run these tests after an image successfully builds:TESTIMAGE_AUTO = "1"For more information on enabling, running, and writing these tests, see the "Performing Automated Runtime Testing" section in the Yocto Project Development Tasks Manual and the "
testimage*.bbclass" section.- THISDIR¶
The directory in which the file BitBake is currently parsing is located. Do not manually set this variable.
- TIME¶
The time the build was started. Times appear using the hour, minute, and second (HMS) format (e.g. "140159" for one minute and fifty-nine seconds past 1400 hours).
- TMPDIR¶
This variable is the base directory the OpenEmbedded build system uses for all build output and intermediate files (other than the shared state cache). By default, the
TMPDIRvariable points totmpwithin the Build Directory.If you want to establish this directory in a location other than the default, you can uncomment and edit the following statement in the
conf/local.conffile in the Source Directory:#TMPDIR = "${TOPDIR}/tmp"An example use for this scenario is to set
TMPDIRto a local disk, which does not use NFS, while having the Build Directory use NFS.The filesystem used by
TMPDIRmust have standard filesystem semantics (i.e. mixed-case files are unique, POSIX file locking, and persistent inodes). Due to various issues with NFS and bugs in some implementations, NFS does not meet this minimum requirement. Consequently,TMPDIRcannot be on NFS.- TOOLCHAIN_HOST_TASK¶
This variable lists packages the OpenEmbedded build system uses when building an SDK, which contains a cross-development environment. The packages specified by this variable are part of the toolchain set that runs on the
SDKMACHINE, and each package should usually have the prefixnativesdk-. For example, consider the following command when building an SDK:$ bitbake -c populate_sdkimagenameIn this case, a default list of packages is set in this variable, but you can add additional packages to the list. See the "Adding Individual Packages to the Standard SDK" section in the Yocto Project Application Development and the Extensible Software Development Kit (eSDK) manual for more information.
For background information on cross-development toolchains in the Yocto Project development environment, see the "Cross-Development Toolchain Generation" section in the Yocto Project Overview and Concepts Manual. For information on setting up a cross-development environment, see the Yocto Project Application Development and the Extensible Software Development Kit (eSDK) manual.
- TOOLCHAIN_OUTPUTNAME¶
This variable defines the name used for the toolchain output. The
populate_sdk_baseclass sets theTOOLCHAIN_OUTPUTNAMEvariable as follows:TOOLCHAIN_OUTPUTNAME ?= "${SDK_NAME}-toolchain-${SDK_VERSION}"See the
SDK_NAMEandSDK_VERSIONvariables for additional information.- TOOLCHAIN_TARGET_TASK¶
This variable lists packages the OpenEmbedded build system uses when it creates the target part of an SDK (i.e. the part built for the target hardware), which includes libraries and headers. Use this variable to add individual packages to the part of the SDK that runs on the target. See the "Adding Individual Packages to the Standard SDK" section in the Yocto Project Application Development and the Extensible Software Development Kit (eSDK) manual for more information.
For background information on cross-development toolchains in the Yocto Project development environment, see the "Cross-Development Toolchain Generation" section in the Yocto Project Overview and Concepts Manual. For information on setting up a cross-development environment, see the Yocto Project Application Development and the Extensible Software Development Kit (eSDK) manual.
- TOPDIR¶
The top-level Build Directory. BitBake automatically sets this variable when you initialize your build environment using
oe-init-build-env.- TRANSLATED_TARGET_ARCH¶
A sanitized version of
TARGET_ARCH. This variable is used where the architecture is needed in a value where underscores are not allowed, for example within package filenames. In this case, dash characters replace any underscore characters used inTARGET_ARCH.Do not edit this variable.
- TUNE_ARCH¶
The GNU canonical architecture for a specific architecture (i.e.
arm,armeb,mips,mips64, and so forth). BitBake uses this value to setup configuration.TUNE_ARCHdefinitions are specific to a given architecture. The definitions can be a single static definition, or can be dynamically adjusted. You can see details for a given CPU family by looking at the architecture'sREADMEfile. For example, themeta/conf/machine/include/mips/READMEfile in the Source Directory provides information forTUNE_ARCHspecific to themipsarchitecture.TUNE_ARCHis tied closely toTARGET_ARCH, which defines the target machine's architecture. The BitBake configuration file (meta/conf/bitbake.conf) setsTARGET_ARCHas follows:TARGET_ARCH = "${TUNE_ARCH}"The following list, which is by no means complete since architectures are configurable, shows supported machine architectures:
arm i586 x86_64 powerpc powerpc64 mips mipsel- TUNE_ASARGS¶
Specifies architecture-specific assembler flags for the target system. The set of flags is based on the selected tune features.
TUNE_ASARGSis set using the tune include files, which are typically undermeta/conf/machine/include/and are influenced throughTUNE_FEATURES. For example, themeta/conf/machine/include/x86/arch-x86.incfile defines the flags for the x86 architecture as follows:TUNE_ASARGS += "${@bb.utils.contains("TUNE_FEATURES", "mx32", "-x32", "", d)}"Note
Board Support Packages (BSPs) select the tune. The selected tune, in turn, affects the tune variables themselves (i.e. the tune can supply its own set of flags).- TUNE_CCARGS¶
Specifies architecture-specific C compiler flags for the target system. The set of flags is based on the selected tune features.
TUNE_CCARGSis set using the tune include files, which are typically undermeta/conf/machine/include/and are influenced throughTUNE_FEATURES.Note
Board Support Packages (BSPs) select the tune. The selected tune, in turn, affects the tune variables themselves (i.e. the tune can supply its own set of flags).- TUNE_LDARGS¶
Specifies architecture-specific linker flags for the target system. The set of flags is based on the selected tune features.
TUNE_LDARGSis set using the tune include files, which are typically undermeta/conf/machine/include/and are influenced throughTUNE_FEATURES. For example, themeta/conf/machine/include/x86/arch-x86.incfile defines the flags for the x86 architecture as follows:TUNE_LDARGS += "${@bb.utils.contains("TUNE_FEATURES", "mx32", "-m elf32_x86_64", "", d)}"Note
Board Support Packages (BSPs) select the tune. The selected tune, in turn, affects the tune variables themselves (i.e. the tune can supply its own set of flags).- TUNE_FEATURES¶
Features used to "tune" a compiler for optimal use given a specific processor. The features are defined within the tune files and allow arguments (i.e.
TUNE_*ARGS) to be dynamically generated based on the features.The OpenEmbedded build system verifies the features to be sure they are not conflicting and that they are supported.
The BitBake configuration file (
meta/conf/bitbake.conf) definesTUNE_FEATURESas follows:TUNE_FEATURES ??= "${TUNE_FEATURES_tune-${DEFAULTTUNE}}"See the
DEFAULTTUNEvariable for more information.- TUNE_PKGARCH¶
The package architecture understood by the packaging system to define the architecture, ABI, and tuning of output packages. The specific tune is defined using the "_tune" override as follows:
TUNE_PKGARCH_tune-tune= "tune"These tune-specific package architectures are defined in the machine include files. Here is an example of the "core2-32" tuning as used in the
meta/conf/machine/include/tune-core2.incfile:TUNE_PKGARCH_tune-core2-32 = "core2-32"- TUNEABI¶
An underlying Application Binary Interface (ABI) used by a particular tuning in a given toolchain layer. Providers that use prebuilt libraries can use the
TUNEABI,TUNEABI_OVERRIDE, andTUNEABI_WHITELISTvariables to check compatibility of tunings against their selection of libraries.If
TUNEABIis undefined, then every tuning is allowed. See thesanityclass to see how the variable is used.- TUNEABI_OVERRIDE¶
If set, the OpenEmbedded system ignores the
TUNEABI_WHITELISTvariable. Providers that use prebuilt libraries can use theTUNEABI_OVERRIDE,TUNEABI_WHITELIST, andTUNEABIvariables to check compatibility of a tuning against their selection of libraries.See the
sanityclass to see how the variable is used.- TUNEABI_WHITELIST¶
A whitelist of permissible
TUNEABIvalues. IfTUNEABI_WHITELISTis not set, all tunes are allowed. Providers that use prebuilt libraries can use theTUNEABI_WHITELIST,TUNEABI_OVERRIDE, andTUNEABIvariables to check compatibility of a tuning against their selection of libraries.See the
sanityclass to see how the variable is used.- TUNECONFLICTS[
feature]¶ Specifies CPU or Application Binary Interface (ABI) tuning features that conflict with
feature.Known tuning conflicts are specified in the machine include files in the Source Directory. Here is an example from the
meta/conf/machine/include/mips/arch-mips.incinclude file that lists the "o32" and "n64" features as conflicting with the "n32" feature:TUNECONFLICTS[n32] = "o32 n64"- TUNEVALID[
feature]¶ Specifies a valid CPU or Application Binary Interface (ABI) tuning feature. The specified feature is stored as a flag. Valid features are specified in the machine include files (e.g.
meta/conf/machine/include/arm/arch-arm.inc). Here is an example from that file:TUNEVALID[bigendian] = "Enable big-endian mode."See the machine include files in the Source Directory for these features.
U
- UBOOT_CONFIG¶
Configures the
UBOOT_MACHINEand can also defineIMAGE_FSTYPESfor individual cases.Following is an example from the
meta-fsl-armlayer.UBOOT_CONFIG ??= "sd" UBOOT_CONFIG[sd] = "mx6qsabreauto_config,sdcard" UBOOT_CONFIG[eimnor] = "mx6qsabreauto_eimnor_config" UBOOT_CONFIG[nand] = "mx6qsabreauto_nand_config,ubifs" UBOOT_CONFIG[spinor] = "mx6qsabreauto_spinor_config"In this example, "sd" is selected as the configuration of the possible four for the
UBOOT_MACHINE. The "sd" configuration defines "mx6qsabreauto_config" as the value forUBOOT_MACHINE, while the "sdcard" specifies theIMAGE_FSTYPESto use for the U-boot image.For more information on how the
UBOOT_CONFIGis handled, see theuboot-configclass.- UBOOT_ENTRYPOINT¶
Specifies the entry point for the U-Boot image. During U-Boot image creation, the
UBOOT_ENTRYPOINTvariable is passed as a command-line parameter to theuboot-mkimageutility.- UBOOT_LOADADDRESS¶
Specifies the load address for the U-Boot image. During U-Boot image creation, the
UBOOT_LOADADDRESSvariable is passed as a command-line parameter to theuboot-mkimageutility.- UBOOT_LOCALVERSION¶
Appends a string to the name of the local version of the U-Boot image. For example, assuming the version of the U-Boot image built was "2013.10, the full version string reported by U-Boot would be "2013.10-yocto" given the following statement:
UBOOT_LOCALVERSION = "-yocto"- UBOOT_MACHINE¶
Specifies the value passed on the
makecommand line when building a U-Boot image. The value indicates the target platform configuration. You typically set this variable from the machine configuration file (i.e.conf/machine/).machine_name.confPlease see the "Selection of Processor Architecture and Board Type" section in the U-Boot README for valid values for this variable.
- UBOOT_MAKE_TARGET¶
Specifies the target called in the
Makefile. The default target is "all".- UBOOT_SUFFIX¶
Points to the generated U-Boot extension. For example,
u-boot.sbhas a.sbextension.The default U-Boot extension is
.bin- UBOOT_TARGET¶
Specifies the target used for building U-Boot. The target is passed directly as part of the "make" command (e.g. SPL and AIS). If you do not specifically set this variable, the OpenEmbedded build process passes and uses "all" for the target during the U-Boot building process.
- UNKNOWN_CONFIGURE_WHITELIST¶
Specifies a list of options that, if reported by the configure script as being invalid, should not generate a warning during the
do_configuretask. Normally, invalid configure options are simply not passed to the configure script (e.g. should be removed fromEXTRA_OECONForPACKAGECONFIG_CONFARGS). However, common options, for example, exist that are passed to all configure scripts at a class level that might not be valid for some configure scripts. It follows that no benefit exists in seeing a warning about these options. For these cases, the options are added toUNKNOWN_CONFIGURE_WHITELIST.The configure arguments check that uses
UNKNOWN_CONFIGURE_WHITELISTis part of theinsaneclass and is only enabled if the recipe inherits theautotoolsclass.- UPDATERCPN¶
For recipes inheriting the
update-rc.dclass,UPDATERCPNspecifies the package that contains the initscript that is enabled.The default value is "${PN}". Given that almost all recipes that install initscripts package them in the main package for the recipe, you rarely need to set this variable in individual recipes.
- UPSTREAM_CHECK_GITTAGREGEX¶
When the
distrodataclass is enabled globally, you can perform a per-recipe check for what the latest upstream source code version is by callingbitbake -c checkpkgrecipe. If the recipe source code is provided from Git repositories, the OpenEmbedded build system determines the latest upstream version by picking the latest tag from the list of all repository tags. You can use theUPSTREAM_CHECK_GITTAGREGEXvariable to provide a regular expression to filter only the relevant tags should the default filter not work correctly.UPSTREAM_CHECK_GITTAGREGEX = "git_tag_regex"- UPSTREAM_CHECK_REGEX¶
When the
distrodataclass is enabled globally, use theUPSTREAM_CHECK_REGEXvariable to specify a different regular expression instead of the default one when the package checking system is parsing the page found usingUPSTREAM_CHECK_URI.UPSTREAM_CHECK_REGEX = "package_regex"- UPSTREAM_CHECK_URI¶
When the
distrodataclass is enabled globally, you can perform a per-recipe check for what the latest upstream source code version is by callingbitbake -c checkpkgrecipe. If the source code is provided from tarballs, the latest version is determined by fetching the directory listing where the tarball is and attempting to find a later tarball. When this approach does not work, you can useUPSTREAM_CHECK_URIto provide a different URI that contains the link to the latest tarball.UPSTREAM_CHECK_URI = "recipe_url"- USE_DEVFS¶
Determines if
devtmpfsis used for/devpopulation. The default value used forUSE_DEVFSis "1" when no value is specifically set. Typically, you would setUSE_DEVFSto "0" for a statically populated/devdirectory.See the "Selecting a Device Manager" section in the Yocto Project Development Tasks Manual for information on how to use this variable.
- USE_VT¶
When using SysVinit, determines whether or not to run a getty on any virtual terminals in order to enable logging in through those terminals.
The default value used for
USE_VTis "1" when no default value is specifically set. Typically, you would setUSE_VTto "0" in the machine configuration file for machines that do not have a graphical display attached and therefore do not need virtual terminal functionality.- USER_CLASSES¶
A list of classes to globally inherit. These classes are used by the OpenEmbedded build system to enable extra features (e.g.
buildstats,image-mklibs, and so forth).The default list is set in your
local.conffile:USER_CLASSES ?= "buildstats image-mklibs image-prelink"For more information, see
meta-poky/conf/local.conf.samplein the Source Directory.- USERADD_ERROR_DYNAMIC¶
If set to "error", forces the OpenEmbedded build system to produce an error if the user identification (
uid) and group identification (gid) values are not defined infiles/passwdandfiles/groupfiles. If set to "warn", a warning will be issued instead.The default behavior for the build system is to dynamically apply
uidandgidvalues. Consequently, theUSERADD_ERROR_DYNAMICvariable is by default not set. If you plan on using statically assignedgidanduidvalues, you should set theUSERADD_ERROR_DYNAMICvariable in yourlocal.conffile as follows:USERADD_ERROR_DYNAMIC = "error"Overriding the default behavior implies you are going to also take steps to set static
uidandgidvalues through use of theUSERADDEXTENSION,USERADD_UID_TABLES, andUSERADD_GID_TABLESvariables.- USERADD_GID_TABLES¶
Specifies a password file to use for obtaining static group identification (
gid) values when the OpenEmbedded build system adds a group to the system during package installation.When applying static group identification (
gid) values, the OpenEmbedded build system looks inBBPATHfor afiles/groupfile and then applies thoseuidvalues. Set the variable as follows in yourlocal.conffile:USERADD_GID_TABLES = "files/group"Note
Setting theUSERADDEXTENSIONvariable to "useradd-staticids" causes the build system to use staticgidvalues.- USERADD_PACKAGES¶
When inheriting the
useraddclass, this variable specifies the individual packages within the recipe that require users and/or groups to be added.You must set this variable if the recipe inherits the class. For example, the following enables adding a user for the main package in a recipe:
USERADD_PACKAGES = "${PN}"Note
It follows that if you are going to use theUSERADD_PACKAGESvariable, you need to set one or more of theUSERADD_PARAM,GROUPADD_PARAM, orGROUPMEMS_PARAMvariables.- USERADD_PARAM¶
When inheriting the
useraddclass, this variable specifies for a package what parameters should pass to theuseraddcommand if you add a user to the system when the package is installed.Here is an example from the
dbusrecipe:USERADD_PARAM_${PN} = "--system --home ${localstatedir}/lib/dbus \ --no-create-home --shell /bin/false \ --user-group messagebus"For information on the standard Linux shell command
useradd, see http://linux.die.net/man/8/useradd.- USERADD_UID_TABLES¶
Specifies a password file to use for obtaining static user identification (
uid) values when the OpenEmbedded build system adds a user to the system during package installation.When applying static user identification (
uid) values, the OpenEmbedded build system looks inBBPATHfor afiles/passwdfile and then applies thoseuidvalues. Set the variable as follows in yourlocal.conffile:USERADD_UID_TABLES = "files/passwd"Note
Setting theUSERADDEXTENSIONvariable to "useradd-staticids" causes the build system to use staticuidvalues.- USERADDEXTENSION¶
When set to "useradd-staticids", causes the OpenEmbedded build system to base all user and group additions on a static
passwdandgroupfiles found inBBPATH.To use static user identification (
uid) and group identification (gid) values, set the variable as follows in yourlocal.conffile:USERADDEXTENSION = "useradd-staticids"Note
Setting this variable to use staticuidandgidvalues causes the OpenEmbedded build system to employ theuseradd-staticidsclass.If you use static
uidandgidinformation, you must also specify thefiles/passwdandfiles/groupfiles by setting theUSERADD_UID_TABLESandUSERADD_GID_TABLESvariables. Additionally, you should also set theUSERADD_ERROR_DYNAMICvariable.
V
- VOLATILE_LOG_DIR¶
Specifies the persistence of the target's
/var/logdirectory, which is used to house postinstall target log files.By default,
VOLATILE_LOG_DIRis set to "yes", which means the file is not persistent. You can override this setting by setting the variable to "no" to make the log directory persistent.
W
- WARN_QA¶
Specifies the quality assurance checks whose failures are reported as warnings by the OpenEmbedded build system. You set this variable in your distribution configuration file. For a list of the checks you can control with this variable, see the "
insane.bbclass" section.- WKS_FILE_DEPENDS¶
When placed in the recipe that builds your image, this variable lists build-time dependencies. The
WKS_FILE_DEPENDSvariable is only applicable when Wic images are active (i.e. whenIMAGE_FSTYPEScontains entries related to Wic). If your recipe does not create Wic images, the variable has no effect.The
WKS_FILE_DEPENDSvariable is similar to theDEPENDSvariable. When you use the variable in your recipe that builds the Wic image, dependencies you list in theWIC_FILE_DEPENDSvariable are added to theDEPENDSvariable.With the
WKS_FILE_DEPENDSvariable, you have the possibility to specify a list of additional dependencies (e.g. native tools, bootloaders, and so forth), that are required to build Wic images. Following is an example:WKS_FILE_DEPENDS = "some-native-tool"In the previous example,
some-native-toolwould be replaced with an actual native tool on which the build would depend.- WKS_FILE¶
Specifies the location of the Wic kickstart file that is used by the OpenEmbedded build system to create a partitioned image (
image.wic). For information on how to create a partitioned image, see the "Creating Partitioned Images Using Wic" section in the Yocto Project Development Tasks Manual. For details on the kickstart file format, see the "OpenEmbedded Kickstart (.wks) Reference Chapter.- WORKDIR¶
The pathname of the work directory in which the OpenEmbedded build system builds a recipe. This directory is located within the
TMPDIRdirectory structure and is specific to the recipe being built and the system for which it is being built.The
WORKDIRdirectory is defined as follows:${TMPDIR}/work/${MULTIMACH_TARGET_SYS}/${PN}/${EXTENDPE}${PV}-${PR}The actual directory depends on several things:
As an example, assume a Source Directory top-level folder name
poky, a default Build Directory atpoky/build, and aqemux86-poky-linuxmachine target system. Furthermore, suppose your recipe is namedfoo_1.3.0-r0.bb. In this case, the work directory the build system uses to build the package would be as follows:poky/build/tmp/work/qemux86-poky-linux/foo/1.3.0-r0
X
- XSERVER¶
Specifies the packages that should be installed to provide an X server and drivers for the current machine, assuming your image directly includes
packagegroup-core-x11-xserveror, perhaps indirectly, includes "x11-base" inIMAGE_FEATURES.The default value of
XSERVER, if not specified in the machine configuration, is "xserver-xorg xf86-video-fbdev xf86-input-evdev".
Chapter 14. Variable Context¶
Table of Contents
While you can use most variables in almost any context such as
.conf, .bbclass,
.inc, and .bb files,
some variables are often associated with a particular locality or context.
This chapter describes some common associations.
14.1. Configuration¶
The following subsections provide lists of variables whose context is configuration: distribution, machine, and local.
14.1.1. Distribution (Distro)¶
This section lists variables whose configuration context is the distribution, or distro.
14.1.3. Local¶
This section lists variables whose configuration context is the
local configuration through the local.conf
file.
14.2. Recipes¶
The following subsections provide lists of variables whose context is recipes: required, dependencies, path, and extra build information.
14.2.1. Required¶
This section lists variables that are required for recipes.
SRC_URI- used in recipes that fetch local or remote files.
14.2.4. Extra Build Information¶
This section lists variables that define extra build information for recipes.
Chapter 15. FAQ¶
- 15.1. How does Poky differ from OpenEmbedded?
- 15.2. My development system does not meet the required Git, tar, and Python versions. In particular, I do not have Python 3.4.0 or greater. Can I still use the Yocto Project?
- 15.3. How can you claim Poky / OpenEmbedded-Core is stable?
- 15.4. How do I get support for my board added to the Yocto Project?
- 15.5. Are there any products built using the OpenEmbedded build system?
- 15.6. What does the OpenEmbedded build system produce as output?
- 15.7. How do I add my package to the Yocto Project?
- 15.8. Do I have to reflash my entire board with a new Yocto Project image when recompiling a package?
- 15.9. I see the error 'chmod: XXXXX new permissions are r-xrwxrwx, not r-xr-xr-x'. What is wrong?
- 15.10. I see lots of 404 responses for files when the OpenEmbedded build system is trying to download sources. Is something wrong?
- 15.11. I have machine-specific data in a package for one machine only but the package is being marked as machine-specific in all cases, how do I prevent this?
- 15.12. I'm behind a firewall and need to use a proxy server. How do I do that?
- 15.13. What’s the difference between target and target-native?
- 15.14. I'm seeing random build failures. Help?!
- 15.15. When I try to build a native recipe, the build fails with iconv.h problems.
- 15.16. What do we need to ship for license compliance?
- 15.17. How do I disable the cursor on my touchscreen device?
- 15.18. How do I make sure connected network interfaces are brought up by default?
- 15.19. How do I create images with more free space?
- 15.20. Why don't you support directories with spaces in the pathnames?
- 15.21. How do I use an external toolchain?
- 15.22. How does the OpenEmbedded build system obtain source code and will it work behind my firewall or proxy server?
- 15.23. Can I get rid of build output so I can start over?
- 15.24. Why do ${bindir} and ${libdir} have strange values for -native recipes?
- 15.25. The files provided by my *-native recipe do not appear to be available to other recipes. Files are missing from the native sysroot, my recipe is installing to the wrong place, or I am getting permissions errors during the do_install task in my recipe! What is wrong?
15.1. | How does Poky differ from OpenEmbedded? |
The term "Poky" refers to the specific reference build system that the Yocto Project provides. Poky is based on OE-Core and BitBake. Thus, the generic term used here for the build system is the "OpenEmbedded build system." Development in the Yocto Project using Poky is closely tied to OpenEmbedded, with changes always being merged to OE-Core or BitBake first before being pulled back into Poky. This practice benefits both projects immediately. | |
15.2. | My development system does not meet the required Git, tar, and Python versions. In particular, I do not have Python 3.4.0 or greater. Can I still use the Yocto Project? |
You can get the required tools on your host development system a couple different ways (i.e. building a tarball or downloading a tarball). See the "Required Git, tar, and Python Versions" section for steps on how to update your build tools. | |
15.3. | How can you claim Poky / OpenEmbedded-Core is stable? |
There are three areas that help with stability;
| |
15.4. | How do I get support for my board added to the Yocto Project? |
Support for an additional board is added by creating a Board Support Package (BSP) layer for it. For more information on how to create a BSP layer, see the "Understanding and Creating Layers" section in the Yocto Project Development Tasks Manual and the Yocto Project Board Support Package (BSP) Developer's Guide. Usually, if the board is not completely exotic, adding support in the Yocto Project is fairly straightforward. | |
15.5. | Are there any products built using the OpenEmbedded build system? |
The software running on the Vernier LabQuest is built using the OpenEmbedded build system. See the Vernier LabQuest website for more information. There are a number of pre-production devices using the OpenEmbedded build system and the Yocto Project team announces them as soon as they are released. | |
15.6. | What does the OpenEmbedded build system produce as output? |
Because you can use the same set of recipes to create output of various formats, the output of an OpenEmbedded build depends on how you start it. Usually, the output is a flashable image ready for the target device. | |
15.7. | How do I add my package to the Yocto Project? |
To add a package, you need to create a BitBake recipe. For information on how to create a BitBake recipe, see the "Writing a New Recipe" section in the Yocto Project Development Tasks Manual. | |
15.8. | Do I have to reflash my entire board with a new Yocto Project image when recompiling a package? |
The OpenEmbedded build system can build packages in various
formats such as IPK for OPKG, Debian package
( | |
15.9. |
I see the error ' |
You are probably running the build on an NTFS filesystem.
Use | |
15.10. | I see lots of 404 responses for files when the OpenEmbedded build system is trying to download sources. Is something wrong? |
Nothing is wrong. The OpenEmbedded build system checks any configured source mirrors before downloading from the upstream sources. The build system does this searching for both source archives and pre-checked out versions of SCM-managed software. These checks help in large installations because it can reduce load on the SCM servers themselves. The address above is one of the default mirrors configured into the build system. Consequently, if an upstream source disappears, the team can place sources there so builds continue to work. | |
15.11. | I have machine-specific data in a package for one machine only but the package is being marked as machine-specific in all cases, how do I prevent this? |
Set | |
15.12. | I'm behind a firewall and need to use a proxy server. How do I do that? |
Most source fetching by the OpenEmbedded build system is done
by
Following is the applicable code for setting various proxy
types in the
# You can set the default proxies for Wget to use for http, https, and ftp.
# They will override the value in the environment.
#https_proxy = http://proxy.yoyodyne.com:18023/
#http_proxy = http://proxy.yoyodyne.com:18023/
#ftp_proxy = http://proxy.yoyodyne.com:18023/
# If you do not want to use proxy at all, set this to off.
#use_proxy = on
The Yocto Project also includes a
| |
15.13. |
What’s the difference between |
The | |
15.14. | I'm seeing random build failures. Help?! |
If the same build is failing in totally different and random ways, the most likely explanation is:
The OpenEmbedded build system processes a massive amount of data that causes lots of network, disk and CPU activity and is sensitive to even single-bit failures in any of these areas. True random failures have always been traced back to hardware or virtualization issues. | |
15.15. |
When I try to build a native recipe, the build fails with |
If you get an error message that indicates GNU
#error GNU libiconv not in use but included iconv.h is from libiconv
If you find a previously installed file, you should either uninstall it or temporarily rename it and try the build again.
This issue is just a single manifestation of "system
leakage" issues caused when the OpenEmbedded build system
finds and uses previously installed files during a native
build.
This type of issue might not be limited to
| |
15.16. | What do we need to ship for license compliance? |
This is a difficult question and you need to consult your lawyer for the answer for your specific case. It is worth bearing in mind that for GPL compliance, there needs to be enough information shipped to allow someone else to rebuild and produce the same end result you are shipping. This means sharing the source code, any patches applied to it, and also any configuration information about how that package was configured and built. You can find more information on licensing in the "Licensing" section in the Yocto Project Overview and Concepts Manual and also in the "Maintaining Open Source License Compliance During Your Product's Lifecycle" section in the Yocto Project Development Tasks Manual. | |
15.17. | How do I disable the cursor on my touchscreen device? |
You need to create a form factor file as described in the
"Miscellaneous BSP-Specific Recipe Files"
section in the Yocto Project Board Support Packages (BSP)
Developer's Guide.
Set the
HAVE_TOUCHSCREEN=1
| |
15.18. | How do I make sure connected network interfaces are brought up by default? |
The default interfaces file provided by the netbase recipe does not automatically bring up network interfaces. Therefore, you will need to add a BSP-specific netbase that includes an interfaces file. See the "Miscellaneous BSP-Specific Recipe Files" section in the Yocto Project Board Support Packages (BSP) Developer's Guide for information on creating these types of miscellaneous recipe files. For example, add the following files to your layer:
meta-MACHINE/recipes-bsp/netbase/netbase/MACHINE/interfaces
meta-MACHINE/recipes-bsp/netbase/netbase_5.0.bbappend
| |
15.19. | How do I create images with more free space? |
By default, the OpenEmbedded build system creates images that are 1.3 times the size of the populated root filesystem. To affect the image size, you need to set various configurations:
| |
15.20. | Why don't you support directories with spaces in the pathnames? |
The Yocto Project team has tried to do this before but too
many of the tools the OpenEmbedded build system depends on,
such as | |
15.21. | How do I use an external toolchain? |
The toolchain configuration is very flexible and customizable.
It is primarily controlled with the
The default value of
In addition to the toolchain configuration, you also need a
corresponding toolchain recipe file.
This recipe file needs to package up any pre-built objects in
the toolchain such as | |
15.22. | How does the OpenEmbedded build system obtain source code and will it work behind my firewall or proxy server? |
The way the build system obtains source code is highly configurable. You can setup the build system to get source code in most environments if HTTP transport is available.
When the build system searches for source code, it first
tries the local download directory.
If that location fails, Poky tries
Assuming your distribution is "poky", the OpenEmbedded build
system uses the Yocto Project source
As an example, you could add a specific server for the
build system to attempt before any others by adding something
like the following to the
PREMIRRORS_prepend = "\
git://.*/.* http://www.yoctoproject.org/sources/ \n \
ftp://.*/.* http://www.yoctoproject.org/sources/ \n \
http://.*/.* http://www.yoctoproject.org/sources/ \n \
https://.*/.* http://www.yoctoproject.org/sources/ \n"
These changes cause the build system to intercept Git, FTP,
HTTP, and HTTPS requests and direct them to the
Aside from the previous technique, these options also exist:
BB_NO_NETWORK = "1"
This statement tells BitBake to issue an error instead of trying to access the Internet. This technique is useful if you want to ensure code builds only from local sources. Here is another technique:
BB_FETCH_PREMIRRORONLY = "1"
This statement limits the build system to pulling source
from the Here is another technique:
BB_GENERATE_MIRROR_TARBALLS = "1"
This statement tells the build system to generate mirror tarballs. This technique is useful if you want to create a mirror server. If not, however, the technique can simply waste time during the build.
Finally, consider an example where you are behind an
HTTP-only firewall.
You could make the following changes to the
PREMIRRORS_prepend = "\
ftp://.*/.* http://www.yoctoproject.org/sources/ \n \
http://.*/.* http://www.yoctoproject.org/sources/ \n \
https://.*/.* http://www.yoctoproject.org/sources/ \n"
BB_FETCH_PREMIRRORONLY = "1"
These changes would cause the build system to successfully
fetch source over HTTP and any network accesses to anything
other than the
The build system also honors the standard shell environment
variables NoteYou can find more information on the "Working Behind a Network Proxy" Wiki page. | |
15.23. | Can I get rid of build output so I can start over? |
Yes - you can easily do this.
When you use BitBake to build an image, all the build output
goes into the directory created when you run the
build environment setup script (i.e.
Within the Build Directory, is the | |
15.24. |
Why do |
Executables and libraries might need to be used from a directory other than the directory into which they were initially installed. Complicating this situation is the fact that sometimes these executables and libraries are compiled with the expectation of being run from that initial installation target directory. If this is the case, moving them causes problems.
This scenario is a fundamental problem for package maintainers
of mainstream Linux distributions as well as for the
OpenEmbedded build system.
As such, a well-established solution exists.
Makefiles, Autotools configuration scripts, and other build
systems are expected to respect environment variables such as
When the OpenEmbedded build system uses a recipe to build a
target-architecture program (i.e. one that is intended for
inclusion on the image being built), that program eventually
runs from the root file system of that image.
Thus, the build system provides a value of "/usr/bin" for
Meanwhile, NoteDue to these lengthy examples, the paths are artificially broken across lines for readability.
/home/maxtothemax/poky-bootchart2/build/tmp/work/i586-poky-linux/zlib/
1.2.8-r0/sysroot-destdir/usr/bin
/home/maxtothemax/poky-bootchart2/build/tmp/work/x86_64-linux/
zlib-native/1.2.8-r0/sysroot-destdir/home/maxtothemax/poky-bootchart2/
build/tmp/sysroots/x86_64-linux/usr/bin
Even if the paths look unusual, they both are correct -
the first for a target and the second for a native recipe.
These paths are a consequence of the
| |
15.25. |
The files provided by my |
This situation results when a build system does
not recognize the environment variables supplied to it by
BitBake.
The incident that prompted this FAQ entry involved a Makefile
that used an environment variable named
|
Chapter 16. Contributions and Additional Information¶
Table of Contents
16.1. Introduction¶
The Yocto Project team is happy for people to experiment with the Yocto Project. A number of places exist to find help if you run into difficulties or find bugs. This presents information about contributing and participating in the Yocto Project.
16.2. Contributions¶
The Yocto Project gladly accepts contributions. You can submit changes to the project either by creating and sending pull requests, or by submitting patches through email. For information on how to do both as well as information on how to identify the maintainer for each area of code, see the "Submitting a Change to the Yocto Project" section in the Yocto Project Development Tasks Manual.
16.3. Yocto Project Bugzilla¶
The Yocto Project uses its own implementation of Bugzilla to track defects (bugs). Implementations of Bugzilla work well for group development because they track bugs and code changes, can be used to communicate changes and problems with developers, can be used to submit and review patches, and can be used to manage quality assurance.
Sometimes it is helpful to submit, investigate, or track a bug against the Yocto Project itself (e.g. when discovering an issue with some component of the build system that acts contrary to the documentation or your expectations).
A general procedure and guidelines exist for when you use Bugzilla to submit a bug. For information on how to use Bugzilla to submit a bug against the Yocto Project, see the following:
The "Submitting a Defect Against the Yocto Project" section in the Yocto Project Development Tasks Manual.
The Yocto Project Bugzilla wiki page
For information on Bugzilla in general, see http://www.bugzilla.org/about/.
16.4. Mailing lists¶
A number of mailing lists maintained by the Yocto Project exist as well as related OpenEmbedded mailing lists for discussion, patch submission and announcements. To subscribe to one of the following mailing lists, click on the appropriate URL in the following list and follow the instructions:
http://lists.yoctoproject.org/listinfo/yocto - General Yocto Project discussion mailing list.
http://lists.openembedded.org/mailman/listinfo/openembedded-core - Discussion mailing list about OpenEmbedded-Core (the core metadata).
http://lists.openembedded.org/mailman/listinfo/openembedded-devel - Discussion mailing list about OpenEmbedded.
http://lists.openembedded.org/mailman/listinfo/bitbake-devel - Discussion mailing list about the BitBake build tool.
http://lists.yoctoproject.org/listinfo/poky - Discussion mailing list about Poky.
http://lists.yoctoproject.org/listinfo/yocto-announce - Mailing list to receive official Yocto Project release and milestone announcements.
For more Yocto Project-related mailing lists, see the Yocto Project Website.
16.5. Internet Relay Chat (IRC)¶
Two IRC channels on freenode are available for the Yocto Project and Poky discussions:
#yocto#poky
16.6. Links and Related Documentation¶
Here is a list of resources you might find helpful:
The Yocto Project website: The home site for the Yocto Project.
The Yocto Project Main Wiki Page: The main wiki page for the Yocto Project. This page contains information about project planning, release engineering, QA & automation, a reference site map, and other resources related to the Yocto Project.
OpenEmbedded: The build system used by the Yocto Project. This project is the upstream, generic, embedded distribution from which the Yocto Project derives its build system (Poky) and to which it contributes.
BitBake: The tool used to process metadata.
BitBake User Manual: A comprehensive guide to the BitBake tool. If you want information on BitBake, see this manual.
Yocto Project Quick Build: This short document lets you experience building an image using the Yocto Project without having to understand any concepts or details.
Yocto Project Overview and Concepts Manual: This manual provides overview and conceptual information about the Yocto Project.
Yocto Project Development Tasks Manual: This manual is a "how-to" guide that presents procedures useful to both application and system developers who use the Yocto Project.
Yocto Project Application Development and the Extensible Software Development Kit (eSDK) manual: This guide provides information that lets you get going with the standard or extensible SDK. An SDK, with its cross-development toolchains, allows you to develop projects inside or outside of the Yocto Project environment.
Yocto Project Board Support Package (BSP) Developer's Guide: This guide defines the structure for BSP components. Having a commonly understood structure encourages standardization.
Yocto Project Linux Kernel Development Manual: This manual describes how to work with Linux Yocto kernels as well as provides a bit of conceptual information on the construction of the Yocto Linux kernel tree.
Yocto Project Reference Manual: This manual provides reference material such as variable, task, and class descriptions.
Yocto Project Mega-Manual: This manual is simply a single HTML file comprised of the bulk of the Yocto Project manuals. The Mega-Manual primarily exists as a vehicle by which you can easily search for phrases and terms used in the Yocto Project documentation set.
Yocto Project Profiling and Tracing Manual: This manual presents a set of common and generally useful tracing and profiling schemes along with their applications (as appropriate) to each tool.
Toaster User Manual: This manual introduces and describes how to set up and use Toaster. Toaster is an Application Programming Interface (API) and web-based interface to the OpenEmbedded Build System, which uses BitBake, that reports build information.
Eclipse IDE Yocto Plug-in: Instructions that demonstrate how an application developer uses the Eclipse Yocto Project Plug-in feature within the Eclipse IDE.
FAQ: A list of commonly asked questions and their answers.
Release Notes: Features, updates and known issues for the current release of the Yocto Project. To access the Release Notes, go to the Downloads page on the Yocto Project website and click on the "RELEASE INFORMATION" link for the appropriate release.
Bugzilla: The bug tracking application the Yocto Project uses. If you find problems with the Yocto Project, you should report them using this application.
Bugzilla Configuration and Bug Tracking Wiki Page: Information on how to get set up and use the Yocto Project implementation of Bugzilla for logging and tracking Yocto Project defects.
Internet Relay Chat (IRC): Two IRC channels on freenode are available for Yocto Project and Poky discussions:
#yoctoand#poky, respectively.Quick EMUlator (QEMU): An open-source machine emulator and virtualizer.